本文主要是介绍Data Mining数据挖掘—5. Association Analysis关联分析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
6. Association Analysis
Given a set of records each of which contains some number of items from a given collection.
Produce dependency rules that will predict the occurrence of an item based on occurrences of other items.
Application area: Marketing and Sales Promotion, Content-based recommendation, Customer loyalty programs
Initially used for Market Basket Analysis to find how items purchased by customers are related. Later extended to more complex data structures: sequential patterns and subgraph patterns
6.1 Simple Approach: Pearson’s correlation coefficient
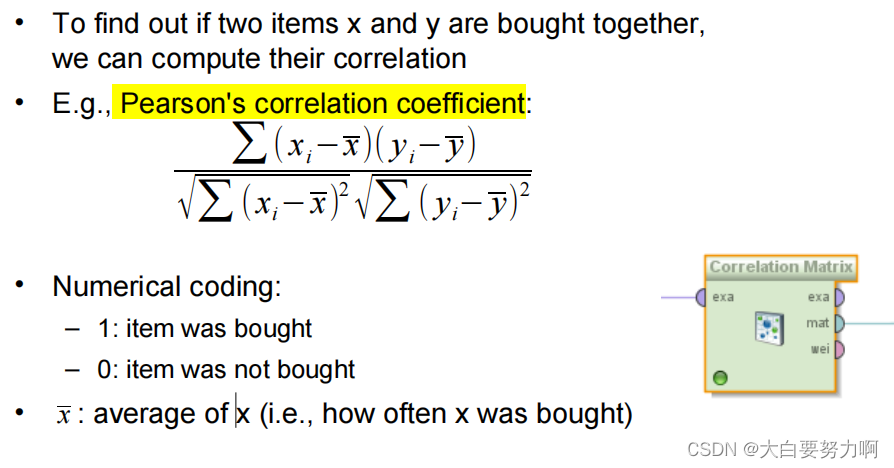
