本文主要是介绍文献速递:肺癌早期诊断---早期肺癌诊断:基于深度学习的循环外泌体光谱分析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Title
题目
Early-Stage Lung Cancer Diagnosis by Deep Learning-Based Spectroscopic Analysis of Circulating Exosomes
早期肺癌诊断:基于深度学习的循环外泌体光谱分析
Abstract
摘要
Lung cancer has a high mortality rate, but an early diagnosis can contribute to a favorable prognosis. A liquid biopsy that captures and detects tumor-related biomarkers in body fluids has great potential for early-stage diagnosis.Exosomes, nanosized extracellular vesicles found in blood,have been proposed as promising biomarkers for liquid biopsy. Here, we demonstrate an accurate diagnosis of early-stage lung cancer, using deep learning-based surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) of the exosomes. Our approach was to explore the features of cell exosomes through deep learning and figure out the similarity in human plasma exosomes, without learning insufficient human data. The deep learning model was trained with SERS signals of exosomes derived from normal and lung cancer cell lines and could classify them with an accuracy of 95%. In 43 patients, including stage I and II cancer patients, the deep learning model predicted that plasma exosomes of 90.7% patients had higher similarity to lung cancer cellexosomes than the average of the healthy controls. Such similarity was proportional to the progression of cancer. Notably, the model predicted lung cancer with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.912 for the whole cohort and stage I patients with an AUC of 0.910. These results suggest the great potential of the combination of exosome analysis and deep learning as a method for early-stage liquid biopsy of lung cancer.
肺癌的死亡率很高,但早期诊断可以带来较好的预后。液体活检通过捕获和检测体液中的肿瘤相关生物标志物,对早期诊断具有巨大潜力。外泌体是在血液中发现的纳米级细胞外囊泡,已被提议作为液体活检的有希望的生物标志物。在这里,我们展示了一种使用基于深度学习的表面增强拉曼光谱(SERS)分析外泌体进行早期肺癌准确诊断的方法。我们的方法是通过深度学习探索细胞外泌体的特征,并找出人体血浆外泌体的相似性,而不需要依赖人类数据的充分学习。深度学习模型训练了来自正常和肺癌细胞系的外泌体的SERS信号,并能以95%的准确率进行分类。在包括I期和II期癌症患者在内的43位患者中,深度学习模型预测90.7%的患者的血浆外泌体与肺癌细胞外泌体的相似性高于健康对照组的平均水平。这种相似性与癌症的进展成正比。值得注意的是,该模型预测肺癌的整个队列的曲线下面积(AUC)为0.912,I期患者的AUC为0.910。这些结果表明,外泌体分析与深度学习结合作为肺癌早期液体活检的方法具有巨大潜力。
Conclusions
结论
In conclusion, we demonstrate that the deep learning analysis of the nanoplasmonic sensing technique can be used to identify early-stage lung cancer patients, with high accuracy. Without specific biomarkers, our method was able to detect the signal feature of lung cancer cell-derived exosomes among plasma exosomes. The deep learning model supervised by cellular exosomes successfully identified the lung cancer patients and even detected stage I patients. Our method basically relies on anoninvasive, safe, and sensitive analytic method for detecting lung cancer cell-derived exosomes in blood. These suggest that our method can be used as a routine prescreening tool for lungcancer.
综上所述,我们证明了纳米光学感知技术的深度学习分析可以用于高准确度地识别早期肺癌患者。在没有特定生物标志物的情况下,我们的方法能够在血浆外泌体中检测到肺癌细胞来源的外泌体的信号特征。由细胞外泌体监督的深度学习模型成功地识别了肺癌患者,甚至检测到了 I 期患者。我们的方法基本上依赖于一种非侵入性、安全和敏感的分析方法,用于检测血液中的肺癌细胞来源的外泌体。这些结果表明,我们的方法可以作为肺癌的常规筛查工具使用。
Results
结果
Evaluation of Isolated Exosomes. To characterize SERS signals of exosomes from lung-related cells, we employed human pulmonary alveolar epithelial cells (HPAEpiC) for normal cellexosome and A549, H460, H1299, H1763, and PC9 cells for cancer cell exosomes. To differentiate cancer patients from healthy controls, we collected human plasma samples from 20 healthy controls and 43 lung adenocarcinoma patients, with 22 patients in stage IA, 16 in stage IB, and 5 in stage IIB (Table S1). Since all patients have undergone surgical resection, the pathological stage was confirmed.
