本文主要是介绍从零开始搭二维激光SLAM --- 简单重写 Hector SLAM,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
上篇文章讲解了如何在固定位置使用Hector构建单帧的栅格地图,以及知道了SLAM的本质就是将不同时刻的scan在正确的位置上写成栅格地图.
本篇文章将对 Hector 进行简单的重写,使得其代码更简单,更清晰.
这也是本系列教程第一次成功建出一张比较好的地图.
先放图,虽然有些瑕疵,但是整体还是不错的.
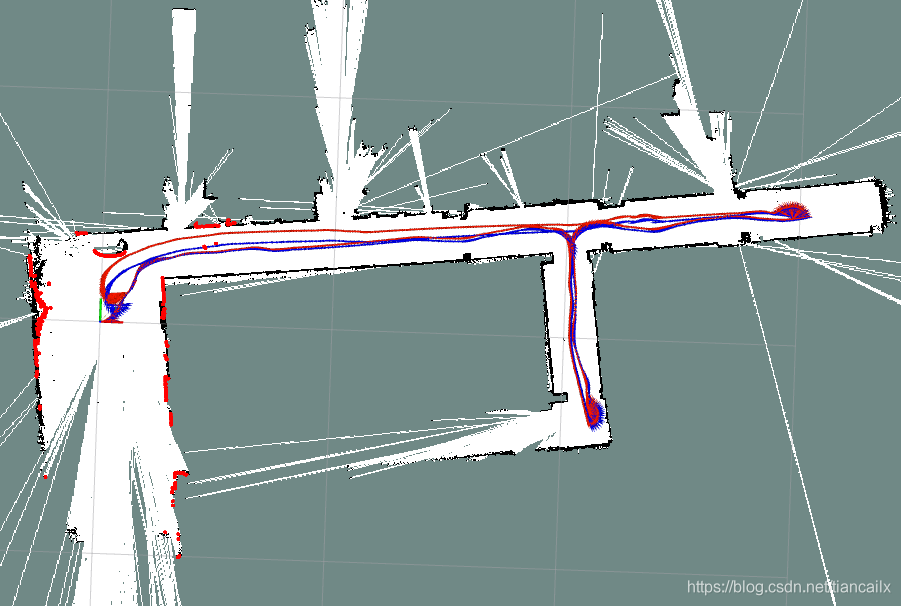
话不多说,先说明一下对代码做了那些改变,然后再着重讲解一下 Hector是如何做scan match的.
1 代码简单重构
相对于原版Hector做了哪些改变
- 重写了原版的HectorMappingRos.cpp,使得代码变得更加简单与清晰
- 发布了 map -> odom -> base_link 的 TF树
- 去掉了原版的 DebugInfo 以及 Drawing 这两个功能以及代码文件.个人感觉这两个功能用不上,导致代码复杂
- 更改了一些文件的位置,使得现在的.cc文件只有一个,其余全是头文件.原版的src文件夹下有很多文件
- 对很多文件进行了注释
2 代码讲解
2.1 获取代码
代码已经提交在github上了,如果不知道github的地址的朋友, 请在我的公众号: 从零开始搭激光SLAM 中回复 开源地址 获得。
推荐使用 git clone 的方式进行下载, 因为代码是正处于更新状态的, git clone 下载的代码可以使用 git pull 很方便地进行更新.
本篇文章对应的代码为 Creating-2D-laser-slam-from-scratch/lesson4/src/hector_mapping/ 与 Creating-2D-laser-slam-from-scratch/lesson4/include/hector_mapping/hector_slam.cc
2.2 构造函数
在构造函数中 首先调用 InitParams 进行了 ROS参数的初始化.
之后对 HectorSlamProcessor 对象进行初始化.
再之后对多层地图进行了初始化,并调用 setMapInfo() 进行 ROS地图的内存的分配.
最后,查找从 base_link 到 雷达坐标系 间的坐标变换.
