本文主要是介绍realsense2+faster-rcnn+物体深度+物体宽度,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
pcl-python官方文档:
http://www.dabeaz.com/ply/ply.html
建议大家到官网下载,直接利用源代码安装
sudo python setup.py install
偷懒一点的朋友,也可以直接用apt安装,
sudo apt-get install python-ply
官方py文档:pyrealsense2
https://intelrealsense.github.io/librealsense/python_docs/_generated/pyrealsense2.html#module-pyrealsense2
dianyunxianshi:
https://github.com/dorodnic/binder_test/blob/master/pointcloud.ipynb
上一篇文章
https://blog.csdn.net/baidu_40840693/article/details/102918931
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/tree/master/wrappers/python/examples
python -mpip install pyglet==1.3.0
python -mpip install pyrealsense2
python -mpip install pyntcloud
官方例子
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/blob/jupyter/notebooks/depth_filters.ipynb
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/blob/jupyter/notebooks/distance_to_object.ipynb
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/tree/jupyter/notebooks
下载文件:
http://realsense-hw-public.s3.amazonaws.com/rs-tests/TestData/object_detection.bag
bag我没用上,因为bag是该设备保存的格式,代码中的
cfg.enable_device_from_file("../object_detection.bag")是载入这个视频的意思,我们也可以保存,方式是
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/issues/3029
config = rs.config()
config.enable_record_to_file('test.bag')
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/chuanqi305/MobileNet-SSD/f5d072ccc7e3dcddaa830e9805da4bf1000b2836/MobileNetSSD_deploy.prototxt
http://realsense-hw-public.s3.amazonaws.com/rs-tests/TestData/MobileNetSSD_deploy.caffemodel
例子:
import cv2 # state of the art computer vision algorithms library
import numpy as np # fundamental package for scientific computing
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 2D plotting library producing publication quality figures
import pyrealsense2 as rs # Intel RealSense cross-platform open-source API
print("Environment Ready")# Setup:
pipe = rs.pipeline()
cfg = rs.config()
#cfg.enable_device_from_file("../object_detection.bag")
cfg.enable_stream(rs.stream.depth, 640, 360, rs.format.z16, 30)
#cfg.enable_stream(rs.stream.color, 640, 480, rs.format.bgr8, 30)
cfg.enable_stream(rs.stream.color, 640, 480, rs.format.rgb8, 30)
profile = pipe.start(cfg)# Skip 5 first frames to give the Auto-Exposure time to adjust
for x in range(100):pipe.wait_for_frames()# Store next frameset for later processing:
frameset = pipe.wait_for_frames()
color_frame = frameset.get_color_frame()
depth_frame = frameset.get_depth_frame()# Cleanup:
pipe.stop()
print("Frames Captured")color = np.asanyarray(color_frame.get_data())
plt.rcParams["axes.grid"] = False
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [12, 6]
plt.imshow(color)
plt.show()colorizer = rs.colorizer()
colorized_depth = np.asanyarray(colorizer.colorize(depth_frame).get_data())
plt.imshow(colorized_depth)
plt.show()# Create alignment primitive with color as its target stream:
align = rs.align(rs.stream.color)
frameset = align.process(frameset)# Update color and depth frames:
aligned_depth_frame = frameset.get_depth_frame()
colorized_depth = np.asanyarray(colorizer.colorize(aligned_depth_frame).get_data())# Show the two frames together:
images = np.hstack((color, colorized_depth))
plt.imshow(images)
plt.show()# Standard OpenCV boilerplate for running the net:
height, width = color.shape[:2]
expected = 300
aspect = width / height
resized_image = cv2.resize(color, (round(expected * aspect), expected))
crop_start = round(expected * (aspect - 1) / 2)
crop_img = resized_image[0:expected, crop_start:crop_start+expected]net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe("./MobileNetSSD_deploy.prototxt", "./MobileNetSSD_deploy.caffemodel")
inScaleFactor = 0.007843
meanVal = 127.53
classNames = ("background", "aeroplane", "bicycle", "bird", "boat","bottle", "bus", "car", "cat", "chair","cow", "diningtable", "dog", "horse","motorbike", "person", "pottedplant","sheep", "sofa", "train", "tvmonitor")blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(crop_img, inScaleFactor, (expected, expected), meanVal, False)
net.setInput(blob, "data")
detections = net.forward("detection_out")label = detections[0,0,0,1]
conf = detections[0,0,0,2]
xmin = detections[0,0,0,3]
ymin = detections[0,0,0,4]
xmax = detections[0,0,0,5]
ymax = detections[0,0,0,6]className = classNames[int(label)]cv2.rectangle(crop_img, (int(xmin * expected), int(ymin * expected)),(int(xmax * expected), int(ymax * expected)), (255, 255, 255), 2)
cv2.putText(crop_img, className,(int(xmin * expected), int(ymin * expected) - 5),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 0.5, (255,255,255))plt.imshow(crop_img)
plt.show()scale = height / expected
xmin_depth = int((xmin * expected + crop_start) * scale)
ymin_depth = int((ymin * expected) * scale)
xmax_depth = int((xmax * expected + crop_start) * scale)
ymax_depth = int((ymax * expected) * scale)
xmin_depth,ymin_depth,xmax_depth,ymax_depth
cv2.rectangle(colorized_depth, (xmin_depth, ymin_depth),(xmax_depth, ymax_depth), (255, 255, 255), 2)
plt.imshow(colorized_depth)
plt.show()depth = np.asanyarray(aligned_depth_frame.get_data())
# Crop depth data:
depth = depth[xmin_depth:xmax_depth,ymin_depth:ymax_depth].astype(float)# Get data scale from the device and convert to meters
depth_scale = profile.get_device().first_depth_sensor().get_depth_scale()
depth = depth * depth_scale
dist,_,_,_ = cv2.mean(depth)
print("Detected a {0} {1:.3} meters away.".format(className, dist))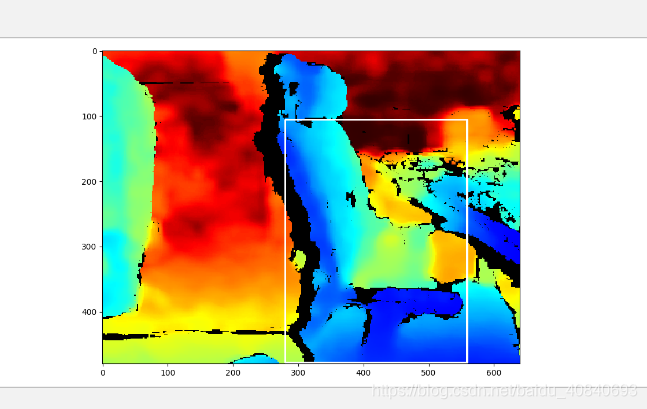
注释修改版:
# -*-coding:utf-8-*-
import cv2 # state of the art computer vision algorithms library
import numpy as np # fundamental package for scientific computing
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 2D plotting library producing publication quality figures
import pyrealsense2 as rs # Intel RealSense cross-platform open-source API
print("Environment Ready")# 创建一个管道
pipe = rs.pipeline()
# 配置要流式传输的管道
# 颜色和深度流的不同分辨率
cfg = rs.config()
#cfg.enable_device_from_file("../object_detection.bag")
#1280, 720
cfg.enable_stream(rs.stream.depth, 640, 360, rs.format.z16, 30)
#cfg.enable_stream(rs.stream.color, 640, 480, rs.format.bgr8, 30)
cfg.enable_stream(rs.stream.color, 640, 480, rs.format.rgb8, 30)
# 开始流式传输
profile = pipe.start(cfg)# 跳过前300帧以设置自动曝光时间
for x in range(100):pipe.wait_for_frames()# 拿到301帧
frameset = pipe.wait_for_frames()
# RGB图
color_frame = frameset.get_color_frame()
# 深度图
depth_frame = frameset.get_depth_frame()# 停止管道传输
pipe.stop()
print("Frames Captured")# 显示RGB颜色图像color_frame
color = np.asanyarray(color_frame.get_data())
# 一些可视化显示设置,不用管
plt.rcParams["axes.grid"] = False
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [12, 6]
plt.imshow(color)
plt.show()# 显示深度图
# (360, 640) uint16
depth_image_ori = np.asanyarray(depth_frame.get_data())
plt.imshow(depth_image_ori)
plt.show()
# https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/issues/3665
# 不使用int8是因为精度不够cm
depth_image_ori_int8 = depth_image_ori.astype('uint8')
plt.imshow(depth_image_ori_int8)
plt.show()# 创建colorizer滤波对象 将深度图映射成彩色图像显示
colorizer = rs.colorizer()
colorized_depth = np.asanyarray(colorizer.colorize(depth_frame).get_data())
plt.imshow(colorized_depth)
plt.show()# 创建对齐对象
# rs.align允许我们执行深度帧与其他帧的对齐
# “frameset”是我们计划对齐深度帧的流类型。
# 将深度框与颜色框对齐
# 将深度对齐到颜色
align = rs.align(rs.stream.color)
frameset = align.process(frameset)# 获取对齐更新后的深度图
aligned_depth_frame = frameset.get_depth_frame()
# 将深度图映射成彩色图像显示
colorized_depth = np.asanyarray(colorizer.colorize(aligned_depth_frame).get_data())# np.vstack():在竖直方向上堆叠
# np.hstack():在水平方向上平铺
images = np.hstack((color, colorized_depth))
plt.imshow(images)
plt.show()# np.vstack():在竖直方向上堆叠
# np.hstack():在水平方向上平铺
images = np.vstack((color, colorized_depth))
plt.imshow(images)
plt.show()# 通过对齐后的深度图,对齐原始RGB:color_frame,保存彩色点云
pc = rs.pointcloud()
pc.map_to(color_frame)
points = pc.calculate(aligned_depth_frame)
points.export_to_ply('./out.ply', color_frame)
#pcd = read_point_cloud(file_path)
# Visualize PLY
#draw_geometries([pcd])#pc.map_to(colorizer.colorize(aligned_depth_frame))
#points.export_to_ply('./out.ply', colorizer.colorize(aligned_depth_frame))# 480*640*3
height, width = color.shape[:2]
expected = 300
# 1.333333... 原始图像的宽高比
aspect = width / height
# 300*400*3 新的图像也满足此宽高比
resized_image = cv2.resize(color, (round(expected * aspect), expected))
# 50
crop_start = round(expected * (aspect - 1) / 2)
# 300*300*3 H,W
crop_img = resized_image[0:expected, crop_start:crop_start+expected]
plt.imshow(crop_img)
plt.show()# VOC目标检测网络
net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe("./MobileNetSSD_deploy.prototxt", "./MobileNetSSD_deploy.caffemodel")
inScaleFactor = 0.007843
meanVal = 127.53
classNames = ("background", "aeroplane", "bicycle", "bird", "boat","bottle", "bus", "car", "cat", "chair","cow", "diningtable", "dog", "horse","motorbike", "person", "pottedplant","sheep", "sofa", "train", "tvmonitor")blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(crop_img, inScaleFactor, (expected, expected), meanVal, False)
net.setInput(blob, "data")
# 1*1*100*7[1-6]
detections = net.forward("detection_out")# 输出检测结果
# label = detections[0,0,0,1]
# conf = detections[0,0,0,2]
# xmin = detections[0,0,0,3]
# ymin = detections[0,0,0,4]
# xmax = detections[0,0,0,5]
# ymax = detections[0,0,0,6]
# className = classNames[int(label)]
# cv2.rectangle(crop_img, (int(xmin * expected), int(ymin * expected)),
# (int(xmax * expected), int(ymax * expected)), (255, 255, 255), 2)
# cv2.putText(crop_img, className,
# (int(xmin * expected), int(ymin * expected) - 5),
# cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 0.5, (255,255,255))
# plt.imshow(crop_img)
# plt.show()# scale = height / expected
# xmin_depth = int((xmin * expected + crop_start) * scale)
# ymin_depth = int((ymin * expected) * scale)
# xmax_depth = int((xmax * expected + crop_start) * scale)
# ymax_depth = int((ymax * expected) * scale)
# xmin_depth,ymin_depth,xmax_depth,ymax_depth
# cv2.rectangle(colorized_depth, (xmin_depth, ymin_depth),
# (xmax_depth, ymax_depth), (255, 255, 255), 2)
# plt.imshow(colorized_depth)
# plt.show()label1 = detections[0,0,:,1]
conf1 = detections[0,0,:,2]
