本文主要是介绍四叉树和KD树,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1. 简介
四叉树和KD树都是用于空间数据索引和检索的树状数据结构。它们通过将空间递归地划分为更小的区域,并存储每个区域内的点,来实现快速搜索和范围查询。
2. 四叉树
2.1 定义
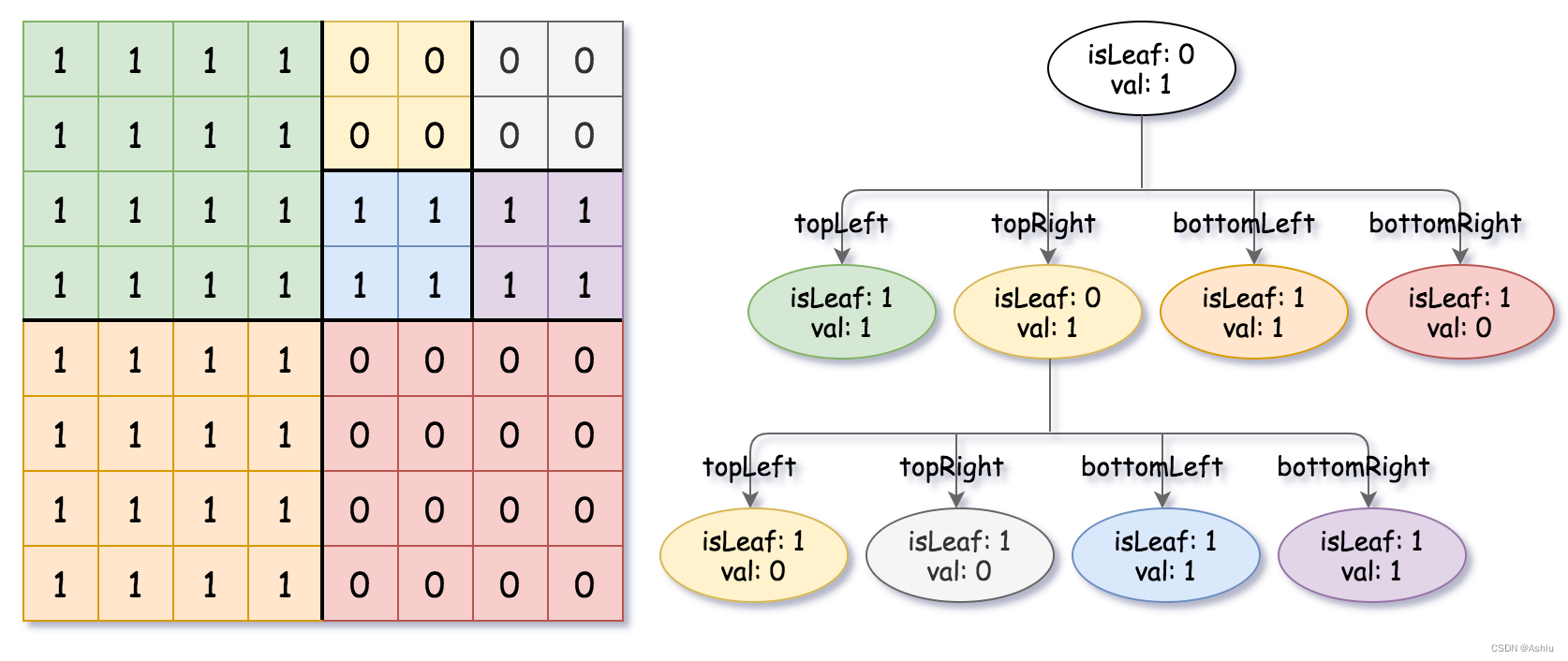
四叉树是一种树状数据结构,它将二维空间递归地划分为四个相等的子区域,直到每个子区域只包含一个点或为空。每个节点代表一个矩形区域,并存储该区域内的所有点。
2.2 构建
构建四叉树的过程如下:
- 将整个空间划分为四个相等的子区域。
- 将每个点分配到相应的子区域。
- 递归地对每个子区域进行步骤 1 和 2,直到每个子区域只包含一个点或为空。
2.3 搜索
搜索四叉树的过程如下:
- 从根节点开始,检查当前节点的区域是否包含目标点。
- 如果包含,则递归地搜索该节点的四个子节点。
- 如果不包含,则搜索失败。
2.4 范围查询
范围查询是指查找所有位于给定矩形区域内的点。搜索过程与搜索单个点类似,但需要遍历所有与查询区域相交的节点。
2.5 Kotlin 代码演示
data class Point(val x: Double, val y: Double)data class Rectangle(val x: Double, val y: Double, val width: Double, val height: Double) {fun contains(point: Point): Boolean {return point.x >= x && point.x <= x + width && point.y >= y && point.y <= y + height}fun intersects(other: Rectangle): Boolean {return !(other.x + other.width < x ||other.x > x + width ||other.y + other.height < y ||other.y > y + height)}
}class QuadTree(val boundary: Rectangle, val capacity: Int = 1) {private var points: MutableList<Point> = mutableListOf()private var children: Array<QuadTree?> = arrayOfNulls(4)fun insert(point: Point): Boolean {if (!boundary.contains(point)) {return false}if (points.size < capacity) {points.add(point)return true}if (children[0] == null) {subdivide()}for (i in 0..3) {if (children[i]!!.insert(point)) {return true}}return false}private fun subdivide() {val xMid = boundary.x + boundary.width / 2val yMid = boundary.y + boundary.height / 2children[0] = QuadTree(Rectangle(boundary.x, boundary.y, xMid, yMid), capacity)children[1] = QuadTree(Rectangle(xMid, boundary.y, boundary.x + boundary.width, yMid), capacity)children[2] = QuadTree(Rectangle(boundary.x, yMid, xMid, boundary.y + boundary.height), capacity)children[3] = QuadTree(Rectangle(xMid, yMid, boundary.x + boundary.width, boundary.y + boundary.height), capacity)for (point in points) {for (i in 0..3) {if (children[i]!!.insert(point)) {break}}}points.clear()}fun query(range: Rectangle): List<Point> {val foundPoints = mutableListOf<Point>()if (!boundary.intersects(range)) {return foundPoints}for (point in points) {if (range.contains(point)) {foundPoints.add(point)}}if (children[0] != null) {for (child in children) {if (child != null) {foundPoints.addAll(child.query(range))}}}return foundPoints}
}fun main() {val boundary = Rectangle(0.0, 0.0, 10.0, 10.0)val quadTree = QuadTree(boundary, 4)val points = listOf(Point(1.0, 1.0),Point(2.0, 2.0),Point(3.0, 3.0),Point(4.0, 4.0),Point(5.0, 5.0),Point(6.0, 6.0),Point(7.0, 7.0),Point(8.0, 8.0),Point(9.0, 9.0))for (point in points) {quadTree.insert(point)}val queryRange = Rectangle(0.0, 0.0, 5.6, 4.4)val foundPoints = quadTree.query(queryRange)println("Points in range:")for (point in foundPoints) {println("(${point.x}, ${point.y})")}
}3. KD树
3.1 定义
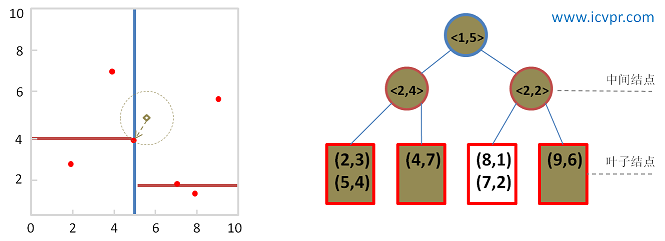
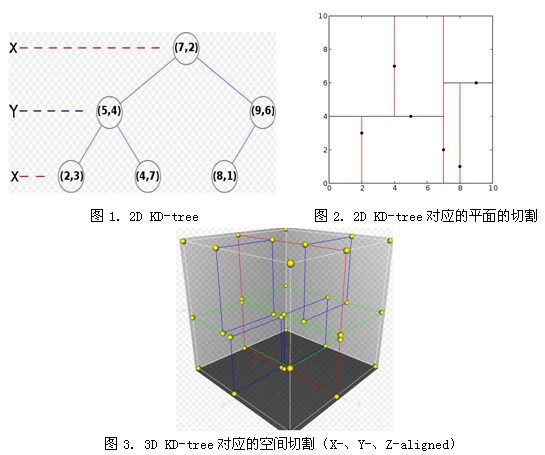
KD树是一种树状数据结构,它将多维空间递归地划分为两个子空间,每个子空间由一个超平面分割。每个节点代表一个超矩形区域,并存储该区域内的所有点。
3.2 构建
构建KD树的过程如下:
- 选择一个维度作为分割维度,并找到该维度上的中位数。
- 使用中位数将空间划分为两个子空间。
- 递归地对每个子空间进行步骤 1 和 2,直到每个子空间只包含一个点或为空。
3.3 搜索
搜索KD树的过程如下:
- 从根节点开始,检查当前节点的区域是否包含目标点。
- 如果包含,则根据目标点的坐标选择相应的子节点进行递归搜索。
- 如果不包含,则搜索失败。
3.4 范围查询
范围查询是指查找所有位于给定超矩形区域内的点。搜索过程与搜索单个点类似,但需要遍历所有与查询区域相交的节点。
3.5 Kotlin 代码演示
// Define the Point class
internal class Point(var x: Double, var y: Double) {override fun toString(): String {return "($x, $y)"}
}// Define the k-d tree node class
internal class KDNode(var point: Point) {var left: KDNode? = nullvar right: KDNode? = null
}// Define the k-d tree class
internal class KDTree(points: List<Point>) {private val root: KDNode?init {this.root = buildTree(points, 0)}private fun buildTree(points: List<Point>, depth: Int): KDNode? {if (points.isEmpty()) {return null}val axis = depth % Kval sortedPoints = points.sortedWith(Comparator { a, b ->if (axis == 0) {a.x.compareTo(b.x)} else {a.y.compareTo(b.y)}})val