本文主要是介绍HDU 4678 Mine (博弈SG+自由度原理),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Problem Description
Have you ever played a game in Windows: Mine?
This game is played on a n*m board, just like the Pic(1)
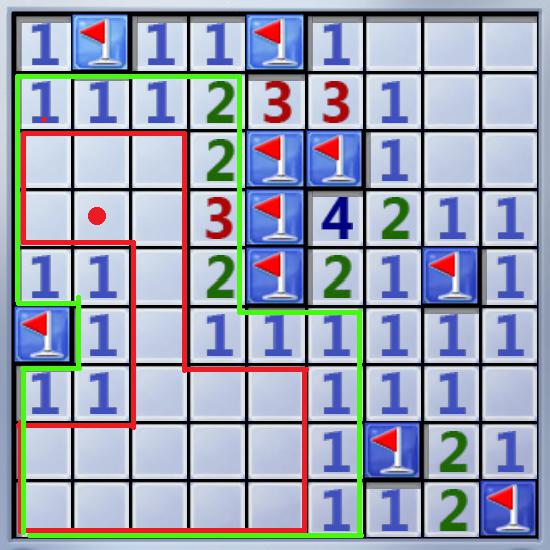

On the board, Under some grids there are mines (represent by a red flag). There are numbers ‘A(i,j)’ on some grids means there’re A(i,j) mines on the 8 grids which shares a corner or a line with gird(i,j). Some grids are blank means there’re no mines on the 8 grids which shares a corner or a line with them.
At the beginning, all grids are back upward.
In each turn, Player should choose a back upward grid to click.
If he clicks a mine, Game over.
If he clicks a grid with a number on it , the grid turns over.
If he clicks a blank grid, the grid turns over, then check grids in its 8 directions.If the new grid is a blank gird or a grid with a number,it will be clicked too.
So If we click the grid with a red point in Pic(1), grids in the area be encompassed with green line will turn over.
Now Xiemao and Fanglaoshi invent a new mode of playing Mine. They have found out coordinates of all grids with mine in a game. They also find that in a game there is no grid will turn over twice when click 2 different connected components.(In the Pic(2), grid at (1,1) will turn over twice when player clicks (0,0) and (2,2) , test data will not contain these cases).
Then, starting from Xiemao, they click the grid in turns. They both use the best strategy. Both of them will not click any grids with mine, and the one who have no grid to click is the loser.
Now give you the size of board N, M, number of mines K, and positions of every mine X i,Y i. Please output who will win.
This game is played on a n*m board, just like the Pic(1)


On the board, Under some grids there are mines (represent by a red flag). There are numbers ‘A(i,j)’ on some grids means there’re A(i,j) mines on the 8 grids which shares a corner or a line with gird(i,j). Some grids are blank means there’re no mines on the 8 grids which shares a corner or a line with them.
At the beginning, all grids are back upward.
In each turn, Player should choose a back upward grid to click.
If he clicks a mine, Game over.
If he clicks a grid with a number on it , the grid turns over.
If he clicks a blank grid, the grid turns over, then check grids in its 8 directions.If the new grid is a blank gird or a grid with a number,it will be clicked too.
So If we click the grid with a red point in Pic(1), grids in the area be encompassed with green line will turn over.
Now Xiemao and Fanglaoshi invent a new mode of playing Mine. They have found out coordinates of all grids with mine in a game. They also find that in a game there is no grid will turn over twice when click 2 different connected components.(In the Pic(2), grid at (1,1) will turn over twice when player clicks (0,0) and (2,2) , test data will not contain these cases).
Then, starting from Xiemao, they click the grid in turns. They both use the best strategy. Both of them will not click any grids with mine, and the one who have no grid to click is the loser.
Now give you the size of board N, M, number of mines K, and positions of every mine X i,Y i. Please output who will win.
Input
Multicase
The first line of the date is an integer T, which is the number of the text cases. (T<=50)
Then T cases follow, each case starts with 3 integers N, M, K indicates the size of the board and the number of mines.Then goes K lines, the ith line with 2 integer X i,Y i means the position of the ith mine.
1<=N,M<=1000 0<=K<=N*M 0<=X i<N 0<=Y i<M
The first line of the date is an integer T, which is the number of the text cases. (T<=50)
Then T cases follow, each case starts with 3 integers N, M, K indicates the size of the board and the number of mines.Then goes K lines, the ith line with 2 integer X i,Y i means the position of the ith mine.
