本文主要是介绍yolo-inference多后端+多任务+多算法+多精度模型 框架开发记录(python版),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
先贴出github地址,欢迎大家批评指正:https://github.com/taifyang/yolo-inference
不知不觉LZ已经快工作两年了,由于之前的工作内容主要和模型部署相关,想着利用闲暇时间写一些推理方面的经验总结,于是有了这个工程。其实本来也是自己写了玩的,不过已经陆续迭代半年多了,期间也通过借签优秀代码吸收了经验,索性总结一下心得~
1.0 初始版本
1.1 支持多精度模型
1.2 支持tensorrt的cuda前后处理
1.3 支持onnxruntime的int8推理
1.4 onnxruntime推理代码采用cpp风格接口
1.5 采用抽象工厂和单例模式重构代码
1.6 增加cmake编译支持和重构python代码
1.7 增加Linux系统编译支持
2.0 增加yolov8检测器支持
2.1 增加cmake条件编译选项和自动化测试脚本
3.0 增加分类和分割算法支持
3.1 重构代码结构和缺陷修复
初始版本的接口类定义如下:
import cv2
import numpy as np
from enum import Enum
from abc import ABC, abstractclassmethod...class Device_Type(Enum):CPU = 0GPU = 1class YOLOv5(ABC):def infer(self, image_path:str) -> None:self.image = cv2.imread(image_path)self.result = self.image.copy()self.pre_process()self.process()self.post_process()cv2.imwrite("result.jpg", self.result)cv2.imshow("result", self.result)cv2.waitKey(0)@abstractclassmethoddef pre_process(self) -> None:pass@abstractclassmethoddef process(self) -> None:pass @abstractclassmethoddef post_process(self) -> None:pass
子类如YOLOv5_ONNXRuntime继承上述类:
import onnxruntime
from yolov5 import *
from utils import *class YOLOv5_ONNXRuntime(YOLOv5):def __init__(self, model_path:str, device_type:Device_Type) -> None:super().__init__()if device_type == Device_Type.CPU:self.onnx_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(model_path, providers=['CPUExecutionProvider'])if device_type == Device_Type.GPU:self.onnx_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(model_path, providers=['CUDAExecutionProvider'])self.input_name = []for node in self.onnx_session.get_inputs():self.input_name.append(node.name)self.output_name = []for node in self.onnx_session.get_outputs():self.output_name.append(node.name)self.inputs = {}def pre_process(self) -> None:input = letterbox(self.image, input_shape)input = input[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1).astype(dtype=np.float32) #BGR2RGB和HWC2CHWinput = input / 255.0input = np.expand_dims(input, axis=0)for name in self.input_name:self.inputs[name] = inputdef process(self) -> None:self.outputs = self.onnx_session.run(None, self.inputs)def post_process(self) -> None:self.outputs = np.squeeze(self.outputs)self.outputs = self.outputs[self.outputs[..., 4] > confidence_threshold]classes_scores = self.outputs[..., 5:] boxes = []scores = []class_ids = []for i in range(len(classes_scores)):class_id = np.argmax(classes_scores[i])self.outputs[i][4] *= classes_scores[i][class_id]self.outputs[i][5] = class_idif self.outputs[i][4] > score_threshold:boxes.append(self.outputs[i][:6])scores.append(self.outputs[i][4])class_ids.append(self.outputs[i][5]) boxes = np.array(boxes)boxes = xywh2xyxy(boxes)scores = np.array(scores)indices = nms(boxes, scores, score_threshold, nms_threshold) boxes = boxes[indices]draw(self.result, boxes)
调用demo如下:
from yolov5_onnxruntime import *yolov5 = YOLOv5_ONNXRuntime(model_path="yolov5n.onnx", device_type=Device_Type.CPU)
yolov5.infer("bus.jpg")
后续支持其他功能后调用demo增加了parse_args解析命令参数,通过importlib导入相应模块,并通过getattr通过类名获取类(反射机制),具体内容如下:
import argparse
import importlib
