本文主要是介绍@Inherited,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
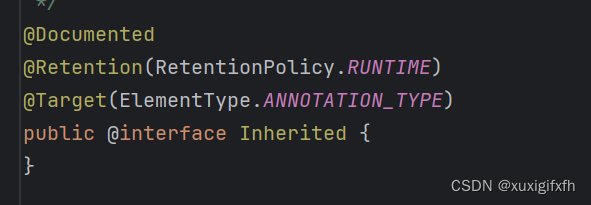
@Inherited是一个标识,用来修饰注解
作用:如果一个类用上了@Inherited修饰的注解,那么其子类也会继承这个注解
注意:
接口用上个@Inherited修饰的注解,其实现类不会继承这个注解
父类的方法用了@Inherited修饰的注解,子类也不会继承这个注解
当用了@Inherited修饰的注解的@Retention是RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME,则增强了继承性,在反射中可以获取得到
代码演示:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
public @interface ATable {
public String name() default "";
}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface BTable {
public String name() default "";
}
//作为父类
@ATable
public class Super {
private int superx;
public int supery;
public Super() {
}
//私有
private int superX(){
return 0;
}
//公有
public int superY(){
return 0;
}
}
@BTable
public class Sub extends Super {
private int subx;
public int suby;
private Sub() {
}
public Sub(int i) {
}
//私有
private int subX() {
return 0;
}
//公有
public int subY() {
return 0;
}
}
class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<Sub> clazz = Sub.class;
System.out.println("============================AnnotatedElement===========================");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(clazz.getAnnotations())); //获取自身和父亲的注解。如果@ATable未加@Inherited修饰,则获取的只是自身的注解而无法获取父亲的注解。
System.out.println("------------------");
}
}
以下是对反射的拓展,与上文无关:
class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class<Sub> clazz = Sub.class;
System.out.println("============================Field===========================");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(clazz.getFields())); // 自身和父亲的公有字段
System.out.println("------------------");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(clazz.getDeclaredFields())); //自身所有字段
System.out.println("============================Method===========================");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(clazz.getMethods())); //自身和父亲的公有方法
System.out.println("------------------");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(clazz.getDeclaredMethods()));// 自身所有方法
System.out.println("============================Constructor===========================");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(clazz.getConstructors())); //自身公有的构造方法
System.out.println("------------------");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(clazz.getDeclaredConstructors())); //自身的所有构造方法
System.out.println("============================AnnotatedElement===========================");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(clazz.getAnnotations())); //获取自身和父亲的注解
System.out.println("------------------");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(clazz.getDeclaredAnnotations())); //只获取自身的注解
System.out.println("------------------");
}
}
通过代码的结果得知:子类继承了父类(由于继承特性,子类会拥有父类的公有一切),在通过反射获取子类所有公有字段/方法/构造器的时候,会获取得到自身和父亲的所有public字段/方法/构造器,而通过反射获取所有任何字段/方法/构造器的时候,只能得到自身的所有任何访问权限修饰符的字段/方法/构造器,不会得到父类的任何字段/方法/构造器。然注解不一样,只有当父类的注解中用@Inherited修饰,子类的getAnnotations()才能获取得到父亲的注解以及自身的注解,而getDeclaredAnnotations()只会获取自身的注解,无论如何都不会获取父亲的注解。
还有下面几个注解经常和Inherited一起出现
@Target:注解的作用目标
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)——接口、类、枚举、注解
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)——字段、枚举的常量
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)——方法
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)——方法参数
@Target(ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR) ——构造函数
@Target(ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE)——局部变量
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)——注解
@Target(ElementType.PACKAGE)——包
@Retention:注解的保留位置
RetentionPolicy.SOURCE:这种类型的Annotations只在源代码级别保留,编译时就会被忽略,在class字节码文件中不包含。
RetentionPolicy.CLASS:这种类型的Annotations编译时被保留,默认的保留策略,在class文件中存在,但JVM将会忽略,运行时无法获得。
RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME:这种类型的Annotations将被JVM保留,所以他们能在运行时被JVM或其他使用反射机制的代码所读取和使用。
@Document:说明该注解将被包含在javadoc中
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「fengcai0123」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/fengcai0123/article/details/90544338
这篇关于@Inherited的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




![‘XXX‘has sample time [0, 1]. Only constant (inf) or inherited (-1) sample times are allowed in‘XXX‘](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/a449fd840548fb649a4b6ca8506e9f22.png)