correlation not equals to causality
6.2 Definitoin
6.2.1 Frequent Itemset
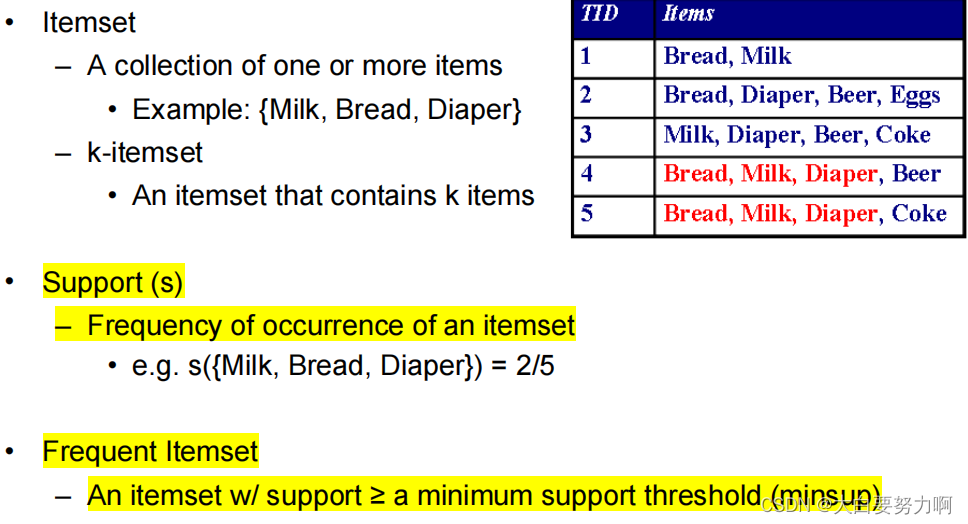
6.2.2 Association Rule
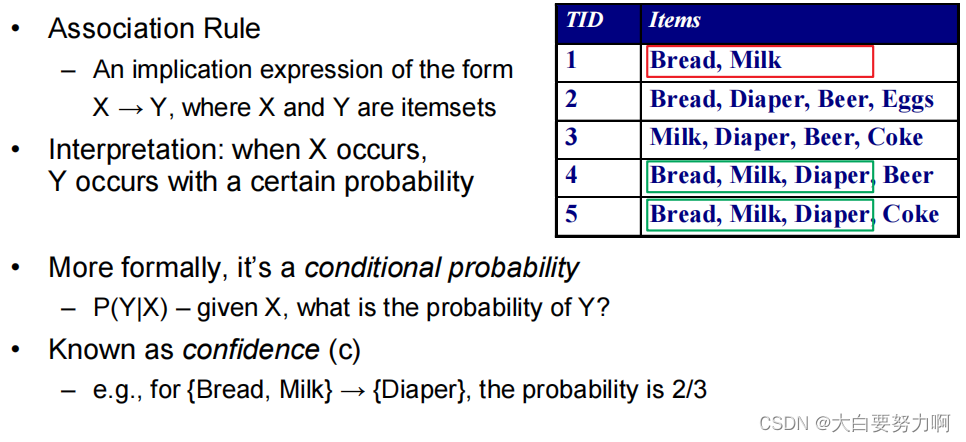
6.2.3 Evaluation Metrics
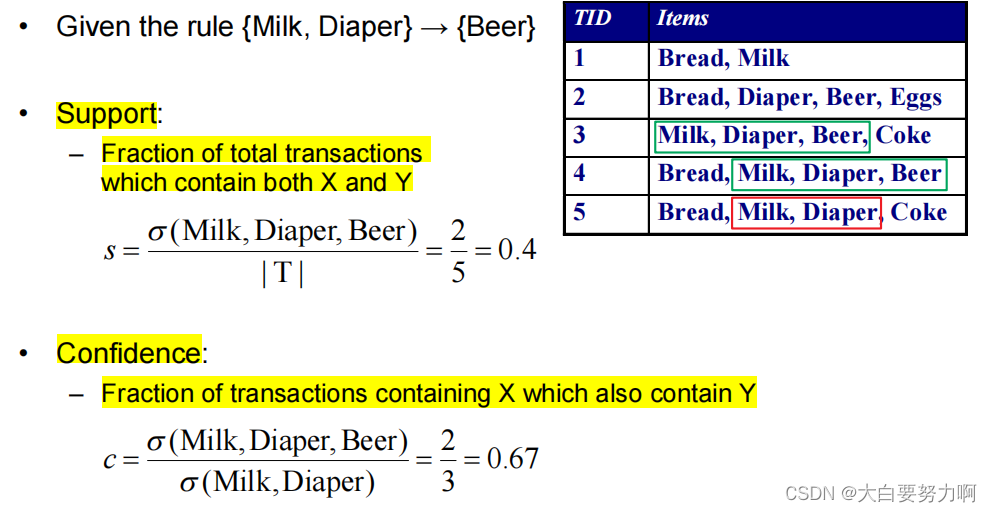
6.3 Associate Rule Mining Task
Given a set of transactions T, the goal of association rule mining is to find all rules having
– support ≥ minsup threshold
– confidence ≥ minconf threshold
minsup and minconf are provided by the user
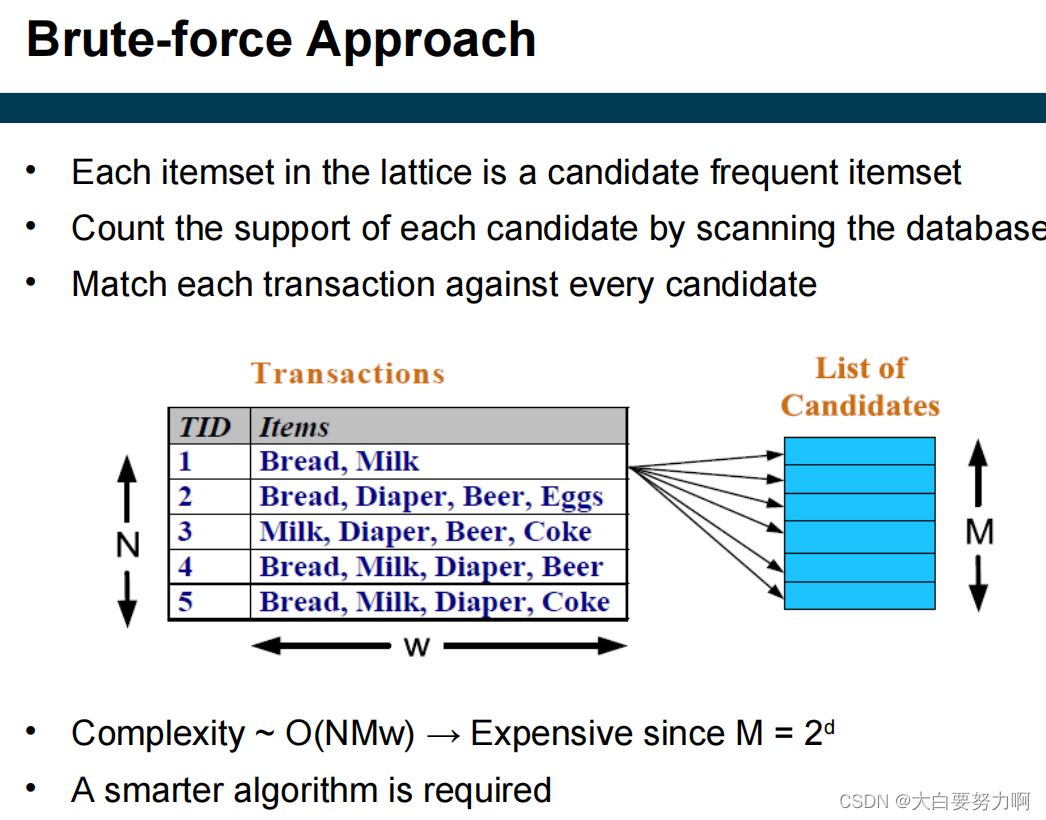
Brute-force approach
Step1: List all possible association rules
Step2: Compute the support and confidence for each rule
Step3: Remove rules that fail the minsup and minconf thresholds