// 构造函数
HectorMappingRos::HectorMappingRos(): private_node_("~"), lastGetMapUpdateIndex(-100), tfB_(0), map_publish_thread_(0)
{ROS_INFO_STREAM("\033[1;32m----> Hector SLAM started.\033[0m");// 参数初始化InitParams();laser_scan_subscriber_ = node_handle_.subscribe(p_scan_topic_, p_scan_subscriber_queue_size_, &HectorMappingRos::scanCallback, this); // 雷达数据处理if (p_pub_odometry_){odometryPublisher_ = node_handle_.advertise<nav_msgs::Odometry>("odom_hector", 50);}tfB_ = new tf::TransformBroadcaster();slamProcessor = new hectorslam::HectorSlamProcessor(static_cast<float>(p_map_resolution_),p_map_size_, p_map_size_,Eigen::Vector2f(p_map_start_x_, p_map_start_y_),p_map_multi_res_levels_);slamProcessor->setUpdateFactorFree(p_update_factor_free_); // 0.4slamProcessor->setUpdateFactorOccupied(p_update_factor_occupied_); // 0.9slamProcessor->setMapUpdateMinDistDiff(p_map_update_distance_threshold_); // 0.4slamProcessor->setMapUpdateMinAngleDiff(p_map_update_angle_threshold_); // 0.9// 多层地图的初始化int mapLevels = slamProcessor->getMapLevels();mapLevels = 1; // 这里设置成只发布最高精度的地图,如果有其他需求,如进行路径规划等等需要多层地图时,注释本行。std::string mapTopic_ = "map";for (int i = 0; i < mapLevels; ++i){mapPubContainer.push_back(MapPublisherContainer());slamProcessor->addMapMutex(i, new HectorMapMutex());std::string mapTopicStr(mapTopic_);if (i != 0){mapTopicStr.append("_" + boost::lexical_cast<std::string>(i));}std::string mapMetaTopicStr(mapTopicStr);mapMetaTopicStr.append("_metadata");MapPublisherContainer &tmp = mapPubContainer[i];tmp.mapPublisher_ = node_handle_.advertise<nav_msgs::OccupancyGrid>(mapTopicStr, 1, true);tmp.mapMetadataPublisher_ = node_handle_.advertise<nav_msgs::MapMetaData>(mapMetaTopicStr, 1, true);setMapInfo(tmp.map_, slamProcessor->getGridMap(i)); // 设置地图服务if (i == 0){mapPubContainer[i].mapMetadataPublisher_.publish(mapPubContainer[i].map_.map.info);}}// 新建一个线程用来发布地图map_publish_thread_ = new boost::thread(boost::bind(&HectorMappingRos::publishMapLoop, this, p_map_pub_period_));map_to_odom_.setIdentity();// 查找 base_link -> front_laser_link 的tf,循环5次以确保其能找到int count = 5;ros::Duration dur(0.5);while (count-- != 0){if (tf_.waitForTransform(p_base_frame_, p_scan_frame_, ros::Time(0), dur)){tf_.lookupTransform(p_base_frame_, p_scan_frame_, ros::Time(0), laserTransform_);break;}else{ROS_WARN("lookupTransform laser frame into base_link timed out.");}}
}
2.3 回调函数
首先进行了雷达数据格式的转换. 先通过 laser_geometry 这个包将 LaserScan 转换成 PointCloud 格式,这个很简单,我之前的文章已经实现过了,这里懒的改了.
之后是将雷达数据从点云形式转换到Hector自己的雷达数据存储格式.
再之后就是进行扫描匹配与地图更新.
扫描匹配计算完成之后再发布里程计 topic 与 tf,tf将根据不同的配置决定是发布 map -> base_link 还是 map -> odom -> base_link.
想要看输出的里程计信息 topic 就必须要有odom坐标系.
这里将 map 与 odom 的坐标系重合了( 没有对 map_to_odom_ 再赋值 ) ,所以 base_link 在 map 与 odom 下的坐标是相同的.
在发布TF的时候,将TF的时间戳都设置成了雷达的时间戳,这块好像有问题,会导致在rviz里 fixed frame 设置成map时看不到hector发布的odom数据。
我也将时间戳改成了 ros::Time::now() ,改完了之后有时能看到有时看不到,还不清楚原因,所以先在rviz里将 fixed frame 设置成了odom.