1<=N,M<=1000 0<=K<=N*M 0<=X i<N 0<=Y i<M
Output
For each case, first you should print "Case #x: ", where x indicates the case number between 1 and T . Then output the winner of the game, either ”Xiemao” or “Fanglaoshi”. (without quotes)
Sample Input
2 3 3 0 3 3 1 1 1
Sample Output
Case #1: Xiemao Case #2: Fanglaoshi
Source
2013 Multi-University Training Contest 8
不懂博弈的话,这题很难做~
题意:
给出一个N*M的格子图,给出K个雷的坐标,模拟扫雷游戏,当翻开空白格子是,它周围的格子会翻开(除了有雷的格子)
当翻开数字格子则显示数字,两个人轮流翻,最后没有格子可以翻的人败
分析:
首先,理解一下自由度原理。( POJ 2348 Euclid's Game,这个题就初步用到了自由度的原理)
在博弈的过程中可能会遇到很多局面,有的局面有够做出多种性质不同的选择,而有的局面只能做出同种性质的选择。
在博弈过程中,当我们走到没有自由度的局面,基本就只能按一个模式走下去了。
比如说这题,当我们将所有的空白点都翻完之后,(也就是只剩下数字点可选的局面),那么胜负已经确定了
因为面对这样的局面,游戏就变成你翻一个数字点我翻一个数字点的模拟。
在博弈里面,游戏双方为了选择最优策略,一定是先选择有自由度的空白点去翻,直到将所有的空白点翻完。
也就是在求SG值的异或和的时候,必须按照先空白点后数字点去求异或和
其次,分析一个局面的SG值。
懂博弈的自然知道,当前局面的SG值是所有格子的异或和(不懂的可参看挑程316面或者查阅其他资料)
所以分析整个棋盘的SG值就是要求每一个点的SG值
(sg在挑程上的定义: 除 任意一步所能转移到的子局面的SG值以外 的 最小非负整数 。)
首先最简单的是有雷的点,这样的点显然是必败点,sg = 0
而由于求异或和的时候,0在异或中是不起作用的(即a^0 = a),故而可以不管雷的点
然后分析数字点,这里是指“未翻开状态的数字点”,它的子状态是“已经被翻开的数字点”,子状态的sg = 0,
故而“未翻开的数字点”的sg = 除了0(它的子状态的sg值)以外的最小非负整数1
最后是空白点,首先要明确的一点是,随着这个空白点翻开的有数字点有空白点,但是它的sg是与随他翻开的空白的无关
而仅与随他翻开的数字点有关的,为什么,因为在这一片的空白点中,你随便翻哪一个都能导致同样的局面,所以我们只算其中
一个空白点的SG,很显然,相同的数异或和是为0的(即a^a = 0),所以随这个空白点被翻开的数字点的异或和要么为0,要么为1
当周围的数字是奇数个时,异或和为1,那么这个空白点的sg = 除了0和1(子状态的sg)之外的2,
当周围的数字是偶数个时,异或和为0,那么这个空白点的sg = 除了0(子状态的sg)之外的1
然后结合之前所说的自由度原理,此题只需按照空白点,数字点的顺序求SG异或和即可
至于找到空白点周围的数字点的个数,简单bfs就可以了
#define mem(a,x) memset(a,x,sizeof(a))
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1007;
bool mine[N][N];
bool vis[N][N];
const int dx[] = {0,0,1,1,1,-1,-1,-1};
const int dy[] = {-1,1,1,-1,0,1,-1,0};
struct Node
{int x,y;
};
int n,m;
bool ok(int x,int y)
{return x>=0&&y>=0&&x<n&&y<m;
}
bool check(int x,int y)//判断这个点是不是数字点(周围有没有雷)
{for (int i = 0;i < 8;++i){int xx = x + dx[i];int yy = y + dy[i];if (ok(xx,yy)&&mine[xx][yy]) return 1;}return 0;
}
int bfs(int sx,int sy)//返回这个空白点周围的数字点的个数
{queue<Node>q;Node h;h.x = sx,h.y = sy;int t = 0;vis[sx][sy] = 1;q.push(h);while (!q.empty()){h = q.front();q.pop();if (check(h.x,h.y))//这个点是数字点{++t;continue;} for (int i = 0;i < 8;++i){Node nx = h;nx.x += dx[i];nx.y += dy[i];if (ok(nx.x,nx.y)){if (vis[nx.x][nx.y]) continue;if (mine[nx.x][nx.y]) continue;q.push(nx);vis[nx.x][nx.y] = 1;}}}return t;
}
int main()
{int T,kas = 0;scanf("%d",&T);while (T--){int k;scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k);mem(mine,0);mem(vis,0);for (int i = 0,x,y;i < k;++i){scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);mine[x][y] = 1;}int s = 0; for (int i = 0;i < n;++i) //选择所有的空白点去翻 {for (int j = 0;j < m;++j){if (!vis[i][j]&&!mine[i][j]&&!check(i,j)){if (bfs(i,j)&1)//奇数个 sg = 2{s ^= 2;} else //偶数个 sg = 1 {s ^= 1; }}}}for (int i = 0;i < n;++i) //直到所有空白点翻完,选择数字点(其实这里直接判断剩下的数字点的个数也可以) {for (int j = 0;j < m;++j){if (!vis[i][j]&&!mine[i][j]&&check(i,j)){s ^= 1;}}}printf("Case #%d: ",++kas);if (s) puts("Xiemao"); //非0 即 胜态 else puts("Fanglaoshi");}return 0;
} 这篇关于HDU 4678 Mine (博弈SG+自由度原理)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