from yolov5 import *def parse_args():parser = argparse.ArgumentParser('yolov5')parser.add_argument('--algo_type', default='ONNXRuntime', type=str, help='ONNXRuntime, OpenCV, OpenVINO, TensorRT')parser.add_argument('--model_path', default='yolov5n_fp32.onnx', type=str, help='the path of model')parser.add_argument('--device_type', default='cpu', type=str, help='cpu, gpu')parser.add_argument('--model_type', default='fp32', type=str, help='fp32, fp16, int8')return parser.parse_args()if __name__ == '__main__':args = parse_args()algo_type = args.algo_typealgo = importlib.import_module('yolov5_' + algo_type.lower()) YOLOv5 = getattr(algo, 'YOLOv5_' + algo_type)model_path = args.model_pathif args.device_type == 'cpu':device_type = Device_Type.CPUelif args.device_type == 'gpu':device_type = Device_Type.GPUif args.model_type == 'fp32':model_type = Model_Type.FP32elif args.model_type == 'fp16':model_type = Model_Type.FP16elif args.model_type == 'int8':model_type = Model_Type.INT8yolov5 = YOLOv5(model_path, device_type, model_type)yolov5.infer("test.mp4")
在3.0版本中由于增加了对分类和分割算法的支持,以onnxruntime框架为例具体实现类如下:
import onnxruntime
from yolo import *
from utils import *class YOLO_ONNXRuntime(YOLO):def __init__(self, algo_type:Algo_Type, device_type:Device_Type, model_type:Model_Type, model_path:str) -> None:super().__init__()assert os.path.exists(model_path), "model not exists!"if device_type == Device_Type.CPU:self.onnx_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(model_path, providers=['CPUExecutionProvider'])elif device_type == Device_Type.GPU:self.onnx_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(model_path, providers=['CUDAExecutionProvider'])self.algo_type = algo_typeself.model_type = model_typeself.input_name = []for node in self.onnx_session.get_inputs(): self.input_name.append(node.name)self.output_name = []for node in self.onnx_session.get_outputs():self.output_name.append(node.name)self.input = {}@abstractclassmethod def pre_process(self) -> None:passdef process(self) -> None:self.output = self.onnx_session.run(None, self.input)@abstractclassmethod def post_process(self) -> None:passclass YOLO_ONNXRuntime_Classification(YOLO_ONNXRuntime): def pre_process(self) -> None:if self.algo_type == Algo_Type.YOLOv5:crop_size = min(self.image.shape[0], self.image.shape[1])left = (self.image.shape[1] - crop_size) // 2top = (self.image.shape[0] - crop_size) // 2crop_image = self.image[top:(top+crop_size), left:(left+crop_size), ...]input = cv2.resize(crop_image, self.input_shape)input = input / 255.0input = input - np.array([0.406, 0.456, 0.485])input = input / np.array([0.225, 0.224, 0.229])if self.algo_type == Algo_Type.YOLOv8:self.input_shape = (224, 224)if self.image.shape[1] > self.image.shape[0]:self.image = cv2.resize(self.image, (self.input_shape[0]*self.image.shape[1]//self.image.shape[0], self.input_shape[0]))else:self.image = cv2.resize(self.image, (self.input_shape[1], self.input_shape[1]*self.image.shape[0]//self.image.shape[1]))crop_size = min(self.image.shape[0], self.image.shape[1])left = (self.image.shape[1] - crop_size) // 2top = (self.image.shape[0] - crop_size) // 2crop_image = self.image[top:(top+crop_size), left:(left+crop_size), ...]input = cv2.resize(crop_image, self.input_shape)input = input / 255.0input = input[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) #BGR2RGB和HWC2CHWif