xmin1 = detections[0,0,:,3]
ymin1 = detections[0,0,:,4]
xmax1 = detections[0,0,:,5]
ymax1 = detections[0,0,:,6]
# 获取满足阈值的框
# 框的x1y1 x2y2 是百分比,相对于300*300
inds = np.where(conf1[:] > 0.3)[0]
for index in inds:className = classNames[int(label1[index])]cv2.rectangle(crop_img, (int(xmin1[index] * expected), int(ymin1[index] * expected)),(int(xmax1[index] * expected), int(ymax1[index] * expected)), (255, 255, 255), 2)cv2.putText(crop_img, className,(int(xmin1[index] * expected), int(ymin1[index] * expected) - 5),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 0.5, (255,255,255))
plt.imshow(crop_img)
plt.show()# 对于300,原始图像的扩大比为多少
# 对齐后的深度图:aligned_depth_frame
# 对齐后的深度图的彩色图:colorized_depth
# xmin1[index] * expected 300*300检测图的坐标
# xmin1[index] * expected + crop_start 300*400*3的坐标
# (xmin1[index] * expected + crop_start) * scale 480*640*3的坐标
depth = np.asanyarray(aligned_depth_frame.get_data())
depth_scale = profile.get_device().first_depth_sensor().get_depth_scale()
aa = profile.get_device()scale = height / expected
from decimal import Decimal
for index in inds:xmin_depth = int((xmin1[index] * expected + crop_start) * scale)ymin_depth = int((ymin1[index] * expected) * scale)xmax_depth = int((xmax1[index] * expected + crop_start) * scale)ymax_depth = int((ymax1[index] * expected) * scale)#xmin_depth,ymin_depth,xmax_depth,ymax_depth#depth_temp = depth[xmin_depth:xmax_depth, ymin_depth:ymax_depth].astype(float)depth_temp = depth[ymin_depth:ymax_depth, xmin_depth:xmax_depth].astype(float)depth_temp = depth_temp * depth_scaledist, _, _, _ = cv2.mean(depth_temp)cv2.rectangle(colorized_depth, (xmin_depth, ymin_depth),(xmax_depth, ymax_depth), (255, 255, 255), 2)# 取小数点后3位dist_temp = Decimal(dist).quantize(Decimal('0.000'))cv2.putText(colorized_depth, str(dist_temp),(xmin_depth, ymin_depth - 5),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 0.5, (255,255,255))
plt.imshow(colorized_depth)
plt.show()
plt.close()# # 对齐后的深度图:aligned_depth_frame
# # 对齐后的深度图的彩色图:colorized_depth
# depth = np.asanyarray(aligned_depth_frame.get_data())
# # crop深度数据
# depth = depth[xmin_depth:xmax_depth,ymin_depth:ymax_depth].astype(float)
# # 计算深度
# # 设备获取数据比例并转换为m
# depth_scale = profile.get_device().first_depth_sensor().get_depth_scale()
# depth = depth * depth_scale
# # 取均值获取到物体的距离
# dist,_,_,_ = cv2.mean(depth)
# print("Detected a {0} {1:.3} meters away.".format(className, dist))改一改:
# -*-coding:utf-8-*-
import cv2 # state of the art computer vision algorithms library
import numpy as np # fundamental package for scientific computing
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 2D plotting library producing publication quality figures
import pyrealsense2 as rs # Intel RealSense cross-platform open-source API
print("Environment Ready")# 创建一个管道
pipe = rs.pipeline()
# 配置要流式传输的管道
# 颜色和深度流的不同分辨率
cfg = rs.config()
#cfg.enable_device_from_file("./object_detection.bag")
#cfg.enable_stream(rs.stream.depth, 640, 480, rs.format.z16, 30)
#cfg.enable_stream(rs.stream.color, 640, 480, rs.format.bgr8, 30)#1280, 720
cfg.enable_stream(rs.stream.depth, 1280, 720, rs.format.z16, 30)
#cfg.enable_stream(rs.stream.color, 640, 480, rs.format.bgr8, 30)
cfg.enable_stream(rs.stream.color, 1280, 720, rs.format.rgb8, 30)# 开始流式传输
profile = pipe.start(cfg)# 跳过前300帧以设置自动曝光时间
for x in range(100):pipe.wait_for_frames()# 拿到301帧
frameset = pipe.wait_for_frames()
# RGB图
color_frame = frameset.get_color_frame()
# 深度图
depth_frame = frameset.get_depth_frame()# 停止管道传输
pipe.stop()
print("Frames Captured")# 获取内参外参矩阵
# Intrinsics & Extrinsics
depth_intrin = depth_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsics
color_intrin = color_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsics
# 外参矩阵-深度图相对于彩色图像的外参
depth_to_color_extrin = depth_frame.profile.get_extrinsics_to(color_frame.profile)
print("内参ppx,ppy",depth_intrin.ppx, ':', depth_intrin.ppy)
print("内参矩阵",depth_intrin)# 显示RGB颜色图像color_frame
color = np.asanyarray(color_frame.get_data())
# 一些可视化显示设置,不用管
plt.rcParams["axes.grid"] = False
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [12, 6]
plt.imshow(color)
plt.show()# 显示深度图
# (360, 640) uint16
depth_image_ori = np.asanyarray(depth_frame.get_data())
plt.imshow(depth_image_ori)
plt.show()
# https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/issues/3665
# 不使用int8是因为精度不够cm
depth_image_ori_int8 = depth_image_ori.astype('uint8')
plt.imshow(depth_image_ori_int8)
plt.show()# 创建colorizer滤波对象 将深度图映射成彩色图像显示
colorizer = rs.colorizer()
colorized_depth = np.asanyarray(colorizer.colorize(depth_frame).get_data())
plt.imshow(colorized_depth)
plt.show()# 创建对齐对象
# rs.align允许我们执行深度帧与其他帧的对齐
# “frameset”是我们计划对齐深度帧的流类型。
# 将深度框与颜色框对齐
# 将深度对齐到颜色
align = rs.align(rs.stream.color)
frameset = align.process(frameset)# 获取对齐更新后的深度图
aligned_depth_frame = frameset.get_depth_frame()
# 将深度图映射成彩色图像显示
colorized_depth = np.asanyarray(colorizer.colorize(aligned_depth_frame).get_data())
new_depth_image_array = np.asanyarray(aligned_depth_frame.get_data())
np.save("out_ori.npy",new_depth_image_array)
x = np.load("out_ori.npy")
print(x-new_depth_image_array)bgr_color = cv2.cvtColor(color,cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
cv2.imwrite("out_ori.jpg",bgr_color)# np.vstack():在竖直方向上堆叠
# np.hstack():在水平方向上平铺
images = np.hstack((color, colorized_depth))
plt.imshow(images)
plt.show()# np.vstack():在竖直方向上堆叠
# np.hstack():在水平方向上平铺
images = np.vstack((color, colorized_depth))
plt.imshow(images)
plt.show()# 通过对齐后的深度图,对齐原始RGB:color_frame,保存彩色点云
pc = rs.pointcloud()
points = rs.points()
pc.map_to(color_frame)
points = pc.calculate(depth_frame)
points.export_to_ply('./out_ori.ply', color_frame)
#pcd = read_point_cloud(file_path)
# Visualize PLY
#draw_geometries([pcd])#pc.map_to(colorizer.colorize(aligned_depth_frame))
#points.export_to_ply('./out.ply', colorizer.colorize(aligned_depth_frame))# 480*640*3
height, width = color.shape[:2]
expected = 300
# 1.333333... 原始图像的宽高比
aspect = width / height
# 300*400*3 新的图像也满足此宽高比
resized_image = cv2.resize(color, (round(expected * aspect), expected))
# 50
crop_start = round(expected * (aspect - 1) / 2)
# 300*300*3 H,W
crop_img = resized_image[0:expected, crop_start:crop_start+expected]
plt.imshow(crop_img)
plt.show()# VOC目标检测网络
net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromCaffe("./MobileNetSSD_deploy.prototxt", "./MobileNetSSD_deploy.caffemodel")
inScaleFactor = 0.007843
meanVal = 127.53
classNames = ("background", "aeroplane", "bicycle", "bird", "boat","bottle", "bus", "car", "cat", "chair","cow", "diningtable", "dog", "horse","motorbike", "person", "pottedplant","sheep", "sofa", "train", "tvmonitor")blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(crop_img, inScaleFactor, (expected, expected), meanVal, False)
net.setInput(blob, "data")
# 1*1*100*7[1-6]
detections = net.forward("detection_out")# 输出检测结果
# label = detections[0,0,0,1]
# conf = detections[0,0,0,2]
# xmin = detections[0,0,0,3]
# ymin = detections[0,0,0,4]
# xmax = detections[0,0,0,5]
# ymax = detections[0,0,0,6]
# className = classNames[int(label)]
# cv2.rectangle(crop_img, (int(xmin * expected), int(ymin * expected)),
# (int(xmax * expected), int(ymax * expected)), (255, 255, 255), 2)
# cv2.putText(crop_img, className,
# (int(xmin * expected), int(ymin * expected) - 5),
# cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 0.5, (255,255,255))
# plt.imshow(crop_img)
# plt.show()# scale = height / expected
# xmin_depth = int((xmin * expected + crop_start) * scale)
# ymin_depth = int((ymin * expected) * scale)
# xmax_depth = int((xmax * expected + crop_start) * scale)
# ymax_depth = int((ymax * expected) * scale)
# xmin_depth,ymin_depth,xmax_depth,ymax_depth
# cv2.rectangle(colorized_depth, (xmin_depth, ymin_depth),
# (xmax_depth, ymax_depth), (255, 255, 255), 2)
# plt.imshow(colorized_depth)
# plt.show()label1 = detections[0,0,:,1]
conf1 = detections[0,0,:,2]
xmin1 = detections[0,0,:,3]
ymin1 = detections[0,0,:,4]
xmax1 = detections[0,0,:,5]
ymax1 = detections[0,0,:,6]
# 获取满足阈值的框
# 框的x1y1 x2y2 是百分比,相对于300*300
inds = np.where(conf1[:] > 0.3)[0]
for index in inds:className = classNames[int(label1[index])]cv2.rectangle(crop_img, (int(xmin1[index] * expected), int(ymin1[index] * expected)),(int(xmax1[index] * expected), int(ymax1[index] * expected)), (255, 255, 255), 2)cv2.putText(crop_img, className,(int(xmin1[index] * expected), int(ymin1[index] * expected) - 5),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 0.5, (255,255,255))
plt.imshow(crop_img)
plt.show()# 对于300,原始图像的扩大比为多少
# 对齐后的深度图:aligned_depth_frame
# 对齐后的深度图的彩色图:colorized_depth
# xmin1[index] * expected 300*300检测图的坐标
# xmin1[index] * expected + crop_start 300*400*3的坐标
# (xmin1[index] * expected + crop_start) * scale 480*640*3的坐标
depth = np.asanyarray(aligned_depth_frame.get_data())
depth_scale = profile.get_device().first_depth_sensor().get_depth_scale()
aa = profile.get_device()scale = height / expected
from decimal import Decimal
for index in inds:xmin_depth = int((xmin1[index] * expected + crop_start) * scale)ymin_depth = int((ymin1[index] * expected) * scale)xmax_depth = int((xmax1[index] * expected + crop_start) * scale)ymax_depth = int((ymax1[index] * expected) * scale)depth_temp = depth[ymin_depth:ymax_depth, xmin_depth:xmax_depth].astype(float)#print(depth_temp.shape)depth_temp = depth_temp * depth_scale#dis = depth_temp[depth_tem,depth_temp]dist, _, _, _ = cv2.mean(depth_temp)cv2.rectangle(colorized_depth, (xmin_depth, ymin_depth),(xmax_depth, ymax_depth), (255, 255, 255), 2)# 取小数点后3位dist_temp = Decimal(dist).quantize(Decimal('0.000'))cv2.putText(colorized_depth, str(dist_temp),(xmin_depth, ymin_depth - 5),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 1.5, (255,255,255))
plt.imshow(colorized_depth)