But Computationally prohibitive due to large number of candidates!
6.4 Apriori Algorithm
Two-step approach
Step1: Frequent Itemset Generation (Generate all itemsets whose support ≥ minsup)
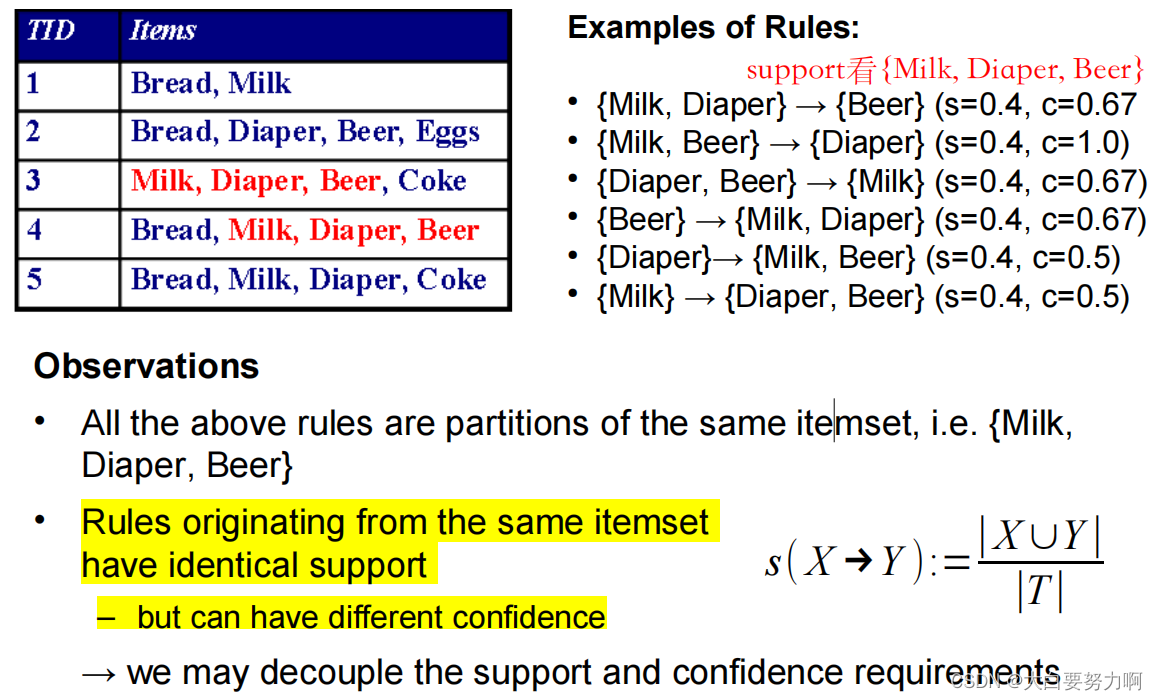
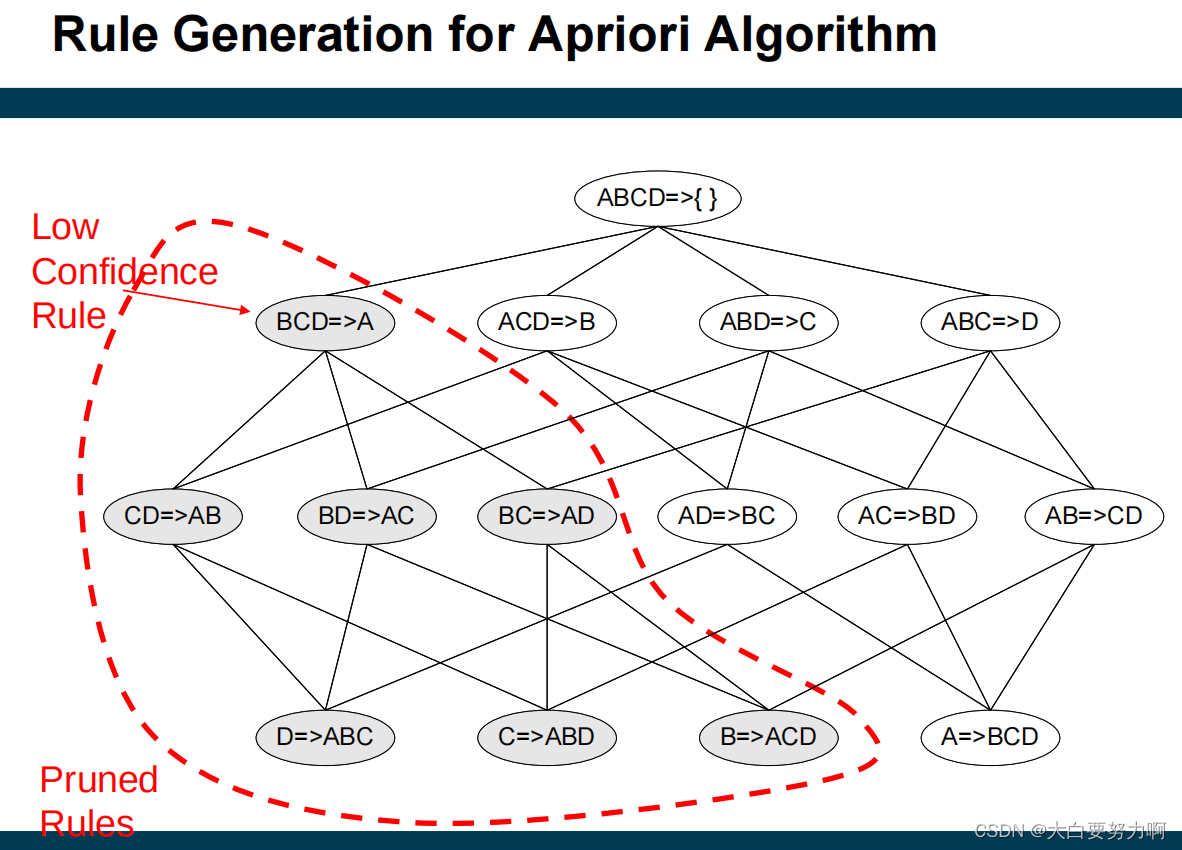
Step2: Rule Generation (Generate high confidence rules from each frequent itemset; where each rule is a binary partitioning of a frequent itemset)
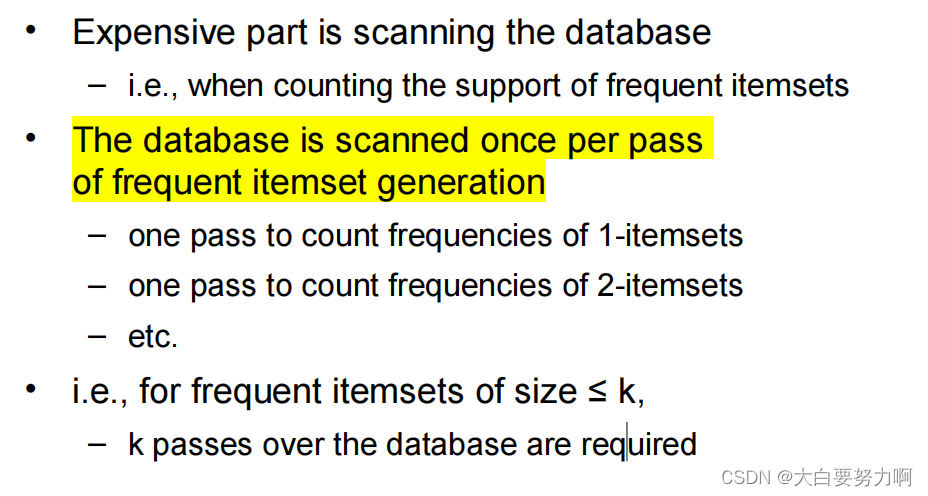
However, frequent itemset generation is still computationally expensive… Given d items, there are 2^d candidate itemsets!
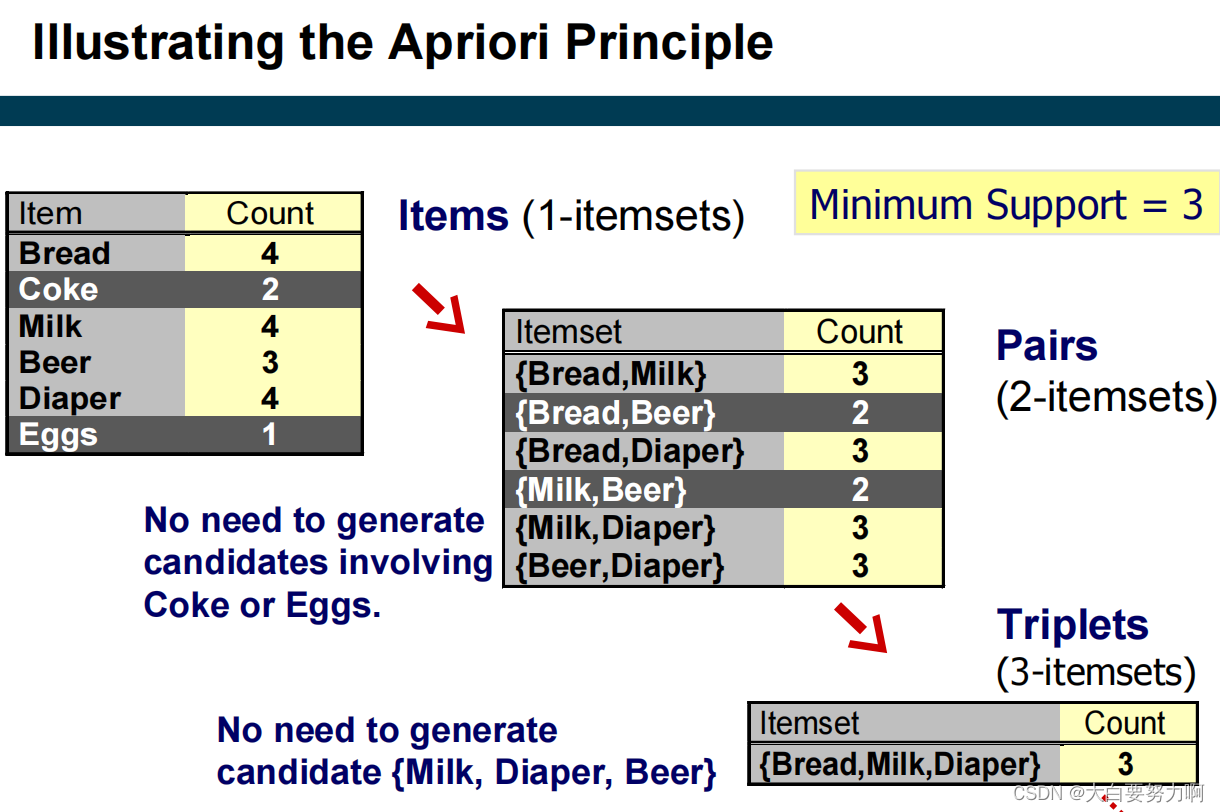
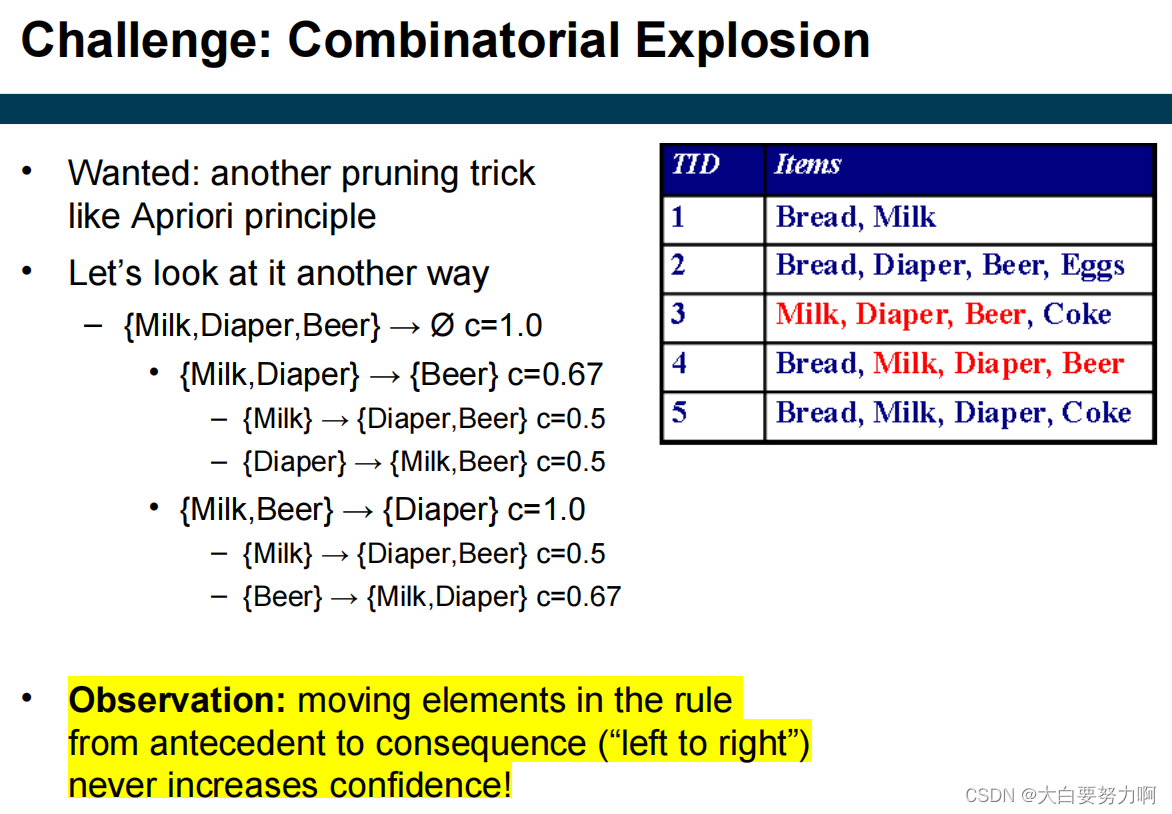