self.model_type == Model_Type.FP32 or self.model_type == Model_Type.INT8:input = np.expand_dims(input, axis=0).astype(dtype=np.float32)elif self.model_type == Model_Type.FP16:input = np.expand_dims(input, axis=0).astype(dtype=np.float16)for name in self.input_name:self.input[name] = inputdef post_process(self) -> None:output = np.squeeze(self.output).astype(dtype=np.float32)if self.algo_type == Algo_Type.YOLOv5:print("class:", np.argmax(output), " scores:", np.exp(np.max(output))/np.sum(np.exp(output)))if self.algo_type == Algo_Type.YOLOv8:print("class:", np.argmax(output), " scores:", np.max(output))class YOLO_ONNXRuntime_Detection(YOLO_ONNXRuntime):def pre_process(self) -> None:input = letterbox(self.image, self.input_shape)input = input[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) #BGR2RGB和HWC2CHWinput = input / 255.0if self.model_type == Model_Type.FP32 or self.model_type == Model_Type.INT8:input = np.expand_dims(input, axis=0).astype(dtype=np.float32)elif self.model_type == Model_Type.FP16:input = np.expand_dims(input, axis=0).astype(dtype=np.float16)for name in self.input_name:self.input[name] = inputdef post_process(self) -> None:output = np.squeeze(self.output[0]).astype(dtype=np.float32)boxes = []scores = []class_ids = []if self.algo_type == Algo_Type.YOLOv5:output = output[output[..., 4] > self.confidence_threshold]classes_scores = output[..., 5:85] for i in range(output.shape[0]):class_id = np.argmax(classes_scores[i])obj_score = output[i][4]cls_score = classes_scores[i][class_id]output[i][4] = obj_score * cls_scoreoutput[i][5] = class_idif output[i][4] > self.score_threshold:boxes.append(output[i][:6])scores.append(output[i][4])class_ids.append(output[i][5]) output[i][5:] *= obj_scoreif self.algo_type == Algo_Type.YOLOv8: for i in range(output.shape[0]):classes_scores = output[..., 4:] class_id = np.argmax(classes_scores[i])output[i][4] = classes_scores[i][class_id]output[i][5] = class_idif output[i][4] > self.score_threshold:boxes.append(output[i, :6])scores.append(output[i][4])class_ids.append(output[i][5]) boxes = np.array(boxes)boxes = xywh2xyxy(boxes)scores = np.array(scores)indices = nms(boxes, scores, self.score_threshold, self.nms_threshold) boxes = boxes[indices]self.result = draw(self.image, boxes)class YOLO_ONNXRuntime_Segmentation(YOLO_ONNXRuntime):def pre_process(self) -> None:input = letterbox(self.image, self.input_shape)input = input[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) #BGR2RGB和HWC2CHWinput = input / 255.0if self.model_type == Model_Type.FP32 or self.model_type == Model_Type.INT8:input = np.expand_dims(input, axis=0).astype(dtype=np.float32)elif self.model_type == Model_Type.FP16:input = np.expand_dims(input, axis=0).astype(dtype=np.float16)for name in self.input_name:self.input[name] = inputdef post_process(self) -> None:output = np.squeeze(self.output[0]).astype(dtype=np.float32)boxes = []scores = []class_ids = []preds = []if self.algo_type == Algo_Type.YOLOv5:output = output[output[..., 4] > self.confidence_threshold]classes_scores = output[..., 5:85] for i in range(output.shape[0]):class_id = np.argmax(classes_scores[i])obj_score = output[i][4]cls_score = classes_scores[i][class_id]output[i][4] = obj_score * cls_scoreoutput[i][5] = class_idif output[i][4] > self.score_threshold:boxes.append(output[i][:6])scores.append(output[i][4])class_ids.append(output[i][5]) output[i][5:] *= obj_scorepreds.append(output[i])if self.algo_type == Algo_Type.YOLOv8: for i in range(output.shape[0]):classes_scores = output[..., 4:84] class_id = np.argmax(classes_scores[i])output[i][4] = classes_scores[i][class_id]output[i][5] = class_idif output[i][4] > self.score_threshold:boxes.append(output[i, :6])scores.append(output[i][4])class_ids.append(output[i][5]) preds.append(output[i]) boxes = np.array(boxes)boxes = xywh2xyxy(boxes)scores = np.array(scores)indices = nms(boxes, scores, self.score_threshold, self.nms_threshold) boxes = boxes[indices]masks_in = np.array(preds)[indices][..., -32:]proto= np.squeeze(self.output[1]).astype(dtype=np.float32)c, mh, mw = proto.shape masks = (1/ (1 + np.exp(-masks_in @ proto.reshape(c, -1)))).reshape(-1, mh, mw)downsampled_bboxes = boxes.copy()downsampled_bboxes[:, 0] *= mw / self.input_shape[0]downsampled_bboxes[:, 2] *= mw / self.input_shape[0]downsampled_bboxes[:, 3] *= mh / self.input_shape[1]downsampled_bboxes[:, 1] *= mh / self.input_shape[1]masks = crop_mask(masks, downsampled_bboxes)self.result = draw(self.image, boxes, masks)
即YOLO基类派生出YOLO_ONNXRuntime等类,再由YOLO_ONNXRuntime类派生一系列具体算法实现子类。由于功能的扩充,此时调用方法变得比较臃肿:
import argparse
import importlib
from yolo import *def parse_args():parser = argparse.ArgumentParser('yolo_inference')parser.add_argument('--algo_type', default='YOLOv8', type=str, help='YOLOv5, YOLOv8')parser.add_argument('--backend_type', default='TensorRT', type=str, help='ONNXRuntime, OpenCV, OpenVINO, TensorRT')parser.add_argument('--task_type', default='Segmentation', type=str, help='Classification, Detection, Segmentation')parser.add_argument('--device_type', default='GPU', type=str, help='CPU, GPU')parser.add_argument('--model_type', default='FP32', type=str, help='FP32, FP16, INT8')parser.add_argument('--model_path', default='yolov8n_seg_fp32.engine', type=str, help='the path of model')parser.add_argument('--input_path', default="bus.jpg", type=str, help='save result')parser.add_argument('--output_path', default="", type=str, help='save result')parser.add_argument('--show_result', default=False, type=bool, help='show result')parser.add_argument('--save_result', default=True, type=bool, help='save result')return parser.parse_args()if __name__ == '__main__':args = parse_args()backend_type = args.backend_typebackend = importlib.import_module('yolo_' + backend_type.lower()) yolo = getattr(backend, 'YOLO_' + backend_type + '_' + args.task_type)model_path = args.model_pathif args.algo_type == 'YOLOv5':algo_type = Algo_Type.YOLOv5if args.algo_type == 'YOLOv8':algo_type = Algo_Type.YOLOv8if args.task_type == 'Classification':task_type = Task_Type.Classificationif args.task_type == 'Detection':task_type = Task_Type.Detectionif args.task_type == 'Segmentation':task_type = Task_Type.Segmentation if args.device_type == 'CPU':device_type = Device_Type.CPUif args.device_type == 'GPU':device_type = Device_Type.GPUif args.model_type == 'FP32':model_type = Model_Type.FP32if args.model_type == 'FP16':model_type = Model_Type.FP16if