plt.show()# # 对齐后的深度图:aligned_depth_frame
# # 对齐后的深度图的彩色图:colorized_depth
# depth = np.asanyarray(aligned_depth_frame.get_data())
# # crop深度数据
# depth = depth[xmin_depth:xmax_depth,ymin_depth:ymax_depth].astype(float)
# # 计算深度
# # 设备获取数据比例并转换为m
# depth_scale = profile.get_device().first_depth_sensor().get_depth_scale()
# depth = depth * depth_scale
# # 取均值获取到物体的距离
# dist,_,_,_ = cv2.mean(depth)
# print("Detected a {0} {1:.3} meters away.".format(className, dist))点云程序:
# License: Apache 2.0. See LICENSE file in root directory.
# Copyright(c) 2015-2017 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved."""
OpenGL Pointcloud viewer with http://pyglet.org
Usage:
------
Mouse:Drag with left button to rotate around pivot (thick small axes),with right button to translate and the wheel to zoom.
Keyboard:[p] Pause[r] Reset View[d] Cycle through decimation values[z] Toggle point scaling[x] Toggle point distance attenuation[c] Toggle color source[l] Toggle lighting[f] Toggle depth post-processing[s] Save PNG (./out.png)[e] Export points to ply (./out.ply)[q/ESC] Quit
Notes:
------
Using deprecated OpenGL (FFP lighting, matrix stack...) however, draw calls
are kept low with pyglet.graphics.* which uses glDrawArrays internally.
Normals calculation is done with numpy on CPU which is rather slow, should really
be done with shaders but was omitted for several reasons - brevity, for lowering
dependencies (pyglet doesn't ship with shader support & recommends pyshaders)
and for reference.
"""import math
import ctypes
import pyglet
import pyglet.gl as gl
import numpy as np
import pyrealsense2 as rs# https://stackoverflow.com/a/6802723
def rotation_matrix(axis, theta):"""Return the rotation matrix associated with counterclockwise rotation aboutthe given axis by theta radians."""axis = np.asarray(axis)axis = axis / math.sqrt(np.dot(axis, axis))a = math.cos(theta / 2.0)b, c, d = -axis * math.sin(theta / 2.0)aa, bb, cc, dd = a * a, b * b, c * c, d * dbc, ad, ac, ab, bd, cd = b * c, a * d, a * c, a * b, b * d, c * dreturn np.array([[aa + bb - cc - dd, 2 * (bc + ad), 2 * (bd - ac)],[2 * (bc - ad), aa + cc - bb - dd, 2 * (cd + ab)],[2 * (bd + ac), 2 * (cd - ab), aa + dd - bb - cc]])class AppState:def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):self.pitch, self.yaw = math.radians(-10), math.radians(-15)self.translation = np.array([0, 0, 1], np.float32)self.distance = 2self.mouse_btns = [False, False, False]self.paused = Falseself.decimate = 0self.scale = Trueself.attenuation = Falseself.color = Trueself.lighting = Falseself.postprocessing = Falsedef reset(self):self.pitch, self.yaw, self.distance = 0, 0, 2self.translation[:] = 0, 0, 1@propertydef rotation(self):Rx = rotation_matrix((1, 0, 0), math.radians(-self.pitch))Ry = rotation_matrix((0, 1, 0), math.radians(-self.yaw))return np.dot(Ry, Rx).astype(np.float32)state = AppState()# Configure streams
pipeline = rs.pipeline()
config = rs.config()
config.enable_stream(rs.stream.depth, 640, 480, rs.format.z16, 30)
# other_stream, other_format = rs.stream.infrared, rs.format.y8
other_stream, other_format = rs.stream.color, rs.format.rgb8
config.enable_stream(other_stream, 640, 480, other_format, 30)# Start streaming
pipeline.start(config)
profile = pipeline.get_active_profile()depth_sensor = profile.get_device().first_depth_sensor()
depth_scale = depth_sensor.get_depth_scale()depth_profile = rs.video_stream_profile(profile.get_stream(rs.stream.depth))
depth_intrinsics = depth_profile.get_intrinsics()
w, h = depth_intrinsics.width, depth_intrinsics.height# Processing blocks
pc = rs.pointcloud()
decimate = rs.decimation_filter()
decimate.set_option(rs.option.filter_magnitude, 2 ** state.decimate)
colorizer = rs.colorizer()
filters = [rs.disparity_transform(),rs.spatial_filter(),rs.temporal_filter(),rs.disparity_transform(False)]# pyglet
window = pyglet.window.Window(config=gl.Config(double_buffer=True,samples=8 # MSAA),resizable=True, vsync=True)
keys = pyglet.window.key.KeyStateHandler()
window.push_handlers(keys)def convert_fmt(fmt):"""rs.format to pyglet format string"""return {rs.format.rgb8: 'RGB',rs.format.bgr8: 'BGR',rs.format.rgba8: 'RGBA',rs.format.bgra8: 'BGRA',rs.format.y8: 'L',}[fmt]# Create a VertexList to hold pointcloud data
# Will pre-allocates memory according to the attributes below
vertex_list = pyglet.graphics.vertex_list(w * h, 'v3f/stream', 't2f/stream', 'n3f/stream')
# Create and allocate memory for our color data
other_profile = rs.video_stream_profile(profile.get_stream(other_stream))
image_data = pyglet.image.ImageData(w, h, convert_fmt(other_profile.format()), (gl.GLubyte * (w * h * 3))())fps_display = pyglet.clock.ClockDisplay()@window.event
def on_mouse_drag(x, y, dx, dy, buttons, modifiers):w, h = map(float, window.get_size())if buttons & pyglet.window.mouse.LEFT:state.yaw -= dx * 0.5state.pitch -= dy * 0.5if buttons & pyglet.window.mouse.RIGHT:dp = np.array((dx / w, -dy / h, 0), np.float32)state.translation += np.dot(state.rotation, dp)if buttons & pyglet.window.mouse.MIDDLE:dz = dy * 0.01state.translation -= (0, 0, dz)state.distance -= dzdef handle_mouse_btns(x, y, button, modifiers):state.mouse_btns[0] ^= (button & pyglet.window.mouse.LEFT)state.mouse_btns[1] ^= (button & pyglet.window.mouse.RIGHT)state.mouse_btns[2] ^= (button & pyglet.window.mouse.MIDDLE)window.on_mouse_press = window.on_mouse_release = handle_mouse_btns@window.event
def on_mouse_scroll(x, y, scroll_x, scroll_y):dz = scroll_y * 0.1state.translation -= (0, 0, dz)state.distance -= dzdef on_key_press(symbol, modifiers):if symbol == pyglet.window.key.R:state.reset()if symbol == pyglet.window.key.P:state.paused ^= Trueif symbol == pyglet.window.key.D:state.decimate = (state.decimate + 1) % 3decimate.set_option(rs.option.filter_magnitude, 2 ** state.decimate)if symbol == pyglet.window.key.C:state.color ^= Trueif symbol == pyglet.window.key.Z:state.scale ^= Trueif symbol == pyglet.window.key.X:state.attenuation ^= Trueif symbol == pyglet.window.key.L:state.lighting ^= Trueif symbol == pyglet.window.key.F:state.postprocessing ^= Trueif symbol == pyglet.window.key.S:pyglet.image.get_buffer_manager().get_color_buffer().save('out.png')if symbol == pyglet.window.key.Q:window.close()window.push_handlers(on_key_press)def axes(size=1, width=1):"""draw 3d axes"""gl.glLineWidth(width)pyglet.graphics.draw(6, gl.GL_LINES,('v3f', (0, 0, 0, size, 0, 0,0, 0, 0, 0, size, 0,0, 0, 0, 0, 0, size)),('c3f', (1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,)))def frustum(intrinsics):"""draw camera's frustum"""w, h = intrinsics.width, intrinsics.heightbatch = pyglet.graphics.Batch()for d in range(1, 6, 2):def get_point(x, y):p = rs.rs2_deproject_pixel_to_point(intrinsics, [x, y], d)batch.add(2, gl.GL_LINES, None, ('v3f', [0, 0, 0] + p))return ptop_left = get_point(0, 0)top_right = get_point(w, 0)bottom_right = get_point(w, h)bottom_left = get_point(0, h)batch.add(2, gl.GL_LINES, None, ('v3f', top_left + top_right))batch.add(2, gl.GL_LINES, None, ('v3f', top_right + bottom_right))batch.add(2, gl.GL_LINES, None, ('v3f', bottom_right + bottom_left))batch.add(2, gl.GL_LINES, None, ('v3f', bottom_left + top_left))batch.draw()def grid(size=1, n=10, width=1):"""draw a grid on xz plane"""gl.glLineWidth(width)s = size / float(n)s2 = 0.5 * sizebatch = pyglet.graphics.Batch()for i in range(0, n + 1):x = -s2 + i * sbatch.add(2, gl.GL_LINES, None, ('v3f', (x, 0, -s2, x, 0, s2)))for i in range(0, n + 1):z = -s2 + i * sbatch.add(2, gl.GL_LINES, None, ('v3f', (-s2, 0, z, s2, 0, z)))batch.draw()@window.event