孤立外泌体的评估。为了表征与肺相关的细胞产生的外泌体的 SERS 信号,我们利用人肺泡上皮细胞(HPAEpiC)作为正常细胞外泌体的来源,以及 A549、H460、H1299、H1763 和 PC9 细胞作为癌细胞外泌体的来源。为了区分癌症患者和健康对照者,我们收集了20名健康对照者和43名肺腺癌患者的人血浆样本,其中22名患者处于IA期,16名处于IB期,5名处于IIB期(表 S1)。由于所有患者均接受了手术切除,因此病理分期得以确认。
Figure
图
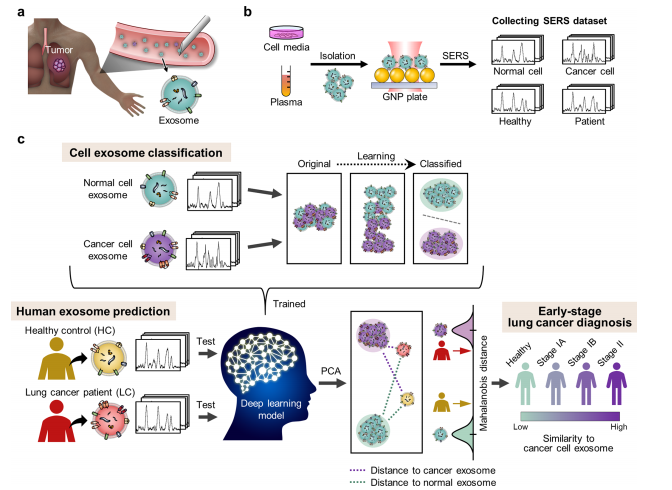
Figure 1. Schematic illustration of deep learning-based circulating exosome analysis for lung cancer diagnosis. (a) Circulation of lung cancertumor exosomes in the bloodstream. (b) Collection of spectroscopic data of exosomes by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). (c)Overview of deep learning-based cell exosome classification and lung cancer diagnosis using exosomal SERS signal patterns.
图 1. 基于深度学习的循环外泌体分析用于肺癌诊断的示意图。(a) 肺癌肿瘤外泌体在血液中的循环。(b) 通过表面增强拉曼光谱(SERS)收集外泌体的光谱数据。(c) 使用外泌体SERS信号模式的基于深度学习的细胞外泌体分类及肺癌诊断概览。
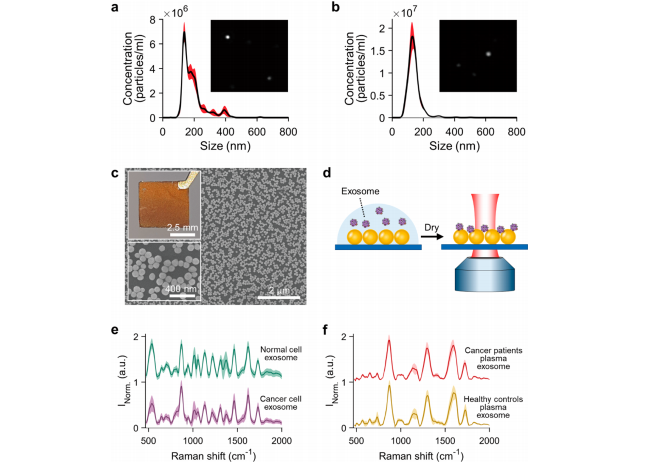
Figure 2. SERS detection of the isolated exosomes. (a, b) NTA results of (a) cell culture media and (b) human plasma-derived exosomes. The insets show observed particles by NTA. (c) Photograph and SEM images of the SERS substrate that is covered with 100 nm GNPs. (d) Detecting method of the exosomes on the SERS substrate. (e, f) Average SERS signals of (e) cell media supernatant-derived and (f) human plasma-derived exosomes.
图2. 分析孤立的外泌体的 SERS 检测结果。(a, b) (a) 细胞培养基和 (b) 人血浆来源的外泌体的 NTA 结果。插图显示了 NTA 观察到的颗粒。(c) 被 100 纳米 GNPs 覆盖的 SERS 衬底的照片和 SEM 图像。(d) 在 SERS 衬底上检测外泌体的方法。(e, f) (e) 细胞培养基上清液来源和 (f) 人血浆来源的外泌体的平均 SERS 信号。
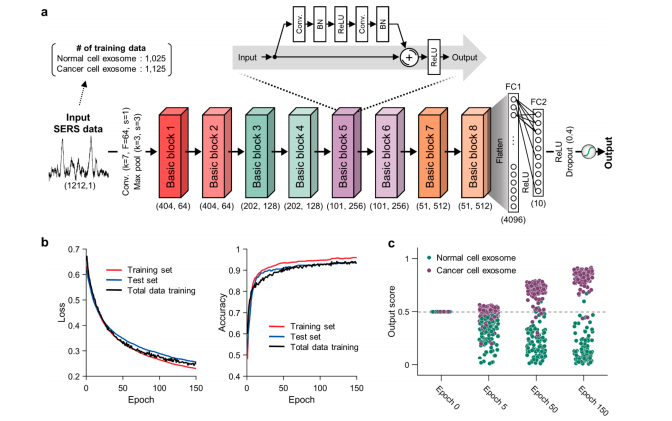
Figure 3. Deep learning-based cell exosome classification. (a) Architecture of the Resnet-based deep learning model. One-directional input data extended their channel by initial convolutional layer, which has 64 filters and reduced data length by the pooling layer, which has a kernel size of After basic blocks, two FC layers with a ReLU activation layer and a 40% dropout layer were connected. The numbers below the basic block indicate the length and number of channels at the output, respectively. (b) Training loss and accuracy. The displayed loss and accuracy were the values obtained with the dropout layer deactivated after training at each epoch. (c) Final output score of 200 representative data by training iterations.
