本文主要是介绍RedisCluster-Pipeline操作,提升10倍以上响应速度2021-03-15,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
什么是pipeLine 为什么使用pipeLine ?
为什么RedisCluster无法使用pipeline?
如何基于JedisCluster扩展pipeline?
性能对比(提升10倍以上):
本文中的代码来自我正在写的分布式缓存框架(主要解决缓存使用中的各种痛点:缓存穿透\redis-cluster pipeline\注解使用等等)。后续内部推广使用后、成熟后会开源回馈大家。
什么是pipeLine 为什么使用pipeLine ?
管道(pipeline)将客户端 client 与服务器端的交互明确划分为单向的发送请求(Send Request)和接收响应(Receive Response):用户可以将多个操作连续发给服务器,但在此期间服务器端并不对每个操作命令发送响应数据;全部请求发送完毕后用户关闭请求,开始接收响应获取每个操作命令的响应结果。
管道(pipeline)在某些场景下非常有用,比如有多个操作命令需要被迅速提交至服务器端,但用户并不依赖每个操作返回的响应结果,对结果响应也无需立即获得,那么管道就可以用来作为优化性能的批处理工具。性能提升的原因主要是减少了 TCP 连接中交互往返的开销。
不过在程序中使用管道请注意,使用 pipeline 时客户端将独占与服务器端的连接,此期间将不能进行其他“非管道”类型操作,直至 pipeline 被关闭;如果要同时执行其他操作,可以为 pipeline 操作单独建立一个连接,将其与常规操作分离开来。
从原理上来看,pipeline就是用一个redis 的Socket连接 去多次执行redis命令(发送请求)而不必等待响应,当所有请求都执行完毕后再一次性的从这个socket中读取请求。期间减少了在网络上的无用等待,通常会有3-10倍以上的速度提升:
//非pipeline
[req1]
[==waiting===]
[resp1]
[req2]
[====waiting=====]
[resp2]
//pipeline
[req1][==waiting===]
[req2][==waiting===]
[resp1] [resp2]
pipeline代码示例
@Test
public void pipeline() throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
Pipeline p = jedis.pipelined();
p.set("foo", "bar");
p.get("foo");
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
p.set("foo"+i, "bar");
}
List<Object> results = p.syncAndReturnAll();
}
为什么RedisCluster无法使用pipeline?
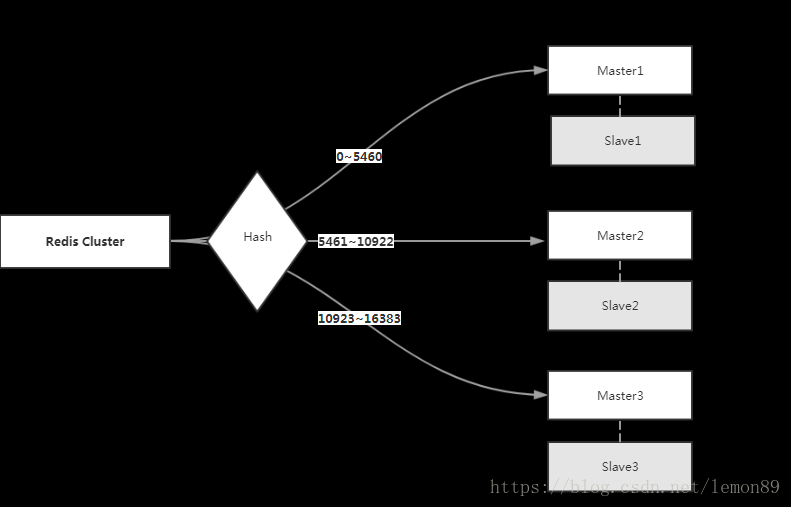
主要是因为redis-cluster的hash分片,如下图一个3master-3slave 的 redisCluster:
具体的redis命令,会根据key计算出一个槽位(slot),然后根据槽位去特定的节点redis上执行操作。
其中master1代表了 0~5460的槽位,master2代表了 5461~10922的槽位,master1代表了 10923~16383的槽位。
master1(slave1): 0~5460
master2(slave2):5461~10922
master3(slave3):10923~16383
以以下代码为例:
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
p.set("foo"+i, "bar");
}
那么pipeline中每个单独的操作,需要根据“key”运算一个槽位(JedisClusterCRC16.getSlot(key)),然后根据槽位去特定的机器执行命令。也就是说一次pipeline操作会使用多个节点的redis连接,而目前JedisCluster是无法支持的。
如何基于JedisCluster扩展pipeline?
