本文主要是介绍在Postgresql中计算工单的对应的GPS轨迹距离,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、概述
在某个App开发中,要求记录用户的日常轨迹,在用户巡逻设备的时,将记录的轨迹点当做该设备巡逻时候的轨迹。
由于业务逻辑上没有明确的指示人员巡逻工单-GPS位置之间的关系,所以通过时间关系进行轨迹划定。
二、创建测试表
首先创建测试表,包括用户表、工单表以及GPS轨迹表。
- 用户表
--用户表
CREATE TABLE a_users (userid varchar NULL,username varchar NULL
);
- 工单表
--用户表
CREATE TABLE a_orders (orderid varchar NULL,relateduserid varchar NULL,order_time timestamptz NULL
);
- GPS轨迹表
--GPS记录表
CREATE TABLE a_gps_recording (gpsid int4 NULL,userid varchar NULL,x float4 NULL,y float4 NULL,recordtime timestamptz NULL
);
三、插入测试数据
为三张表分别插入测试数据。
--测试数据
---- 轨迹数据
INSERT INTO a_gps_recording
(gpsid, userid, x, y, recordtime)
VALUES(900000001, '0', 124.00001, 34.00001, '2024-08-30 08:56:39.000 +0800');
INSERT INTO a_gps_recording
(gpsid, userid, x, y, recordtime)
VALUES(900000002, '0', 124.00001, 34.00002, '2024-08-30 08:56:39.500 +0800');
INSERT INTO a_gps_recording
(gpsid, userid, x, y, recordtime)
VALUES(900000003, '0', 124.00002, 34.00003, '2024-08-30 08:56:39.600 +0800');
INSERT INTO a_gps_recording
(gpsid, userid, x, y, recordtime)
VALUES(900000004, '0', 124.00003, 34.00004, '2024-08-30 08:56:39.700 +0800');
INSERT INTO a_gps_recording
(gpsid, userid, x, y, recordtime)
VALUES(900000005, '0', 124.00004, 34.00005, '2024-08-30 08:56:39.800 +0800');
INSERT INTO a_gps_recording
(gpsid, userid, x, y, recordtime)
VALUES(900000006, '1', 124.10004, 34.00005, '2024-08-30 05:55:00.000 +0800');
INSERT INTO a_gps_recording
(gpsid, userid, x, y, recordtime)
VALUES(900000007, '1', 124.20004, 34.00005, '2024-08-30 05:56:00.000 +0800');
INSERT INTO a_gps_recording
(gpsid, userid, x, y, recordtime)
VALUES(900000008, '1', 124.30004, 34.00005, '2024-08-30 05:57:00.000 +0800');
INSERT INTO a_gps_recording
(gpsid, userid, x, y, recordtime)
VALUES(900000009, '1', 124.40004, 34.00005, '2024-08-30 06:00:00.000 +0800');
INSERT INTO a_gps_recording
(gpsid, userid, x, y, recordtime)
VALUES(900000010, '1', 124.50004, 34.00005, '2024-08-30 06:01:00.000 +0800');
INSERT INTO a_gps_recording
(gpsid, userid, x, y, recordtime)
VALUES(900000011, '1', 124.60004, 34.00005, '2024-08-30 06:02:00.000 +0800');
---- 工单数据
INSERT INTO a_orders
(orderid, relateduserid, order_time)
VALUES('100000', '0', '2024-08-30 08:56:39.000');
INSERT INTO a_orders
(orderid, relateduserid, order_time)
VALUES('100001', '1', '2024-08-30 07:20:39.000');
INSERT INTO a_orders