def on_draw():window.clear()gl.glEnable(gl.GL_DEPTH_TEST)gl.glEnable(gl.GL_LINE_SMOOTH)width, height = window.get_size()gl.glViewport(0, 0, width, height)gl.glMatrixMode(gl.GL_PROJECTION)gl.glLoadIdentity()gl.gluPerspective(60, width / float(height), 0.01, 20)gl.glMatrixMode(gl.GL_TEXTURE)gl.glLoadIdentity()# texcoords are [0..1] and relative to top-left pixel corner, add 0.5 to centergl.glTranslatef(0.5 / image_data.width, 0.5 / image_data.height, 0)# texture size may be increased by pyglet to a power of 2tw, th = image_data.texture.owner.width, image_data.texture.owner.heightgl.glScalef(image_data.width / float(tw),image_data.height / float(th), 1)gl.glMatrixMode(gl.GL_MODELVIEW)gl.glLoadIdentity()gl.gluLookAt(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, -1, 0)gl.glTranslatef(0, 0, state.distance)gl.glRotated(state.pitch, 1, 0, 0)gl.glRotated(state.yaw, 0, 1, 0)if any(state.mouse_btns):axes(0.1, 4)gl.glTranslatef(0, 0, -state.distance)gl.glTranslatef(*state.translation)gl.glColor3f(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)gl.glPushMatrix()gl.glTranslatef(0, 0.5, 0.5)grid()gl.glPopMatrix()psz = max(window.get_size()) / float(max(w, h)) if state.scale else 1gl.glPointSize(psz)distance = (0, 0, 1) if state.attenuation else (1, 0, 0)gl.glPointParameterfv(gl.GL_POINT_DISTANCE_ATTENUATION,(gl.GLfloat * 3)(*distance))if state.lighting:ldir = [0.5, 0.5, 0.5] # world-space lightingldir = np.dot(state.rotation, (0, 0, 1)) # MeshLab style lightingldir = list(ldir) + [0] # w=0, directional lightgl.glLightfv(gl.GL_LIGHT0, gl.GL_POSITION, (gl.GLfloat * 4)(*ldir))gl.glLightfv(gl.GL_LIGHT0, gl.GL_DIFFUSE,(gl.GLfloat * 3)(1.0, 1.0, 1.0))gl.glLightfv(gl.GL_LIGHT0, gl.GL_AMBIENT,(gl.GLfloat * 3)(0.75, 0.75, 0.75))gl.glEnable(gl.GL_LIGHT0)gl.glEnable(gl.GL_NORMALIZE)gl.glEnable(gl.GL_LIGHTING)gl.glColor3f(1, 1, 1)texture = image_data.get_texture()gl.glEnable(texture.target)gl.glBindTexture(texture.target, texture.id)gl.glTexParameteri(gl.GL_TEXTURE_2D, gl.GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, gl.GL_NEAREST)# comment this to get round points with MSAA ongl.glEnable(gl.GL_POINT_SPRITE)if not state.scale and not state.attenuation:gl.glDisable(gl.GL_MULTISAMPLE) # for true 1px points with MSAA onvertex_list.draw(gl.GL_POINTS)gl.glDisable(texture.target)if not state.scale and not state.attenuation:gl.glEnable(gl.GL_MULTISAMPLE)gl.glDisable(gl.GL_LIGHTING)gl.glColor3f(0.25, 0.25, 0.25)frustum(depth_intrinsics)axes()gl.glMatrixMode(gl.GL_PROJECTION)gl.glLoadIdentity()gl.glOrtho(0, width, 0, height, -1, 1)gl.glMatrixMode(gl.GL_MODELVIEW)gl.glLoadIdentity()gl.glMatrixMode(gl.GL_TEXTURE)gl.glLoadIdentity()gl.glDisable(gl.GL_DEPTH_TEST)fps_display.draw()def run(dt):global w, hwindow.set_caption("RealSense (%dx%d) %dFPS (%.2fms) %s" %(w, h, 0 if dt == 0 else 1.0 / dt, dt * 1000,"PAUSED" if state.paused else ""))if state.paused:returnsuccess, frames = pipeline.try_wait_for_frames(timeout_ms=0)if not success:returndepth_frame = frames.get_depth_frame()other_frame = frames.first(other_stream).as_video_frame()depth_frame = decimate.process(depth_frame)if state.postprocessing:for f in filters:depth_frame = f.process(depth_frame)# Grab new intrinsics (may be changed by decimation)depth_intrinsics = rs.video_stream_profile(depth_frame.profile).get_intrinsics()w, h = depth_intrinsics.width, depth_intrinsics.heightcolor_image = np.asanyarray(other_frame.get_data())colorized_depth = colorizer.colorize(depth_frame)depth_colormap = np.asanyarray(colorized_depth.get_data())if state.color:mapped_frame, color_source = other_frame, color_imageelse:mapped_frame, color_source = colorized_depth, depth_colormappoints = pc.calculate(depth_frame)pc.map_to(mapped_frame)# handle color source or size changefmt = convert_fmt(mapped_frame.profile.format())global image_dataif (image_data.format, image_data.pitch) != (fmt, color_source.strides[0]):empty = (gl.GLubyte * (w * h * 3))()image_data = pyglet.image.ImageData(w, h, fmt, empty)# copy image data to pygletimage_data.set_data(fmt, color_source.strides[0], color_source.ctypes.data)verts = np.asarray(points.get_vertices(2)).reshape(h, w, 3)texcoords = np.asarray(points.get_texture_coordinates(2))if len(vertex_list.vertices) != verts.size:vertex_list.resize(verts.size // 3)# need to reassign after resizingvertex_list.vertices = verts.ravel()vertex_list.tex_coords = texcoords.ravel()# copy our data to pre-allocated buffers, this is faster than assigning...# pyglet will take care of uploading to GPUdef copy(dst, src):"""copy numpy array to pyglet array"""# timeit was mostly inconclusive, favoring slice assignment for safetynp.array(dst, copy=False)[:] = src.ravel()# ctypes.memmove(dst, src.ctypes.data, src.nbytes)copy(vertex_list.vertices, verts)copy(vertex_list.tex_coords, texcoords)if state.lighting:# compute normalsdy, dx = np.gradient(verts, axis=(0, 1))n = np.cross(dx, dy)# can use this, np.linalg.norm or similar to normalize, but OpenGL can do this for us, see GL_NORMALIZE above# norm = np.sqrt((n*n).sum(axis=2, keepdims=True))# np.divide(n, norm, out=n, where=norm != 0)# import cv2# n = cv2.bilateralFilter(n, 5, 1, 1)copy(vertex_list.normals, n)if keys[pyglet.window.key.E]:points.export_to_ply('./out.ply', mapped_frame)pyglet.clock.schedule(run)try:pyglet.app.run()
finally:pipeline.stop()原始程序有个bug
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/issues/3887
加上
.as_video_frame()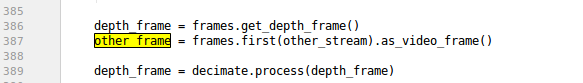
接下来物体宽度:
官方文档:
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/wiki/Projection-in-RealSense-SDK-2.0#point-coordinates
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/tree/master/examples/measure
大家提的问题:
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/issues/1904
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/issues/1231
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/issues/1904
https://forums.intel.com/s/question/0D50P0000490XJBSA2/accuracy-in-real-world-xyz-coordinates?language=zh_CN
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/issues/1413#
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/issues/5135
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/blob/master/examples/example.hpp
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/tree/master/examples/measure
关于例子:机翻
// License: Apache 2.0. See LICENSE file in root directory.