/*** 激光数据处理回调函数,将ros数据格式转换为算法中的格式,并转换成地图尺度,交由slamProcessor处理。* 算法中所有的计算都是在地图尺度下进行。 */
void HectorMappingRos::scanCallback(const sensor_msgs::LaserScan &scan)
{start_time_ = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();ros::WallTime startTime = ros::WallTime::now();// 将 scan 转换成 点云格式projector_.projectLaser(scan, laser_point_cloud_, 30.0);Eigen::Vector3f startEstimate(Eigen::Vector3f::Zero());// 将雷达数据的点云格式 更改成 hector 内部的数据格式if (rosPointCloudToDataContainer(laser_point_cloud_, laserTransform_, laserScanContainer, slamProcessor->getScaleToMap())){// 首先获取上一帧的位姿,作为初值startEstimate = slamProcessor->getLastScanMatchPose();// 进入扫描匹配与地图更新slamProcessor->update(laserScanContainer, startEstimate);}end_time_ = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();time_used_ = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::duration<double>>(end_time_ - start_time_);std::cout << "数据转换与扫描匹配用时: " << time_used_.count() << " 秒。" << std::endl;if (p_timing_output_){ros::WallDuration duration = ros::WallTime::now() - startTime;ROS_INFO("HectorSLAM Iter took: %f milliseconds", duration.toSec() * 1000.0f);}// 更新存储的位姿, 这里的位姿是 base_link 在 map 下的位姿poseInfoContainer_.update(slamProcessor->getLastScanMatchPose(), slamProcessor->getLastScanMatchCovariance(), scan.header.stamp, p_map_frame_);// 发布 odom topicif (p_pub_odometry_){nav_msgs::Odometry tmp;tmp.pose = poseInfoContainer_.getPoseWithCovarianceStamped().pose;tmp.header = poseInfoContainer_.getPoseWithCovarianceStamped().header;tmp.child_frame_id = p_base_frame_;odometryPublisher_.publish(tmp);}if (pub_map_to_baselink_tf_){// pub map -> odom -> base_link tfif (p_pub_map_odom_transform_){tfB_->sendTransform(tf::StampedTransform(map_to_odom_, scan.header.stamp, p_map_frame_, p_odom_frame_));tfB_->sendTransform(tf::StampedTransform(poseInfoContainer_.getTfTransform(), scan.header.stamp, p_odom_frame_, p_tf_map_scanmatch_transform_frame_name_));}// pub map -> base_link tfelse{tfB_->sendTransform(tf::StampedTransform(poseInfoContainer_.getTfTransform(), scan.header.stamp, p_map_frame_, p_tf_map_scanmatch_transform_frame_name_));}}
}
2.4 转换scan格式的函数
这里的 laserTransform 指的是从 base_link 到 雷达坐标系 间的坐标变换.
首先将base_link到雷达坐标系的坐标转换 乘以地图分辨率 设置为这帧数据的 origo.
之后对每个雷达数据进行距离判定,如果距离太近或者太远就跳过.
这里还进行了如果距离大于 雷达数据的最大使用距离 的判断,因为雷达数据太远时的数据跳动比较厉害,所以这里将 p_use_max_scan_range_ 之外的数据也过滤掉不进行使用.
之后就是将数据点进行坐标变换,通过左乘laserTransform得到在base_link下的正确的x y 值,因为只进行了一次左乘laserTransform,所以转换后的z坐标是不正确的,通过再次减去laserTransform才得到正确的z坐标.
最后将base_link下的xy乘以分辨率放入dataContainer中.