图3. 基于深度学习的细胞外泌体分类。(a)基于 Resnet 的深度学习模型架构。单向输入数据通过初始卷积层扩展其通道,该卷积层具有64个滤波器,并通过具有3个内核大小的池化层减少数据长度。在基本块之后,连接了两个具有 ReLU 激活层和40% 丢失率的全连接层。基本块下面的数字分别表示输出的长度和通道数量。(b)训练损失和准确率。显示的损失和准确率是在每个周期训练后关闭了丢失率层后得到的值。(c)经过训练迭代的200个代表性数据的最终输出分数。
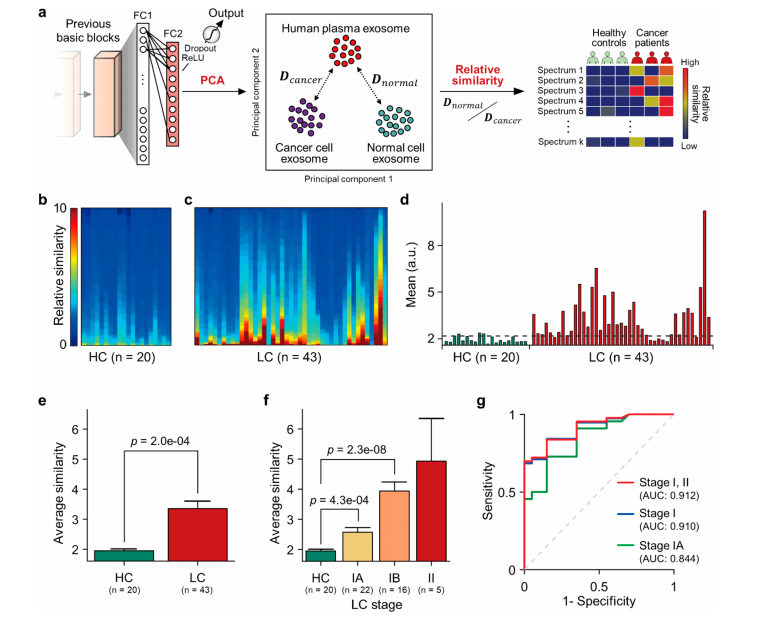
Figure 4. Deep learning-based diagnosis of lung cancer patients. (a) Schematic overview of calculation of the relative similarity with cancer cell derived exosome spectra. D indicates Mahalanobis distance between PC scores of the observed plasma and supervised cellular exome data. (b,c) Heat map of the relative similarity to the cancer cell exosomes of (b) 20 healthy controls (HC) and (c) 43 lung cancer patients (LC). Thevalues are displayed in ascending order. (d) Bar graph showing the average similarity to cancer cell exosomes. The dotted gray line indicates theoptimized cutoff value. (e) Comparison of total HC and LC. (f) Gradual increase of the similarity by advancing lung cancer stages. All error bars represent standard errors. The p-values were calculated with the independent two-sample t test. (g) ROC curves and their AUC values.
图4. 基于深度学习的肺癌患者诊断。(a)计算与癌细胞来源的外泌体光谱相对相似度的示意概述。D 表示观察到的血浆和受监督的细胞外泌体数据之间的 PC 分数的马氏距离。(b, c)相对于癌细胞外泌体的相对相似度热图,分别为(b)20名健康对照者(HC)和(c)43名肺癌患者(LC)。数值按升序显示。(d)显示平均相似度到癌细胞外泌体的条形图。虚线灰线表示优化的截止值。(e)总健康对照者和肺癌患者的比较。(f)随着肺癌分期的推进,相似度逐渐增加的对比。所有误差线代表标准误差。p 值是用独立双样本 t 检验计算的。(g)ROC 曲线及其 AUC 值。
Table
表
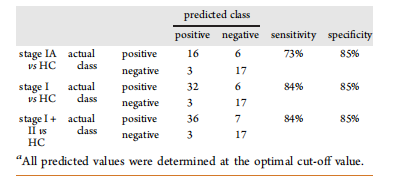
Table 1. Confusion Matrix of Our Deep Learning Modela
表1. 我们的深度学习模型的混淆矩阵
这篇关于文献速递:肺癌早期诊断---早期肺癌诊断:基于深度学习的循环外泌体光谱分析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