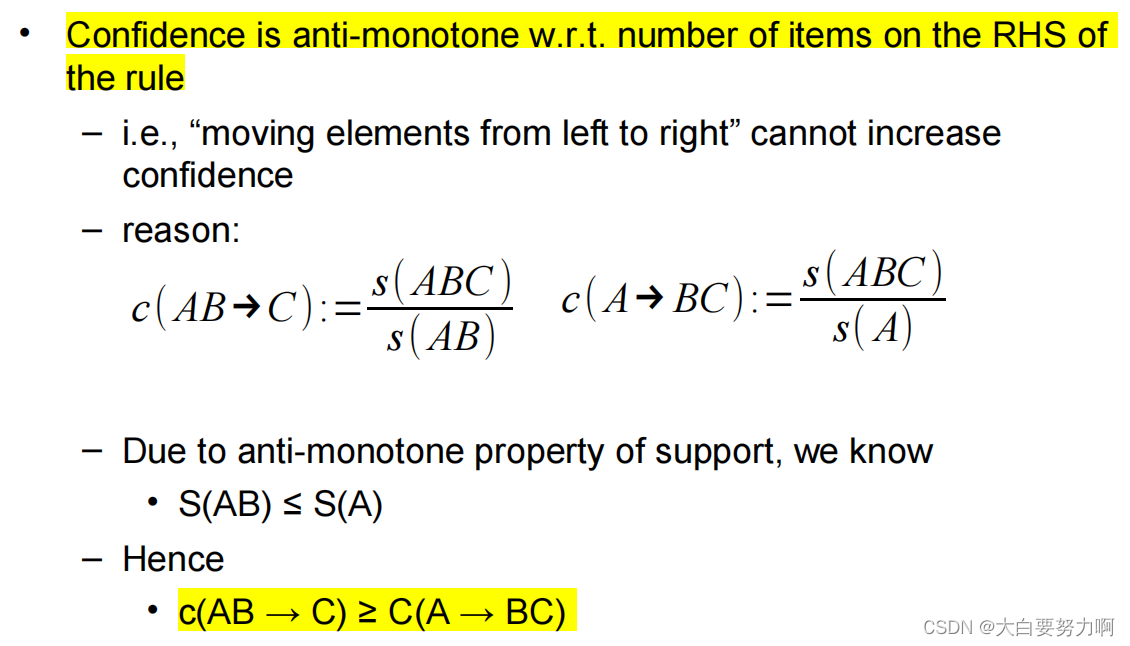
Anti-Monotonicity of Support

Steps
- Start at k=1
- Generate frequent itemsets of length k=1
- Repeat until no new frequent itemsets are identified
- Generate length (k+1) candidate itemsets from length k frequent itemsets; increase k
- Prune candidate itemsets that cannot be frequent because they contain subsets of length k that are infrequent (Apriori Principle)
- Count the support of each remaining candidate by scanning the DB
- Eliminate candidates that are infrequent, leaving only those that are frequent
From Frequent Itemsets to Rules

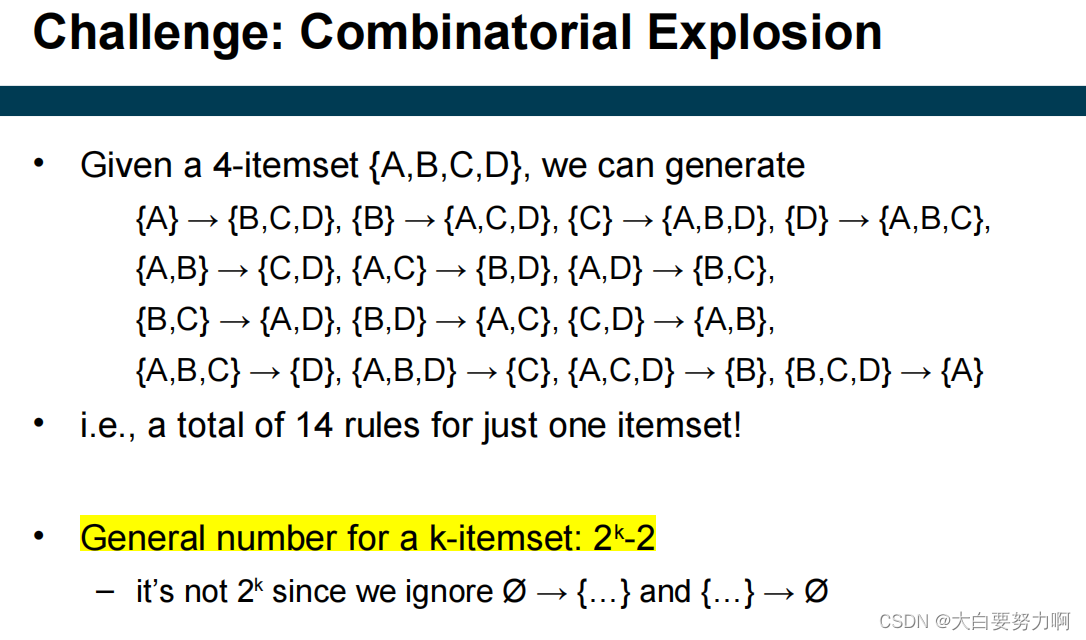
Complexity of Apriori Algorithm
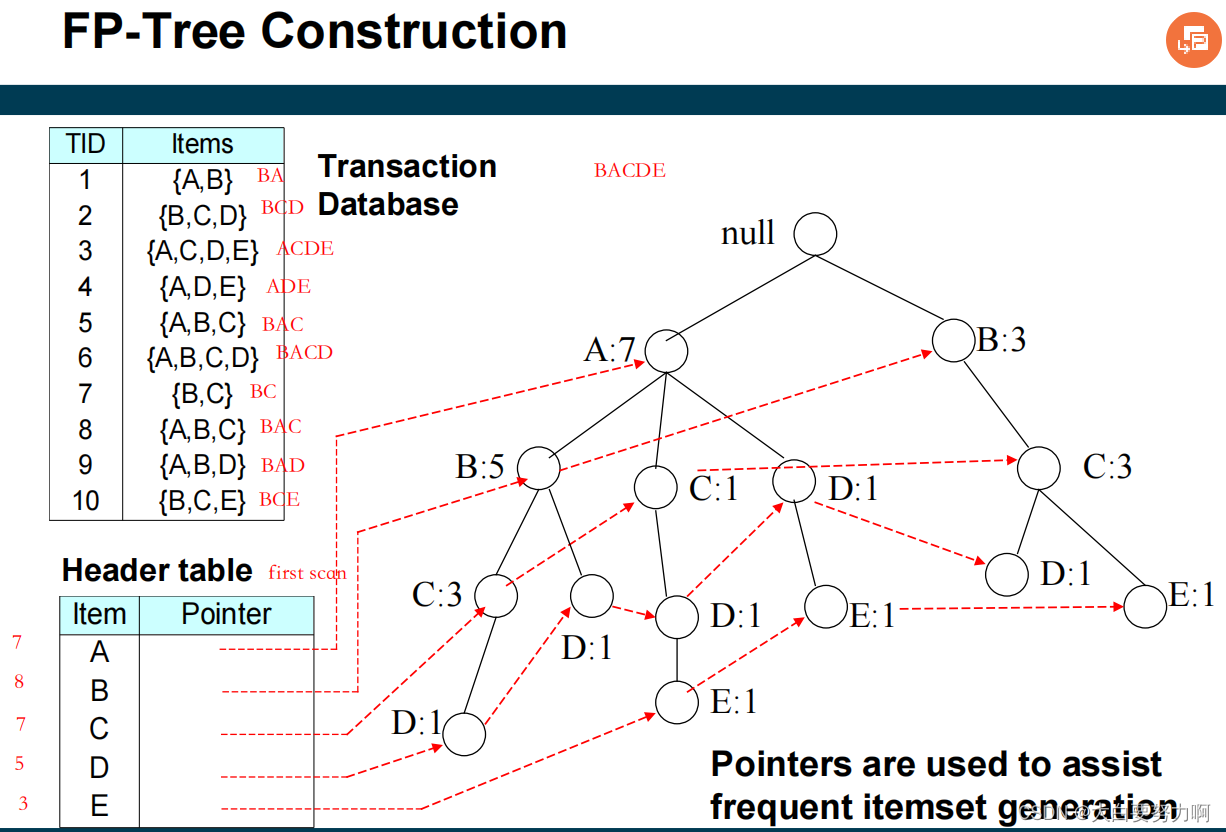