// 将点云数据转换成Hector中雷达数据的格式
bool HectorMappingRos::rosPointCloudToDataContainer(const sensor_msgs::PointCloud &pointCloud, const tf::StampedTransform &laserTransform, hectorslam::DataContainer &dataContainer, float scaleToMap)
{size_t size = pointCloud.points.size();dataContainer.clear();tf::Vector3 laserPos(laserTransform.getOrigin());// dataContainer.setOrigo(Eigen::Vector2f::Zero());// 将base_link到雷达坐标系的坐标转换 乘以地图分辨率 当成这帧数据的 origodataContainer.setOrigo(Eigen::Vector2f(laserPos.x(), laserPos.y()) * scaleToMap);for (size_t i = 0; i < size; ++i){const geometry_msgs::Point32 &currPoint(pointCloud.points[i]);float dist_sqr = currPoint.x * currPoint.x + currPoint.y * currPoint.y;if ((dist_sqr > p_sqr_laser_min_dist_) && (dist_sqr < p_sqr_laser_max_dist_)){if ((currPoint.x < 0.0f) && (dist_sqr < 0.50f)){continue;}// 距离太远的点跳动太大,如果距离大于使用距离(20m),就跳过if (dist_sqr > p_use_max_scan_range_ * p_use_max_scan_range_)continue;// 点的坐标左乘base_link->laser_link的tf 将得到该点在base_link下的 xy 坐标, 但是z坐标是不正确tf::Vector3 pointPosBaseFrame(laserTransform * tf::Vector3(currPoint.x, currPoint.y, currPoint.z));// 通过再减去 base_link->laser_link的tf的z的值,得到该点在base_link下正确的 z 坐标float pointPosLaserFrameZ = pointPosBaseFrame.z() - laserPos.z();if (pointPosLaserFrameZ > p_laser_z_min_value_ && pointPosLaserFrameZ < p_laser_z_max_value_){// 将雷达数据的 x y 都乘地图的分辨率 0.05 再放入dataContainer中dataContainer.add(Eigen::Vector2f(pointPosBaseFrame.x(), pointPosBaseFrame.y()) * scaleToMap);}}}return true;
}
2.5 update()
update() 函数位于 Creating-2D-laser-slam-from-scratch/lesson4/include/lesson4/hector_mapping/slam_main/HectorSlamProcessor.h中.
将scan_match与地图更新分成了2步进行.
scan_match是调用mapRep->matchData()函数,返回了当前scan在与地图进行扫描匹配后的地图坐标系下的位姿.
之后调用了updateByScan()进行了地图的更新,这块代码已经在上一篇文章中讲过了,所以这里就不再进行讲解了.
/*** 对每一帧的激光数据进行处理* @param dataContainer 激光数据存储容器,坐标已转换成地图尺度,为地图中激光系的坐标* @param poseHintWorld 激光系在地图中的初始pose* @param map_without_matching 是否进行匹配*/void update(const DataContainer &dataContainer, const Eigen::Vector3f &poseHintWorld, bool map_without_matching = false){//std::cout << "\nph:\n" << poseHintWorld << "\n";/** 1. 位姿匹配 **/Eigen::Vector3f newPoseEstimateWorld;if (!map_without_matching){// 进行 scan to map 的地方newPoseEstimateWorld = (mapRep->matchData(poseHintWorld, dataContainer, lastScanMatchCov));}else{newPoseEstimateWorld = poseHintWorld;}lastScanMatchPose = newPoseEstimateWorld;/** 2.地图更新 **/if (util::poseDifferenceLargerThan(newPoseEstimateWorld, lastMapUpdatePose, paramMinDistanceDiffForMapUpdate, paramMinAngleDiffForMapUpdate) || map_without_matching){ // 仅在位姿变化大于阈值 或者 map_without_matching为真 的时候进行地图更新mapRep->updateByScan(dataContainer, newPoseEstimateWorld);mapRep->onMapUpdated();lastMapUpdatePose = newPoseEstimateWorld;}}2.5.1 matchData()_1
第一个matchData() 位于 Creating-2D-laser-slam-from-scratch/lesson4/include/lesson4/hector_mapping/slam_main/MapRepMultiMap.h中.
假设一共3层多分辨率地图,这里首先使用 setFrom() 将雷达数据dataContainer进行长度的缩短,对每个原始数据都乘以 1/(2的n次方) , n是 2, 1, 0.
之后使用缩短后的雷达数据,与对应分辨率的地图进行扫描匹配.
也就是在粗分辨率地图上先进行扫描匹配,得出的结果 再传入 更精细分辨率地图上进行扫描匹配.
最终返回一个在map坐标系下的位姿.
