本文主要是介绍RecyclerView中ItemDecoration的基础,粘性头部及点击事件,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
RecyclerView中ItemDecoration的基础,粘性头部及点击事件
- 前言
- 一、ItemDecoration是什么?
- 二、基础使用
- 1.getItemOffsets()
- 2.onDraw()
- 二、进阶使用
- 1.onDrawOver()实现粘性头部
- OnItemTouchListener实现ItemDecoration点击事件
- 总结
前言
在工作中遇到ItemDecoration相关需求,发现自己以前学习的太过粗糙,特此重新学习记录相关知识。
一、ItemDecoration是什么?
RecyclerView中的ItemDecoration是用于给列表项添加修饰的一种方式,例如给列表项之间添加分割线、设置边距等。
二、基础使用
对于ItemDecoration的使用,我们需要创建自定义ItemDecoration类,继承自RecyclerView.ItemDecoration。并重写onDraw()和getItemOffsets()方法。并调用RecyclerView.addItemDecoration方法添加分割线。必要时,通过RecyclerView.removeItemDecoration方法移除分割线。值得一提的是,ItemDecoration可以添加多个
1.getItemOffsets()
getItemOffsets()是RecyclerView.ItemDecoration类的一个方法,用于为RecyclerView中的每个item设置偏移量(即设置item之间的间距)。
该方法有四个参数:
- outRect:用于保存当前item的偏移量,即item的四个边距(left、top、right、bottom)的距离。默认实现将outRect的边界设置为0并返回。
- view:当前item的View对象。
- parent:RecyclerView对象。
- state:RecyclerView状态对象。
例如,在实现一个垂直方向的等间距ItemDecoration时,可以使用如下代码:
public class VerticalSpaceItemDecoration extends RecyclerView.ItemDecoration {private final int verticalSpaceHeight;public VerticalSpaceItemDecoration(int verticalSpaceHeight) {this.verticalSpaceHeight = verticalSpaceHeight;}@Overridepublic void getItemOffsets(Rect outRect, View view, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) {if (parent.getChildAdapterPosition(view) != parent.getAdapter().getItemCount() - 1) {outRect.bottom = verticalSpaceHeight;}}
}在上述代码中,我们通过判断当前item是否为列表最后一个item,来确定是否为其设置底部偏移量。如果不是最后一个item,则为其设置一个指定高度的底部偏移量,即实现了等间距效果。
用我自己的话来总结的话,重写getItemOffsets方法就是重写为RecyclerView中的item设置padding值。换一种看法也是为其设置填充的空间。
下面这张图是从深入理解 RecyclerView 系列之一:ItemDecoration摘录的,便于,可以看图更便于理解这个方法。
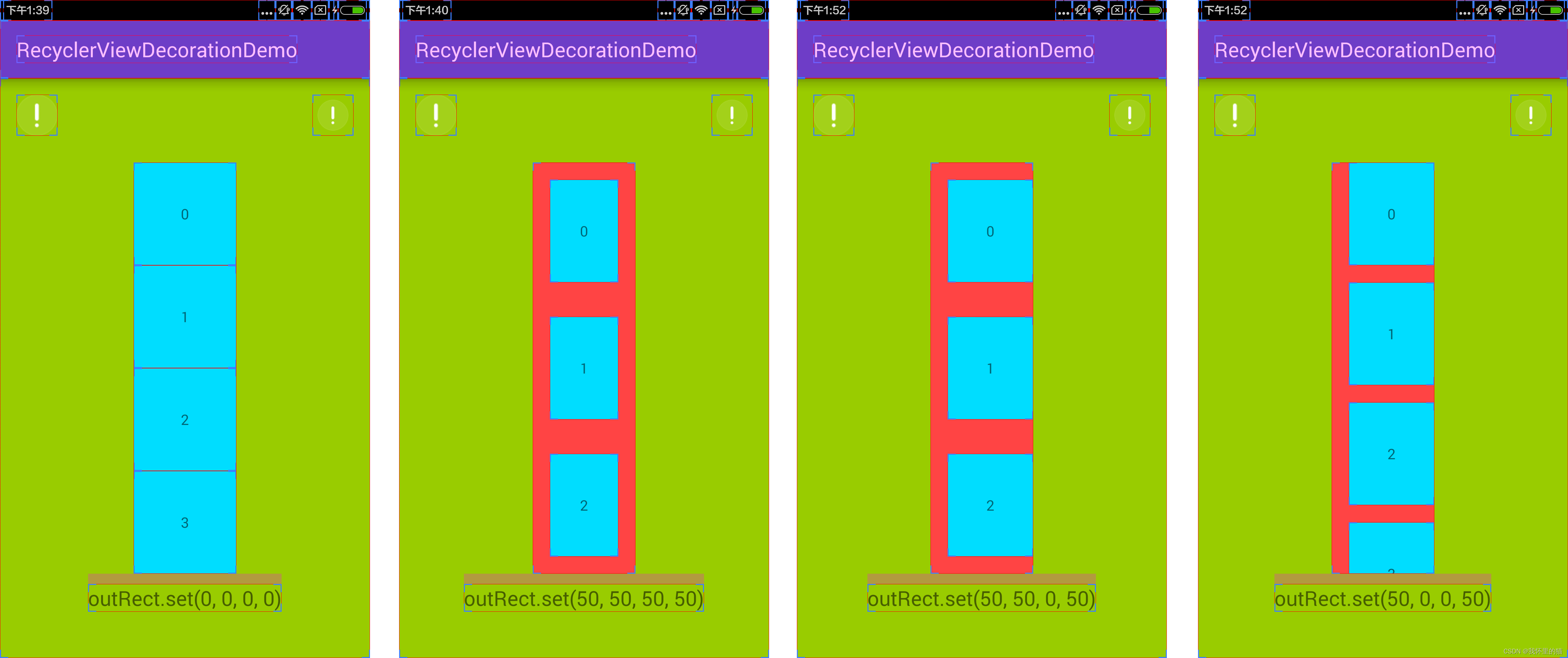
2.onDraw()
onDraw()方法会在RecyclerView的绘制流程中被调用,每次绘制一个Item时都会执行一次,用于绘制对应Item的Decoration。这也是view最基础的方法。
该方法有三个参数:
- canvas:绘制到父对象中的画布。
- parent:RecyclerView对象。
- state:RecyclerView状态对象。
下面是一个示例代码,它将在RecyclerView中的每个Item之间绘制一条红色的线,线的宽度为2像素:
class MyItemDecoration : RecyclerView.ItemDecoration() {private val paint = Paint()init {paint.color = Color.REDpaint.strokeWidth = 2f}override fun onDraw(c: Canvas, parent: RecyclerView, state: RecyclerView.State) {super.onDraw(c, parent, state)for (i in 0 until parent.childCount - 1) {val child = parent.getChildAt(i)val nextChild = parent.getChildAt(i + 1)val xStart = child.left.toFloat()val yStart = child.bottom.toFloat()val xEnd = nextChild.right.toFloat()val yEnd = yStartc.drawLine(xStart, yStart, xEnd, yEnd, paint)}}