args.model_type == 'INT8':model_type = Model_Type.INT8show_result = args.show_result and (task_type == Task_Type.Detection or task_type == Task_Type.Segmentation)save_result = args.save_result and (task_type == Task_Type.Detection or task_type == Task_Type.Segmentation)args.output_path = "./result/"+str(args.algo_type)+"_"+str(args.backend_type)+"_"+str(args.task_type)+"_"+str(args.device_type)+"_"+str(args.model_type)+".jpg"yolo = yolo(algo_type, device_type, model_type, model_path)yolo.infer(args.input_path, args.output_path, show_result, save_result)
3.1版本中,借签了https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics的做法,项目层级划分如下:
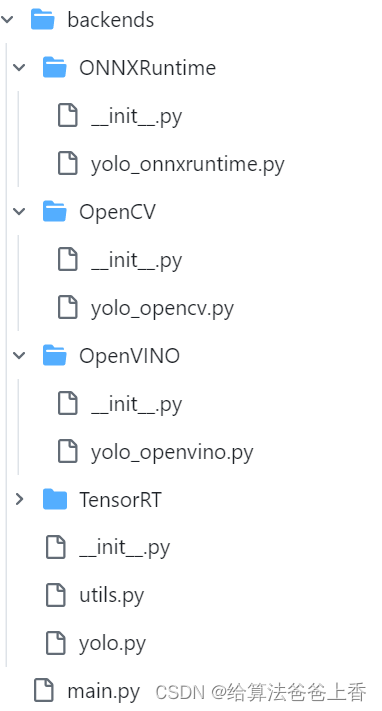
即将不同推理后端封装入算法包,此时yolo.py内容如下:
import os
import cv2
import time
from enum import Enum
import backendsclass YOLO: def __init__(self) -> None:super().__init__()self.score_threshold = 0.2self.nms_threshold = 0.5self.confidence_threshold = 0.2 self.input_shape = (640, 640) def task_map(self):return {'ONNXRuntime':{'Classify':backends.ONNXRuntime.YOLO_ONNXRuntime_Classify,'Detect':backends.ONNXRuntime.YOLO_ONNXRuntime_Detect,'Segment':backends.ONNXRuntime.YOLO_ONNXRuntime_Segment,},'OpenCV':{'Classify':backends.OpenCV.YOLO_OpenCV_Classify,'Detect':backends.OpenCV.YOLO_OpenCV_Detect,#'Segment':tasks.OpenCV.YOLO_OpenCV_Segment,},'OpenVINO':{'Classify':backends.OpenVINO.YOLO_OpenVINO_Classify,'Detect':backends.OpenVINO.YOLO_OpenVINO_Detect,'Segment':backends.OpenVINO.YOLO_OpenVINO_Segment,},'TensorRT':{'Classify':backends.TensorRT.YOLO_TensorRT_Classify,'Detect':backends.TensorRT.YOLO_TensorRT_Detect,'Segment':backends.TensorRT.YOLO_TensorRT_Segment,},}def infer(self, input_path:str, output_path:str, show_result:bool, save_result:bool) -> None:assert os.path.exists(input_path), 'input not exists!'if input_path.endswith('.bmp') or input_path.endswith('.jpg') or input_path.endswith('.png'):self.image = cv2.imread(input_path)self.pre_process()self.process()self.post_process()if save_result and output_path!='':cv2.imwrite(output_path, self.result)if show_result:cv2.imshow('result', self.result)cv2.waitKey(0)elif input_path.endswith('.mp4'):cap = cv2.VideoCapture(input_path)start = time.time()if save_result and output_path!='':fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'XVID')wri = cv2.VideoWriter(output_path, fourcc, 30.0, (1280,720))while True:ret, self.image = cap.read()if not ret:breakself.result = self.image.copy()self.pre_process()self.process()self.post_process()if show_result:cv2.imshow('result', self.result)cv2.waitKey(1)if save_result and output_path!='':wri.write(self.result)end = time.time()print((end-start)*1000, 'ms')
即通过task_map接口返回具体算法类的实现。其同级的__init__.py文件内容如下:
from backends import ONNXRuntime, OpenCV, OpenVINO, TensorRT__all__ = 'ONNXRuntime', 'OpenCV', 'OpenVINO', 'TensorRT'
用来初始化ONNXRuntime,OpenCV,OpenVINO,TensorRT四个package。ONNXRuntime文件夹下的yolo_onnxruntime.py内容为:
import onnxruntime
from backends.yolo import *