/*** 地图匹配,通过多分辨率地图求解当前激光帧的pose。*/virtual Eigen::Vector3f matchData(const Eigen::Vector3f &beginEstimateWorld, const DataContainer &dataContainer, Eigen::Matrix3f &covMatrix){size_t size = mapContainer.size();Eigen::Vector3f tmp(beginEstimateWorld);/// coarse to fine 的pose求精过程,i层的求解结果作为i-1层的求解初始值。for (int index = size - 1; index >= 0; --index){//std::cout << " m " << i;if (index == 0){tmp = (mapContainer[index].matchData(tmp, dataContainer, covMatrix, 5)); /// 输入数据dataContainer 对应 mapContainer[0]}else{// 根据地图层数对原始激光数据坐标进行缩小,得到对应图层尺寸的激光数据dataContainers[index - 1].setFrom(dataContainer, static_cast<float>(1.0 / pow(2.0, static_cast<double>(index))));tmp = (mapContainer[index].matchData(tmp, dataContainers[index - 1], covMatrix, 3));/// dataContainers[i]对应mapContainer[i+1]}}return tmp;}
2.5.2 matchData()_2
第二个machData() 位于 Creating-2D-laser-slam-from-scratch/lesson4/include/lesson4/hector_mapping/slam_main/MapProcContainer.h 中.
可以看到,这个函数中并没有额外的操作,只是将对应分辨率的地图也一起传入到第三个mathcData() 中.
/*** 给定位姿初值,估计当前scan在当前图层中的位姿 ---- 位姿为世界系下的pose 、 dataContainer应与当前图层尺度匹配* @param beginEstimateWorld 世界系下的位姿* @param dataContainer 激光数据* @param covMatrix scan-match的不确定性 -- 协方差矩阵* @param maxIterations 最大的迭代次数* @return*/Eigen::Vector3f matchData(const Eigen::Vector3f &beginEstimateWorld, const DataContainer &dataContainer, Eigen::Matrix3f &covMatrix, int maxIterations){return scanMatcher->matchData(beginEstimateWorld, *gridMapUtil, dataContainer, covMatrix, maxIterations);}
2.5.3 matchData()_3
第三个 matchData() 位于 Creating-2D-laser-slam-from-scratch/lesson4/include/lesson4/hector_mapping/matcher/ScanMatcher.h 中.
这回终于是真正进行扫描匹配的地方了.
首先说一下hector world坐标系与hector map坐标系
之前说的这个初始位姿一直都是world坐标系下的坐标,Hector中认为实际物理坐标表示成的坐标为world坐标,以左上角为原点的.
而hector map坐标就是用 world坐标再除以地图的分辨率0.05(也就是乘以20),再加上map坐标系的原点 得到的.也就是像素坐标.
这段代码先将给定的初始位姿转换成Hector的map坐标系下的像素坐标.
之后调用了 estimateTransformationLogLh() 进行计算位姿,之后又通过多次调用这个函数使结果更加准确.
求解的过程就在 estimateTransformationLogLh() 里.
这里的H矩阵是这个类的私有变量,代表hessian, 也就是要返回的协方差矩阵.
然后,将estimate从地图坐标系下转到world坐标系下,再返回.
/*** 实际进行位姿估计的函数* @param beginEstimateWorld 位姿初值* @param gridMapUtil 网格地图工具,这里主要是用来做坐标变换* @param dataContainer 激光数据* @param covMatrix 协方差矩阵* @param maxIterations 最大迭代次数* @return*/Eigen::Vector3f matchData(const Eigen::Vector3f &beginEstimateWorld,ConcreteOccGridMapUtil &gridMapUtil, const DataContainer &dataContainer,Eigen::Matrix3f &covMatrix, int maxIterations){if (dataContainer.getSize() != 0){// 1. 初始pose转换为地图尺度下的pose --仿射变换,包括位姿的尺度和偏移,旋转在 X Y 同尺度变化时保持不变Eigen::Vector3f beginEstimateMap(gridMapUtil.getMapCoordsPose(beginEstimateWorld));Eigen::Vector3f estimate(beginEstimateMap);// 2. 第一次迭代estimateTransformationLogLh(estimate, gridMapUtil, dataContainer);int numIter = maxIterations;/** 3. 多次迭代求解 **/for (int i = 0; i < numIter; ++i){estimateTransformationLogLh(estimate, gridMapUtil, dataContainer);}// 角度正则化estimate[2] = util::normalize_angle(estimate[2]);covMatrix = Eigen::Matrix3f::Zero();//covMatrix.block<2,2>(0,0) = (H.block<2,2>(0,0).inverse());//covMatrix.block<2,2>(0,0) = (H.block<2,2>(0,0));// 使用Hessian矩阵近似协方差矩阵covMatrix = H;// 结果转换回物理坐标系下 -- 转换回实际尺度return gridMapUtil.getWorldCoordsPose(estimate);}return beginEstimateWorld;}
2.6 estimateTransformationLogLh()
这个函数也位于 Creating-2D-laser-slam-from-scratch/lesson4/include/lesson4/hector_mapping/matcher/ScanMatcher.h 中.