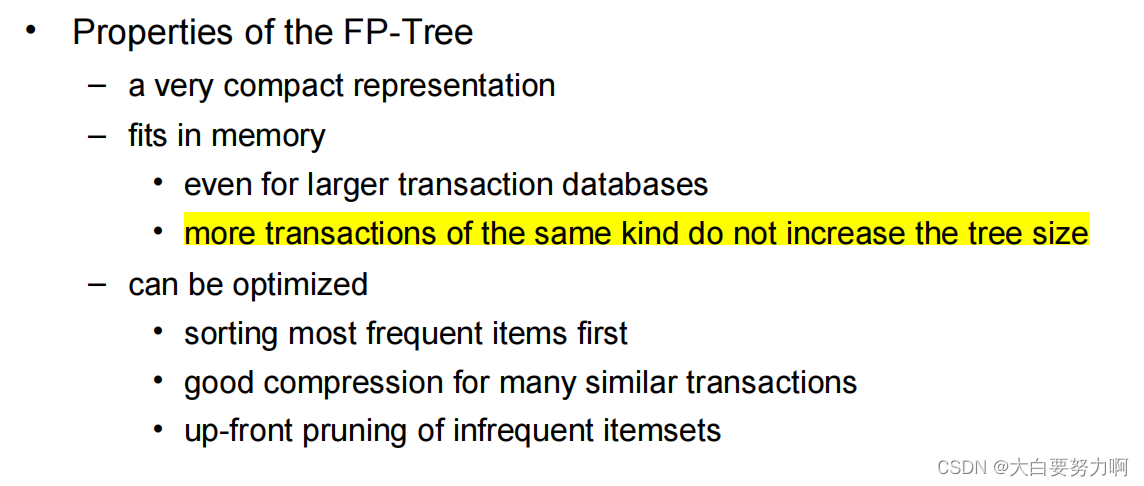
6.5 FP-growth Algorithm
usually faster than Apriori, requires at most two passes over the database
Use a compressed representation of the database using an FP-tree
Once an FP-tree has been constructed, it uses a recursive divide-and-conquer approach to mine the frequent itemsets

6.6 Interestingness Measures
Interestingness measures can be used to prune or rank the derived rules
In the original formulation of association rules, support & confidence are the only interest measures used
various other measures have been proposed
Drawback of Confidence
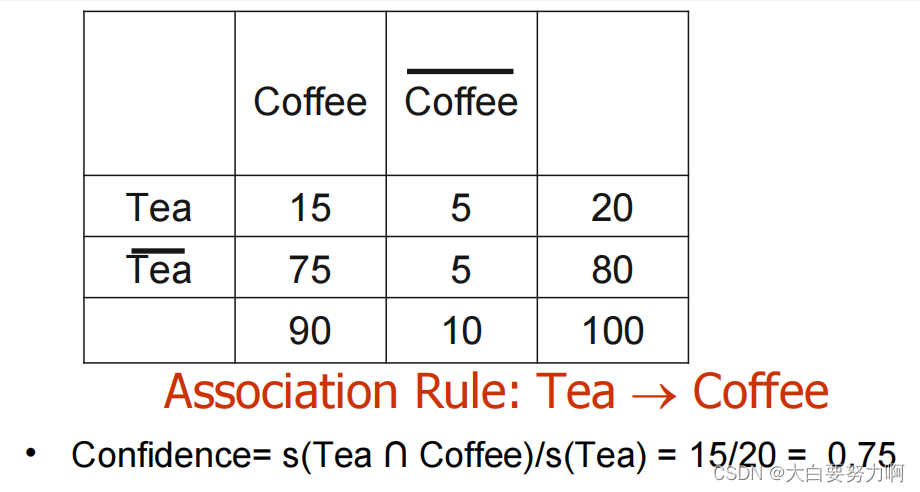

6.6.1 Correlation
Correlation takes into account all data at once.
