本文主要是介绍一篇足矣,带你吃透STL源码中hash table(哈希表)与关联式容器hash_set、hash_map,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、哈希介绍
- 前面介绍的二叉搜索树和平衡二叉搜索树。二叉搜索树具有对数平均时间的表现,但这样的表现构造在一个假设上:输入数据有足够的随机性
- 文本要介绍一种名为hash table(哈希表/散列表)的数据结构,这种结构在插入、删除、搜索等操作上也具有“常数平均时间”的表现,而且这种表现是以统计为基础,不需依赖输入元素的随机性
- 哈希表可以在本人的数据结构文章中查看,文本就不再详细介绍了:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41453285/article/details/103517420、https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41453285/article/details/103533372、https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41453285/article/details/103534526
- hash table是作为hash_set、hash_map、hash_multiset、hash_multimap容器的底层实现
- 并且hash table解决哈希冲突的方式是链地址法(开链)的形式
- SGI STL的哈希表结构:
- 哈希表用vector实现
- vector的一个索引出代表一个桶子(bucket)
- 每个桶子内含有一串链表,链中有含有节点
- 下图是以链地址法完成的hash table形式:

二、哈希冲突
- 哈希表的基本概念就不介绍了,直接介绍哈希冲突
线性探测(Linear Probing)
- 根据元素的值然后除以数组大小,然后插入指定的位置

- 主集团现象:在上图中,如果我们插入的新元素为8、9、0、1、2、3中,第一次的落脚点一定在#3上,这就造成了性能的降低,平均插入成本增加,这种现象在哈希过程中称为主集团(primary clustering)
二次探测(quadratic probing)
- 二次探测用来解决主集团问题的。其解决哈希冲突的方式下列公式:
![]()
- 也就说,如果新元素的起始插入位置为H的话但是H已被占用,那么就会依次尝试
、
、...、+
- 下图是一个二次探测的例子

- 二次探测带来一些疑问:
- ①线性探测每次探测的都必然是一个不同的位置,二次探测能够保证如此?二次探测能否保证如果表格之中没有X,那么我们插入X一定能够成功?
- ②线性探测的运算过程机器简单,二次探测则显式复杂一些。这是否会在执行效率上带来太多的负面影响
- ③不论线性探测还是二次探测,当负载稀疏过高时,表格能够够动态成长?
- 疑惑①:幸运的是,如果假设表格大小为质数,而且永远保持负载系数在0.5以下(也就是说超过0.5就要重新配置表格),那么就可以确定每插入一个元素所需要的探测次数不多于2
- 疑惑②:至于复杂度问题,一般总是这样考虑:收获的比付出的多,才值得这么做。我们增加了探测次数,所获得的利益好歹比二次函数计算所花的时间多。线性探测需要的是一个加法(加1),一个测试(看是否回头),以及一个可能用到的减法(用以绕转回头)。二次探测需要的则是一个加法(从i-1到i)、一个乘法(计算
),另一个加法以及一个mod运算。看起来得不偿失。然而中间却又一些技巧,可以除去耗时的乘法和除法:
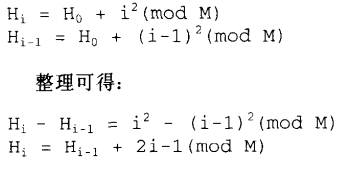
- 因此,如果我们能够以前一个H值来计算下一个H值,就不需要执行二次方所需要的乘法了。虽然还是一个乘法,但那是乘以2,可以位移位快速完成。置于mod运算,也可证明并非真有需要
- 疑惑③:array的增长。如果想要扩充表格,首先必须要找出下一个新的且足够大(大约两倍)的质数,然后考虑表格重建的成本——不仅要拷贝元素,还需要考虑元素在新表格中的位置然后再插入
- 二次探测可以消除主集团,却可能造成次集团:两个元素经由哈希函数计算出来的位置若相同,则插入时所探测的位置页相同,形成了某种浪费。消除次集团的方法也有,例如复式散列
开链(链地址法)
- 所谓的开链,就是在一个表格元素中维护一个链表
- 使用这种方法,表格的负载系数将大于1
- SGI STL的哈希表便是采用这种做法
三、hash table的节点定义(_Hashtable_node)
template <class _Val>
struct _Hashtable_node
{_Hashtable_node* _M_next;_Val _M_val;
}; 
四、hash table的迭代器(_Hashtable_iterator )
- 下面是迭代器的定义:迭代器必须永远维系着与整个“bucket vector”的关系,并记录目前所知的节点
template <class _Val, class _Key, class _HashFcn,class _ExtractKey, class _EqualKey, class _Alloc>
struct _Hashtable_iterator {typedef hashtable<_Val,_Key,_HashFcn,_ExtractKey,_EqualKey,_Alloc>_Hashtable;typedef _Hashtable_iterator<_Val, _Key, _HashFcn, _ExtractKey, _EqualKey, _Alloc>iterator;typedef _Hashtable_const_iterator<_Val, _Key, _HashFcn, _ExtractKey, _EqualKey, _Alloc>const_iterator;typedef _Hashtable_node<_Val> _Node;typedef forward_iterator_tag iterator_category;typedef _Val value_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;typedef size_t size_type;typedef _Val& reference;typedef _Val* pointer;_Node* _M_cur; //迭代器目前所指节点_Hashtable* _M_ht;//保持对容器的连结关系(因为可能需要从bucket跳到bucket)_Hashtable_iterator(_Node* __n, _Hashtable* __tab) : _M_cur(__n), _M_ht(__tab) {}_Hashtable_iterator() {}reference operator*() const { return _M_cur->_M_val; }
#ifndef __SGI_STL_NO_ARROW_OPERATORpointer operator->() const { return &(operator*()); }
#endif /* __SGI_STL_NO_ARROW_OPERATOR */iterator& operator++();iterator operator++(int);bool operator==(const iterator& __it) const{ return _M_cur == __it._M_cur; }bool operator!=(const iterator& __it) const{ return _M_cur != __it._M_cur; }
};- 迭代器没有后退操作(operator--),也没有定义所谓的你想迭代器(reverse iterator)
- 迭代器前进操作(operator++):
- 其前进操作时首先尝试从目前所知的节点出发,前进一个位置(节点),由于节点被安置于list内,所以利用节点的next指针即可轻易达到进行的目的
- 如果目前节点正巧是list的尾端,就跳到下一个bucket内,跳过之后指向下一个list的头节点
- 下面是operator++的定义
template <class _Val, class _Key, class _HF, class _ExK, class _EqK, class _All>
_Hashtable_iterator<_Val,_Key,_HF,_ExK,_EqK,_All>&
_Hashtable_iterator<_Val,_Key,_HF,_ExK,_EqK,_All>::operator++()
{const _Node* __old = _M_cur;_M_cur = _M_cur->_M_next; //如果存在,就是它,否则进入ifif (!_M_cur) {//根据元素值,定位出下一个bucket。其起头处就是我们的目的地size_type __bucket = _M_ht->_M_bkt_num(__old->_M_val);while (!_M_cur && ++__bucket < _M_ht->_M_buckets.size())//注意operator++_M_cur = _M_ht->_M_buckets[__bucket];}return *this;
}template <class _Val, class _Key, class _HF, class _ExK, class _EqK, class _All>
inline _Hashtable_iterator<_Val,_Key,_HF,_ExK,_EqK,_All>
_Hashtable_iterator<_Val,_Key,_HF,_ExK,_EqK,_All>::operator++(int)
{iterator __tmp = *this;++*this; //调用operator++()return __tmp;
}五、hash table的数据结构(hashtable)
- 下面就是哈希表的结构,其内部是以vector实现的
- 模板参数比较多,包括:
- _Val:节点的实值类型
- _Key:节点的键值类型
- _HF:hash function的函数类型
- _Ex:从节点取出键值的方法(函数或仿函数)
- _Eq:判断键值相同与否的方法(函数或仿函数)
- _All:空间配置器。缺省使用std::alloc
template <class _Val, class _Key, class _HF, class _Ex, class _Eq, class _All>
class hashtable;template <class _Val, class _Key, class _HashFcn,class _ExtractKey, class _EqualKey, class _Alloc>
class hashtable {
public:typedef _Key key_type;typedef _Val value_type;typedef _HashFcn hasher; //为template类型参数重新定义一个名字typedef _EqualKey key_equal;//为template类型参数重新定义一个名字typedef size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;typedef value_type* pointer;typedef const value_type* const_pointer;typedef value_type& reference;typedef const value_type& const_reference;hasher hash_funct() const { return _M_hash; }key_equal key_eq() const { return _M_equals; }private:typedef _Hashtable_node<_Val> _Node;#ifdef __STL_USE_STD_ALLOCATORS
