本文主要是介绍【C++】POCO学习总结(十九):哈希、URL、UUID、配置文件、日志配置、动态库加载,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
【C++】郭老二博文之:C++目录
1、哈希
1.1 说明
std::map和std::set 的性能是:O(log n)
POCO哈希的性能比STL容器更好,大约快两;
POCO中对应std::map的是:Poco::HashMap;
POCO中对应std::set的是 Poco::HashSet;
使用方法、迭代器都和STL类似。
POCO哈希在执行插入或者删除操作时不会导致性能下降(当数据不足时不需要重新哈希)
HashMap 和 HashSet 使用线性哈希表LinearHashTable作为基础数据结构。
使用时还必须提供一个哈希函数:Poco/Hash.h中预定义了关于整数和std::string的函数
namespace Poco {
std::size_t hash(Int8 n);
std::size_t hash(UInt8 n);
std::size_t hash(Int16 n);
std::size_t hash(UInt16 n);
std::size_t hash(Int32 n);
std::size_t hash(UInt32 n);
std::size_t hash(Int64 n);
std::size_t hash(UInt64 n);
std::size_t hash(const std::string& str);
}
Poco::LinearHashTable<Key, Hash = Poco::Hash<Key>
1.2 示例
#include "Poco/LinearHashTable.h"
#include "Poco/HashMap.h"
#include <iterator>
#include <iostream>
using namespace Poco;
int main()
{const int N = 20;LinearHashTable<int, Hash<int> > ht;for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)ht.insert(i);LinearHashTable<int, Hash<int> >::Iterator it = ht.begin();while (it != ht.end()){std::cout << "[" << *it << "]";++it;}
}
编译:
g++ hash.cpp -I ~/git/poco/install/include -L ~/git/poco/install/lib -lPocoFoundationd
输出
[0][17][2][19][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13][14][15][16][1][18][3]
2、POCO::URI
2.1 说明
POCO提供了POCO::URI类,该类可用于构建和存储URI,并且解析、拆分URI。
URI结构:协议(scheme)、主机名(host)、用户(user)、端口号(port)、路径(path)、查询(query)、资源(Fragment)等
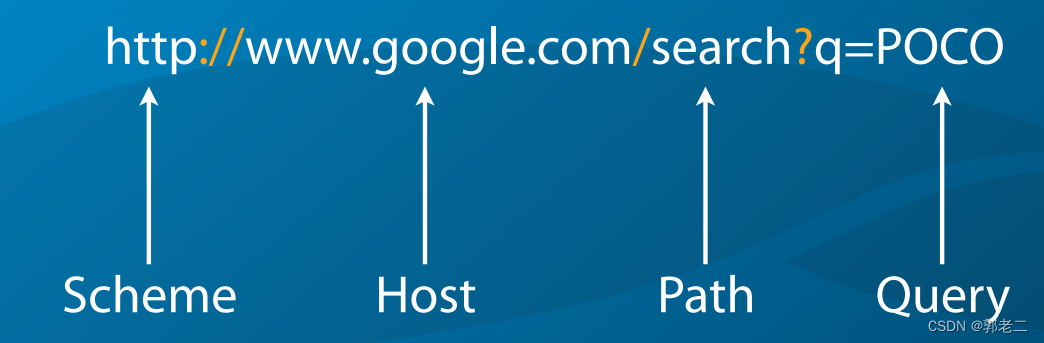
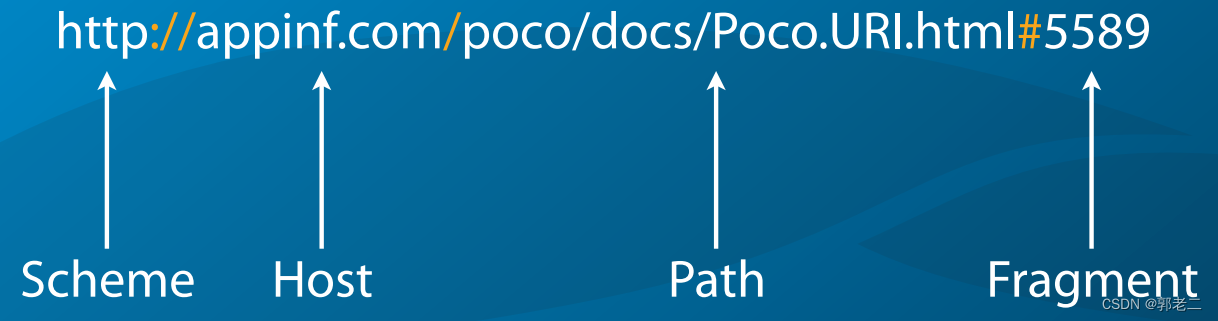
2.2 示例
#include "Poco/URI.h"
#include <iostream>
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{Poco::URI uri1("http://www.appinf.com:88/sample?example-query#frag");std::string scheme(uri1.getScheme()); // "http"std::string auth(uri1.getAuthority()); // "www.appinf.com:88"std::string host(uri1.getHost()); // "www.appinf.com"unsigned short port = uri1.getPort(); // 88std::string path(uri1.getPath()); // "/sample"std::string query(uri1.getQuery()); // "example-query"std::string frag(uri1.getFragment()); // "frag"std::string pathEtc(uri1.getPathEtc()); // "/sample?examplequery#frag"Poco::URI uri2;uri2.setScheme("https");uri2.setAuthority("www.appinf.com");uri2.setPath("/another sample");std::string s(uri2.toString()); // "https://www.appinf.com/another%20sample"std::string uri3("http://www.appinf.com");uri3.resolve("/poco/info/index.html");s = uri3.toString(); // "http://www.appinf.com/poco/info/index.html"uri3.resolve("support.html");s = uri3.toString(); // "http://www.appinf.com/poco/info/support.html"uri3.resolve("http://sourceforge.net/projects/poco");s = uri3.toString(); // "http://sourceforge.net/projects/poco"return 0;
}
3、UUID
3.1 说明
UUID(通用唯一标识符)是一种标识符,它在空间和时间上相对于所有UUID的空间都是唯一的。
Poco::UUID支持包括所有关系操作符在内的全值语义,和字符串之间进行转换。
3.2 示例
#include "Poco/UUID.h"
#include "Poco/UUIDGenerator.h"
#include <iostream>
using Poco::UUID;