// Copyright(c) 2017 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved.#include <librealsense2/rs.hpp> // Include RealSense Cross Platform API
#include <librealsense2/rsutil.h>
#include "example.hpp" // Include short list of convenience functions for rendering
// 包括用于渲染的便捷功能的简短列表// This example will require several standard data-structures and algorithms:
#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES
#include <math.h>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <map>
#include <thread>
#include <atomic>
#include <mutex>using pixel = std::pair<int, int>;// Distance 3D is used to calculate real 3D distance between two pixels
// 距离3D用于计算两个像素之间的真实3D距离
float dist_3d(const rs2::depth_frame& frame, pixel u, pixel v);// Toggle helper class will be used to render the two buttons
// controlling the edges of our ruler
// Toggle helper类将用于渲染控制标尺边缘的两个按钮
struct toggle
{toggle() : x(0.f), y(0.f) {}toggle(float xl, float yl): x(std::min(std::max(xl, 0.f), 1.f)),y(std::min(std::max(yl, 0.f), 1.f)){}// Move from [0,1] space to pixel space of specific frame// 从[0,1]空间移至特定帧的像素空间pixel get_pixel(rs2::depth_frame frm) const{int px = x * frm.get_width();int py = y * frm.get_height();return{ px, py };}void render(const window& app){glColor4f(0.f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.2f);render_circle(app, 10);render_circle(app, 8);glColor4f(1.f, 0.9f, 1.0f, 1.f);render_circle(app, 6);}void render_circle(const window& app, float r){const float segments = 16;glBegin(GL_TRIANGLE_STRIP);for (auto i = 0; i <= segments; i++){auto t = 2 * M_PI * float(i) / segments;glVertex2f(x * app.width() + cos(t) * r,y * app.height() + sin(t) * r);glVertex2f(x * app.width(),y * app.height());}glEnd();}// This helper function is used to find the button// closest to the mouse cursor// Since we are only comparing this distance, sqrt can be safely skipped// 此辅助函数用于查找最接近鼠标光标的按钮// 由于我们仅比较此距离,因此可以安全地跳过sqrtfloat dist_2d(const toggle& other) const{return pow(x - other.x, 2) + pow(y - other.y, 2);}float x;float y;bool selected = false;
};// Application state shared between the main-thread and GLFW events
// 主线程和GLFW事件之间共享的应用程序状态
struct state
{bool mouse_down = false;toggle ruler_start;toggle ruler_end;
};// Helper function to register to UI events
// 帮助程序功能注册到UI事件
void register_glfw_callbacks(window& app, state& app_state);// Distance rendering functions:
// 距离渲染功能:// Simple distance is the classic pythagorean distance between 3D points
// This distance ignores the topology of the object and can cut both through
// air and through solid
// 简单距离是3D点之间的经典勾股距离
// 这个距离忽略了物体的拓扑结构,可以穿过空气和固体
void render_simple_distance(const rs2::depth_frame& depth,const state& s,const window& app);int main(int argc, char * argv[]) try
{// OpenGL textures for the color and depth frames// 彩色和深度帧的OpenGL纹理texture depth_image, color_image;// Colorizer is used to visualize depth data// 着色器用于可视化深度数据rs2::colorizer color_map;// Use black to white color map// 使用黑色到白色的颜色图color_map.set_option(RS2_OPTION_COLOR_SCHEME, 2.f);// Decimation filter reduces the amount of data (while preserving best samples)// 抽取滤波器可减少数据量(同时保留最佳样本)rs2::decimation_filter dec;// If the demo is too slow, make sure you run in Release (-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release)// 如果速度太慢,请确保在Release (-DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release)中运行// but you can also increase the following parameter to decimate depth more (reducing quality)// 但您也可以增加以下参数来进一步降低深度(降低质量)dec.set_option(RS2_OPTION_FILTER_MAGNITUDE, 2);// Define transformations from and to Disparity domain// 定义视差域之间的转换rs2::disparity_transform depth2disparity;rs2::disparity_transform disparity2depth(false);// Define spatial filter (edge-preserving)// 定义空间过滤器(边缘保留)rs2::spatial_filter spat;// Enable hole-filling// Hole filling is an agressive heuristic and it gets the depth wrong many times// However, this demo is not built to handle holes// (the shortest-path will always prefer to "cut" through the holes since they have zero 3D distance)// 启用孔填充// 孔填充是一种攻击性的启发式方法,它多次导致深度错误// 但是,此演示不是为处理孔洞而构建的//(最短路径始终喜欢通过孔洞“切”,因为它们的零3D距离为零)spat.set_option(RS2_OPTION_HOLES_FILL, 5); // 5 = fill all the zero pixels// Define temporal filter// 定义时间过滤器rs2::temporal_filter temp;// Spatially align all streams to depth viewport// We do this because:// a. Usually depth has wider FOV, and we only really need depth for this demo// b. We don't want to introduce new holes// 在空间上将所有流与深度视口对齐// 我们这样做是因为:// 通常,深度具有较宽的FOV,我们只需要此演示的深度// 我们不想引入新的孔洞rs2::align align_to(RS2_STREAM_DEPTH);// Declare RealSense pipeline, encapsulating the actual device and sensors// 声明RealSense管道,封装实际的设备和传感器rs2::pipeline pipe;rs2::config cfg;cfg.enable_stream(RS2_STREAM_DEPTH); // Enable default depth //启用默认深度// For the color stream, set format to RGBA// To allow blending of the color frame on top of the depth frame// 对于颜色流,将格式设置为RGBA// 允许在深度框上方混合颜色框cfg.enable_stream(RS2_STREAM_COLOR, RS2_FORMAT_RGBA8);auto profile = pipe.start(cfg);auto sensor = profile.get_device().first<rs2::depth_sensor>();// Set the device to High Accuracy preset of the D400 stereoscopic cameras// 将设备设置为D400立体摄像机的“高精度”预设if (sensor && sensor.is<rs2::depth_stereo_sensor>()){sensor.set_option(RS2_OPTION_VISUAL_PRESET, RS2_RS400_VISUAL_PRESET_HIGH_ACCURACY);}auto stream = profile.get_stream(RS2_STREAM_DEPTH).as<rs2::video_stream_profile>();// Create a simple OpenGL window for rendering:// 创建一个简单的OpenGL窗口进行渲染:window app(stream.width(), stream.height(), "RealSense Measure Example");// Define application state and position the ruler buttons// 定义应用程序状态并定位标尺按钮state app_state;app_state.ruler_start = { 0.45f, 0.5f };app_state.ruler_end = { 0.55f, 0.5f };register_glfw_callbacks(app, app_state);// After initial post-processing, frames will flow into this queue:// 初始后处理后,帧将流入此队列:rs2::frame_queue postprocessed_frames;// Alive boolean will signal the worker threads to finish-up// 激活的布尔值将指示工作线程完成std::atomic_bool alive{ true };// Video-processing thread will fetch frames from the camera,// apply post-processing and send the result to the main thread for rendering// It recieves synchronized (but not spatially aligned) pairs// and outputs synchronized and aligned pairs// 视频处理线程将从摄像头获取帧,进行后处理并将结果发送到主线程进行渲染// 接收同步(但在空间上不对齐)对,并输出同步和对齐对std::thread video_processing_thread([&]() {while (alive){// Fetch frames from the pipeline and send them for processing// 从管道中获取帧并将其发送以进行处理rs2::frameset data;if (pipe.poll_for_frames(&data)){// First make the frames spatially aligned// 首先使框架在空间上对齐data = data.apply_filter(align_to);// Decimation will reduce the resultion of the depth image,// closing small holes and speeding-up the algorithm// 抽取会降低深度图像的分辨率,关闭小孔并加快算法data = data.apply_filter(dec);// To make sure far-away objects are filtered proportionally// we try to switch to disparity domain// 确保远处的对象按比例过滤// 我们尝试切换到视差域data = data.apply_filter(depth2disparity);// Apply spatial filtering// 应用空间过滤data = data.apply_filter(spat);// Apply temporal filtering// 应用时间过滤data = data.apply_filter(temp);// If we are in disparity domain, switch back to depth// 如果我们处于视差域,请切换回深度data = data.apply_filter(disparity2depth);Apply color map for visualization of depth// 应用颜色图以可视化深度data = data.apply_filter(color_map);// Send resulting frames for visualization in the main thread// 发送结果帧以在主线程中进行可视化postprocessed_frames.enqueue(data);}}});rs2::frameset current_frameset;while(app) // Application still alive?//应用程序还在激活状态吗{// Fetch the latest available post-processed frameset// 获取最新的可用后处理框架集postprocessed_frames.poll_for_frame(¤t_frameset);if (current_frameset){auto depth = current_frameset.get_depth_frame();auto color = current_frameset.get_color_frame();auto colorized_depth = current_frameset.first(RS2_STREAM_DEPTH, RS2_FORMAT_RGB8);glEnable(GL_BLEND);// Use the Alpha channel for blending// 使用Alpha通道进行混合glBlendFunc(GL_SRC_ALPHA, GL_ONE_MINUS_SRC_ALPHA);// First render the colorized depth image// 首先渲染彩色深度图像depth_image.render(colorized_depth, { 0, 0, app.width(), app.height() });// Render the color frame (since we have selected RGBA format// pixels out of FOV will appear transparent)// 渲染颜色框(因为我们从FOV中选择了RGBA格式的像素将显示为透明)color_image.render(color, { 0, 0, app.width(), app.height() });// Render the simple pythagorean distance// 渲染简单的勾股距离render_simple_distance(depth, app_state, app);// Render the ruler// 渲染标尺app_state.ruler_start.render(app);app_state.ruler_end.render(app);glColor3f(1.f, 1.f, 1.f);glDisable(GL_BLEND);}}// Signal threads to finish and wait until they do// 通知线程完成并等待它们完成alive = false;video_processing_thread.join();return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
catch (const rs2::error & e)
{std::cerr << "RealSense error calling " << e.get_failed_function() << "(" << e.get_failed_args() << "):\n " << e.what() << std::endl;return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
catch (const std::exception& e)
{std::cerr << e.what() << std::endl;return EXIT_FAILURE;
}float dist_3d(const rs2::depth_frame& frame, pixel u, pixel v)
{float upixel[2]; // From pixel像素float upoint[3]; // From point (in 3D)float vpixel[2]; // To pixelfloat vpoint[3]; // To point (in 3D)// Copy pixels into the arrays (to match rsutil signatures)// 将像素复制到数组中(以匹配rsutil签名)upixel[0] = u.first;upixel[1] = u.second;vpixel[0] = v.first;vpixel[1] = v.second;// Query the frame for distance// Note: this can be optimized// It is not recommended to issue an API call for each pixel// (since the compiler can't inline these)// However, in this example it is not one of the bottlenecks// 查询框架的距离// 注意:可以优化// 不建议为每个像素发出API调用//(因为编译器无法内联这些代码)// 但是,在此示例中,这不是瓶颈之一auto udist = frame.get_distance(upixel[0], upixel[1]);auto vdist = frame.get_distance(vpixel[0], vpixel[1]);// Deproject from pixel to point in 3D// 在3D模式下从像素投影到点rs2_intrinsics intr = frame.get_profile().as<rs2::video_stream_profile>().get_intrinsics(); // Calibration datars2_deproject_pixel_to_point(upoint, &intr, upixel, udist);rs2_deproject_pixel_to_point(vpoint, &intr, vpixel, vdist);// Calculate euclidean distance between the two points// 计算两点之间的欧几里得距离return sqrt(pow(upoint[0] - vpoint[0], 2) +pow(upoint[1] - vpoint[1], 2) +pow(upoint[2] - vpoint[2], 2));