public:typedef typename _Alloc_traits<_Val,_Alloc>::allocator_type allocator_type;allocator_type get_allocator() const { return _M_node_allocator; }
private:typename _Alloc_traits<_Node, _Alloc>::allocator_type _M_node_allocator;_Node* _M_get_node() { return _M_node_allocator.allocate(1); }void _M_put_node(_Node* __p) { _M_node_allocator.deallocate(__p, 1); }
# define __HASH_ALLOC_INIT(__a) _M_node_allocator(__a),
#else /* __STL_USE_STD_ALLOCATORS */
public:typedef _Alloc allocator_type;allocator_type get_allocator() const { return allocator_type(); }
private:typedef simple_alloc<_Node, _Alloc> _M_node_allocator_type;_Node* _M_get_node() { return _M_node_allocator_type::allocate(1); }void _M_put_node(_Node* __p) { _M_node_allocator_type::deallocate(__p, 1); }
# define __HASH_ALLOC_INIT(__a)
#endif /* __STL_USE_STD_ALLOCATORS */private:hasher _M_hash;key_equal _M_equals;_ExtractKey _M_get_key;vector<_Node*,_Alloc> _M_buckets; //哈希表以vector实现size_type _M_num_elements;public:typedef _Hashtable_iterator<_Val,_Key,_HashFcn,_ExtractKey,_EqualKey,_Alloc>iterator;typedef _Hashtable_const_iterator<_Val,_Key,_HashFcn,_ExtractKey,_EqualKey,_Alloc>const_iterator;friend struct_Hashtable_iterator<_Val,_Key,_HashFcn,_ExtractKey,_EqualKey,_Alloc>;friend struct_Hashtable_const_iterator<_Val,_Key,_HashFcn,_ExtractKey,_EqualKey,_Alloc>;public:hashtable(size_type __n,const _HashFcn& __hf,const _EqualKey& __eql,const _ExtractKey& __ext,const allocator_type& __a = allocator_type()): __HASH_ALLOC_INIT(__a)_M_hash(__hf),_M_equals(__eql),_M_get_key(__ext),_M_buckets(__a),_M_num_elements(0){_M_initialize_buckets(__n);}hashtable(size_type __n,const _HashFcn& __hf,const _EqualKey& __eql,const allocator_type& __a = allocator_type()): __HASH_ALLOC_INIT(__a)_M_hash(__hf),_M_equals(__eql),_M_get_key(_ExtractKey()),_M_buckets(__a),_M_num_elements(0){_M_initialize_buckets(__n);}hashtable(const hashtable& __ht): __HASH_ALLOC_INIT(__ht.get_allocator())_M_hash(__ht._M_hash),_M_equals(__ht._M_equals),_M_get_key(__ht._M_get_key),_M_buckets(__ht.get_allocator()),_M_num_elements(0){_M_copy_from(__ht);}#undef __HASH_ALLOC_INIThashtable& operator= (const hashtable& __ht){if (&__ht != this) {clear();_M_hash = __ht._M_hash;_M_equals = __ht._M_equals;_M_get_key = __ht._M_get_key;_M_copy_from(__ht);}return *this;}~hashtable() { clear(); }size_type size() const { return _M_num_elements; }size_type max_size() const { return size_type(-1); }bool empty() const { return size() == 0; }void swap(hashtable& __ht){__STD::swap(_M_hash, __ht._M_hash);__STD::swap(_M_equals, __ht._M_equals);__STD::swap(_M_get_key, __ht._M_get_key);_M_buckets.swap(__ht._M_buckets);__STD::swap(_M_num_elements, __ht._M_num_elements);}iterator begin(){ for (size_type __n = 0; __n < _M_buckets.size(); ++__n)if (_M_buckets[__n])return iterator(_M_buckets[__n], this);return end();}iterator end() { return iterator(0, this); }const_iterator begin() const{for (size_type __n = 0; __n < _M_buckets.size(); ++__n)if (_M_buckets[__n])return const_iterator(_M_buckets[__n], this);return end();}const_iterator end() const { return const_iterator(0, this); }#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATEStemplate <class _Vl, class _Ky, class _HF, class _Ex, class _Eq, class _Al>friend bool operator== (const hashtable<_Vl, _Ky, _HF, _Ex, _Eq, _Al>&,const hashtable<_Vl, _Ky, _HF, _Ex, _Eq, _Al>&);
#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */friend bool __STD_QUALIFIERoperator== __STL_NULL_TMPL_ARGS (const hashtable&, const hashtable&);
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */public://返回vector的大小size_type bucket_count() const { return _M_buckets.size(); }size_type max_bucket_count() const{ return __stl_prime_list[(int)__stl_num_primes - 1]; } size_type elems_in_bucket(size_type __bucket) const{size_type __result = 0;for (_Node* __cur = _M_buckets[__bucket]; __cur; __cur = __cur->_M_next)__result += 1;return __result;}pair<iterator, bool> insert_unique(const value_type& __obj){resize(_M_num_elements + 1);return insert_unique_noresize(__obj);}iterator insert_equal(const value_type& __obj){resize(_M_num_elements + 1);return insert_equal_noresize(__obj);}pair<iterator, bool> insert_unique_noresize(const value_type& __obj);iterator insert_equal_noresize(const value_type& __obj);#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATEStemplate <class _InputIterator>void insert_unique(_InputIterator __f, _InputIterator __l){insert_unique(__f, __l, __ITERATOR_CATEGORY(__f));}template <class _InputIterator>void insert_equal(_InputIterator __f, _InputIterator __l){insert_equal(__f, __l, __ITERATOR_CATEGORY(__f));}template <class _InputIterator>void insert_unique(_InputIterator __f, _InputIterator __l,input_iterator_tag){for ( ; __f != __l; ++__f)insert_unique(*__f);}template <class _InputIterator>void insert_equal(_InputIterator __f, _InputIterator __l,input_iterator_tag){for ( ; __f != __l; ++__f)insert_equal(*__f);}template <class _ForwardIterator>void insert_unique(_ForwardIterator __f, _ForwardIterator __l,forward_iterator_tag){size_type __n = 0;distance(__f, __l, __n);resize(_M_num_elements + __n);for ( ; __n > 0; --__n, ++__f)insert_unique_noresize(*__f);}template <class _ForwardIterator>void insert_equal(_ForwardIterator __f, _ForwardIterator __l,forward_iterator_tag){size_type __n = 0;distance(__f, __l, __n);resize(_M_num_elements + __n);for ( ; __n > 0; --__n, ++__f)insert_equal_noresize(*__f);}#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */void insert_unique(const value_type* __f, const value_type* __l){size_type __n = __l - __f;resize(_M_num_elements + __n);for ( ; __n > 0; --__n, ++__f)insert_unique_noresize(*__f);}void insert_equal(const value_type* __f, const value_type* __l){size_type __n = __l - __f;resize(_M_num_elements + __n);for ( ; __n > 0; --__n, ++__f)insert_equal_noresize(*__f);}void insert_unique(const_iterator __f, const_iterator __l){size_type __n = 0;distance(__f, __l, __n);resize(_M_num_elements + __n);for ( ; __n > 0; --__n, ++__f)insert_unique_noresize(*__f);}void insert_equal(const_iterator __f, const_iterator __l){size_type __n = 0;distance(__f, __l, __n);resize(_M_num_elements + __n);for ( ; __n > 0; --__n, ++__f)insert_equal_noresize(*__f);}
#endif /*__STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */reference find_or_insert(const value_type& __obj);iterator find(const key_type& __key) {size_type __n = _M_bkt_num_key(__key);_Node* __first;for ( __first = _M_buckets[__n];__first && !_M_equals(_M_get_key(__first->_M_val), __key);__first = __first->_M_next){}return iterator(__first, this);} const_iterator find(const key_type& __key) const{size_type __n = _M_bkt_num_key(__key);const _Node* __first;for ( __first = _M_buckets[__n];__first && !_M_equals(_M_get_key(__first->_M_val), __key);__first = __first->_M_next){}return const_iterator(__first, this);} size_type count(const key_type& __key) const{const size_type __n = _M_bkt_num_key(__key);size_type __result = 0;for (const _Node* __cur = _M_buckets[__n]; __cur; __cur = __cur->_M_next)if (_M_equals(_M_get_key(__cur->_M_val), __key))++__result;return __result;}pair<iterator, iterator> equal_range(const key_type& __key);pair<const_iterator, const_iterator> equal_range(const key_type& __key) const;size_type erase(const key_type& __key);void erase(const iterator& __it);void erase(iterator __first, iterator __last);void erase(const const_iterator& __it);void erase(const_iterator __first, const_iterator __last);void resize(size_type __num_elements_hint);void clear();private:size_type _M_next_size(size_type __n) const{ return __stl_next_prime(__n); }void _M_initialize_buckets(size_type __n){const size_type __n_buckets = _M_next_size(__n);_M_buckets.reserve(__n_buckets);_M_buckets.insert(_M_buckets.end(), __n_buckets, (_Node*) 0);_M_num_elements = 0;}size_type _M_bkt_num_key(const key_type& __key) const{return _M_bkt_num_key(__key, _M_buckets.size());}size_type _M_bkt_num(const value_type& __obj) const{return _M_bkt_num_key(_M_get_key(__obj));}size_type _M_bkt_num_key(const key_type& __key, size_t __n) const{return _M_hash(__key) % __n;}size_type _M_bkt_num(const value_type& __obj, size_t __n) const{return _M_bkt_num_key(_M_get_key(__obj), __n);}_Node* _M_new_node(const value_type& __obj){_Node* __n = _M_get_node();__n->_M_next = 0;__STL_TRY {construct(&__n->_M_val, __obj);return __n;}__STL_UNWIND(_M_put_node(__n));}void _M_delete_node(_Node* __n){destroy(&__n->_M_val);_M_put_node(__n);}void _M_erase_bucket(const size_type __n, _Node* __first, _Node* __last);void _M_erase_bucket(const size_type __n, _Node* __last);void _M_copy_from(const hashtable& __ht);};系统预定义的哈希大小
- 虽然链地址法并不要求哈希表大小必须为质数,但SGI STL仍然以质数来设计哈希表大小,并且先将28个质数(主键呈现大约2倍的关系)计算好,以备随时使用,同时提供一个函数,用来查询在这28个质数之中,“最接某数并大于某数”的质数
//下面的都是全局枚举与全局函数//假设long至少有32bits
enum { __stl_num_primes = 28 };static const unsigned long __stl_prime_list[__stl_num_primes] =
{53ul, 97ul, 193ul, 389ul, 769ul,1543ul, 3079ul, 6151ul, 12289ul, 24593ul,49157ul, 98317ul, 196613ul, 393241ul, 786433ul,1572869ul, 3145739ul, 6291469ul, 12582917ul, 25165843ul,50331653ul, 100663319ul, 201326611ul, 402653189ul, 805306457ul, 1610612741ul, 3221225473ul, 4294967291ul
};//以下找出上述28个质数之中,最接近并大于n的那个质数
inline unsigned long __stl_next_prime(unsigned long __n)
{const unsigned long* __first = __stl_prime_list;const unsigned long* __last = __stl_prime_list + (int)__stl_num_primes;const unsigned long* pos = lower_bound(__first, __last, __n);//以上lower_bound()是泛型算法//使用lower_bound(),序列需先排序return pos == __last ? *(__last - 1) : *pos;
}template <class _Val, class _Key, class _HashFcn,class _ExtractKey, class _EqualKey, class _Alloc>
class hashtable {
//...
public://总共可以有多少bucketssize_type max_bucket_count() const{ return __stl_prime_list[(int)__stl_num_primes - 1]; }
//...
};六、hash table的构造与内存管理
- 在hashtable类中有一个专属的节点配置器_M_node_allocator_type
template <class _Val, class _Key, class _HF, class _Ex, class _Eq, class _All>
class hashtable;template <class _Val, class _Key, class _HashFcn,class _ExtractKey, class _EqualKey, class _Alloc>
class hashtable {
//...
private:typedef simple_alloc<_Node, _Alloc> _M_node_allocator_type;
//...