设计思路(ShardedJedis、redisson也可供参考,):
1.首先要根据key计算出此次pipeline会使用到的节点对于的连接(也就是jedis对象,通常每个节点对应一个Pool)。
2.相同槽位的key,使用同一个jedis.pipeline去执行 命令。
3.合并此次pipeline所有的response返回。
4.连接释放返回到池中。
也就是讲一个JedisCluster下的pipeline分解为每个单节点下独立的jedisPipeline操作,最后合并response返回。
分享以下部分核心代码:
/**
* @author zhangshuo
*/
@Slf4j
public class JedisClusterPipeLine extends PipelineBase implements Closeable {
......
......
private final Queue<Client> orderedClients = new LinkedList<Client>();
/** 一次pipeline过程中使用到的jedis缓存 */
private final Map<JedisPool, Jedis> poolToJedisMap = new HashMap<JedisPool, Jedis>();
private final JedisSlotBasedConnectionHandler connectionHandler;
private final JedisClusterInfoCache clusterInfoCache;
public JedisClusterPipeLine(JedisCluster jedisCluster) {
this.connectionHandler = ClassUtils.getValue(jedisCluster, SLOT_BASED__CONNECTION_HANDLER_FIELD);
this.clusterInfoCache = ClassUtils.getValue(connectionHandler, CLUSTER_INFO_CACHE_FIELD);
}
@Override
protected Client getClient(String key) {
return getClient(SafeEncoder.encode(key));
}
@Override
protected Client getClient(byte[] key) {
Client client;
log.debug("size of orderedClients : {} , size of poolToJedis : {} ", orderedClients.size(),
poolToJedisMap.size());
int slot = JedisClusterCRC16.getSlot(key);
JedisPool pool = clusterInfoCache.getSlotPool(slot);
Jedis borrowedJedis = poolToJedisMap.get(pool);
if (null == borrowedJedis) {
borrowedJedis = pool.getResource();
poolToJedisMap.put(pool, borrowedJedis);
}
client = borrowedJedis.getClient();
orderedClients.add(client);
return client;
}
@Override
public void close() {
for (Jedis jedis : poolToJedisMap.values()) {
jedis.close();
}
clean();
orderedClients.clear();
poolToJedisMap.clear();
}
public void sync() {
for (Client client : orderedClients) {
generateResponse(client.getOne());
}
}
/**
* go through all the responses and generate the right response type (warning :
* usually it is a waste of time).
*
* @return A list of all the responses in the order
*/
public List<Object> syncAndReturnAll() {
List<Object> formatted = new ArrayList<Object>();
for (Client client : orderedClients) {
formatted.add(generateResponse(client.getOne()).get());
}
return formatted;
}
public void refreshNodesInfo() {
connectionHandler.renewSlotCache();
}
......
......
}
性能对比(提升10倍以上):
@Test
public void jedisTest() throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
long start2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
try (JedisClusterClient<Object> jc = jedisClusterClient) {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
jc.set("NO." + i, "value" + i);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - start2);// 5688ms
}
/**
*
*/
@Test
public void clusterPipeline() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try (JedisClusterPipeLine pipeline = jedisClusterClient.pipelined()) {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
pipeline.set("NO." + i, "value" + i);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis() - start);// 174ms
}
}
结论:对于批量操作,响应提升明显:如上本机测试中,提升了约50倍。
这篇关于RedisCluster-Pipeline操作,提升10倍以上响应速度2021-03-15的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!