using Poco::UUIDGenerator;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{UUIDGenerator& generator = UUIDGenerator::defaultGenerator();UUID uuid1(generator.create()); // time basedUUID uuid2(generator.createRandom());UUID uuid3(generator.createFromName(UUID::uri(), "http://appinf.com");std::cout << uuid1.toString() << std::endl;std::cout << uuid2.toString() << std::endl;std::cout << uuid3.toString() << std::endl;return 0;
}
4、配置文件
4.1 说明
Poco::Util::AbstractConfiguration提供了一个公共接口,用于访问来自不同来源的配置信息。
配置设置基本上是键/值对,其中键和值都是字符串。
键具有层次结构,由以句点分隔的名称组成。
值可以转换为整数、双精度和布尔值。
一个可选的默认值可以在getter函数中指定。
4.2 用法
- bool hasProperty(const std::string& key)
- std::string getString(const std::string& key [, const std::string& default])
- int getInt(const std::string& key [, int default])
- getDouble()
- getBool()
- setString(),
- setInt()
- setDouble()
- setBool()
- keys()
4.3 Poco::Util::IniFileConfiguration ini配置文件
Poco::Util::IniFileConfiguration支持普通的旧INI格式文件,主要用于Windows。
- 键名不区分大小写。
- 从键和值中删除前导和尾随空格。
- 只读
格式:
; comment
[MyApplication]
somePath = C:\test.dat
someValue = 123
解析:
using Poco::AutoPtr;
using Poco::Util::IniFileConfiguration;
AutoPtr<IniFileConfiguration> pConf(new IniFileConfiguration("test.ini"));
std::string path = pConf->getString("MyApplication.somePath");
int value = pConf->getInt("MyApplication.someValue");
value = pConf->getInt("myapplication.SomeValue");
value = pConf->getInt("myapplication.SomeOtherValue", 456);
4.4 Poco::Util::PropertyFileConfiguration 属性文件
格式:
# a comment
! another comment
key1 = value1
key2: 123
key3.longValue = this is a very \
long value
path = c:\\test.dat
解析:
using Poco::AutoPtr;
using Poco::Util::PropertyFileConfiguration;
AutoPtr<PropertyFileConfiguration> pConf;
pConf = new PropertyFileConfiguration("test.properties");
std::string key1 = pConf->getString("key1");
int value = pConf->getInt("key2");
std::string longVal = pConf->getString("key3.longValue");
4.5 Poco::Util::XMLConfiguration XML配置文件
格式:
<config><prop1>value1</prop1><prop2>123</prop2><prop3><prop4 attr="value3"/><prop4 attr="value4"/></prop3>
</config>
解析
using Poco::AutoPtr;
using Poco::Util::XMLConfiguration;
AutoPtr<XMLConfiguration> pConf(new XMLConfiguration("test.xml"));
std::string prop1 = pConf->getString("prop1");
int prop2 = pConf->getInt("prop2");
std::string prop3 = pConf->getString("prop3"); // ""
std::string prop4 = pConf->getString("prop3.prop4"); // ""
prop4 = pConf->getString("prop3.prop4[@attr]"); // "value3"
prop4 = pConf->getString("prop3.prop4[1][@attr]"); // "value4"
5、日志配置
5.1 说明
Poco::Util::LoggingConfigurator类使用来自Poco::Util::AbstractConfiguration的配置信息来设置和连接日志格式化、通道和记录器。
Poco::Util::Application自动初始化一个LoggingConfigurator及其配置。
所有用于日志记录的配置属性都是以“logging”为键值。
5.2 格式化配置
格式化配置以“logging.formatters”开头;
每个格式化都有一个内部名称,该名称仅用于配置目的,用于将格式化程序连接到通道。
该名称成为属性名称的一部分。其中class属性是必须的,它指定实现格式化程序的类。
logging.formatters.f1.class = PatternFormatter
logging.formatters.f1.pattern = %s: [%p] %t