};- 下面是定义在hashtable类中的节点的配置函数与释放函数
_Node* _M_new_node(const value_type& __obj)
{_Node* __n = _M_get_node();__n->_M_next = 0;__STL_TRY {construct(&__n->_M_val, __obj);return __n;}__STL_UNWIND(_M_put_node(__n));
}void _M_delete_node(_Node* __n)
{destroy(&__n->_M_val);_M_put_node(__n);
}void _M_put_node(_Node* __p) { _M_node_allocator.deallocate(__p, 1); }构造函数
- hashtable没有提供默认的构造函数。下面是一种构造函数
template <class _Val, class _Key, class _HashFcn,class _ExtractKey, class _EqualKey, class _Alloc>
class hashtable {
public:hashtable(size_type __n,const _HashFcn& __hf,const _EqualKey& __eql,const _ExtractKey& __ext,const allocator_type& __a = allocator_type()): __HASH_ALLOC_INIT(__a)_M_hash(__hf),_M_equals(__eql),_M_get_key(__ext),_M_buckets(__a),_M_num_elements(0){_M_initialize_buckets(__n);}
private:void _M_initialize_buckets(size_type __n){const size_type __n_buckets = _M_next_size(__n);//调用_M_next_size//举例:传入50,返回53.以下首先保留53个元素空间,然后将其全部填0_M_buckets.reserve(__n_buckets);_M_buckets.insert(_M_buckets.end(), __n_buckets, (_Node*) 0);_M_num_elements = 0;}//该函数返回最近接n并大于n的质数。其中调用了我们上面介绍的__stl_next_prime函数size_type _M_next_size(size_type __n) const{ return __stl_next_prime(__n); }
};- 例如下面我们定义一个hashtable就会调用上面的构造函数
hashtable<int,int,hash<iny>,identity<int>,equal_to<int>,alloc> iht(50,hash<int>(),equal_to<int>());std::cout<<iht.size()<<std::endl; //0
std::cout<<iht.bucket_count()<<std::endl; //53。STL提供的第一个质数插入操作(insert_unique)和表格重整(resize)
- insert_unique():插入元素,不允许重复
pair<iterator, bool> insert_unique(const value_type& __obj)
{resize(_M_num_elements + 1); //判断是否需要重建表格return insert_unique_noresize(__obj); //在不需要重建表格的情况下插入节点,键值不允许重复
}- resize()函数:
//以下函数判断是否需要重建表格。不需要就返回
template <class _Val, class _Key, class _HF, class _Ex, class _Eq, class _All>
void hashtable<_Val,_Key,_HF,_Ex,_Eq,_All>::resize(size_type __num_elements_hint)
{//下面是否重建表格的判断原则很奇怪,是拿元素个数(把新增元素计入后)和bucket vector的大小来比较//如果前者大于后者,就重建表格//由此可知,每个bucket(list)的最大容量和buckets vector的大小相同const size_type __old_n = _M_buckets.size();if (__num_elements_hint > __old_n) { //确定真的需要重新配置const size_type __n = _M_next_size(__num_elements_hint);//找出下一个质数if (__n > __old_n) {vector<_Node*, _All> __tmp(__n, (_Node*)(0),_M_buckets.get_allocator()); //建立新的buckets__STL_TRY {//以下处理每一个旧的bucketfor (size_type __bucket = 0; __bucket < __old_n; ++__bucket) {_Node* __first = _M_buckets[__bucket];while (__first) {size_type __new_bucket = _M_bkt_num(__first->_M_val, __n);_M_buckets[__bucket] = __first->_M_next;__first->_M_next = __tmp[__new_bucket];__tmp[__new_bucket] = __first;__first = _M_buckets[__bucket]; }}_M_buckets.swap(__tmp);}
# ifdef __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONScatch(...) {for (size_type __bucket = 0; __bucket < __tmp.size(); ++__bucket) {while (__tmp[__bucket]) {_Node* __next = __tmp[__bucket]->_M_next;_M_delete_node(__tmp[__bucket]);__tmp[__bucket] = __next;}}throw;}
# endif /* __STL_USE_EXCEPTIONS */}}
}- 在上面的resize()函数中,如果有必要就做表格重建。操作分解如下:
_M_buckets[__bucket] = __first->_M_next; //(1)令旧的bucket指向其所对应之链表的下一个节点
__first->_M_next = __tmp[__new_bucket]; //(2)(3)将当前节点插入到新bucket内,成为其对应链表的第一个节点
__tmp[__new_bucket] = __first; //(4)回到旧的bucket所指的待处理链表,准备处理下一个节点 
//在不需要重建表格的情况下插入节点,键值不允许重复
template <class _Val, class _Key, class _HF, class _Ex, class _Eq, class _All>
pair<typename hashtable<_Val,_Key,_HF,_Ex,_Eq,_All>::iterator, bool>
hashtable<_Val,_Key,_HF,_Ex,_Eq,_All>::insert_unique_noresize(const value_type& __obj)
{const size_type __n = _M_bkt_num(__obj); //决定obj应位于#n bucket_Node* __first = _M_buckets[__n]; //令first指向bucket对应之串行头部//如果buckets[n]已被占用,此时first将不为0,于是进入以下循环,走过bucket所对应的整个链表for (_Node* __cur = __first; __cur; __cur = __cur->_M_next) if (_M_equals(_M_get_key(__cur->_M_val), _M_get_key(__obj)))//如果发现与链表中的某键值相同,就不插入,立即返回return pair<iterator, bool>(iterator(__cur, this), false);//离开循环(或根本不进入循环)时,first指向bucket所指链表的头结点_Node* __tmp = _M_new_node(__obj);__tmp->_M_next = __first;_M_buckets[__n] = __tmp; //令新节点称为链表的第一个节点++_M_num_elements; //节点个数累加1return pair<iterator, bool>(iterator(__tmp, this), true);
}插入操作(insert_equal)
iterator insert_equal(const value_type& __obj)
{resize(_M_num_elements + 1); //在上面已介绍return insert_equal_noresize(__obj);
}//在不需要重建表格的情况下插入新节点,键值允许重复
template <class _Val, class _Key, class _HF, class _Ex, class _Eq, class _All>
typename hashtable<_Val,_Key,_HF,_Ex,_Eq,_All>::iterator
hashtable<_Val,_Key,_HF,_Ex,_Eq,_All>::insert_equal_noresize(const value_type& __obj)
{const size_type __n = _M_bkt_num(__obj);_Node* __first = _M_buckets[__n];for (_Node* __cur = __first; __cur; __cur = __cur->_M_next) if (_M_equals(_M_get_key(__cur->_M_val), _M_get_key(__obj))) {_Node* __tmp = _M_new_node(__obj);__tmp->_M_next = __cur->_M_next;__cur->_M_next = __tmp;++_M_num_elements;return iterator(__tmp, this);}_Node* __tmp = _M_new_node(__obj);__tmp->_M_next = __first;_M_buckets[__n] = __tmp;++_M_num_elements;return iterator(__tmp, this);
}判断元素落脚点(bkt_num)
- 插入元素之后需要知道某个元素落脚于哪一个bucket内。这本来是哈希函数的责任,但是SGI把这个任务包装了一层,先交给bkt_num()函数,再由此函数调用哈希函数,取得一个可以执行modulus(取模)运算的数值
- 为什么要这么做?因为有些函数类型无法直接拿来对哈表表的大小进行模运算,例如字符串,这时候我们需要做一些转换
- 下面是bkt_num函数:
//版本1:接受实值(value)和buckets个数
size_type _M_bkt_num(const value_type& __obj, size_t __n) const
{return _M_bkt_num_key(_M_get_key(__obj), __n); //调用版本4
}//版本2:只接受实值(value)
size_type _M_bkt_num(const value_type& __obj) const
{return _M_bkt_num_key(_M_get_key(__obj)); //调用版本3
}//版本3,只接受键值
size_type _M_bkt_num_key(const key_type& __key) const
{return _M_bkt_num_key(__key, _M_buckets.size()); //调用版本4
}//版本4:接受键值和buckets个数
size_type _M_bkt_num_key(const key_type& __key, size_t __n) const
{return _M_hash(__key) % __n; //SGI的所有内建的hash(),在后面的hash functions中介绍
}复制(copy_from)和整体删除(clear)
- 由于整个哈希表由vector和链表组成,因此,复制和整体删除,都需要特别注意内存的释放问题。下面是clear()的定义:
template <class _Val, class _Key, class _HF, class _Ex, class _Eq, class _All>
void hashtable<_Val,_Key,_HF,_Ex,_Eq,_All>::clear()