}在上面的代码中,我们首先创建一个Paint对象,并设置它的颜色为红色,宽度为2像素。然后,在onDraw方法中,我们遍历RecyclerView的子View,对于每两个相邻的子View,我们计算它们之间需要绘制的线段的起点和终点,然后调用Canvas的drawLine方法来绘制线段。
二、进阶使用
在基础使用中我们学习了如何使用ItemDecoration,接下来介绍如何实现粘性头部及其点击事件
1.onDrawOver()实现粘性头部
onDrawOver()方法是RecyclerView的ItemDecoration类中的一个方法,用于在RecyclerView的Item视图上方绘制内容,例如悬浮的标题或标签等。该方法是在Item视图之后绘制的,因此可以遮盖Item视图的一部分。
以下是一个简单的代码示例,演示如何使用onDrawOver()方法来绘制悬浮标题:
public class TitleDecoration extends RecyclerView.ItemDecoration {private int titleHeight;private Paint paint;private int textSize;private Rect bounds;public TitleDecoration(Context context) {titleHeight = context.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.title_height);paint = new Paint();paint.setColor(ContextCompat.getColor(context, R.color.colorAccent));paint.setAntiAlias(true);textSize = context.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.title_text_size);paint.setTextSize(textSize);bounds = new Rect();}@Overridepublic void onDrawOver(Canvas canvas, RecyclerView parent, RecyclerView.State state) {super.onDrawOver(canvas, parent, state);int itemCount = parent.getAdapter().getItemCount();for (int i = 0; i < itemCount; i++) {View child = parent.getChildAt(i);RecyclerView.LayoutParams params = (RecyclerView.LayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();int position = params.getViewAdapterPosition();if (position == 0) {// 第一个Item的标题始终悬浮在顶部int top = parent.getPaddingTop();int bottom = top + titleHeight;canvas.drawRect(parent.getLeft(), top, parent.getRight(), bottom, paint);String text = "Title 1";paint.getTextBounds(text, 0, text.length(), bounds);int x = parent.getWidth() / 2 - bounds.width() / 2;int y = top + (titleHeight + textSize) / 2;canvas.drawText(text, x, y, paint);} else {// 其他Item的标题在下一个Item之前悬浮View prevChild = parent.getChildAt(i - 1);RecyclerView.LayoutParams prevParams = (RecyclerView.LayoutParams) prevChild.getLayoutParams();int prevPosition = prevParams.getViewAdapterPosition();if (prevPosition == 0) {int top = child.getTop() - titleHeight;int bottom = child.getTop();canvas.drawRect(parent.getLeft(), top, parent.getRight(), bottom, paint);String text = "Title 1";paint.getTextBounds(text, 0, text.length(), bounds);int x = parent.getWidth() / 2 - bounds.width() / 2;int y = top + (titleHeight + textSize) / 2;canvas.drawText(text, x, y, paint);}}}}
}此示例演示了如何在RecyclerView中实现一个ItemDecoration类,用于在第一个Item的顶部绘制一个悬浮标题,以及在其他Item的上方绘制悬浮标题,直到下一个标题出现。onDrawOver()方法在这里用于绘制悬浮标题的矩形和文本。
OnItemTouchListener实现ItemDecoration点击事件