from backends.utils import *class YOLO_ONNXRuntime(YOLO):def __init__(self, algo_type:str, device_type:str, model_type:str, model_path:str) -> None:super().__init__()assert os.path.exists(model_path), "model not exists!"if device_type == 'CPU':self.onnx_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(model_path, providers=['CPUExecutionProvider'])elif device_type == 'GPU':self.onnx_session = onnxruntime.InferenceSession(model_path, providers=['CUDAExecutionProvider'])self.algo_type = algo_typeself.model_type = model_typeself.input_name = []for node in self.onnx_session.get_inputs(): self.input_name.append(node.name)self.output_name = []for node in self.onnx_session.get_outputs():self.output_name.append(node.name)self.input = {}def process(self) -> None:self.output = self.onnx_session.run(None, self.input)class YOLO_ONNXRuntime_Classify(YOLO_ONNXRuntime): def pre_process(self) -> None:if self.algo_type == 'YOLOv5':crop_size = min(self.image.shape[0], self.image.shape[1])left = (self.image.shape[1] - crop_size) // 2top = (self.image.shape[0] - crop_size) // 2crop_image = self.image[top:(top+crop_size), left:(left+crop_size), ...]input = cv2.resize(crop_image, self.input_shape)input = input / 255.0input = input - np.array([0.406, 0.456, 0.485])input = input / np.array([0.225, 0.224, 0.229])if self.algo_type == 'YOLOv8':self.input_shape = (224, 224)if self.image.shape[1] > self.image.shape[0]:self.image = cv2.resize(self.image, (self.input_shape[0]*self.image.shape[1]//self.image.shape[0], self.input_shape[0]))else:self.image = cv2.resize(self.image, (self.input_shape[1], self.input_shape[1]*self.image.shape[0]//self.image.shape[1]))crop_size = min(self.image.shape[0], self.image.shape[1])left = (self.image.shape[1] - crop_size) // 2top = (self.image.shape[0] - crop_size) // 2crop_image = self.image[top:(top+crop_size), left:(left+crop_size), ...]input = cv2.resize(crop_image, self.input_shape)input = input / 255.0input = input[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) #BGR2RGB和HWC2CHWif self.model_type == 'FP32' or self.model_type == 'INT8':input = np.expand_dims(input, axis=0).astype(dtype=np.float32)elif self.model_type == 'FP16':input = np.expand_dims(input, axis=0).astype(dtype=np.float16)for name in self.input_name:self.input[name] = inputdef post_process(self) -> None:output = np.squeeze(self.output).astype(dtype=np.float32)if self.algo_type == 'YOLOv5':print("class:", np.argmax(output), " scores:", np.exp(np.max(output))/np.sum(np.exp(output)))if self.algo_type == 'YOLOv8':print("class:", np.argmax(output), " scores:", np.max(output))class YOLO_ONNXRuntime_Detect(YOLO_ONNXRuntime):def pre_process(self) -> None:input = letterbox(self.image, self.input_shape)input = input[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) #BGR2RGB和HWC2CHWinput = input / 255.0if self.model_type == 'FP32' or self.model_type == 'INT8':input = np.expand_dims(input, axis=0).astype(dtype=np.float32)elif self.model_type == 'FP16':input = np.expand_dims(input, axis=0).astype(dtype=np.float16)for name in self.input_name:self.input[name] = inputdef post_process(self) -> None:output = np.squeeze(self.output[0]).astype(dtype=np.float32)boxes = []scores = []class_ids = []if self.algo_type == 'YOLOv5':output = output[output[..., 4] > self.confidence_threshold]classes_scores = output[..., 5:85] for i in range(output.shape[0]):class_id = np.argmax(classes_scores[i])obj_score = output[i][4]cls_score = classes_scores[i][class_id]output[i][4] = obj_score * cls_scoreoutput[i][5] = class_idif output[i][4] > self.score_threshold:boxes.append(output[i][:6])scores.append(output[i][4])class_ids.append(output[i][5]) output[i][5:] *= obj_scoreif self.algo_type == 'YOLOv8': for i in range(output.shape[0]):classes_scores = output[..., 4:] class_id = np.argmax(classes_scores[i])output[i][4] = classes_scores[i][class_id]output[i][5] = class_idif output[i][4] > self.score_threshold:boxes.append(output[i, :6])scores.append(output[i][4])class_ids.append(output[i][5]) boxes = np.array(boxes)boxes = xywh2xyxy(boxes)scores = np.array(scores)indices = nms(boxes, scores, self.score_threshold, self.nms_threshold) boxes = boxes[indices]self.result = draw(self.image, boxes)class YOLO_ONNXRuntime_Segment(YOLO_ONNXRuntime):def pre_process(self) -> None:input = letterbox(self.image, self.input_shape)input = input[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1) #BGR2RGB和HWC2CHWinput = input / 255.0if self.model_type == 'FP32' or self.model_type == 'INT8':input = np.expand_dims(input, axis=0).astype(dtype=np.float32)elif self.model_type == 'FP16':input = np.expand_dims(input, axis=0).astype(dtype=np.float16)for name in self.input_name:self.input[name] = inputdef post_process(self) -> None:output = np.squeeze(self.output[0]).astype(dtype=np.float32)boxes = []scores = []class_ids = []preds = []if self.algo_type == 'YOLOv5':output = output[output[..., 4] > self.confidence_threshold]classes_scores = output[..., 5:85] for i in range(output.shape[0]):class_id = np.argmax(classes_scores[i])obj_score = output[i][4]cls_score = classes_scores[i][class_id]output[i][4] = obj_score * cls_scoreoutput[i][5] = class_idif output[i][4] > self.score_threshold:boxes.append(output[i][:6])scores.append(output[i][4])class_ids.append(output[i][5]) output[i][5:] *= obj_scorepreds.append(output[i])if self.algo_type == 'YOLOv8': for i in range(output.shape[0]):classes_scores = output[..., 4:84] class_id = np.argmax(classes_scores[i])output[i][4] = classes_scores[i][class_id]output[i][5] = class_idif output[i][4] > self.score_threshold:boxes.append(output[i, :6])scores.append(output[i][4])class_ids.append(output[i][5]) preds.append(output[i]) boxes = np.array(boxes)boxes = xywh2xyxy(boxes)scores = np.array(scores)indices = nms(boxes, scores, self.score_threshold, self.nms_threshold) boxes = boxes[indices]masks_in = np.array(preds)[indices][..., -32:]proto= np.squeeze(self.output[1]).astype(dtype=np.float32)c, mh, mw = proto.shape masks = (1/ (1 + np.exp(-masks_in @ proto.reshape(c, -1)))).reshape(-1, mh, mw)downsampled_bboxes = boxes.copy()downsampled_bboxes[:, 0] *= mw / self.input_shape[0]downsampled_bboxes[:, 2] *= mw / self.input_shape[0]downsampled_bboxes[:, 3] *= mh / self.input_shape[1]downsampled_bboxes[:, 1] *= mh / self.input_shape[1]masks = crop_mask(masks, downsampled_bboxes)self.result = draw(self.image, boxes, masks)
init.py文件内容为:
from backends.ONNXRuntime.yolo_onnxruntime import YOLO_ONNXRuntime_Classify, YOLO_ONNXRuntime_Detect, YOLO_ONNXRuntime_Segment__all__ = "YOLO_ONNXRuntime_Classify", "YOLO_ONNXRuntime_Detect", "YOLO_ONNXRuntime_Segment",
来初始化具体算法实现子类。
这篇关于yolo-inference多后端+多任务+多算法+多精度模型 框架开发记录(python版)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






