题目链接
问题分析
题意即求两个凸包间的最小距离。
一开始十分暴力地写了一个闵可夫斯基和,后来发现变种的旋转卡壳转一转就好了QAQ
闵可夫斯基和的思路十分简单,下面看一下旋转卡壳的做法:
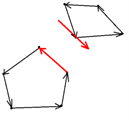
不难发现两个凸包间的最短距离一定像上图那样。所以我们只需要枚举一个凸包的边,找另一个凸包上的对踵点就好了。这个过程需要执行两次。
注意判断线段平行和求点到线段距离的细节。
参考程序
闵可夫斯基和版:
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;const int Maxn = 10010;
const double Eps = 1e-12;
struct point {double x, y;point() {}point( double _x, double _y ) : x( _x ), y( _y ) {}inline point operator + ( const point Other ) const {return point( x + Other.x, y + Other.y );}inline point operator - ( const point Other ) const {return point( x - Other.x, y - Other.y );}inline point operator * ( const double Other ) const {return point( x * Other, y * Other );}inline double operator * ( const point Other ) const {return x * Other.y - Other.x * y;}inline double operator / ( const point Other ) const {return x * Other.x + y * Other.y;}inline double Dis() const { return sqrt( x * x + y * y ); }
};
int N, M, L;
point A[ Maxn ], B[ Maxn ], C[ Maxn << 1 ], Base;inline int Cmp( double x, double y ) {if( fabs( x - y ) <= Eps ) return 0;if( x - y > Eps ) return 1;return -1;
}
inline bool Cmp1( point x, point y ) {return Cmp( ( x - Base ) * ( y - Base ), 0.0 ) == 1 || ( Cmp( ( x - Base ) * ( y - Base ), 0.0 ) == 0 && Cmp( ( x - Base ).Dis(), ( y - Base ).Dis() ) == -1 );
}
void Get( point *A, int &N ) {for( int i = 2; i <= N; ++i )if( Cmp( A[ i ].y, A[ 1 ].y ) == -1 || ( Cmp( A[ i ].y, A[ 1 ].y ) == 0 && Cmp( A[ i ].x, A[ 1 ].x ) == -1 ) )swap( A[ i ], A[ 1 ] );Base = A[ 1 ]; sort( A + 2, A + N + 1, Cmp1 );L = 1; C[ 1 ] = A[ 1 ];for( int i = 2; i <= N; ++i ) {for( ; L > 1 && Cmp( ( A[ i ] - C[ L - 1 ] ) * ( C[ L ] - C[ L - 1 ] ), 0.0 ) >= 0; --L );C[ ++L ] = A[ i ];}N = L; for( int i = 1; i <= L; ++i ) A[ i ] = C[ i ];return;
}
void Merge( point *A, int N, point *B, int M, point *C ) {L = 1; C[ 1 ] = A[ 1 ] + B[ 1 ];A[ ++N ] = A[ 1 ]; B[ ++M ] = B[ 1 ];int i1 = 1, i2 = 1;for( ; i1 < N && i2 < M; ) {if( Cmp( ( A[ i1 + 1 ] - A[ i1 ] ) * ( B[ i2 + 1 ] - B[ i2 ] ), 0.0 ) >= 0 ) {C[ L + 1 ] = C[ L ] + ( A[ i1 + 1 ] - A[ i1 ] ); ++L; ++i1;} else {C[ L + 1 ] = C[ L ] + ( B[ i2 + 1 ] - B[ i2 ] ); ++L; ++i2;}}for( ; i1 < N; ++i1 ) C[ L + 1 ] = C[ L ] + ( A[ i1 + 1 ] - A[ i1 ] ), ++L;for( ; i2 < M; ++i2 ) C[ L + 1 ] = C[ L ] + ( B[ i2 + 1 ] - B[ i2 ] ), ++L;return;
}
bool Check() {for( int i = 1; i < L; ++i )if( Cmp( C[ i + 1 ] * C[ i ], 0.0 ) > 0 ) return false;return true;
}
double GetDis( point A, point B, point C ) {point D = C + point( -( A - B ).y, ( A - B ).x );double T = ( D - A ) * ( C - A ) / ( ( C - B ) * ( D - B ) );if( Cmp( T, 0.0 ) <= 0 ) return min( A.Dis(), B.Dis() );point O = A * ( 1 / ( T + 1.0 ) ) + B * ( T / ( T + 1.0 ) );return ( O - C ).Dis();
}
int main() {scanf( "%d%d", &N, &M );while( N != 0 || M != 0 ) {for( int i = 1; i <= N; ++i ) scanf( "%lf%lf", &A[ i ].x, &A[ i ].y );for( int i = 1; i <= M; ++i ) scanf( "%lf%lf", &B[ i ].x, &B[ i ].y );for( int i = 1; i <= M; ++i ) B[ i ].x = -B[ i ].x, B[ i ].y = -B[ i ].y;Get( A, N ); Get( B, M );Merge( A, N, B, M, C );if( Check() ) printf( "0.000000\n" );else {double Ans = 1000000000.0;for( int i = 1; i < L; ++i ) Ans = min( Ans, GetDis( C[ i ], C[ i + 1 ], point( 0.0, 0.0 ) ) );printf( "%.6lf\n", Ans );}scanf( "%d%d", &N, &M );}return 0;
}旋转卡壳版:
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;const int Maxn = 10010;
const double Eps = 1e-12;
struct point {double x, y;point() {}point( double _x, double _y ) : x( _x ), y( _y ) {}inline point operator + ( const point Other ) const {return point( x + Other.x, y + Other.y );}inline point operator - ( const point Other ) const {return point( x - Other.x, y - Other.y );}inline double operator * ( const point Other ) const {return x * Other.y - Other.x * y;}inline point operator * ( const double Other ) const {return point( x * Other, y * Other );}inline double Mod() const { return sqrt( x * x + y * y ); }
};
int N, M, Size;
point A[ Maxn ], B[ Maxn ], Base, Stack[ Maxn ];int Cmp( double x, double y ) {if( fabs( x - y ) <= Eps ) return 0;if( x - y > Eps ) return 1;return -1;
}
bool Cmp1( point X, point Y ) {return Cmp( ( X - Base ) * ( Y - Base ), 0.0 ) == 1 || ( Cmp( ( X - Base ) * ( Y - Base ), 0.0 ) == 0 && Cmp( ( X - Base ).Mod(), ( Y - Base ).Mod() ) == -1 );
}
void Graham( point *A, int &N ) {for( int i = 2; i <= N; ++i ) if( Cmp( A[ i ].y, A[ 1 ].y ) == -1 || ( Cmp( A[ i ].y, A[ 1 ].y ) == 0 && Cmp( A[ i ].x, A[ 1 ].x ) == -1 ) )swap( A[ i ], A[ 1 ] );Base = A[ 1 ]; sort( A + 2, A + N + 1, Cmp1 );Size = 1; Stack[ 1 ] = A[ 1 ];for( int i = 2; i <= N; ++i ) {for( ; Size > 1 && Cmp( ( A[ i ] - Stack[ Size - 1 ] ) * ( Stack[ Size ] - Stack[ Size - 1 ] ), 0.0 ) >= 0; --Size );Stack[ ++Size ] = A[ i ];}N = Size; for( int i = 1; i <= N; ++i ) A[ i ] = Stack[ i ];return;
}
inline int Pre( int N, int x ) { return ( x - 1 < 1 ) ? N : x - 1; }
inline int Suc( int N, int x ) { return ( x + 1 > N ) ? 1 : x + 1; }
inline double GetDis( point A, point B, point C ) {point D = C + point( -( B - A ).y, ( B - A ).x );double K = ( D - A ) * ( C - A ) / ( ( C - B ) * ( D - B ) );if( Cmp( K, 0.0 ) <= 0 ) return min( ( C - A ).Mod(), ( C - B ).Mod() );point O = A * ( 1.0 / ( K + 1.0 ) ) + B * ( K / ( K + 1.0 ) );return ( C - O ).Mod();
}
double Dis( point *A, int N, point *B, int M ) {int i1 = 1, i2; for( i2 = 1; i2 <= M; ++i2 )if( Cmp( ( A[ Suc( N, i1 ) ] - A[ i1 ] ) * ( B[ i2 ] - B[ Pre( M, i2 ) ] ), 0.0 ) == 1 &&Cmp( ( A[ Suc( N, i1 ) ] - A[ i1 ] ) * ( B[ Suc( M, i2 ) ] - B[ i2 ] ), 0.0 ) <= 0 )break;double Ans = GetDis( A[ Suc( N, i1 ) ], A[ i1 ], B[ i2 ] );if( Cmp( ( A[ Suc( N, i1 ) ] - A[ i1 ] ) * ( B[ Suc( M, i2 ) ] - B[ i2 ] ), 0.0 ) == 0 ) {i2 = Suc( M, i2 );Ans = min( Ans, GetDis( A[ Suc( N, i1 ) ], A[ i1 ], B[ i2 ] ) );}for( ++i1; i1 <= N; ++i1 ) {for( ; Cmp( ( A[ Suc( N, i1 ) ] - A[ i1 ] ) * ( B[ i2 ] - B[ Pre( M, i2 ) ] ), 0.0 ) <= 0 ||Cmp( ( A[ Suc( N, i1 ) ] - A[ i1 ] ) * ( B[ Suc( M, i2 ) ] - B[ i2 ] ), 0.0 ) == 1; i2 = Suc( M, i2 ) );Ans = min( Ans, GetDis( A[ Suc( N, i1 ) ], A[ i1 ], B[ i2 ] ) );if( Cmp( ( A[ Suc( N, i1 ) ] - A[ i1 ] ) * ( B[ Suc( M, i2 ) ] - B[ i2 ] ), 0.0 ) == 0 ) {i2 = Suc( M, i2 );Ans = min( Ans, GetDis( A[ Suc( N, i1 ) ], A[ i1 ], B[ i2 ] ) );}}return Ans;
}
int main() {scanf( "%d%d", &N, &M );for( ; N != 0 || M != 0; scanf( "%d%d", &N, &M ) ) {for( int i = 1; i <= N; ++i ) scanf( "%lf%lf", &A[ i ].x, &A[ i ].y );for( int i = 1; i <= M; ++i ) scanf( "%lf%lf", &B[ i ].x, &B[ i ].y );Graham( A, N ); Graham( B, M );printf( "%.6lf\n", min( Dis( A, N, B, M ), Dis( B, M, A, N ) ) );}return 0;
}