In our scenario: corr(tea,coffee) = -0.25
i.e., the correlation is negative
Interpretation: people who drink tea are less likely to drink coffee
6.6.2 Lift


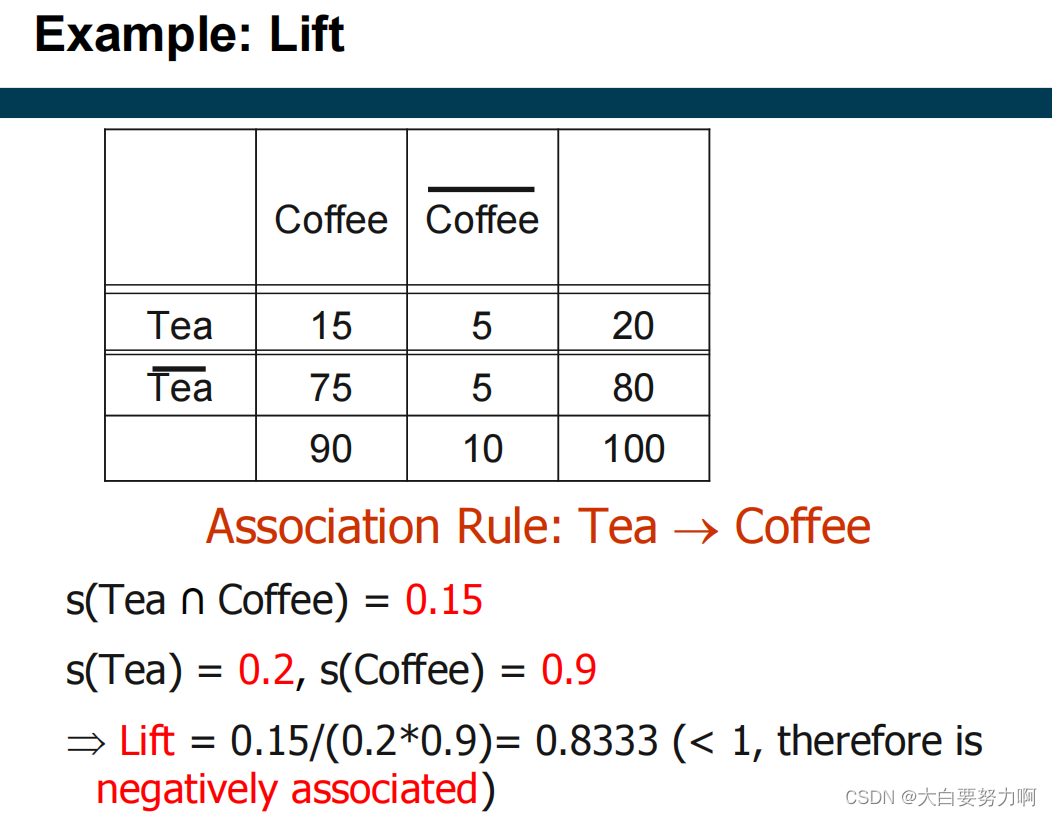
lift and correlation are symmetric [lift(tea → coffee) = lift(coffee → tea)]
confidence is asymmetric
6.6.3 Others
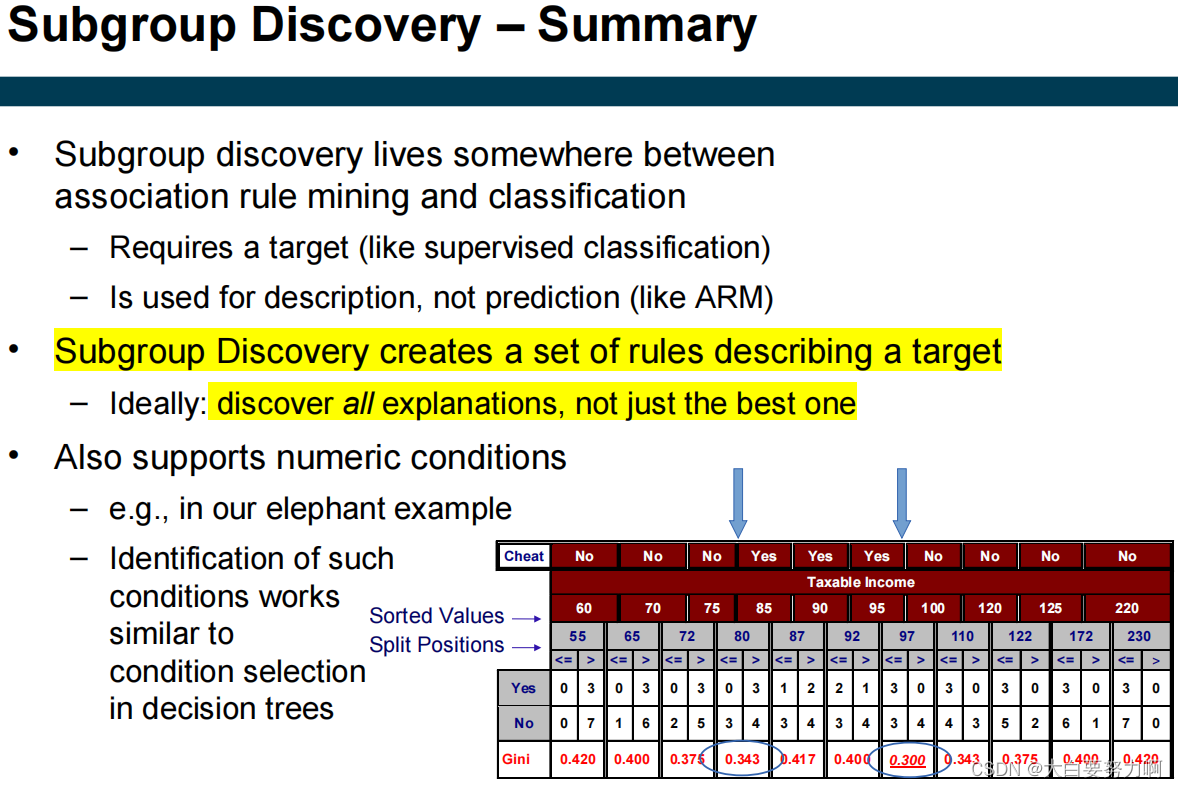
6.7 Handling Continuous and Categorical Attributes
6.7.1 Handling Categorical Attributes
Transform categorical attribute into asymmetric binary variables. Introduce a new “item” for each distinct attribute-value pair -> one-hot-encoding
Potential Issues
(1) Many attribute values
Many of the attribute values may have very low support
Potential solution: Aggregate the low-support attribute values -> bin for “other”
(2) Highly skewed attribute values
Example: 95% of the visitors have Buy = No
Most of the items will be associated with (Buy=No) item
Potential solution: drop the highly frequent items
6.7.2 Handling Continuous Attributes
Transform continuous attribute into binary variables using discretization:
Equal-width binning & Equal-frequency binning
Issue: Size of the intervals affects support & confidence - Too small intervals: not enough support but Too large intervals: not enough confidence
6.8 Effect of Support Distribution
Many real data sets have a skewed support distribution
How to set the appropriate minsup threshold?