medianIndex = sortedPoints.size / 2val node = KDNode(sortedPoints[medianIndex])node.left = buildTree(sortedPoints.subList(0, medianIndex), depth + 1)node.right = buildTree(sortedPoints.subList(medianIndex + 1, sortedPoints.size), depth + 1)return node}fun rangeSearch(lowerLeft: Point, upperRight: Point): List<Point> {val result: MutableList<Point> = ArrayList()rangeSearch(root, lowerLeft, upperRight, 0, result)return result}private fun rangeSearch(node: KDNode?,lowerLeft: Point,upperRight: Point,depth: Int,result: MutableList<Point>) {if (node == null) {return}val point = node.pointif (point.x >= lowerLeft.x && point.x <= upperRight.x && point.y >= lowerLeft.y && point.y <= upperRight.y) {result.add(point)}val axis = depth % Kif (axis == 0) {if (lowerLeft.x <= point.x) {rangeSearch(node.left, lowerLeft, upperRight, depth + 1, result)}if (upperRight.x >= point.x) {rangeSearch(node.right, lowerLeft, upperRight, depth + 1, result)}} else {if (lowerLeft.y <= point.y) {rangeSearch(node.left, lowerLeft, upperRight, depth + 1, result)}if (upperRight.y >= point.y) {rangeSearch(node.right, lowerLeft, upperRight, depth + 1, result)}}}companion object {private const val K = 2 // 2-dimensional space, e.g., x, y, z, t, etc}
}// Example usage
object KDTreeExample {@JvmStaticfun main(args: Array<String>) {val points: MutableList<Point> = ArrayList()points.add(Point(0.5, 0.5))points.add(Point(1.0, 1.0))points.add(Point(1.5, 1.5))points.add(Point(2.0, 2.0))points.add(Point(3.0, 3.0))val kdTree = KDTree(points)val lowerLeft = Point(0.0, 0.0)val upperRight = Point(1.5, 2.2)val result = kdTree.rangeSearch(lowerLeft, upperRight)for (point in result) {println(point)}}
}5. 注意事项
- 四叉树和KD树的构建和搜索时间复杂度取决于数据的分布和查询区域的大小。
- 四叉树和KD树都是用于空间数据索引和检索的有效数据结构。四叉树适用于二维空间,而KD树适用于多维空间。
- 在实际应用中,可以使用各种优化技术来提高性能,例如使用边界框、预分配内存等。
- 对于高维数据,KD树的性能可能会下降,可以使用其他数据结构,例如球树或随机投影树。
这篇关于四叉树和KD树的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!