RecyclerView中的ItemDecoration只能实现对Item的绘制,不能直接实现点击事件。但可以通过实现RecyclerView的OnItemTouchListener接口来实现对ItemDecoration的点击事件。
首先,在RecyclerView的OnTouchListener中判断是否点击在ItemDecoration上。可以通过RecyclerView的getChildAt方法获取RecyclerView中指定位置的子View,然后通过RecyclerView的getItemDecorationAt方法获取指定位置的ItemDecoration,在判断点击位置是否在ItemDecoration的范围内。
如果点击位置在ItemDecoration的范围内,则可以在RecyclerView的OnItemTouchListener的onInterceptTouchEvent方法中处理点击事件。如果要处理点击事件,需要返回true,如果不处理,则返回false。
下面是一个示例代码:
public class MyItemTouchListener extends RecyclerView.SimpleOnItemTouchListener {private final GestureDetectorCompat mGestureDetector;private final RecyclerView mRecyclerView;public MyItemTouchListener(Context context, RecyclerView recyclerView) {mRecyclerView = recyclerView;mGestureDetector = new GestureDetectorCompat(context, new GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener() {@Overridepublic boolean onSingleTapUp(MotionEvent e) {// 获取点击位置int x = (int) e.getX();int y = (int) e.getY();// 获取点击位置对应的ItemView childView = mRecyclerView.findChildViewUnder(x, y);// 获取点击位置对应的ItemDecorationRecyclerView.ItemDecoration itemDecoration = getItemDecorationAt(childView);if (itemDecoration != null) {// 处理点击事件onItemDecorationClick(itemDecoration);return true;}return false;}});}@Overridepublic boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(RecyclerView rv, MotionEvent e) {return mGestureDetector.onTouchEvent(e);}private RecyclerView.ItemDecoration getItemDecorationAt(View childView) {RecyclerView.LayoutManager layoutManager = mRecyclerView.getLayoutManager();int childPosition = mRecyclerView.getChildAdapterPosition(childView);int itemCount = mRecyclerView.getAdapter().getItemCount();for (int i = 0; i < layoutManager.getItemDecorationCount(); i++) {RecyclerView.ItemDecoration decoration = layoutManager.getItemDecorationAt(i);Rect rect = new Rect();decoration.getItemOffsets(rect, childView, mRecyclerView, null);// 判断点击位置是否在ItemDecoration的范围内if (rect.contains((int) childView.getX(), (int) childView.getY())) {return decoration;}}return null;}private void onItemDecorationClick(RecyclerView.ItemDecoration itemDecoration) {// 处理点击事件}
}在Activity或Fragment中,需要创建一个MyItemTouchListener实例,并将其设置为RecyclerView的OnItemTouchListener。
MyItemTouchListener itemTouchListener = new MyItemTouchListener(this, mRecyclerView);
mRecyclerView.addOnItemTouchListener(itemTouchListener);总结
本文介绍了RecyclerView中ItemDecoration的相关方法,从基础的onDraw()和getItemOffsets()到进阶的onDrawOver(),最后还实现了ItemDecoration的点击事件的监听。
这篇关于RecyclerView中ItemDecoration的基础,粘性头部及点击事件的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