If minsup is set too high, we could miss itemsets involving interesting rare items (e.g., expensive products)
If minsup is set too low, it is computationally expensive and the number of itemsets is very large
Using a single minimum support threshold may not be effective
Multiple Minimum Support

6.9 Association Rules with Temporal Components

6.10 Subgroup Discovery
Association Rule Mining: Find all patterns in the data
Classification: Identify the best patterns that can predict a target variable
Find all patterns that can explain a target variable.
从数据集中发现具有特定属性和特征的子群或子集。这个任务的目标是识别数据中与感兴趣的属性或行为相关的子群,以便更深入地理解数据、做出预测或采取相关行动。在某些情况下,子群发现可以用于生成新的特征,然后将这些特征用于分类任务。
子群发现旨在发现数据中的子群,而分类旨在将数据分为已知的类别。子群发现通常更加探索性,而分类通常更加预测性。
we have strong predictor variables. But we are also interested in the weaker ones
Algorithms
Early algorithms: Learn unpruned decision tree; Extract rule; Compute measures for rules, rate and rank
Newer algorithms: Based on association rule mining; Based on evolutionary algorithms
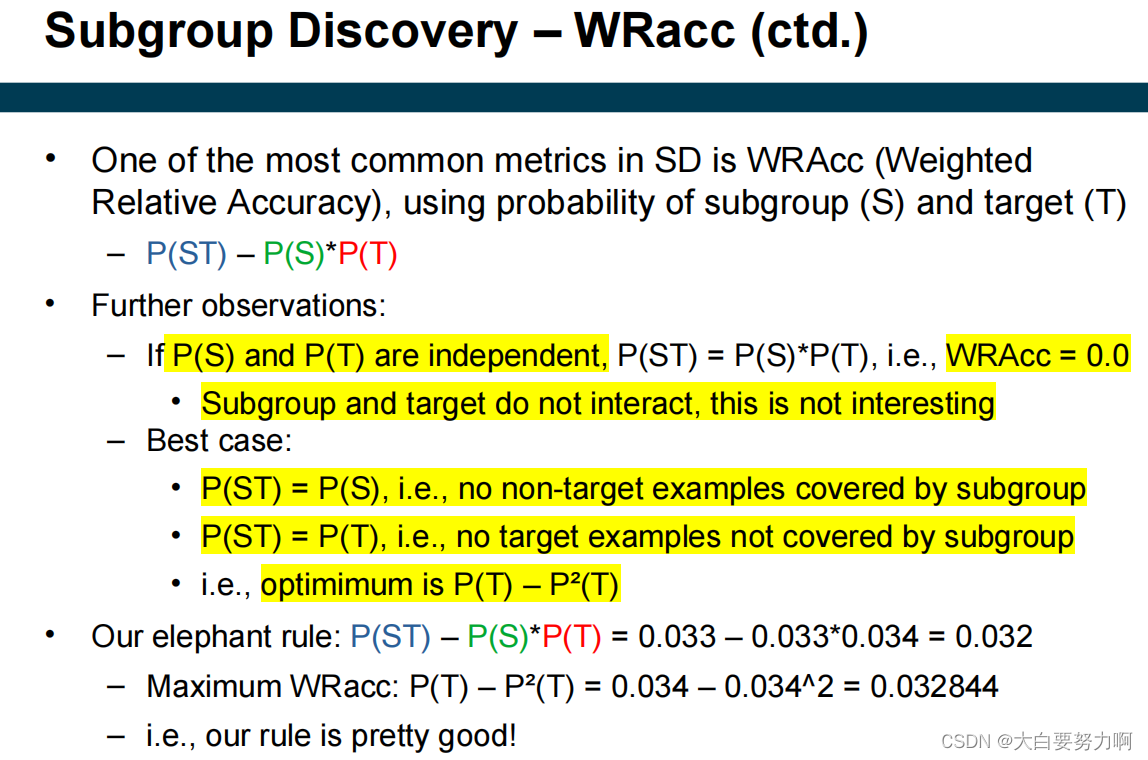
Rating Rules
Goals: rules should be covering many examples & Accurate
Rules of both high coverage and accuracy are interesting
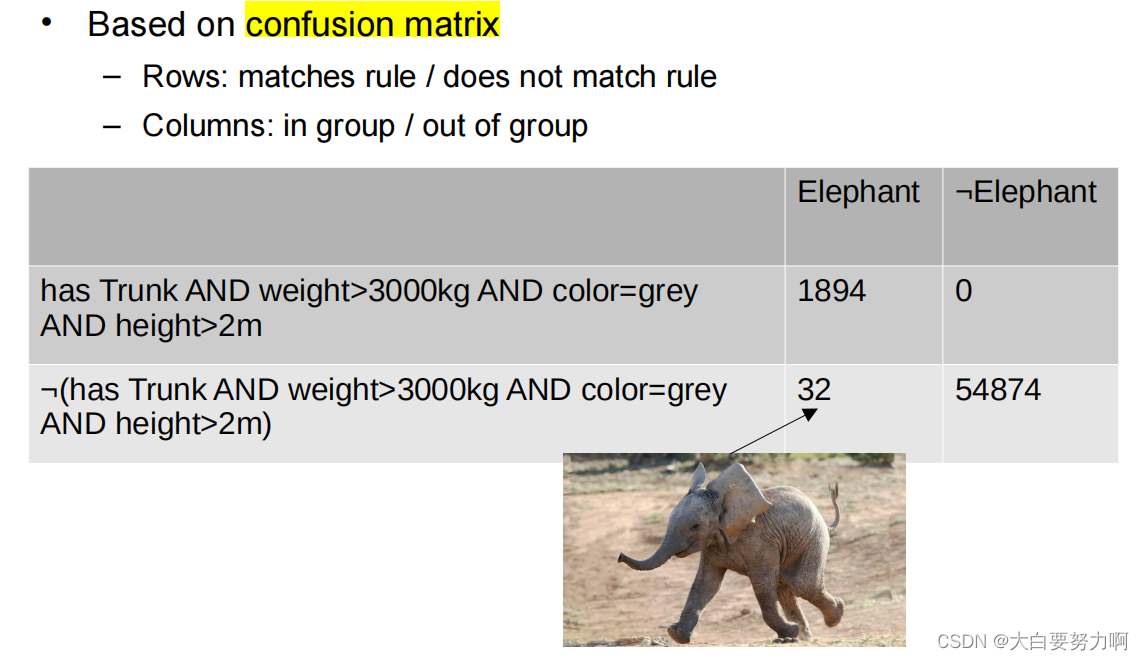
Subgroup Discovery – Metrics
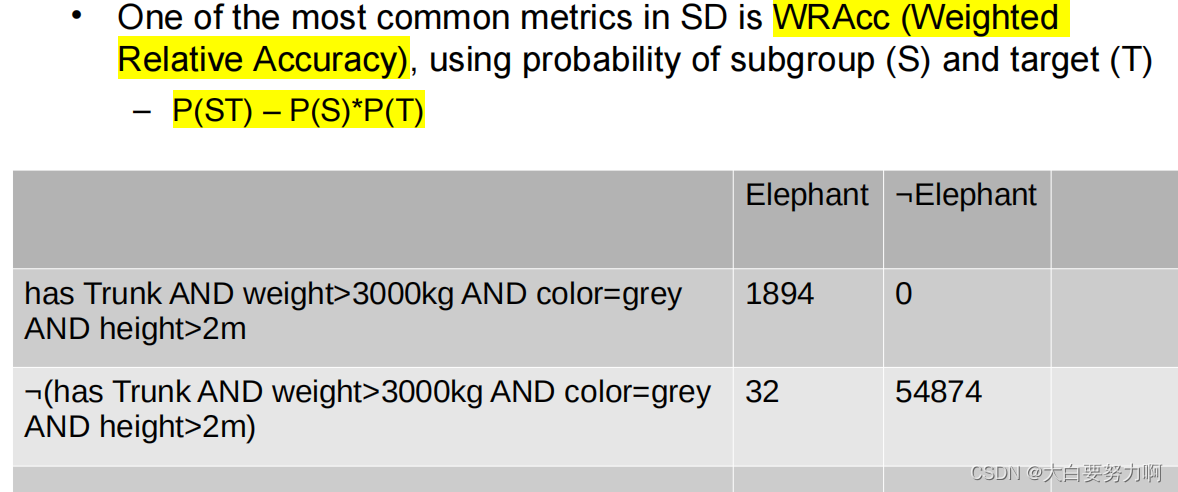
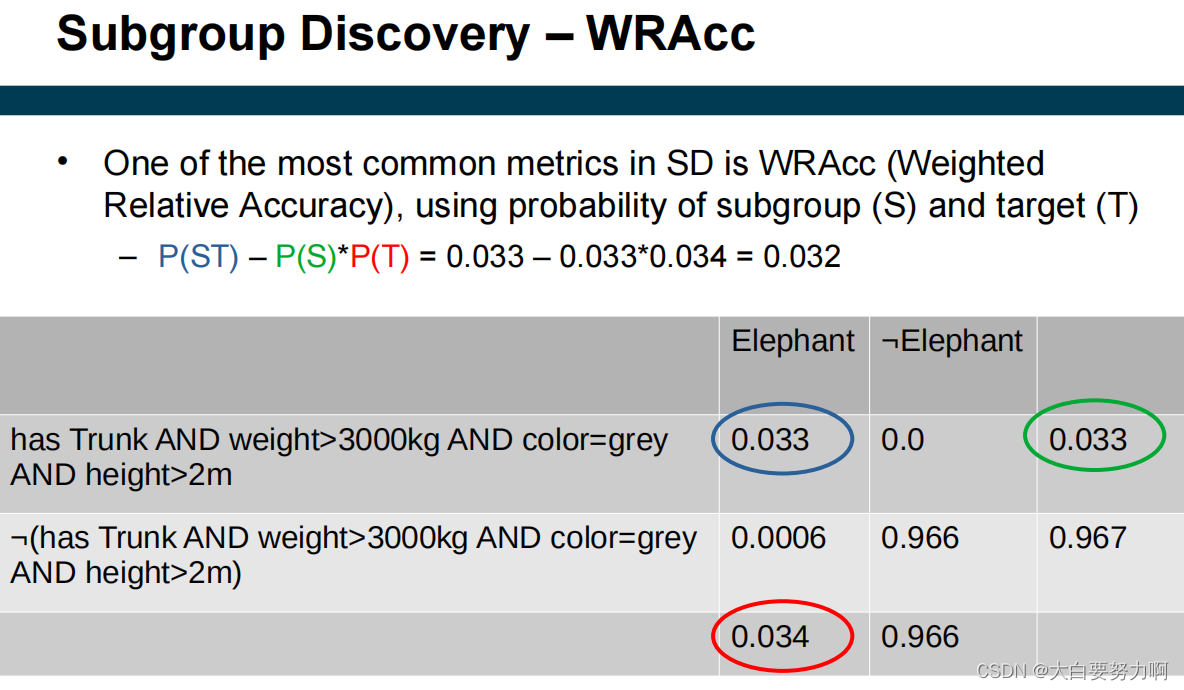
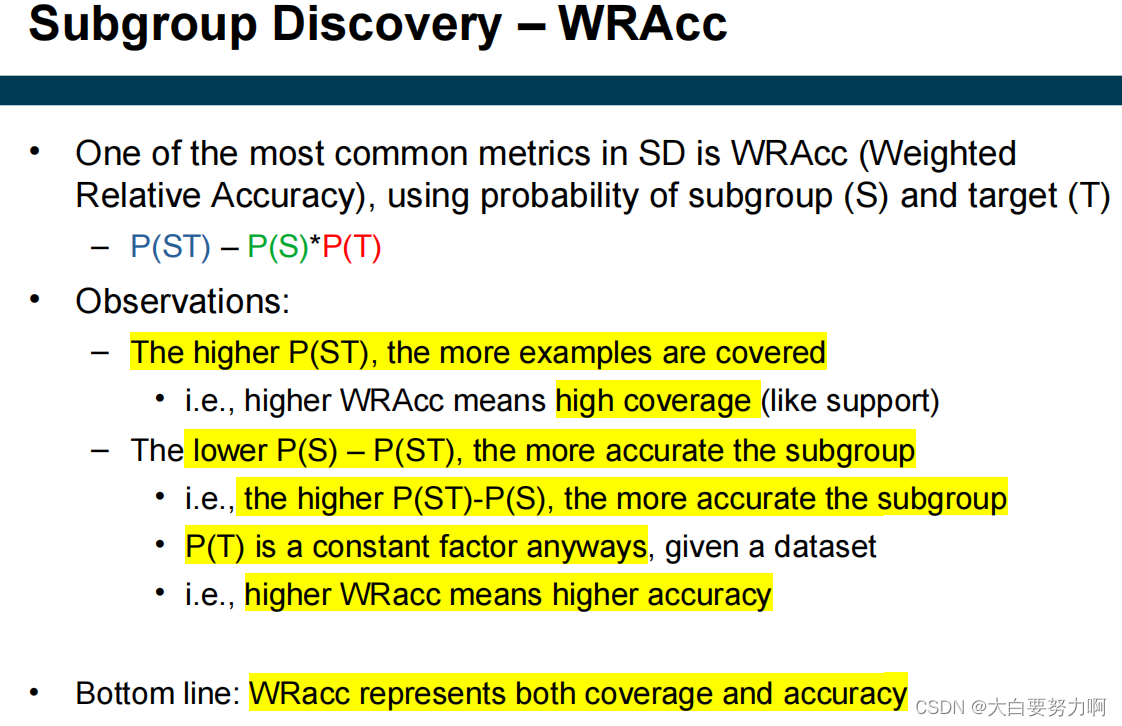
6.11 Summary
| Association Analysis | Apriori & FP-Growth | Subgroup Discovery |
|---|---|---|
| discovering patterns in data; patterns are described by rules | Finds rules with minimum support (i.e., number of transactions) and minimum confidence (i.e., strength of the implication) | Learn rules for a particular target variable; Create a comprehensive model of a class |
这篇关于Data Mining数据挖掘—5. Association Analysis关联分析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