{//针对每一个bucketfor (size_type __i = 0; __i < _M_buckets.size(); ++__i) {_Node* __cur = _M_buckets[__i];//将bucket list中的每一个节点删除while (__cur != 0) {_Node* __next = __cur->_M_next;_M_delete_node(__cur);__cur = __next;}_M_buckets[__i] = 0; //令bucket内容为null指针}_M_num_elements = 0; //令总节点个数为0//注意,buckets vector并未释放迪奥空间,仍然保有原来大小
}- 下面是copy_from()的定义:
template <class _Val, class _Key, class _HF, class _Ex, class _Eq, class _All>
void hashtable<_Val,_Key,_HF,_Ex,_Eq,_All>::_M_copy_from(const hashtable& __ht)
{_M_buckets.clear();//先清除自己的bucket vector//为自己的buvkets vector保留空间,使与对方相同//如果自己空间大于对方就不动。如果自己空间小于对方,就增大_M_buckets.reserve(__ht._M_buckets.size());//从自己的buckets vector尾端开始,插入n个元素,其值为null//注意,此时buckets vector为空,所以所谓尾端,就是起头处_M_buckets.insert(_M_buckets.end(), __ht._M_buckets.size(), (_Node*) 0);__STL_TRY {//针对buckets vectorfor (size_type __i = 0; __i < __ht._M_buckets.size(); ++__i) {//复制vector的每一个元素(是个指针,指向节点)const _Node* __cur = __ht._M_buckets[__i];if (__cur) {_Node* __copy = _M_new_node(__cur->_M_val);_M_buckets[__i] = __copy;//针对同一个bucket list,复制每一个节点for (_Node* __next = __cur->_M_next; __next; __cur = __next, __next = __cur->_M_next) {__copy->_M_next = _M_new_node(__next->_M_val);__copy = __copy->_M_next;}}}_M_num_elements = __ht._M_num_elements; //重新记录节点个数(哈希表的大小)}__STL_UNWIND(clear());
}七、hash functions
- 在<stl_hash_fun.h>中定义了一些hash functions,全都是仿函数。hash functions是计算元素位置的函数
- SGI将这项任务赋予了先前提到过的bkt_num()函数,再由bkt_num()函数调用这些hash function,取得一个可以对hashtable进行模运算的值
- 针对char、int、long等整数类型,这里大部分的hash function什么都没有做,只是直接返回原值。但是对于字符串类型,就设计了一个转换函数如下:
template <class _Key> struct hash { };inline size_t __stl_hash_string(const char* __s)
{unsigned long __h = 0; for ( ; *__s; ++__s)__h = 5*__h + *__s;return size_t(__h);
}//以下所有的__STL_TEMPLATE_NULL在<stl_config.h>中被定义为template<>
__STL_TEMPLATE_NULL struct hash<char*>
{size_t operator()(const char* __s) const { return __stl_hash_string(__s); }
};__STL_TEMPLATE_NULL struct hash<const char*>
{size_t operator()(const char* __s) const { return __stl_hash_string(__s); }
};__STL_TEMPLATE_NULL struct hash<char> {size_t operator()(char __x) const { return __x; }
};
__STL_TEMPLATE_NULL struct hash<unsigned char> {size_t operator()(unsigned char __x) const { return __x; }
};
__STL_TEMPLATE_NULL struct hash<signed char> {size_t operator()(unsigned char __x) const { return __x; }
};
__STL_TEMPLATE_NULL struct hash<short> {size_t operator()(short __x) const { return __x; }
};
__STL_TEMPLATE_NULL struct hash<unsigned short> {size_t operator()(unsigned short __x) const { return __x; }
};
__STL_TEMPLATE_NULL struct hash<int> {size_t operator()(int __x) const { return __x; }
};
__STL_TEMPLATE_NULL struct hash<unsigned int> {size_t operator()(unsigned int __x) const { return __x; }
};
__STL_TEMPLATE_NULL struct hash<long> {size_t operator()(long __x) const { return __x; }
};
__STL_TEMPLATE_NULL struct hash<unsigned long> {size_t operator()(unsigned long __x) const { return __x; }
};hash functions无法处理的类型
- hashtable无法处理上述所列各项类型之外的元素。例如string、double、float等,这些类型用户必须自己定义hash function。下面是处理string所获的错误现象

八、演示案例
- 下面是一个客户端程序
#include <hash_set> //会包含<stl_hashtable.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int main()
{hashtable<int, int, hash<int>, identity<int>, equal_to<int>, alloc>iht(50, hash<int>(), equal_to<int>());std::cout << iht.size() << std::endl; //0std::cout << iht.bucket_count()() << std::endl; //53。这是STL供应的第一个质数std::cout << iht.max_bucket_count() << std::endl; //4294967291,这是STL供应的最后一个质数iht.insert_unique(59);iht.insert_unique(63);iht.insert_unique(108);iht.insert_unique(2);iht.insert_unique(53);iht.insert_unique(55);std::cout << iht.size() << std::endl; //6。这个就是hashtable<T>::num_element//下面声明一个hashtable迭代器hashtable<int, int, hash<int>, identity<int>, equal_to<int>, alloc>::iteratorite = iht.begin();//遍历hashtablefor (int i = 0; i < iht.size(); ++i, ++ite)std::cout << *ite << std::endl; //53 55 2 108 59 53std::cout << std::endl;//遍历所有buckets。如果其节点个数不为0,就打印节点个数for (int i = 0; i < iht.bucket_count(); ++i) {int n = iht.elems_in_bucket(i);if (n != 0)std::cout << "bucket[" << i << "]has"<<n<<"elems." << std::endl;}//会打印如下内容//bucket[0] has 1 elems//bucket[2] has 3 elems//bucket[6] has 1 elems//bucket[10] has 1 elems/*为了验证bucket(list)的容量就是buckets vector的大小,这里从hastable<T>::Resize()得到结果。此处刻意将元素加到54个,看看是否发生”表格重建“*/for (int i = 0; i <= 47; ++i)iht.insert_equal(i);std::cout << iht.size() << std::endl; //54。元素(节点)个数std::cout << iht.bucket_count() << std::endl; //97,buckets个数//遍历所有buckets,如果其节点个数不为0,就打印节点个数for (int i = 0; i < iht.bucket_count(); ++i) {int n = iht.elems_in_bucket(i);if (n != 0)std::cout << "bucket[" << i << "]has" << n << "elems." << std::endl;}//打印的结果为:bucket[2]和bucket[11]的节点个数为2//其余的bucket[0]~bucket[47]的节点个数为1//此外,bucket[53],[55],[59],[63]的节点个数均为1//以迭代器遍历hashtable,将所有节点的值打印出来ite = iht.begin();for (int i = 0; i < iht.size(); ++i, ++ite)std::cout << *ite << " ";std::cout << std::endl;//0 1 2 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 108 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21//22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42//43 44 45 46 47 53 55 59 63std::cout << *(iht.find(2)) << std::endl; //2std::cout << *(iht.count(2)) << std::endl; //2return 0;
}- 一开始保留了50个节点,由于最接近的STL质数为53,所以buckets vector保留的是53个buckets,每个buckets(指针,指向一个hashtable节点)的初值为0
- 接下来,循环加入6个元素:53、55、2、108、59、63。于是hash table变为下面的样子

- 接下来,再插入48个元素,总元素达到54个,超过当时的buckets vector的大小,哈希表需要重建,于是哈希表变为下面的样子

- 程序最后使用了hash table提供的find和count函数,寻找键值为2的元素,以及计算键值为2的元素个数。注意:键值相同的元素,一定落在同一个bucket list中。下面是find和count的源码
iterator find(const key_type& __key)
{size_type __n = _M_bkt_num_key(__key); //查看在哪一个bucket内_Node* __first;//下面,从bucket list的头开始,一一对比每个元素的键值,对比成功就退出for ( __first = _M_buckets[__n];__first && !_M_equals(_M_get_key(__first->_M_val), __key);__first = __first->_M_next){}return iterator(__first, this);
} size_type count(const key_type& __key) const
{const size_type __n = _M_bkt_num_key(__key); //查看在哪一个bucket内size_type __result = 0;//下面,从bucket list的头开始,一一对比每个元素的键值,对比成功就累加1for (const _Node* __cur = _M_buckets[__n]; __cur; __cur = __cur->_M_next)if (_M_equals(_M_get_key(__cur->_M_val), __key))++__result;return __result;