}void draw_line(float x0, float y0, float x1, float y1, int width)
{glPushAttrib(GL_ENABLE_BIT);glLineStipple(1, 0x00ff);glEnable(GL_LINE_STIPPLE);glLineWidth(width);glBegin(GL_LINE_STRIP);glVertex2f(x0, y0);glVertex2f(x1, y1);glEnd();glPopAttrib();
}void render_simple_distance(const rs2::depth_frame& depth,const state& s,const window& app)
{pixel center;glColor4f(0.f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.2f);draw_line(s.ruler_start.x * app.width(),s.ruler_start.y * app.height(),s.ruler_end.x * app.width(),s.ruler_end.y * app.height(), 9);glColor4f(0.f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.3f);draw_line(s.ruler_start.x * app.width(),s.ruler_start.y * app.height(),s.ruler_end.x * app.width(),s.ruler_end.y * app.height(), 7);glColor4f(1.f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.f);draw_line(s.ruler_start.x * app.width(),s.ruler_start.y * app.height(),s.ruler_end.x * app.width(),s.ruler_end.y * app.height(), 3);auto from_pixel = s.ruler_start.get_pixel(depth);auto to_pixel = s.ruler_end.get_pixel(depth);float air_dist = dist_3d(depth, from_pixel, to_pixel);center.first = (from_pixel.first + to_pixel.first) / 2;center.second = (from_pixel.second + to_pixel.second) / 2;std::stringstream ss;ss << int(air_dist * 100) << " cm";auto str = ss.str();auto x = (float(center.first) / depth.get_width()) * app.width() + 15;auto y = (float(center.second) / depth.get_height()) * app.height() + 15;auto w = stb_easy_font_width((char*)str.c_str());// Draw dark background for the text label// 为文字标签绘制深色背景glColor4f(0.f, 0.f, 0.f, 0.4f);glBegin(GL_TRIANGLES);glVertex2f(x - 3, y - 10);glVertex2f(x + w + 2, y - 10);glVertex2f(x + w + 2, y + 2);glVertex2f(x + w + 2, y + 2);glVertex2f(x - 3, y + 2);glVertex2f(x - 3, y - 10);glEnd();// Draw white text label// 绘制白色文字标签glColor4f(1.f, 1.f, 1.f, 1.f);draw_text(x, y, str.c_str());
}// Implement drag&drop behaviour for the buttons:
// 实现按钮的拖放行为:
void register_glfw_callbacks(window& app, state& app_state)
{app.on_left_mouse = [&](bool pressed){app_state.mouse_down = pressed;};app.on_mouse_move = [&](double x, double y){toggle cursor{ float(x) / app.width(), float(y) / app.height() };std::vector<toggle*> toggles{&app_state.ruler_start,&app_state.ruler_end };if (app_state.mouse_down){toggle* best = toggles.front();for (auto&& t : toggles){if (t->dist_2d(cursor) < best->dist_2d(cursor)){best = t;}}best->selected = true;}else{for (auto&& t : toggles) t->selected = false;}for (auto&& t : toggles){if (t->selected) *t = cursor;}};
}计算宽度:
import pyrealsense2 as rs
import numpy as np
import cv2
import os# opencv-haar人脸检测
face_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier('haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml')# Configure depth and color streams
pipeline = rs.pipeline()
config = rs.config()
config.enable_stream(rs.stream.depth, 1280, 720, rs.format.z16, 30)
config.enable_stream(rs.stream.color, 1280, 720, rs.format.bgr8, 30)# Start streaming
pipe_profile = pipeline.start(config)curr_frame = 0try:while True:# Wait for a coherent pair of frames: depth and colorframes = pipeline.wait_for_frames()depth_frame = frames.get_depth_frame()color_frame = frames.get_color_frame()if frames.size() < 2:continueif not depth_frame or not color_frame:continue# Intrinsics & Extrinsics# 深度相机内参矩阵depth_intrin = depth_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsics# RGB相机内参矩阵color_intrin = color_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsics# 深度图到彩图的外参RTdepth_to_color_extrin = depth_frame.profile.get_extrinsics_to(color_frame.profile)# print(depth_intrin.ppx, depth_intrin.ppy)# Convert images to numpy arraysdepth_image = np.asanyarray(depth_frame.get_data())color_image = np.asanyarray(color_frame.get_data())# 将RGB对齐到深度,获取对应下的XYZ#Color->Depthalign = rs.align(rs.stream.depth)frameset = align.process(frames)if frameset.size() < 2:continuedepth_frame = frameset.get_depth_frame()color_frame = frameset.get_color_frame()depth_intrin = depth_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsicscolor_intrin = color_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsicsdepth_image = np.asanyarray(depth_frame.get_data())color_image = np.asanyarray(color_frame.get_data())# 找到人脸# find the human face in the color_imagegray = cv2.cvtColor(color_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)faces = face_cascade.detectMultiScale(gray, 1.3, 5)left = []for (x, y, w, h) in faces:# 当前帧大于100if curr_frame > 100 and curr_frame % 40 == 10:# 取出人脸的深度图和彩色图roi_depth_image = depth_image[y:y+h, x:x+w]roi_color_image = color_image[y:y+h, x:x+w]# 新建os.system('mkdir -p ./3d_output/%d' % curr_frame)# 保存cv2.imwrite('./3d_output/%d/depth.jpg' %curr_frame, roi_depth_image)cv2.imwrite('./3d_output/%d/color.jpg' %curr_frame, roi_color_image)# write the depth data in a depth.txtwith open('./3d_output/%d/depth.csv' % curr_frame, 'w') as f:# Wcols = list(range(x, x+w))# Hrows = list(range(y, y+h))for i in rows: #Hfor j in cols: #W# 坐标变换一定要注意检查# 此时获取的是真实世界坐标的深度# https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/blob/master/include/librealsense2/hpp/rs_frame.hpp#L810depth = depth_frame.get_distance(j, i) # W,H# 给定没有失真或反失真系数的图像中的像素坐标和深度,计算相对于同一相机的3D空间中的对应点# https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/blob/master/include/librealsense2/rsutil.h#L67depth_point = rs.rs2_deproject_pixel_to_point(depth_intrin, [j, i], depth)text = "%.5lf, %.5lf, %.5lf\n" % (depth_point[0], depth_point[1], depth_point[2])f.write(text)if i==rows[0]:left.append(depth_point)print("Finish writing the depth img")temp = np.array(left)index = np.where(temp != 0)[0]#dist2 = np.sqrt(np.square(left[index[-1]][0] - left[index[0]][0])+np.square(left[index[-1]][1] - left[index[0]][1])+np.square(left[index[-1]][2] - left[index[0]][2]))# // 计算两点之间的欧几里得距离# return sqrt(pow(upoint[0] - vpoint[0], 2) +# pow(upoint[1] - vpoint[1], 2) +# pow(upoint[2] - vpoint[2], 2));#这里的距离,收到环境的影响,因为我是直接计算框里面最左端到最右端的距离#如果把背景框进来,那么你测的是两个背景的宽度print("dist","---------------------", str(left[index[-1]][0] - left[index[0]][0]))cv2.putText(color_image, str(left[index[-1]][0] - left[index[0]][0]),(x, y - 30),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 1.5, (255, 255, 255))cv2.rectangle(color_image, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (255, 0, 0), 2)# Apply colormap on depth image (image must be converted to 8-bit per pixel first)depth_colormap = cv2.applyColorMap(cv2.convertScaleAbs(depth_image, alpha=0.03), cv2.COLORMAP_JET)# Stack both images horizontallyimages = np.hstack((color_image, depth_colormap))# Show imagescv2.namedWindow('RealSense', cv2.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE)cv2.imshow('RealSense', images)cv2.waitKey(1)curr_frame += 1
finally:# Stop streamingpipeline.stop()有一个显示相机位置的py例子:
# License: Apache 2.0. See LICENSE file in root directory.
# Copyright(c) 2015-2017 Intel Corporation. All Rights Reserved."""
OpenGL Pointcloud viewer with http://pyglet.orgUsage:
------
Mouse:Drag with left button to rotate around pivot (thick small axes),with right button to translate and the wheel to zoom.Keyboard:[p] Pause[r] Reset View[d] Cycle through decimation values[z] Toggle point scaling[x] Toggle point distance attenuation[c] Toggle color source[l] Toggle lighting[f] Toggle depth post-processing[s] Save PNG (./out.png)[e] Export points to ply (./out.ply)[q/ESC] QuitNotes:
------
Using deprecated OpenGL (FFP lighting, matrix stack...) however, draw calls
are kept low with pyglet.graphics.* which uses glDrawArrays internally.Normals calculation is done with numpy on CPU which is rather slow, should really
be done with shaders but was omitted for several reasons - brevity, for lowering
dependencies (pyglet doesn't ship with shader support & recommends pyshaders)
and for reference.
"""import math
import ctypes
import pyglet
import pyglet.gl as gl
import numpy as np
import pyrealsense2 as rs# https://stackoverflow.com/a/6802723
def rotation_matrix(axis, theta):"""Return the rotation matrix associated with counterclockwise rotation aboutthe given axis by theta radians."""axis = np.asarray(axis)axis = axis / math.sqrt(np.dot(axis, axis))a = math.cos(theta / 2.0)b, c, d = -axis * math.sin(theta / 2.0)aa, bb, cc, dd = a * a, b * b, c * c, d * dbc, ad, ac, ab, bd, cd = b * c, a * d, a * c, a * b, b * d, c * dreturn np.array([[aa + bb - cc - dd, 2 * (bc + ad), 2 * (bd - ac)],[2 * (bc - ad), aa + cc - bb - dd, 2 * (cd + ab)],[2 * (bd + ac), 2 * (cd - ab), aa + dd - bb - cc]])class AppState:def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):self.pitch, self.yaw = math.radians(-10), math.radians(-15)self.translation = np.array([0, 0, 1], np.float32)self.distance = 2self.mouse_btns = [False, False, False]self.paused = Falseself.decimate = 0self.scale = Trueself.attenuation = Falseself.color = Trueself.lighting = Falseself.postprocessing = Falsedef reset(self):self.pitch, self.yaw, self.distance = 0, 0, 2self.translation[:] = 0, 0, 1@propertydef rotation(self):Rx = rotation_matrix((1, 0, 0), math.radians(-self.pitch))Ry = rotation_matrix((0, 1, 0), math.radians(-self.yaw))return np.dot(Ry, Rx).astype(np.float32)state = AppState()# Configure streams
pipeline = rs.pipeline()
config = rs.config()
config.enable_stream(rs.stream.depth, 640, 480, rs.format.z16, 30)
# other_stream, other_format = rs.stream.infrared, rs.format.y8
other_stream, other_format = rs.stream.color, rs.format.rgb8
config.enable_stream(other_stream, 640, 480, other_format, 30)# Start streaming
pipeline.start(config)
profile = pipeline.get_active_profile()depth_sensor = profile.get_device().first_depth_sensor()
depth_scale = depth_sensor.get_depth_scale()depth_profile = rs.video_stream_profile(profile.get_stream(rs.stream.depth))
depth_intrinsics = depth_profile.get_intrinsics()
