理论说明:
上节博文说到对图像的像素进行操作,是基于一幅图像的每个像素。
这节博文所说的是对于多幅图像进行操作,就像PS里面的“蒙板”一样->当两幅图像进行混合的时候可以建立一个蒙版然后对蒙版调整对比度和透明度什么的,然后进行合成。
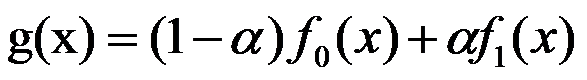 其中 的取值范围为0~1之间
其中 的取值范围为0~1之间 这是线性叠加的理论基础,就是一个加权平均而已。
易错点说明:
首先说一下API函数:Mat.convertTo()函数
假如我的原图读取时CV_8UC3,但是我想对图像的像素进行操作,uchar类型的精度不准确,所以就比比转换类型了,转换成CV_32FC3。
刚开始看书看见converto可以转化类型,就自己试了。但是用imshow显示//不出来。
input_image1.convertTo(input_image1, CV_32FC3);
在知乎上看到一个回答说opencv手册只是转化类型了,比如你想把1—10的数字5转化成10.00—100.00数字50.00,converto是转化了,但是imshow()显示是0-255的RGB颜色空间
所以就需要我们想用imshow显示的时候需要把50.00转化成5.00显示,这种转化是有意义的,1-10才10个数,1.00-10.00,很多很多数了,达成了我们目的:高精度的要求。
input_image1.convertTo(input_image1, CV_32FC3, 1 / 255.0);//所以需要转化成0-255区显示
下面是opencv函数手册的说明:
1 /** @brief Converts an array to another data type with optional scaling.2 3 The method converts source pixel values to the target data type. saturate_cast\<\> is applied at4 the end to avoid possible overflows:5 6 \f[m(x,y) = saturate \_ cast<rType>( \alpha (*this)(x,y) + \beta )\f]7 @param m output matrix; if it does not have a proper size or type before the operation, it is8 reallocated.9 @param rtype desired output matrix type or, rather, the depth since the number of channels are the
10 same as the input has; if rtype is negative, the output matrix will have the same type as the input.
11 @param alpha optional scale factor.
12 @param beta optional delta added to the scaled values.
13 */
1 If the image is 8-bit unsigned, it is displayed as is.
2 - If the image is 16-bit unsigned or 32-bit integer, the pixels are divided by 256. That is, the
3 value range [0,255\*256] is mapped to [0,255].
4 - If the image is 32-bit floating-point, the pixel values are multiplied by 255. That is, the
5 value range [0,1] is mapped to [0,255].
手写API程序:用的是迭代器,当然可以用其它的方法:
1 #include<iostream>2 #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>3 #include <math.h>4 using namespace cv;5 using namespace std;6 7 int main(int argc,char**argv)8 {9 Mat input_image1 = imread("1.jpg");
10 Mat input_image2 = imread("2.jpg");
11 input_image1.convertTo(input_image1, CV_32FC3, 1 / 255.0);
12 input_image2.convertTo(input_image2, CV_32FC3, 1 / 255.0);
13 if (input_image1.data==NULL||input_image2.data==NULL) {
14 return -1; cout << "can't open image.../";
15 }
16 imshow("Sourse image1", input_image1);
17 imshow("Source image2", input_image2);
18 CV_Assert(input_image1.rows == input_image2.rows&&input_image1.cols == input_image2.cols);
19 int Width = input_image1.rows;
20 int length = input_image2.rows;
21 Mat output_image;
22 output_image.create(input_image1.size(), input_image1.type());
23 Mat_<Vec3f>::iterator it1 = input_image1.begin<Vec3f>();
24 Mat_<Vec3f>::iterator it2 = input_image2.begin<Vec3f>();
25 Mat_<Vec3f>::iterator out = output_image.begin<Vec3f>();
26 while (it1 != input_image1.end<Vec3b>())
27 {
28 //---只是初学测试函数,当然可以封装成API一样的函数----//
29 (*out)[0] = 0.5*((*it1)[0]) + 0.5*((*it2)[0]) + 0;
30 (*out)[1] = 0.5*((*it1)[1]) + 0.5*((*it2)[1]) + 0;
31 (*out)[2] = 0.5*((*it1)[2]) + 0.5*((*it2)[2]) + 0;
32 it1++;
33 it2++;
34 out++;
35 }
37 imshow("Destinate image",output_image);
38 waitKey(0);
39 return 0;
40 }
opencv自带API函数:
1 int main(int argc,char**argv)2 {3 Mat input_image1 = imread("1.jpg");4 Mat input_image2 = imread("2.jpg"); 5 //input_image1.convertTo(input_image1, CV_32FC3, 1 / 255.0);6 //input_image2.convertTo(input_image2, CV_32FC3, 1 / 255.0);7 if (input_image1.data==NULL||input_image2.data==NULL) {8 return -1; cout << "can't open image.../";9 }
10 imshow("Sourse image1", input_image1);
11 imshow("Source image2", input_image2);
12 CV_Assert(input_image1.rows == input_image2.rows&&input_image1.cols == input_image2.cols);
13 Mat output_image;
14 addWeighted(input_image1,0.5,input_image2,0.5,0,output_image,-1);
15 add(input_image1,);
16 imshow("Destinate image",output_image);
17 waitKey(0);
18 return 0;
19 }
图片显示:
对于我们这种小白来说,找两张相同像素和尺寸的图片很难:有一篇肖博文帮助 http://www.cnblogs.com/wjy-lulu/p/6644901.html



扩展函数:还有一些线性函数的操作,比如:乘法,除法,减法等等
这些都比较简单,手写也是几行代码而已。
Add():像素加法函数
multiply():像素乘法函数
这里就不加说明和演示了。。。