}九、关联式容器
- 这些关联容器底层都是使用hash table实现的,hash table已经在前面一篇文章介绍了:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41453285/article/details/104260053
- 这几个函数已经过时了,被分别替换成了unordered_set、unordered_multiset、unordered_map、unordered_multimap,详情请参阅:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41453285/article/details/105483561
- 因此,本文也可以作为unordered_xxx系列函数的解析文章
十、hash_set
- 由于hash_set底层是以hash table实现的,因此hash_set只是简单的调用hash table的方法即可
- 与set的异同点:
- hash_set与set都是用来快速查找元素的
- 但是set会对元素自动排序,而hash_set没有
- hash_set和set的使用方法相同
- 在介绍hash table的hash functions的时候说过,hash table有一些无法处理的类型(除非用户自己书写hash function)。因此hash_set也无法自己处理
hash_set源码
//以下代码摘录于stl_hash_set.h
template <class _Value, class _HashFcn, class _EqualKey, class _Alloc>
class hash_set
{// requirements:__STL_CLASS_REQUIRES(_Value, _Assignable);__STL_CLASS_UNARY_FUNCTION_CHECK(_HashFcn, size_t, _Value);__STL_CLASS_BINARY_FUNCTION_CHECK(_EqualKey, bool, _Value, _Value);private://indentity<>定义于<stl_function.h>中typedef hashtable<_Value, _Value, _HashFcn, _Identity<_Value>, _EqualKey, _Alloc> _Ht;_Ht _M_ht; //底层以hash table实现public:typedef typename _Ht::key_type key_type;typedef typename _Ht::value_type value_type;typedef typename _Ht::hasher hasher;typedef typename _Ht::key_equal key_equal;typedef typename _Ht::size_type size_type;typedef typename _Ht::difference_type difference_type;typedef typename _Ht::const_pointer pointer;typedef typename _Ht::const_pointer const_pointer;typedef typename _Ht::const_reference reference;typedef typename _Ht::const_reference const_reference;typedef typename _Ht::const_iterator iterator;typedef typename _Ht::const_iterator const_iterator;typedef typename _Ht::allocator_type allocator_type;hasher hash_funct() const { return _M_ht.hash_funct(); }key_equal key_eq() const { return _M_ht.key_eq(); }allocator_type get_allocator() const { return _M_ht.get_allocator(); }public://缺省使用大小为100的表格,将被hash table调整为最接近且较大的质数hash_set(): _M_ht(100, hasher(), key_equal(), allocator_type()) {}explicit hash_set(size_type __n): _M_ht(__n, hasher(), key_equal(), allocator_type()) {}hash_set(size_type __n, const hasher& __hf): _M_ht(__n, __hf, key_equal(), allocator_type()) {}hash_set(size_type __n, const hasher& __hf, const key_equal& __eql,const allocator_type& __a = allocator_type()): _M_ht(__n, __hf, __eql, __a) {}#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATEStemplate <class _InputIterator>hash_set(_InputIterator __f, _InputIterator __l): _M_ht(100, hasher(), key_equal(), allocator_type()){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }template <class _InputIterator>hash_set(_InputIterator __f, _InputIterator __l, size_type __n): _M_ht(__n, hasher(), key_equal(), allocator_type()){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }template <class _InputIterator>hash_set(_InputIterator __f, _InputIterator __l, size_type __n,const hasher& __hf): _M_ht(__n, __hf, key_equal(), allocator_type()){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }template <class _InputIterator>hash_set(_InputIterator __f, _InputIterator __l, size_type __n,const hasher& __hf, const key_equal& __eql,const allocator_type& __a = allocator_type()): _M_ht(__n, __hf, __eql, __a){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }
#elsehash_set(const value_type* __f, const value_type* __l): _M_ht(100, hasher(), key_equal(), allocator_type()){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }hash_set(const value_type* __f, const value_type* __l, size_type __n): _M_ht(__n, hasher(), key_equal(), allocator_type()){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }hash_set(const value_type* __f, const value_type* __l, size_type __n,const hasher& __hf): _M_ht(__n, __hf, key_equal(), allocator_type()){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }hash_set(const value_type* __f, const value_type* __l, size_type __n,const hasher& __hf, const key_equal& __eql,const allocator_type& __a = allocator_type()): _M_ht(__n, __hf, __eql, __a){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }hash_set(const_iterator __f, const_iterator __l): _M_ht(100, hasher(), key_equal(), allocator_type()){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }hash_set(const_iterator __f, const_iterator __l, size_type __n): _M_ht(__n, hasher(), key_equal(), allocator_type()){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }hash_set(const_iterator __f, const_iterator __l, size_type __n,const hasher& __hf): _M_ht(__n, __hf, key_equal(), allocator_type()){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }hash_set(const_iterator __f, const_iterator __l, size_type __n,const hasher& __hf, const key_equal& __eql,const allocator_type& __a = allocator_type()): _M_ht(__n, __hf, __eql, __a){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }
#endif /*__STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */public://所有操作几乎都有hash table的对应版本。传递调用即可size_type size() const { return _M_ht.size(); }size_type max_size() const { return _M_ht.max_size(); }bool empty() const { return _M_ht.empty(); }void swap(hash_set& __hs) { _M_ht.swap(__hs._M_ht); }#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATEStemplate <class _Val, class _HF, class _EqK, class _Al> friend bool operator== (const hash_set<_Val, _HF, _EqK, _Al>&,const hash_set<_Val, _HF, _EqK, _Al>&);
#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */friend bool __STD_QUALIFIERoperator== __STL_NULL_TMPL_ARGS (const hash_set&, const hash_set&);
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */iterator begin() const { return _M_ht.begin(); }iterator end() const { return _M_ht.end(); }public:pair<iterator, bool> insert(const value_type& __obj){pair<typename _Ht::iterator, bool> __p = _M_ht.insert_unique(__obj);return pair<iterator,bool>(__p.first, __p.second);}