(orderid, relateduserid, order_time)
VALUES('100002', '1', '2024-08-30 06:00:00.000');
---- 用户数据
INSERT INTO a_users (userid, username) VALUES('1', '用户1');
INSERT INTO a_users (userid, username) VALUES('2', '用户2');
INSERT INTO a_users (userid, username) VALUES('3', '用户3');
INSERT INTO a_users (userid, username) VALUES('0', '用户0');
四、查询思路
4.1 建立表工单表和用户表之间的关联,筛选工单
第一个CTE order_user连接a_orders和a_users表,以检索与订单ID“100002”关联的用户名。
4.2 建立订单与轨迹之间的关联查询
- 第二个CTE
order_gps在订单时间的5分钟时间窗口内从a_gps_recording表中选择与用户相关的gps记录。它计算订单时间和GPS记录时间之间的时间差。 - 第三个CTE
ordered_data根据记录时间为每个GPS记录分配一个行号。这将有助于计算连续GPS记录之间的距离。
4.3 距离计算
- 主查询
从ordered_dataCTE中选择所需的列,并使用ST_distance函数计算连续GPS记录之间的距离。ST_Transform函数用于将坐标转换为合适的投影(EPSG:3857)以进行距离计算。 ordered_data(别名od1)和自身(别名od2)之间的左JOIN条件为od1.rn=od2.rn+1,可确保计算连续GPS记录之间的距离。
此查询的结果将是一个表,其中包含订单ID、GPSID、用户ID、坐标、记录时间、时差和连续GPS记录之间的行驶距离列。
请注意,此查询假定数据库中存在a_orders、a_users和a_gps_recording表。确保将表名和列名替换为数据库中的实际名称。
五、查询SQL
--查询指定工单/用户的距离
select orderid,gpsid,userid,x,y,recordtime,time_Diff,distance_in_meters from (-- ■■■■■■order_user■■■■■with order_user as (select ao.*,au.username from a_orders ao left join a_users au on ao.relateduserid = au.userid and ao.orderid = '100002'),-- ■■■■■■order_gps■■■■■order_gps as (select ao.username,ao.orderid,agr.gpsid,agr.userid,agr.x,agr.y,agr.recordtime,abs(EXTRACT(EPOCH FROM age(ao.order_time , agr.recordtime)) / 60) as time_Diff from order_user ao join a_gps_recording agron --距离工单前后5分钟的位置作为工单相关的距离abs(EXTRACT(EPOCH FROM age(ao.order_time , agr.recordtime)) / 60) < 5 --工单号为100002and ao.relateduserid = agr.userid and ao.orderid = '100002'),-- ■■■■■■ordered_data■■■■■ordered_data as (SELECT orderid,gpsid,userid,x,y,recordtime,time_diff,row_number() OVER (ORDER BY recordtime) AS rnFROM order_gps)SELECT od1.orderid,od1.gpsid,od1.userid,od1.x,od1.y,od1.recordtime,od1.time_Diff,od1.recordtime AS time1,od2.recordtime AS time2,-- ■■■■■■转换地理坐标系到平面坐标系,计算距离■■■■■ST_Distance(ST_Transform(ST_SetSRID(ST_MakePoint(od1.x, od1.y), 4326), 3857), ST_Transform(ST_SetSRID(ST_MakePoint(od2.x, od2.y), 4326), 3857)) AS distance_in_metersFROM ordered_data od1left JOIN ordered_data od2 ON od1.rn = od2.rn + 1
) t;
六、测试结果
运行上述SQL,得到如下查询结果,最后一列distance_in_meters为计算出的相邻两个GPS点之间的距离。
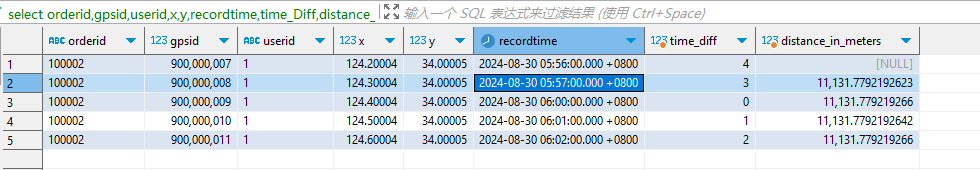
进一步计算工单对应的总距离,只需要运行sum函数查询即可。
这篇关于在Postgresql中计算工单的对应的GPS轨迹距离的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