w, h = depth_intrinsics.width, depth_intrinsics.height# Processing blocks
pc = rs.pointcloud()
decimate = rs.decimation_filter()
decimate.set_option(rs.option.filter_magnitude, 2 ** state.decimate)
colorizer = rs.colorizer()
filters = [rs.disparity_transform(),rs.spatial_filter(),rs.temporal_filter(),rs.disparity_transform(False)]# pyglet
window = pyglet.window.Window(config=gl.Config(double_buffer=True,samples=8 # MSAA),resizable=True, vsync=True)
keys = pyglet.window.key.KeyStateHandler()
window.push_handlers(keys)def convert_fmt(fmt):"""rs.format to pyglet format string"""return {rs.format.rgb8: 'RGB',rs.format.bgr8: 'BGR',rs.format.rgba8: 'RGBA',rs.format.bgra8: 'BGRA',rs.format.y8: 'L',}[fmt]# Create a VertexList to hold pointcloud data
# Will pre-allocates memory according to the attributes below
vertex_list = pyglet.graphics.vertex_list(w * h, 'v3f/stream', 't2f/stream', 'n3f/stream')
# Create and allocate memory for our color data
other_profile = rs.video_stream_profile(profile.get_stream(other_stream))
image_data = pyglet.image.ImageData(w, h, convert_fmt(other_profile.format()), (gl.GLubyte * (w * h * 3))())fps_display = pyglet.clock.ClockDisplay()@window.event
def on_mouse_drag(x, y, dx, dy, buttons, modifiers):w, h = map(float, window.get_size())if buttons & pyglet.window.mouse.LEFT:state.yaw -= dx * 0.5state.pitch -= dy * 0.5if buttons & pyglet.window.mouse.RIGHT:dp = np.array((dx / w, -dy / h, 0), np.float32)state.translation += np.dot(state.rotation, dp)if buttons & pyglet.window.mouse.MIDDLE:dz = dy * 0.01state.translation -= (0, 0, dz)state.distance -= dzdef handle_mouse_btns(x, y, button, modifiers):state.mouse_btns[0] ^= (button & pyglet.window.mouse.LEFT)state.mouse_btns[1] ^= (button & pyglet.window.mouse.RIGHT)state.mouse_btns[2] ^= (button & pyglet.window.mouse.MIDDLE)window.on_mouse_press = window.on_mouse_release = handle_mouse_btns@window.event
def on_mouse_scroll(x, y, scroll_x, scroll_y):dz = scroll_y * 0.1state.translation -= (0, 0, dz)state.distance -= dzdef on_key_press(symbol, modifiers):if symbol == pyglet.window.key.R:state.reset()if symbol == pyglet.window.key.P:state.paused ^= Trueif symbol == pyglet.window.key.D:state.decimate = (state.decimate + 1) % 3decimate.set_option(rs.option.filter_magnitude, 2 ** state.decimate)if symbol == pyglet.window.key.C:state.color ^= Trueif symbol == pyglet.window.key.Z:state.scale ^= Trueif symbol == pyglet.window.key.X:state.attenuation ^= Trueif symbol == pyglet.window.key.L:state.lighting ^= Trueif symbol == pyglet.window.key.F:state.postprocessing ^= Trueif symbol == pyglet.window.key.S:pyglet.image.get_buffer_manager().get_color_buffer().save('out.png')if symbol == pyglet.window.key.Q:window.close()window.push_handlers(on_key_press)def axes(size=1, width=1):"""draw 3d axes"""gl.glLineWidth(width)pyglet.graphics.draw(6, gl.GL_LINES,('v3f', (0, 0, 0, size, 0, 0,0, 0, 0, 0, size, 0,0, 0, 0, 0, 0, size)),('c3f', (1, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0,0, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0,0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 1,)))def frustum(intrinsics):"""draw camera's frustum"""w, h = intrinsics.width, intrinsics.heightbatch = pyglet.graphics.Batch()for d in range(1, 6, 2):def get_point(x, y):p = rs.rs2_deproject_pixel_to_point(intrinsics, [x, y], d)batch.add(2, gl.GL_LINES, None, ('v3f', [0, 0, 0] + p))return ptop_left = get_point(0, 0)top_right = get_point(w, 0)bottom_right = get_point(w, h)bottom_left = get_point(0, h)batch.add(2, gl.GL_LINES, None, ('v3f', top_left + top_right))batch.add(2, gl.GL_LINES, None, ('v3f', top_right + bottom_right))batch.add(2, gl.GL_LINES, None, ('v3f', bottom_right + bottom_left))batch.add(2, gl.GL_LINES, None, ('v3f', bottom_left + top_left))batch.draw()def grid(size=1, n=10, width=1):"""draw a grid on xz plane"""gl.glLineWidth(width)s = size / float(n)s2 = 0.5 * sizebatch = pyglet.graphics.Batch()for i in range(0, n + 1):x = -s2 + i * sbatch.add(2, gl.GL_LINES, None, ('v3f', (x, 0, -s2, x, 0, s2)))for i in range(0, n + 1):z = -s2 + i * sbatch.add(2, gl.GL_LINES, None, ('v3f', (-s2, 0, z, s2, 0, z)))batch.draw()@window.event
def on_draw():window.clear()gl.glEnable(gl.GL_DEPTH_TEST)gl.glEnable(gl.GL_LINE_SMOOTH)width, height = window.get_size()gl.glViewport(0, 0, width, height)gl.glMatrixMode(gl.GL_PROJECTION)gl.glLoadIdentity()gl.gluPerspective(60, width / float(height), 0.01, 20)gl.glMatrixMode(gl.GL_TEXTURE)gl.glLoadIdentity()# texcoords are [0..1] and relative to top-left pixel corner, add 0.5 to centergl.glTranslatef(0.5 / image_data.width, 0.5 / image_data.height, 0)# texture size may be increased by pyglet to a power of 2tw, th = image_data.texture.owner.width, image_data.texture.owner.heightgl.glScalef(image_data.width / float(tw),image_data.height / float(th), 1)gl.glMatrixMode(gl.GL_MODELVIEW)gl.glLoadIdentity()gl.gluLookAt(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, -1, 0)gl.glTranslatef(0, 0, state.distance)gl.glRotated(state.pitch, 1, 0, 0)gl.glRotated(state.yaw, 0, 1, 0)if any(state.mouse_btns):axes(0.1, 4)gl.glTranslatef(0, 0, -state.distance)gl.glTranslatef(*state.translation)gl.glColor3f(0.5, 0.5, 0.5)gl.glPushMatrix()gl.glTranslatef(0, 0.5, 0.5)grid()gl.glPopMatrix()psz = max(window.get_size()) / float(max(w, h)) if state.scale else 1gl.glPointSize(psz)distance = (0, 0, 1) if state.attenuation else (1, 0, 0)gl.glPointParameterfv(gl.GL_POINT_DISTANCE_ATTENUATION,(gl.GLfloat * 3)(*distance))if state.lighting:ldir = [0.5, 0.5, 0.5] # world-space lightingldir = np.dot(state.rotation, (0, 0, 1)) # MeshLab style lightingldir = list(ldir) + [0] # w=0, directional lightgl.glLightfv(gl.GL_LIGHT0, gl.GL_POSITION, (gl.GLfloat * 4)(*ldir))gl.glLightfv(gl.GL_LIGHT0, gl.GL_DIFFUSE,(gl.GLfloat * 3)(1.0, 1.0, 1.0))gl.glLightfv(gl.GL_LIGHT0, gl.GL_AMBIENT,(gl.GLfloat * 3)(0.75, 0.75, 0.75))gl.glEnable(gl.GL_LIGHT0)gl.glEnable(gl.GL_NORMALIZE)gl.glEnable(gl.GL_LIGHTING)gl.glColor3f(1, 1, 1)texture = image_data.get_texture()gl.glEnable(texture.target)gl.glBindTexture(texture.target, texture.id)gl.glTexParameteri(gl.GL_TEXTURE_2D, gl.GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, gl.GL_NEAREST)# comment this to get round points with MSAA ongl.glEnable(gl.GL_POINT_SPRITE)if not state.scale and not state.attenuation:gl.glDisable(gl.GL_MULTISAMPLE) # for true 1px points with MSAA onvertex_list.draw(gl.GL_POINTS)gl.glDisable(texture.target)if not state.scale and not state.attenuation:gl.glEnable(gl.GL_MULTISAMPLE)gl.glDisable(gl.GL_LIGHTING)gl.glColor3f(0.25, 0.25, 0.25)frustum(depth_intrinsics)axes()gl.glMatrixMode(gl.GL_PROJECTION)gl.glLoadIdentity()gl.glOrtho(0, width, 0, height, -1, 1)gl.glMatrixMode(gl.GL_MODELVIEW)gl.glLoadIdentity()gl.glMatrixMode(gl.GL_TEXTURE)gl.glLoadIdentity()gl.glDisable(gl.GL_DEPTH_TEST)fps_display.draw()def run(dt):global w, hwindow.set_caption("RealSense (%dx%d) %dFPS (%.2fms) %s" %(w, h, 0 if dt == 0 else 1.0 / dt, dt * 1000,"PAUSED" if state.paused else ""))if state.paused:returnsuccess, frames = pipeline.try_wait_for_frames(timeout_ms=0)if not success:returndepth_frame = frames.get_depth_frame()other_frame = frames.first(other_stream)depth_frame = decimate.process(depth_frame)if state.postprocessing:for f in filters:depth_frame = f.process(depth_frame)# Grab new intrinsics (may be changed by decimation)depth_intrinsics = rs.video_stream_profile(depth_frame.profile).get_intrinsics()w, h = depth_intrinsics.width, depth_intrinsics.heightcolor_image = np.asanyarray(other_frame.get_data())colorized_depth = colorizer.colorize(depth_frame)depth_colormap = np.asanyarray(colorized_depth.get_data())if state.color:mapped_frame, color_source = other_frame, color_imageelse:mapped_frame, color_source = colorized_depth, depth_colormappoints = pc.calculate(depth_frame)pc.map_to(mapped_frame)# handle color source or size changefmt = convert_fmt(mapped_frame.profile.format())global image_dataif (image_data.format, image_data.pitch) != (fmt, color_source.strides[0]):empty = (gl.GLubyte * (w * h * 3))()image_data = pyglet.image.ImageData(w, h, fmt, empty)# copy image data to pygletimage_data.set_data(fmt, color_source.strides[0], color_source.ctypes.data)verts = np.asarray(points.get_vertices(2)).reshape(h, w, 3)texcoords = np.asarray(points.get_texture_coordinates(2))if len(vertex_list.vertices) != verts.size:vertex_list.resize(verts.size // 3)# need to reassign after resizingvertex_list.vertices = verts.ravel()vertex_list.tex_coords = texcoords.ravel()# copy our data to pre-allocated buffers, this is faster than assigning...# pyglet will take care of uploading to GPUdef copy(dst, src):"""copy numpy array to pyglet array"""# timeit was mostly inconclusive, favoring slice assignment for safetynp.array(dst, copy=False)[:] = src.ravel()# ctypes.memmove(dst, src.ctypes.data, src.nbytes)copy(vertex_list.vertices, verts)copy(vertex_list.tex_coords, texcoords)if state.lighting:# compute normalsdy, dx = np.gradient(verts, axis=(0, 1))n = np.cross(dx, dy)# can use this, np.linalg.norm or similar to normalize, but OpenGL can do this for us, see GL_NORMALIZE above# norm = np.sqrt((n*n).sum(axis=2, keepdims=True))# np.divide(n, norm, out=n, where=norm != 0)# import cv2# n = cv2.bilateralFilter(n, 5, 1, 1)copy(vertex_list.normals, n)if keys[pyglet.window.key.E]:points.export_to_ply('./out.ply', mapped_frame)pyglet.clock.schedule(run)try:pyglet.app.run()
finally:pipeline.stop()结合改进:
import pyrealsense2 as rs
import numpy as np
import cv2
import os# opencv-haar人脸检测
face_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier('haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml')# Configure depth and color streams
pipeline = rs.pipeline()
config = rs.config()
config.enable_stream(rs.stream.depth, 1280, 720, rs.format.z16, 30)
config.enable_stream(rs.stream.color, 1280, 720, rs.format.bgr8, 30)# Start streaming
