本文主要是介绍基于卷积神经网络的大米品种分类系统(pytorch框架)【python源码+UI界面+前端界面+功能源码详解】,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
功能演示:
大米品种分类系统,基于vgg16,resnet50卷积神经网络(pytorch框架)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
(一)简介
基于卷积神经网络的大米品种分类系统是在pytorch框架下实现的,系统中有两个模型可选resnet50模型和VGG16模型,这两个模型可用于模型效果对比。该系统涉及的技术栈有,UI界面:python + pyqt5,前端界面:python flask + vue
该项目是在pycharm和anaconda搭建的虚拟环境执行,pycharm和anaconda安装和配置可观看教程:
超详细的pycharm+anaconda搭建python虚拟环境_pycharm配置anaconda虚拟环境-CSDN博客
pycharm+anaconda搭建python虚拟环境_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
(二)项目介绍
1. pycharm打开项目界面如下
2. 数据集


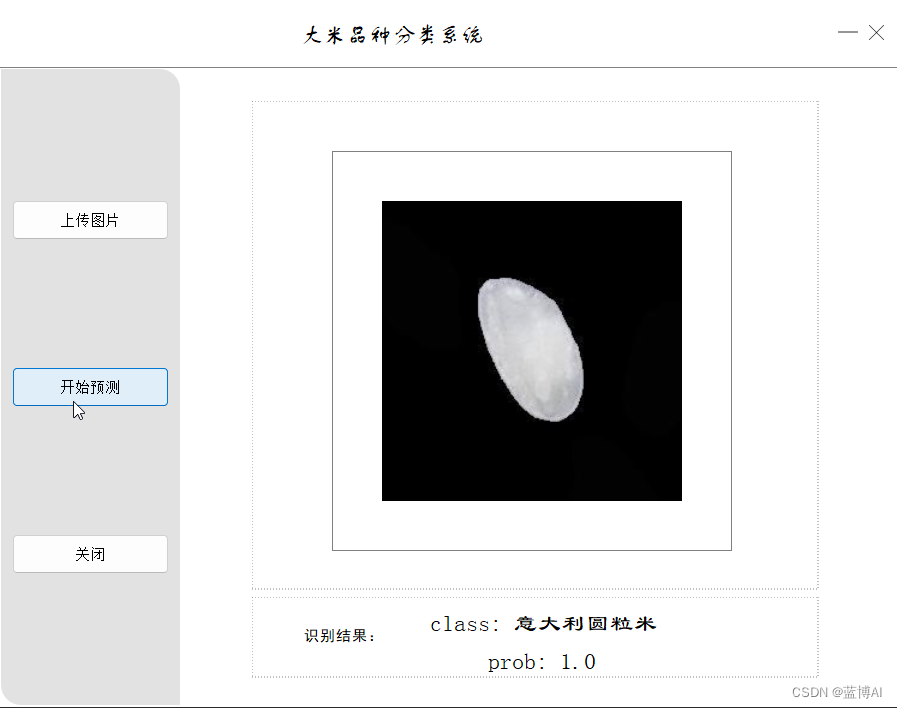
3.GUI界面(技术栈:pyqt5+python)

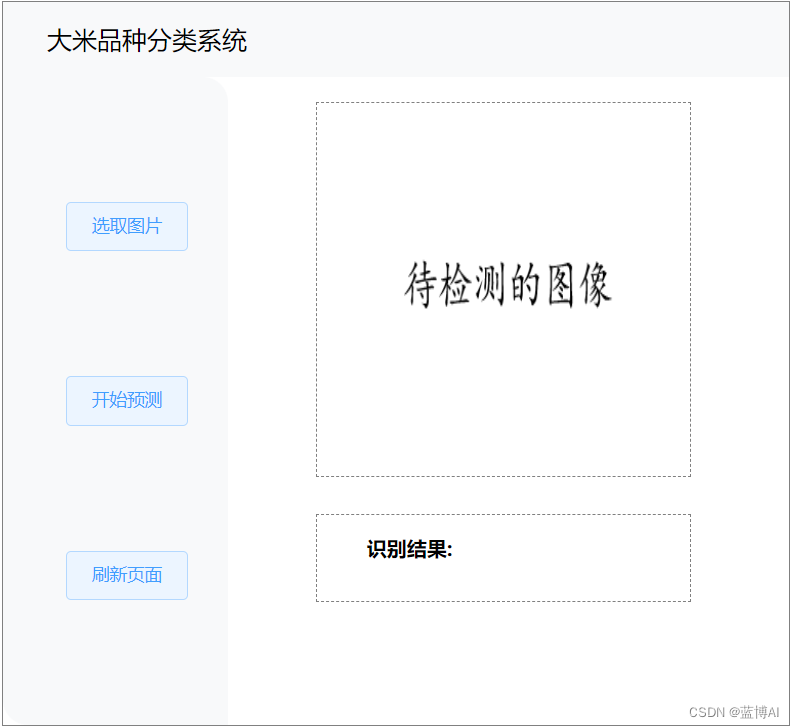
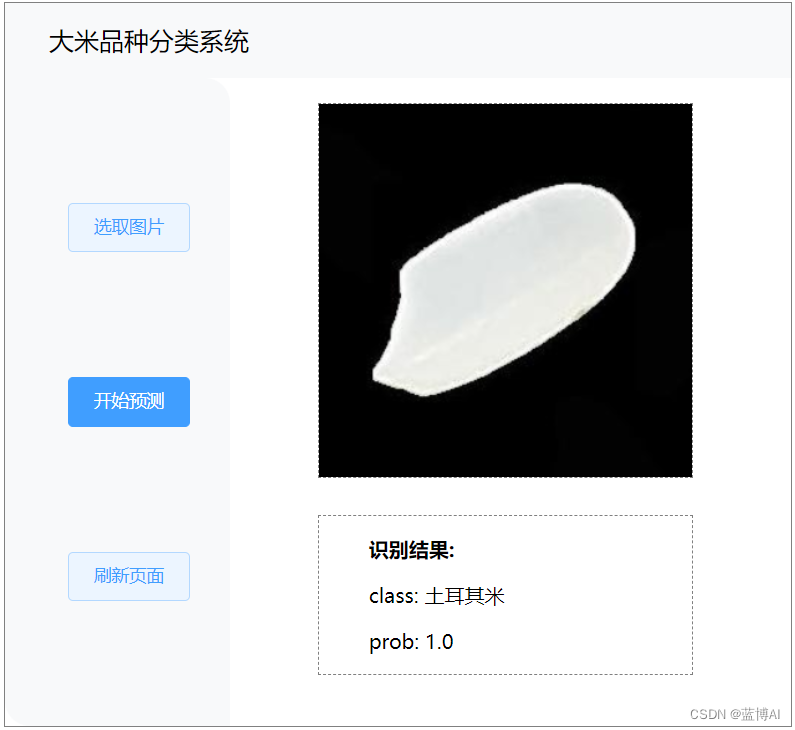
4.前端界面(技术栈:python+flask)
5. 核心代码
class MainProcess:def __init__(self, train_path, test_path, model_name):self.train_path = train_pathself.test_path = test_pathself.model_name = model_nameself.device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")def