本文主要是介绍《PCL点云库学习VS2010(X64)》Part 15 PCL1.72(VTK6.2.0)三角网格化(2)之泊松重构,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
《PCL点云库学习&VS2010(X64)》Part 15 PCL1.72(VTK6.2.0)三角网格化(2)之泊松重构
1、cpp
//点的类型的头文件
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
//点云文件IO(pcd文件和ply文件)
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/io/ply_io.h>
//kd树
#include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree_flann.h>
//特征提取
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d_omp.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
//重构
#include <pcl/surface/gp3.h>
#include <pcl/surface/poisson.h>
//可视化
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
//多线程
#include <boost/thread/thread.hpp>
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
//计时
#include <time.h>int main(int argc, char** argv)
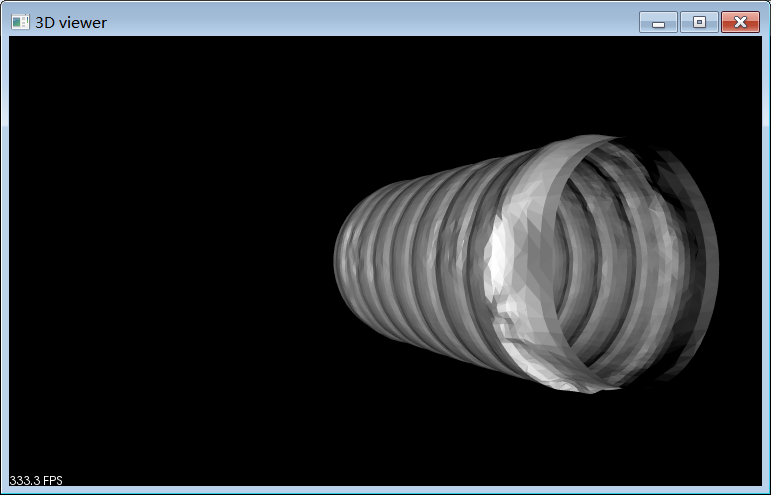
{// 确定文件格式char tmpStr[100];strcpy(tmpStr, argv[1]);char* pext = strrchr(tmpStr, '.');std::string extply("ply");std::string extpcd("pcd");if (pext){*pext = '\0';pext++;}std::string ext(pext);//如果不支持文件格式,退出程序if (!((ext == extply) || (ext == extpcd))){std::cout << "文件格式不支持!" << std::endl;std::cout << "支持文件格式:*.pcd和*.ply!" << std::endl;return(-1);}//根据文件格式选择输入方式pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>); //创建点云对象指针,用于存储输入if (ext == extply){if (pcl::io::loadPLYFile(argv[1], *cloud) == -1){PCL_ERROR("Could not read ply file!\n");return -1;}}else{if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile(argv[1], *cloud) == -1){PCL_ERROR("Could not read pcd file!\n");return -1;}}//create a timerclock_t start, end;// 计算法向量pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr cloud_with_normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointNormal>); //法向量点云对象指针pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> n;//法线估计对象pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normals(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);//存储估计的法线的指针pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);tree->setInputCloud(cloud);n.setInputCloud(cloud);n.setSearchMethod(tree);n.setKSearch(20);n.compute(*normals); //计算法线,结果存储在normals中//将点云和法线放到一起pcl::concatenateFields(*cloud, *normals, *cloud_with_normals);//创建搜索树pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointNormal>::Ptr tree2(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointNormal>);tree2->setInputCloud(cloud_with_normals);//创建Poisson对象,并设置参数pcl::Poisson<pcl::PointNormal> pn;pn.setConfidence(false); //是否使用法向量的大小作为置信信息。如果false,所有法向量均归一化。pn.setDegree(2); //设置参数degree[1,5],值越大越精细,耗时越久。pn.setDepth(8); //树的最大深度,求解2^d x 2^d x 2^d立方体元。由于八叉树自适应采样密度,指定值仅为最大深度。pn.setIsoDivide(8); //用于提取ISO等值面的算法的深度pn.setManifold(false); //是否添加多边形的重心,当多边形三角化时。 设置流行标志,如果设置为true,则对多边形进行细分三角话时添加重心,设置false则不添加pn.setOutputPolygons(false); //是否输出多边形网格(而不是三角化移动立方体的结果)pn.setSamplesPerNode(3.0); //设置落入一个八叉树结点中的样本点的最小数量。无噪声,[1.0-5.0],有噪声[15.-20.]平滑pn.setScale(1.25); //设置用于重构的立方体直径和样本边界立方体直径的比率。pn.setSolverDivide(8); //设置求解线性方程组的Gauss-Seidel迭代方法的深度//pn.setIndices();//设置搜索方法和输入点云pn.setSearchMethod(tree2);pn.setInputCloud(cloud_with_normals);//创建多变形网格,用于存储结果pcl::PolygonMesh mesh;//执行重构start = clock();pn.performReconstruction(mesh);end = clock();//print time of reconstruction std::cerr << (end-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<<"s used!"<< std::endl;//保存网格图pcl::io::savePLYFile("result.ply", mesh);// 显示结果图boost::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer> viewer(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("3D viewer"));viewer->setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 0);viewer->addPolygonMesh(mesh, "my");//viewer->addCoordinateSystem(1.0);//set coordinateSystem viewer->initCameraParameters();//viewer->spin();while (!viewer->wasStopped()){viewer->spinOnce(100);boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::microseconds(100000));}return 0;
}运行效果:
这篇关于《PCL点云库学习VS2010(X64)》Part 15 PCL1.72(VTK6.2.0)三角网格化(2)之泊松重构的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!