本文主要是介绍java-Spring-入门学习-第二天(单例模式和多例模式),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
Bean作用域
单例模式(默认可以不写)
Spring下的 @AutoWired 依赖注入
JaveEE下的 @Resource 依赖注入
多例模式
Bean作用域
在Spring框架中,Bean是按照作用域来创建的,常见的作用域有两种:Singleton 和 Prototype。Singleton (单例)是指整个应用中只有一个实例,并在第一次请求时创建实例
Prototype (多例)是指每次请求都会创建一个新的实例并返回,每个实例之间是相互独立的。
| 取值 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| @Scope("singleton")(默认) | 在IoC容器中,在bean的对象为单实例 |
| @Scoper("prototype") | 在IoC容器中,在bean中有多个实例 |
单例模式(默认可以不写)
Spring下的 @AutoWired 依赖注入
注意的是@Autowired 不能以类的名字来寻找对应的Product的实体类,需要通过@Qualifier来查找对应的接口实体类,不确定对应的实体类的名会报NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException异常。
这个异常表明Spring容器中有多个相同类型的bean候选者,但Spring不知道应该选择哪一个来注入
// 一个接口
interface Product { void test();
} @Component("productDealWith1") // 使用 @Component 并指定 bean 名称
class ProductDealWith1 implements Product { @Override public void test() { System.out.println("ProductDealWith1 test method called."); }
} @Component("productDealWith") // 使用 @Component 并指定 bean 名称
class ProductDealWith implements Product { @Override public void test() { System.out.println("ProductDealWith test method called."); }
} @Component
class ProductOrder { @Autowired @Qualifier("productDealWith1") // 使用 @Qualifier 指定要注入的 bean 名称 private Product product; public void doSomething() { product.test(); // 这将调用 ProductDealWith1 的 test 方法 }
} public class TestProduct { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("demo.test.product"); ProductOrder order = context.getBean(ProductOrder.class); // 获取 ProductOrder 类型的 bean order.doSomething(); // 这将间接调用 ProductDealWith1 的 test 方法 }
}ProductDealWith1 和 ProductDealWith 类都使用了 @Component 注解,并且分别通过 value 参数指定了它们的 bean 名称。在 ProductOrder 类中,通过@Autowired 和 @Qualifier 注解,我们指定了要注入的 Product 类型的 bean 是名为 "productDealWith1" 的那个。在 TestProduct 的 main 方法中,我们通过 context.getBean(ProductOrder.class) 来获取 ProductOrder 类型的 bean,并调用其 doSomething 方法,这将间接调用ProductDealWith1 的 test方法
JaveEE下的 @Resource 依赖注入
这边讲解一下顺便讲解@Resource依靠name找寻接口的实例
因为@Resource是Java EE 的一部分,如果您指定了 name 属性,Spring 将会查找与指定名称匹配的 bean;如果没有指定name 属性,Spring 将会查找与注入点类型匹配的 bean
@Configueration是将该类转变成配置类
其次使用配置类扫描工具@ComponentScan,使其在运行编译过程中优先加载其类
并根据其中的配置创建并管理相应的 bean
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("demo.test.product")
public class AppConfig { // 该配置类告诉Spring在此包及其子包中查找带有@Component注解的类
}
// 一个接口
interface Product { void test();
} @Component(name= "productDealWith1") // 使用 @Component 并指定 bean 名称
class ProductDealWith1 implements Product { @Override public void test() { System.out.println("ProductDealWith1 test method called."); }
} @Component(name="productDealWith") // 使用 @Component 并指定 bean 名称
class ProductDealWith implements Product { @Override public void test() { System.out.println("ProductDealWith test method called."); }
} @Component
class ProductOrder { @Resource(name ="productDealWith1") private Product product; public void doSomething() { product.test(); // 这将调用 ProductDealWith1 的 test 方法 }
} public class TestProduct { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); ProductOrder order = context.getBean(ProductOrder.class); // 获取 ProductOrder 类型的 bean order.doSomething(); // 这将间接调用 ProductDealWith1 的 test 方法 }
}多例模式
//这边是多实例
@Scope(value="prototype")
//这边是单实例
//@Scope(value="singleton")
@Component
class Product{}
public class TestDBConnect {@Testpublic void testScope(){ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext("demo.test.product");// 第一次获取Product product1= context.getBean(product.class);System.out.println(product1);// 第二次获取Product product2 = context.getBean(product.class);System.out.println(product2);}
}多例模式运行
当为多例模式 prototype 时,多次获取bean实例的地址是不同的

单例模式运行
当为单例模式 singleton 时,多次获取bean实例的地址是相同的
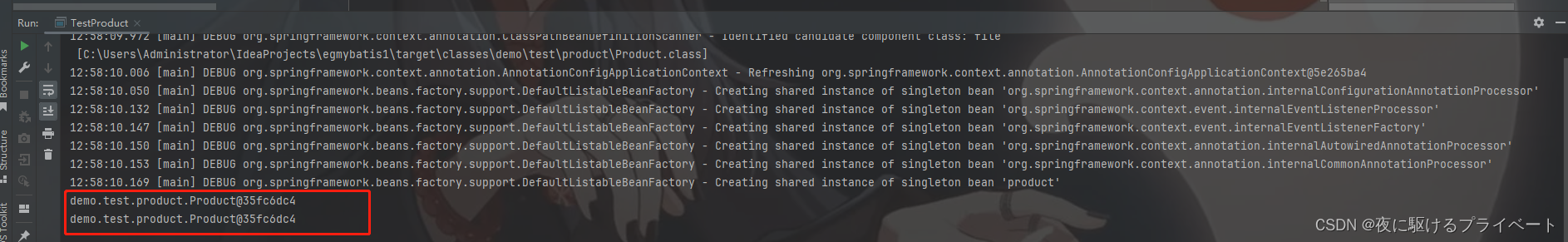
单例模式和多例模式的区别
单例模式适用于需要共享数据并且需要避免重复创建实例的情况。
而多例模式适用于需要动态地创建对象并提供独立实例的情况。
这篇关于java-Spring-入门学习-第二天(单例模式和多例模式)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