main(self, epochs):# 记录训练过程log_file_name = './results/vgg16训练和验证过程.txt'# 记录正常的 print 信息sys.stdout = Logger(log_file_name)print("using {} device.".format(self.device))# 开始训练,记录开始时间begin_time = time()# 加载数据train_loader, validate_loader, class_names, train_num, val_num = self.data_load()print("class_names: ", class_names)train_steps = len(train_loader)val_steps = len(validate_loader)# 加载模型model = self.model_load() # 创建模型# 网络结构可视化x = torch.randn(16, 3, 224, 224) # 随机生成一个输入model_visual_path = 'results/vgg16_visual.onnx' # 模型结构保存路径torch.onnx.export(model, x, model_visual_path) # 将 pytorch 模型以 onnx 格式导出并保存# netron.start(model_visual_path) # 浏览器会自动打开网络结构# load pretrain weights# download url: https://download.pytorch.org/models/vgg16-397923af.pthmodel_weight_path = "models/vgg16-pre.pth"assert os.path.exists(model_weight_path), "file {} does not exist.".format(model_weight_path)model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_weight_path, map_location='cpu'))# 更改Vgg16模型的最后一层model.classifier[-1] = nn.Linear(4096, len(class_names), bias=True)# 将模型放入GPU中model.to(self.device)# 定义损失函数loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()# 定义优化器params = [p for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad]optimizer = optim.Adam(params=params, lr=0.0001)train_loss_history, train_acc_history = [], []test_loss_history, test_acc_history = [], []best_acc = 0.0for epoch in range(0, epochs):# 下面是模型训练model.train()running_loss = 0.0train_acc = 0.0train_bar = tqdm(train_loader, file=sys.stdout)# 进来一个batch的数据,计算一次梯度,更新一次网络for step, data in enumerate(train_bar):images, labels = data # 获取图像及对应的真实标签optimizer.zero_grad() # 清空过往梯度outputs = model(images.to(self.device)) # 得到预测的标签train_loss = loss_function(outputs, labels.to(self.device)) # 计算损失train_loss.backward() # 反向传播,计算当前梯度optimizer.step() # 根据梯度更新网络参数# print statisticsrunning_loss += train_loss.item()predict_y = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)[1] # 每行最大值的索引# torch.eq()进行逐元素的比较,若相同位置的两个元素相同,则返回True;若不同,返回Falsetrain_acc += torch.eq(predict_y, labels.to(self.device)).sum().item()train_bar.desc = "train epoch[{}/{}] loss:{:.3f}".format(epoch + 1,epochs,train_loss)# 下面是模型验证model.eval() # 不启用 BatchNormalization 和 Dropout,保证BN和dropout不发生变化val_acc = 0.0 # accumulate accurate number / epochtesting_loss = 0.0with torch.no_grad(): # 张量的计算过程中无需计算梯度val_bar = tqdm(validate_loader, file=sys.stdout)for val_data in val_bar:val_images, val_labels = val_dataoutputs = model(val_images.to(self.device))val_loss = loss_function(outputs, val_labels.to(self.device)) # 计算损失testing_loss += val_loss.item()predict_y = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)[1] # 每行最大值的索引# torch.eq()进行逐元素的比较,若相同位置的两个元素相同,则返回True;若不同,返回Falseval_acc += torch.eq(predict_y, val_labels.to(self.device)).sum().item()train_loss = running_loss / train_stepstrain_accurate = train_acc / train_numtest_loss = testing_loss / val_stepsval_accurate = val_acc / val_numtrain_loss_history.append(train_loss)train_acc_history.append(train_accurate)test_loss_history.append(test_loss)test_acc_history.append(val_accurate)print('[epoch %d] train_loss: %.3f val_accuracy: %.3f' %(epoch + 1, train_loss, val_accurate))if val_accurate > best_acc:best_acc = val_accuratetorch.save(model.state_dict(), self.model_name)# 记录结束时间end_time = time()run_time = end_time - begin_timeprint('该循环程序运行时间:', run_time, "s")# 绘制模型训练过程图self.show_loss_acc(train_loss_history, train_acc_history,test_loss_history, test_acc_history)# 画热力图self.heatmaps(model, validate_loader, class_names)该系统可以训练自己的数据集,训练过程也比较简单,只需指定自己数据集中训练集和测试集的路径,训练后模型名称和指定训练的轮数即可

训练结束后可输出以下结果:
a. 训练过程的损失曲线
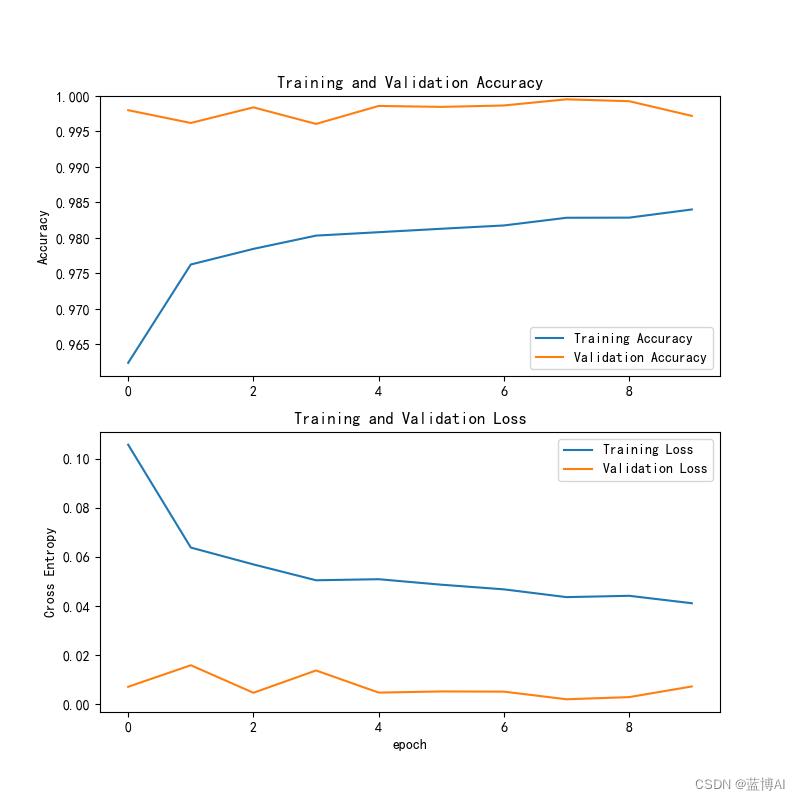
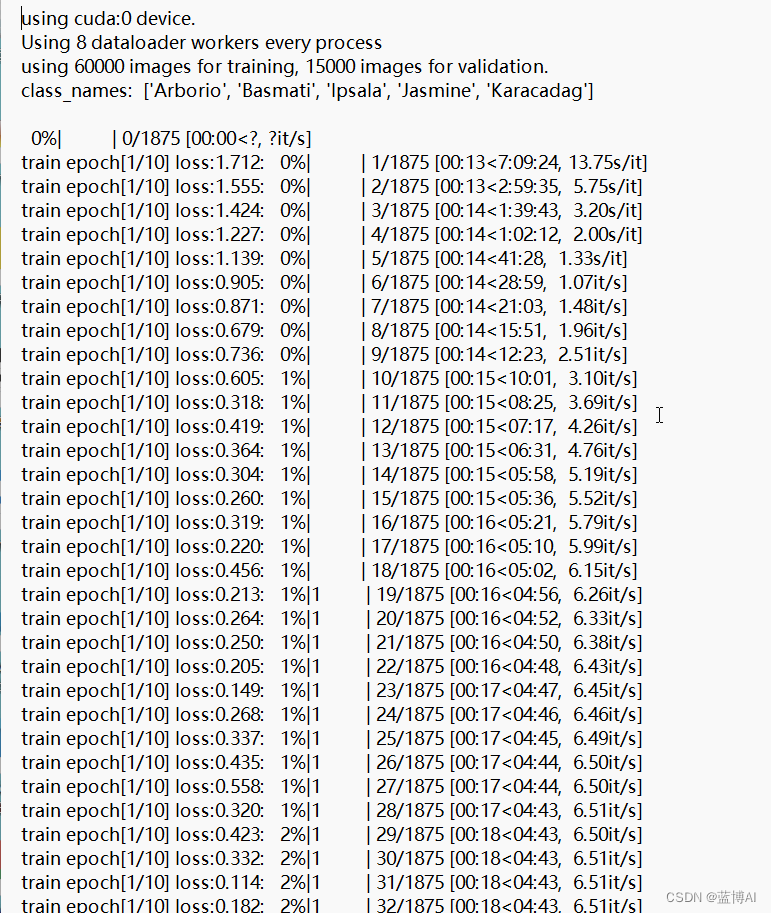
b. 模型训练过程记录,模型每一轮训练的损失和精度数值记录
c. 模型结构

模型评估可输出:
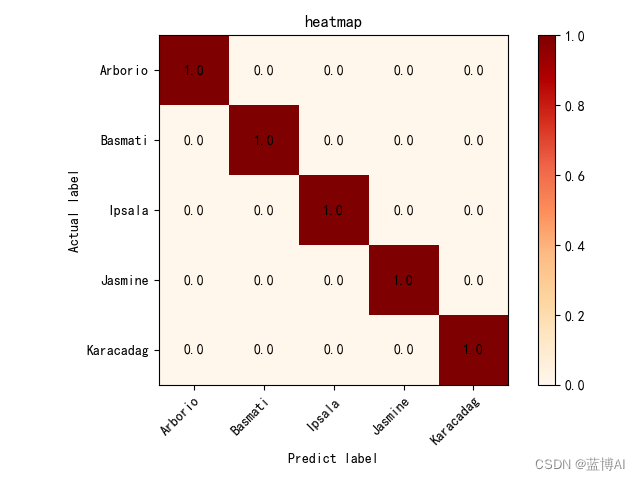
a. 混淆矩阵
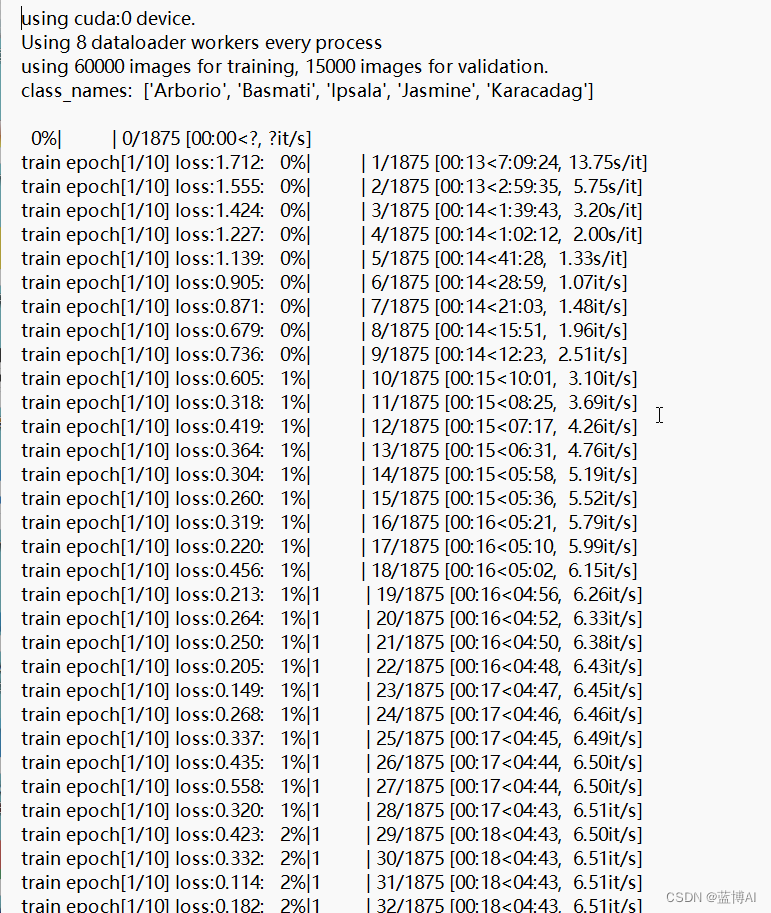
b. 测试过程和精度数值
(三)资源获取方式
编码不易,源码有偿获取喔!

资源主要包括以下内容:完整的程序代码文件、训练好的模型、数据集、UI界面、前端界面。欢迎大家咨询!
这篇关于基于卷积神经网络的大米品种分类系统(pytorch框架)【python源码+UI界面+前端界面+功能源码详解】的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