logging.formatters.f1.times = UTC
5.3 通道配置
通道配置以“logging.channels”开头;class属性是必须的
“formatter”属性既可以用来引用已经定义的格式化,也可以用来指定“内联”格式化定义。在这两种情况下,当存在"formatter"属性时,通道将自动被"包装"在FormattingChannel对象
# External Formatter
logging.channels.c1.class = ConsoleChannel
logging.channels.c1.formatter = f1
# Inline Formatter
logging.channels.c2.class = FileChannel
logging.channels.c2.path = ${system.tempDir}/sample.log
logging.channels.c2.formatter.class = PatternFormatter
logging.channels.c2.formatter.pattern = %Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %s: [%p] %t
# Inline PatternFormatter
logging.channels.c3.class = ConsoleChannel
logging.channels.c3.pattern = %s: [%p] %t
5.4 日志记录器
日志记录器使用“logging.loggers”
与通道 channels 和格式化 formatters 一样,每个日志记录器都有一个内部名称,但是,该名称仅用于确保属性名称的唯一性。请注意,此名称与记录器的全名不同,后者用于在运行时访问记录器。
除了根记录器之外,每个记录器都有一个强制性的“name”属性,用于指定记录器的全名。
# External Channel
logging.loggers.root.channel = c1
logging.loggers.root.level = warning
# Inline Channel with PatternFormatter
logging.loggers.l1.name = logger1
logging.loggers.l1.channel.class = ConsoleChannel
logging.loggers.l1.channel.pattern = %s: [%p] %t
logging.loggers.l1.level = information
# SplitterChannel
logging.channels.splitter.class = SplitterChannel
logging.channels.splitter.channels = l1,l2
logging.loggers.l2.name = logger2
logging.loggers.l2.channel = splitter
6、动态库加载
6.1 说明
大多数现代平台都提供了在运行时以共享库(动态链接库)的形式加载程序模块的功能。
Windows提供了LoadLibrary()函数,大多数Unix平台都有dopen()。
6.2 用法
头文件: #include “Poco/SharedLibrary.h”
Poco::SharedLibrary是Poco与操作系统动态链接器/加载器的接口。
Poco::SharedLibrary提供了加载共享库、查找符号地址和卸载共享库的底层函数。
- void load(const std::string& path):从给定的路径加载共享库
- void unload():卸载共享库
- bool hasSymbol(const std::string& name):如果库中包含具有给定名称的符号,则返回true
- void* getSymbol(const std::string& name):返回给定名称的符号的地址。对于函数,这是函数的入口点。要调用函数,请强制转换为函数指针并通过它调用
6.3 示例
1)动态库:TestLibrary.cpp
#include <iostream>
#if defined(_WIN32)
#define LIBRARY_API __declspec(dllexport)
#else
#define LIBRARY_API
#endif
extern "C" void LIBRARY_API hello();
void hello()
{std::cout << "Hello, world!" << std::endl;
}
2)加载动态库:LibraryLoaderTest.cpp
#include "Poco/SharedLibrary.h"
using Poco::SharedLibrary;
typedef void (*HelloFunc)(); // function pointer type
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{std::string path("TestLibrary");path.append(SharedLibrary::suffix()); // adds ".dll" or ".so"SharedLibrary library(path); // will also load the libraryHelloFunc func = (HelloFunc) library.getSymbol("hello");func();library.unload();return 0;
}
6.4 Poco::ClassLoader 从共享库加载类
Poco::ClassLoader是Poco的高级接口,用于从共享库加载类。它非常适合实现典型的插件架构。
头文件: #include “Poco/ClassLoader.h”
Poco::ClassLoader所有类必须是公共基类的子类。Poco::ClassLoader是一个类模板,必须为基类实例化。
6.5 元对象
Manifest库维护一个包含在动态可加载类库中的所有类的列表。
它将这些信息作为元对象的集合进行管理。
MetaObject管理给定类的对象的生命周期。它用于创建类的实例,并删除它们。
作为一个特殊的特性,类库可以导出单例。
这篇关于【C++】POCO学习总结(十九):哈希、URL、UUID、配置文件、日志配置、动态库加载的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




