本文主要是介绍Reinforcement Learning强化学习系列之五:值近似方法Value Approximation,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
引言
前面说到了强化学习中的蒙特卡洛方法(MC)以及时序差分(TD)的方法,这些方法针对的基本是离散的数据,而一些连续的状态则很难表示,对于这种情况,通常在强化学习里有2中方法,一种是针对value function的方法,也就是本文中提到的值近似(value approximation);另一种则是后面要讲到的policy gradient。
值近似的方法
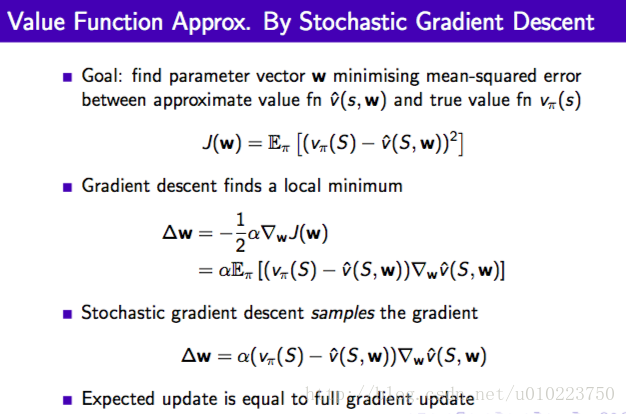
值近似的方法根本上是使用一个值函数来近似表示该状态的返回值,对于状态 S S ,在一个序列中间,我们使用一个参数函数来近似表示观测到的真实值 vπ(S) v π ( S ) ,学习使用普通的梯度下降的方式进行,对于一个观察序列的每一个step均可以作为一个训练的过程。当然这个值函数可以加上动作 a a 表示成为函数的近似 vˆ(S,a,w) v ^ ( S , a , w )
示例
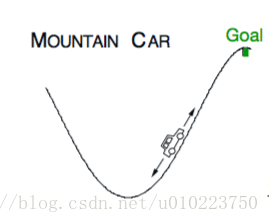
问题描述:一个汽车从谷底向上开,但是汽车的马力不足以支撑其到终点,因此最好的策略是需要先开到谷底的左边然后再加速,利用一部分惯性到达终点。
- 这里面的状态可以描述为: (横向位置xt),(速度xt^) ( 横 向 位 置 x t ) , ( 速 度 x t ^ )
- 动作空间为3个, −1,0,1 − 1 , 0 , 1 ,分别表示全力向左,不动和全力向右
- 状态序列更新的方式为:
xt+1=bound[xt+xt+1^] x t + 1 = b o u n d [ x t + x t + 1 ^ ]
xt+1^=bound[xt^+0.001A−0.0025cos(3xt)] x t + 1 ^ = b o u n d [ x t ^ + 0.001 A − 0.0025 c o s ( 3 x t ) ]
这里bound表示其约束范围,横轴坐标 xt x t 的范围是 −1.5≤xt≤0.5 − 1.5 ≤ x t ≤ 0.5 ,速度的范围是 −0.07≤xt^≤0.07 − 0.07 ≤ x t ^ ≤ 0.07 ,当 xt x t 行到最坐标的时候,将会被置零。
在本示例中,将使用Q-learning的值近似方法,采用的线性函数来表示Q函数。
实验环境
实验将基于openAI所提供的gym包的mountaincar-v0这一个环境,openAI提供了很多的游戏环境,都可以进行相关的强化学习实验。
openAI目前支持mac OS 和Linux环境,可以直接使用pip install gym的方式安装其最新的版本的gym,但是对于python2.7来说,安装最新的版本0.9.6,可能会出现cannot import name spaces的问题,选择安装0.9.5则没有这个问题
关键代码
class Estimator(object):def __init__(self):self.models=[]for _ in range(env.action_space.n):model = SGDRegressor(learning_rate="constant")model.partial_fit([self.feature_state(env.reset())],[0])self.models.append(model)def predict(self,s,a=None):s=self.feature_state(s)if a:return self.models[a].predict([s])[0]else:return [self.models[m].predict([s])[0] for m in range(env.action_space.n)]def update(self,s,a,target):s=self.feature_state(s)self.models[a].partial_fit([s],[target])def feature_state(self,s):return featurizer.transform(scaler.transform([s]))[0]def make_epsilon_greedy_policy(estimator,nA,epsilon):def epsilon_greedy_policy(observation):best_action = np.argmax(estimator.predict(observation))A =np.ones(nA,dtype=np.float32)*epsilon/nAA[best_action] += 1-epsilonreturn Areturn epsilon_greedy_policydef Q_learning_with_value_approximation(env,estimator,epoch_num,discount_factor=1.0, epsilon=0.1, epsilon_decay=1.0):# stats = plotting.EpisodeStats(# episode_lengths=np.zeros(epoch_num),# episode_rewards=np.zeros(epoch_num))for i_epoch_num in range(epoch_num):policy = make_epsilon_greedy_policy\(estimator,env.action_space.n,epsilon*epsilon_decay**i_epoch_num)state = env.reset()for it in itertools.count():action_probs = policy(state)action = np.random.choice(np.arange(len(action_probs)), p=action_probs)next_state,reward,done,_=env.step(action)q_values_next = estimator.predict(next_state)td_target = reward + discount_factor * np.max(q_values_next)estimator.update(state, action, td_target)# stats.episode_rewards[i_epoch_num] += reward# stats.episode_lengths[i_epoch_num] = itprint("\rStep {} @ Episode {}/{}".format(it, i_epoch_num + 1, epoch_num))if done:print itbreakstate = next_state其中,将两个状态参数使用RBF核函数进行转换为一维长度为400的特征向量,使用的普通的SGDRegressor。
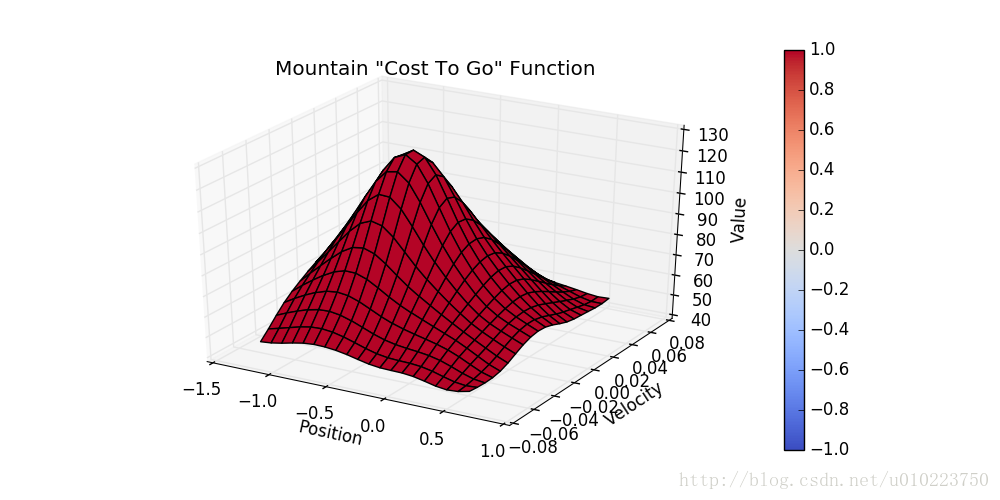
结果
运行100代后的函数cost值为
代码链接
代码可以在我的GitHub链接里找到
这篇关于Reinforcement Learning强化学习系列之五:值近似方法Value Approximation的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!