pipe_profile = pipeline.start(config)curr_frame = 0try:while True:# Wait for a coherent pair of frames: depth and colorframes = pipeline.wait_for_frames()depth_frame = frames.get_depth_frame()color_frame = frames.get_color_frame()if frames.size() < 2:continueif not depth_frame or not color_frame:continue# Intrinsics & Extrinsics# 深度相机内参矩阵depth_intrin = depth_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsics# RGB相机内参矩阵color_intrin = color_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsics# 深度图到彩图的外参RTdepth_to_color_extrin = depth_frame.profile.get_extrinsics_to(color_frame.profile)depth_value = 0.5depth_pixel = [depth_intrin.ppx, depth_intrin.ppy]depth_point = rs.rs2_deproject_pixel_to_point(depth_intrin, depth_pixel, depth_value)print(depth_point)# print(depth_intrin.ppx, depth_intrin.ppy)# Convert images to numpy arraysdepth_image = np.asanyarray(depth_frame.get_data())color_image = np.asanyarray(color_frame.get_data())# 将RGB对齐到深度,获取对应下的XYZ#Color->Depthalign = rs.align(rs.stream.depth)frameset = align.process(frames)if frameset.size() < 2:continuedepth_frame = frameset.get_depth_frame()color_frame = frameset.get_color_frame()depth_intrin = depth_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsicscolor_intrin = color_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsicsdepth_image = np.asanyarray(depth_frame.get_data())color_image = np.asanyarray(color_frame.get_data())# 找到人脸# find the human face in the color_imagegray = cv2.cvtColor(color_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)faces = face_cascade.detectMultiScale(gray, 1.3, 5)left = []for (x, y, w, h) in faces:# 当前帧大于100if curr_frame > 100 and curr_frame % 40 == 10:# 取出人脸的深度图和彩色图roi_depth_image = depth_image[y:y+h, x:x+w]roi_color_image = color_image[y:y+h, x:x+w]# 新建os.system('mkdir -p ./3d_output/%d' % curr_frame)# 保存cv2.imwrite('./3d_output/%d/depth.jpg' %curr_frame, roi_depth_image)cv2.imwrite('./3d_output/%d/color.jpg' %curr_frame, roi_color_image)# write the depth data in a depth.txtwith open('./3d_output/%d/depth.csv' % curr_frame, 'w') as f:# Wcols = list(range(x, x+w))# Hrows = list(range(y, y+h))for i in rows: #Hfor j in cols: #W# 坐标变换一定要注意检查# 此时获取的是真实世界坐标的深度# https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/blob/master/include/librealsense2/hpp/rs_frame.hpp#L810depth = depth_frame.get_distance(j, i) # W,H# 给定没有失真或反失真系数的图像中的像素坐标和深度,计算相对于同一相机的3D空间中的对应点# https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/blob/master/include/librealsense2/rsutil.h#L67depth_point = rs.rs2_deproject_pixel_to_point(depth_intrin, [j, i], depth)text = "%.5lf, %.5lf, %.5lf\n" % (depth_point[0], depth_point[1], depth_point[2])f.write(text)if i==rows[0]:left.append(depth_point)print("Finish writing the depth img")temp = np.array(left)index = np.where(temp != 0)[0]#dist2 = np.sqrt(np.square(left[index[-1]][0] - left[index[0]][0])+np.square(left[index[-1]][1] - left[index[0]][1])+np.square(left[index[-1]][2] - left[index[0]][2]))# // 计算两点之间的欧几里得距离# return sqrt(pow(upoint[0] - vpoint[0], 2) +# pow(upoint[1] - vpoint[1], 2) +# pow(upoint[2] - vpoint[2], 2));#这里的距离,收到环境的影响,因为我是直接计算框里面最左端到最右端的距离#如果把背景框进来,那么你测的是两个背景的宽度print("dist","---------------------", str(left[index[-1]][0] - left[index[0]][0]))# 这里要做很多工作,离群噪声点的去除,去除后矩阵的真实大小判断 很多行,哪一行是最真实的距离cv2.putText(color_image, str(left[index[-1]][0] - left[index[0]][0]),(x, y - 30),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 1.5, (255, 255, 255))cv2.rectangle(color_image, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (255, 0, 0), 2)# Apply colormap on depth image (image must be converted to 8-bit per pixel first)depth_colormap = cv2.applyColorMap(cv2.convertScaleAbs(depth_image, alpha=0.03), cv2.COLORMAP_JET)# Stack both images horizontallyimages = np.hstack((color_image, depth_colormap))# Show imagescv2.namedWindow('RealSense', cv2.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE)cv2.imshow('RealSense', images)cv2.waitKey(1)curr_frame += 1
finally:# Stop streamingpipeline.stop()修改版:
import pyrealsense2 as rs
import numpy as np
import cv2
import os# opencv-haar人脸检测
face_cascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier('haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml')# Configure depth and color streams
pipeline = rs.pipeline()
config = rs.config()
config.enable_stream(rs.stream.depth, 1280, 720, rs.format.z16, 30)
config.enable_stream(rs.stream.color, 1280, 720, rs.format.bgr8, 30)# Start streaming
pipe_profile = pipeline.start(config)curr_frame = 0try:while True:# Wait for a coherent pair of frames: depth and colorframes = pipeline.wait_for_frames()depth_frame = frames.get_depth_frame()color_frame = frames.get_color_frame()if frames.size() < 2:continueif not depth_frame or not color_frame:continue# Intrinsics & Extrinsics# 深度相机内参矩阵depth_intrin = depth_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsics# RGB相机内参矩阵color_intrin = color_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsics# 深度图到彩图的外参RTdepth_to_color_extrin = depth_frame.profile.get_extrinsics_to(color_frame.profile)depth_value = 0.5depth_pixel = [depth_intrin.ppx, depth_intrin.ppy]depth_point = rs.rs2_deproject_pixel_to_point(depth_intrin, depth_pixel, depth_value)#print(depth_point)# print(depth_intrin.ppx, depth_intrin.ppy)# Convert images to numpy arraysdepth_image = np.asanyarray(depth_frame.get_data())color_image = np.asanyarray(color_frame.get_data())# 将RGB对齐到深度,获取对应下的XYZ#Color->Depthalign = rs.align(rs.stream.depth)frameset = align.process(frames)if frameset.size() < 2:continuedepth_frame = frameset.get_depth_frame()color_frame = frameset.get_color_frame()depth_intrin = depth_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsicscolor_intrin = color_frame.profile.as_video_stream_profile().intrinsicsdepth_image = np.asanyarray(depth_frame.get_data())color_image = np.asanyarray(color_frame.get_data())# 找到人脸# find the human face in the color_imagegray = cv2.cvtColor(color_image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)faces = face_cascade.detectMultiScale(gray, 1.3, 5)left = []for (x, y, w, h) in faces:# 当前帧大于100if curr_frame > 100 and curr_frame % 40 == 10:# 取出人脸的深度图和彩色图roi_depth_image = depth_image[y:y+h, x:x+w]roi_color_image = color_image[y:y+h, x:x+w]# Wcols = list(range(x, x+w))# Hrows = list(range(y, y+h))for i in rows: #Hfor j in cols: #W# 坐标变换一定要注意检查# 此时获取的是真实世界坐标的深度# https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/blob/master/include/librealsense2/hpp/rs_frame.hpp#L810depth = depth_frame.get_distance(j, i) # W,H# 给定没有失真或反失真系数的图像中的像素坐标和深度,计算相对于同一相机的3D空间中的对应点# https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/blob/master/include/librealsense2/rsutil.h#L67depth_point = rs.rs2_deproject_pixel_to_point(depth_intrin, [j, i], depth)text = "%.5lf, %.5lf, %.5lf\n" % (depth_point[0], depth_point[1], depth_point[2])#f.write(text)if i==rows[0]:left.append(depth_point)#print("Finish writing the depth img")# temp = np.array(left)# # 求均值# _mean = np.mean(temp, axis=0)# # 求方差# _var = np.var(temp, axis=0)# minmean = _mean - 1 * abs(_mean)# maxmean = _mean + 1 * abs(_mean)# minvar = _var - 1 * abs(_var)# maxvar = _var + 1 * abs(_var)def non_zero_mean(np_arr, axis):exist = (np_arr != 0)num = np_arr.sum(axis=axis)den = exist.sum(axis=axis)return num / dentemp = np.array(left)# 求均值_mean = non_zero_mean(temp, axis=0)# 求方差_var = np.var(temp, axis=0)minmean = _mean - 1 * abs(_mean)maxmean = _mean + 1 * abs(_mean)minvar = _var - 1 * abs(_var)maxvar = _var + 1 * abs(_var)index = []i = 0 # Hfor j in range(len(cols)): # Wif temp[j][0] != 0 and temp[j][1] != 0 and temp[j][2] != 0:if temp[j][0]>minmean[0] and temp[j][0]<maxmean[0]:if temp[j][1] > minmean[1] and temp[j][1] < maxmean[1]:if temp[j][2] > minmean[2] and temp[j][2] < maxmean[2]:index.append(j)#dist2 = np.sqrt(np.square(left[index[-1]][0] - left[index[0]][0])+np.square(left[index[-1]][1] - left[index[0]][1])+np.square(left[index[-1]][2] - left[index[0]][2]))# // 计算两点之间的欧几里得距离# return sqrt(pow(upoint[0] - vpoint[0], 2) +# pow(upoint[1] - vpoint[1], 2) +# pow(upoint[2] - vpoint[2], 2));#这里的距离,收到环境的影响,因为我是直接计算框里面最左端到最右端的距离#如果把背景框进来,那么你测的是两个背景的宽度if len(index) > (len(cols)/2):# 新建os.system('mkdir -p ./3d_output/%d' % curr_frame)# 保存cv2.imwrite('./3d_output/%d/depth.jpg' %curr_frame, roi_depth_image)cv2.imwrite('./3d_output/%d/color.jpg' %curr_frame, roi_color_image)print("dist","---------------------", str(left[index[-1]][0] - left[index[0]][0]))# 这里要做很多工作,离群噪声点的去除,去除后矩阵的真实大小判断 很多行,哪一行是最真实的距离cv2.putText(color_image, str(left[index[-1]][0] - left[index[0]][0]),(x, y - 30),cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 1.5, (255, 255, 255))cv2.rectangle(color_image, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (255, 0, 0), 2)# Apply colormap on depth image (image must be converted to 8-bit per pixel first)depth_colormap = cv2.applyColorMap(cv2.convertScaleAbs(depth_image, alpha=0.03), cv2.COLORMAP_JET)# Stack both images horizontallyimages = np.hstack((color_image, depth_colormap))# Show imagescv2.namedWindow('RealSense', cv2.WINDOW_AUTOSIZE)cv2.imshow('RealSense', images)cv2.waitKey(1)curr_frame += 1
finally:# Stop streamingpipeline.stop()https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/issues/2351
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/issues/2343
https://dev.intelrealsense.com/docs/rs-measure
https://forums.intel.com/s/question/0D50P0000490TLGSA2/measuring-length-of-object-using-depth-and-rgb-frames?language=en_US
https://intelrealsense.github.io/librealsense/python_docs/_generated/pyrealsense2.html
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/tree/master/wrappers/python/examples/box_dimensioner_multicam
计算速度的例子
https://answers.opencv.org/question/209387/measuring-the-speed-of-an-object-with-variable-distance-from-camera/
计算体积的例子
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/issues/4612
https://github.com/IntelRealSense/librealsense/tree/master/wrappers/python/examples/box_dimensioner_multicam
这篇关于realsense2+faster-rcnn+物体深度+物体宽度的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