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATEStemplate <class _InputIterator>void insert(_InputIterator __f, _InputIterator __l) { _M_ht.insert_unique(__f,__l); }
#elsevoid insert(const value_type* __f, const value_type* __l) {_M_ht.insert_unique(__f,__l);}void insert(const_iterator __f, const_iterator __l) {_M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }
#endif /*__STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */pair<iterator, bool> insert_noresize(const value_type& __obj){pair<typename _Ht::iterator, bool> __p = _M_ht.insert_unique_noresize(__obj);return pair<iterator, bool>(__p.first, __p.second);}iterator find(const key_type& __key) const { return _M_ht.find(__key); }size_type count(const key_type& __key) const { return _M_ht.count(__key); }pair<iterator, iterator> equal_range(const key_type& __key) const{ return _M_ht.equal_range(__key); }size_type erase(const key_type& __key) {return _M_ht.erase(__key); }void erase(iterator __it) { _M_ht.erase(__it); }void erase(iterator __f, iterator __l) { _M_ht.erase(__f, __l); }void clear() { _M_ht.clear(); }public:void resize(size_type __hint) { _M_ht.resize(__hint); }size_type bucket_count() const { return _M_ht.bucket_count(); }size_type max_bucket_count() const { return _M_ht.max_bucket_count(); }size_type elems_in_bucket(size_type __n) const{ return _M_ht.elems_in_bucket(__n); }
};template <class _Value, class _HashFcn, class _EqualKey, class _Alloc>
inline bool
operator==(const hash_set<_Value,_HashFcn,_EqualKey,_Alloc>& __hs1,const hash_set<_Value,_HashFcn,_EqualKey,_Alloc>& __hs2)
{return __hs1._M_ht == __hs2._M_ht;
}hash_set使用演示案例
- hash_set并不会对元素进行排序
- 下面演示在hash_set中存储字符串
#include <iostream>
#include <hash_set>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;struct eqstr
{bool operator()(const char* s1, const char* s2){return strcmp(s1, s2) == 0;}
};void loopup(const hash_set<const char*, hash<const char*>, eqstr>& Set,const char* word)
{hash_set<const char*, hash<const char*>, eqstr>::const_iterator it = Set.find(word);std::cout << " " << word << ": " << (it != Set.end() ? "present" : "not present") << std::endl;
}int main()
{hash_set<const char*, hash<const char*>, eqstr> Set;Set.insert("kiwi");Set.insert("plum");Set.insert("apple");Set.insert("mango");Set.insert("apricot");Set.insert("banana");loopup(Set, "mango"); //mango: presentloopup(Set, "apple"); //apple: presentloopup(Set, "durian"); //durian: not present//ite1类型为hash_set<const char*, hash<const char*>, eqstr>::iteratorauto iter = Set.begin();for (; iter != Set.end(); ++iter)std::cout << *iter << ""; //banana plum mango apple kiwi apricotstd::cout << std::endl;return 0;
}- 下面演示在hash_set中存储int整型
int main()
{hash_set<int> Set; //hash_set默认缺省为100。SGI内部采用质数193Set.insert(3); //实际大小为193Set.insert(196);Set.insert(1);Set.insert(389);Set.insert(194);Set.insert(387);//ite1类型为hash_set<const char*, hash<const char*>, eqstr>::iteratorauto iter = Set.begin();for (; iter != Set.end(); ++iter)std::cout << *iter << ""; //387 194 1 389 196 3std::cout << std::endl;return 0;
}- 此时底层的hashtable构造如下:

十一、hash_map
- 由于hash_map底层是以hash table实现的,因此hash_map只是简单的调用hash table的方法即可
- 与map的异同点:
- hash_map与map都是用来快速查找元素的
- 但是map会对元素自动排序,而hash_map没有
- hash_map和map的使用方法相同
- 在介绍hash table的hash functions的时候说过,hash table有一些无法处理的类型(除非用户自己书写hash function)。因此hash_map也无法自己处理
hash_map源码
//以下代码摘录于stl_hash_map.h
//以下的hash<>是个function object,定义于<stl_hash_fun.h>中
//例如:hash<int>::operator()(int x)const{return x;}
template <class _Key, class _Tp, class _HashFcn, class _EqualKey,class _Alloc>
class hash_map
{// requirements:__STL_CLASS_REQUIRES(_Key, _Assignable);__STL_CLASS_REQUIRES(_Tp, _Assignable);__STL_CLASS_UNARY_FUNCTION_CHECK(_HashFcn, size_t, _Key);__STL_CLASS_BINARY_FUNCTION_CHECK(_EqualKey, bool, _Key, _Key);private://以下使用的select1st<>定义在<stl_function.h>中typedef hashtable<pair<const _Key,_Tp>,_Key,_HashFcn,_Select1st<pair<const _Key,_Tp> >,_EqualKey,_Alloc> _Ht;_Ht _M_ht;public:typedef typename _Ht::key_type key_type;typedef _Tp data_type;typedef _Tp mapped_type;typedef typename _Ht::value_type value_type;typedef typename _Ht::hasher hasher;typedef typename _Ht::key_equal key_equal;typedef typename _Ht::size_type size_type;typedef typename _Ht::difference_type difference_type;typedef typename _Ht::pointer pointer;typedef typename _Ht::const_pointer const_pointer;typedef typename _Ht::reference reference;typedef typename _Ht::const_reference const_reference;typedef typename _Ht::iterator iterator;typedef typename _Ht::const_iterator const_iterator;typedef typename _Ht::allocator_type allocator_type;hasher hash_funct() const { return _M_ht.hash_funct(); }key_equal key_eq() const { return _M_ht.key_eq(); }allocator_type get_allocator() const { return _M_ht.get_allocator(); }public://缺省使用大小为100的表格,将被hash table调整为最接近且较大的质数hash_map() : _M_ht(100, hasher(), key_equal(), allocator_type()) {}explicit hash_map(size_type __n): _M_ht(__n, hasher(), key_equal(), allocator_type()) {}hash_map(size_type __n, const hasher& __hf): _M_ht(__n, __hf, key_equal(), allocator_type()) {}hash_map(size_type __n, const hasher& __hf, const key_equal& __eql,const allocator_type& __a = allocator_type()): _M_ht(__n, __hf, __eql, __a) {}#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATEStemplate <class _InputIterator>hash_map(_InputIterator __f, _InputIterator __l): _M_ht(100, hasher(), key_equal(), allocator_type()){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }template <class _InputIterator>hash_map(_InputIterator __f, _InputIterator __l, size_type __n): _M_ht(__n, hasher(), key_equal(), allocator_type()){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }template <class _InputIterator>hash_map(_InputIterator __f, _InputIterator __l, size_type __n,const hasher& __hf): _M_ht(__n, __hf, key_equal(), allocator_type()){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }template <class _InputIterator>hash_map(_InputIterator __f, _InputIterator __l, size_type __n,const hasher& __hf, const key_equal& __eql,const allocator_type& __a = allocator_type()): _M_ht(__n, __hf, __eql, __a){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }#elsehash_map(const value_type* __f, const value_type* __l): _M_ht(100, hasher(), key_equal(), allocator_type()){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }hash_map(const value_type* __f, const value_type* __l, size_type __n): _M_ht(__n, hasher(), key_equal(), allocator_type()){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }hash_map(const value_type* __f, const value_type* __l, size_type __n,const hasher& __hf): _M_ht(__n, __hf, key_equal(), allocator_type()){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }hash_map(const value_type* __f, const value_type* __l, size_type __n,const hasher& __hf, const key_equal& __eql,const allocator_type& __a = allocator_type()): _M_ht(__n, __hf, __eql, __a){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }hash_map(const_iterator __f, const_iterator __l): _M_ht(100, hasher(), key_equal(), allocator_type()){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }hash_map(const_iterator __f, const_iterator __l, size_type __n): _M_ht(__n, hasher(), key_equal(), allocator_type()){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }hash_map(const_iterator __f, const_iterator __l, size_type __n,const hasher& __hf): _M_ht(__n, __hf, key_equal(), allocator_type()){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }hash_map(const_iterator __f, const_iterator __l, size_type __n,const hasher& __hf, const key_equal& __eql,const allocator_type& __a = allocator_type()): _M_ht(__n, __hf, __eql, __a){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }
#endif /*__STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */public://所有操作几乎都有hash table的对应版本。传递调用即可size_type size() const { return _M_ht.size(); }size_type max_size() const { return _M_ht.max_size(); }bool empty() const { return _M_ht.empty(); }void swap(hash_map& __hs) { _M_ht.swap(__hs._M_ht); }#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATEStemplate <class _K1, class _T1, class _HF, class _EqK, class _Al>friend bool operator== (const hash_map<_K1, _T1, _HF, _EqK, _Al>&,const hash_map<_K1, _T1, _HF, _EqK, _Al>&);
#else /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */friend bool __STD_QUALIFIERoperator== __STL_NULL_TMPL_ARGS (const hash_map&, const hash_map&);
#endif /* __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */iterator begin() { return _M_ht.begin(); }iterator end() { return _M_ht.end(); }const_iterator begin() const { return _M_ht.begin(); }const_iterator end() const { return _M_ht.end(); }public:pair<iterator,bool> insert(const value_type& __obj){ return _M_ht.insert_unique(__obj); }
#ifdef __STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATEStemplate <class _InputIterator>void insert(_InputIterator __f, _InputIterator __l){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f,__l); }
#elsevoid insert(const value_type* __f, const value_type* __l) {_M_ht.insert_unique(__f,__l);}void insert(const_iterator __f, const_iterator __l){ _M_ht.insert_unique(__f, __l); }
#endif /*__STL_MEMBER_TEMPLATES */pair<iterator,bool> insert_noresize(const value_type& __obj){ return _M_ht.insert_unique_noresize(__obj); } iterator find(const key_type& __key) { return _M_ht.find(__key); }const_iterator find(const key_type& __key) const { return _M_ht.find(__key); }_Tp& operator[](const key_type& __key) {return _M_ht.find_or_insert(value_type(__key, _Tp())).second;}size_type count(const key_type& __key) const { return _M_ht.count(__key); }pair<iterator, iterator> equal_range(const key_type& __key){ return _M_ht.equal_range(__key); }pair<const_iterator, const_iterator>equal_range(const key_type& __key) const{ return _M_ht.equal_range(__key); }size_type erase(const key_type& __key) {return _M_ht.erase(__key); }void erase(iterator __it) { _M_ht.erase(__it); }void erase(iterator __f, iterator __l) { _M_ht.erase(__f, __l); }void clear() { _M_ht.clear(); }void resize(size_type __hint) { _M_ht.resize(__hint); }size_type bucket_count() const { return _M_ht.bucket_count(); }size_type max_bucket_count() const { return _M_ht.max_bucket_count(); }size_type elems_in_bucket(size_type __n) const{ return _M_ht.elems_in_bucket(__n); }
};template <class _Key, class _Tp, class _HashFcn, class _EqlKey, class _Alloc>
inline bool
operator==(const hash_map<_Key,_Tp,_HashFcn,_EqlKey,_Alloc>& __hm1,const hash_map<_Key,_Tp,_HashFcn,_EqlKey,_Alloc>& __hm2)
{return __hm1._M_ht == __hm2._M_ht;
}hash_map使用演示案例
#include <iostream>
#include <hash_map>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;struct eqstr
{bool operator()(const char* s1, const char* s2){return strcmp(s1, s2) == 0;}
};int main()
{hash_map<const char*, int,hash<const char*>, eqstr> days;days["january"] = 31;days["february"] = 28;days["march"] = 31;days["april"] = 30;days["may"] = 31;days["june"] = 30;days["july"] = 31;days["august"] = 31;days["september"] = 30;days["october"] = 31;days["november"] = 30;days["december"] = 31;std::cout << "september ->" << days["september"] << std::endl;//30std::cout << "june ->" << days["june"] << std::endl; //30std::cout << "february ->" << days["february"] << std::endl; //28std::cout << "december ->" << days["december"] << std::endl; //31//ite1类型为hash_map<const char*, int,hash<const char*>, eqstr>::iteratorauto iter = days.begin();for (; iter != days.end(); ++iter)std::cout << iter->first << "";//september june july may january february december //march april november october auguststd::cout << std::endl;return 0;
}十二、hash_multiset
- hash_multiset与hash_set使用起来相同,只是hash_multiset中允许键值重复
- 在源码中,hash_multiset调用的是insert_equal(),而hash_set调用的是insert_unique()
十三、hash_multimap
- hash_multimap与hash_map使用起来相同,只是hash_multimap中允许键值重复
- 在源码中,hash_multimap调用的是insert_equal(),而hash_map调用的是insert_unique()。
- 我是小董,V公众点击"笔记白嫖"解锁更多【C++ STL源码剖析】资料内容。

这篇关于一篇足矣,带你吃透STL源码中hash table(哈希表)与关联式容器hash_set、hash_map的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