首先,这个函数通过getCompleteHessianDerivs() 计算出了协方差矩阵H , 以及 dTr向量.
之后,通过高斯牛顿法最终推倒出的求根公式: H的逆 乘以 dtr 求出 先验位姿与后验位姿间的增量. 也就是 X = H.inverse() * dTr --> H * X = dTr
最后再将这个增量加上之前的预测值,得到匹配之后的位姿.
/*** 高斯牛顿估计位姿* @param estimate 位姿初始值* @param gridMapUtil 网格地图相关计算工具* @param dataPoints 激光数据* @return 提示是否有解 --- 貌似没用上*/bool estimateTransformationLogLh(Eigen::Vector3f &estimate,ConcreteOccGridMapUtil &gridMapUtil,const DataContainer &dataPoints){/** 核心函数,计算H矩阵和dTr向量(b列向量)---- occGridMapUtil.h 中 **/gridMapUtil.getCompleteHessianDerivs(estimate, dataPoints, H, dTr);//std::cout << "\nH\n" << H << "\n";//std::cout << "\ndTr\n" << dTr << "\n";// 判断H是否可逆, 判断增量非0,避免无用计算if ((H(0, 0) != 0.0f) && (H(1, 1) != 0.0f)){// 求解位姿增量Eigen::Vector3f searchDir(H.inverse() * dTr);// 角度增量不能太大if (searchDir[2] > 0.2f){searchDir[2] = 0.2f;std::cout << "SearchDir angle change too large\n";}else if (searchDir[2] < -0.2f){searchDir[2] = -0.2f;std::cout << "SearchDir angle change too large\n";}/// 更新估计值 --- 结果在地图尺度下updateEstimatedPose(estimate, searchDir);return true;}return false;}void updateEstimatedPose(Eigen::Vector3f &estimate, const Eigen::Vector3f &change){estimate += change;}
由于篇幅限制,getCompleteHessianDerivs() 函数的讲解与hector的公式推倒将在下篇文章中进行说明
3 运行
3.1 运行
本篇文章对应的数据包, 请在我的公众号中回复 lesson1 获得,并将launch中的bag_filename更改成您实际的目录名。
通过如下命令运行本篇文章对应的程序
roslaunch lesson4 hector_slam.launch
因为hector中依赖了 laser_geometry 这个包,如果有同学启动失败,提示缺少这个包,手动安装一下就好了.
3.2 运行结果与分析
启动之后,会在rviz中显示出如下画面.
首先,要说明一点的是rviz中的 Fixed Frame 我设置成了odom,因为我map与odom是重合的,所以这块设置成odom也是可以的.
如果设置成map,odom_hector这块会显示不出来,会提示找不到 TF,这个原因我还不太清楚,猜测是发布map->odom的tf的时间戳设置成雷达的时间戳这块存在问题,但是我没有去深扣它.
Rviz的 Fixed Frame 的意义是:所有显示出来的信息,都要通过 TF 进行坐标变换,变换到Fixed Frame 下,如果在规定的时间内没有查到 TF 就会报错,显示不了信息.
所以我将Fixed Frame设置成odom后,显示的2个odometry插件就不再需要进行坐标变换,可以直接显示出来.
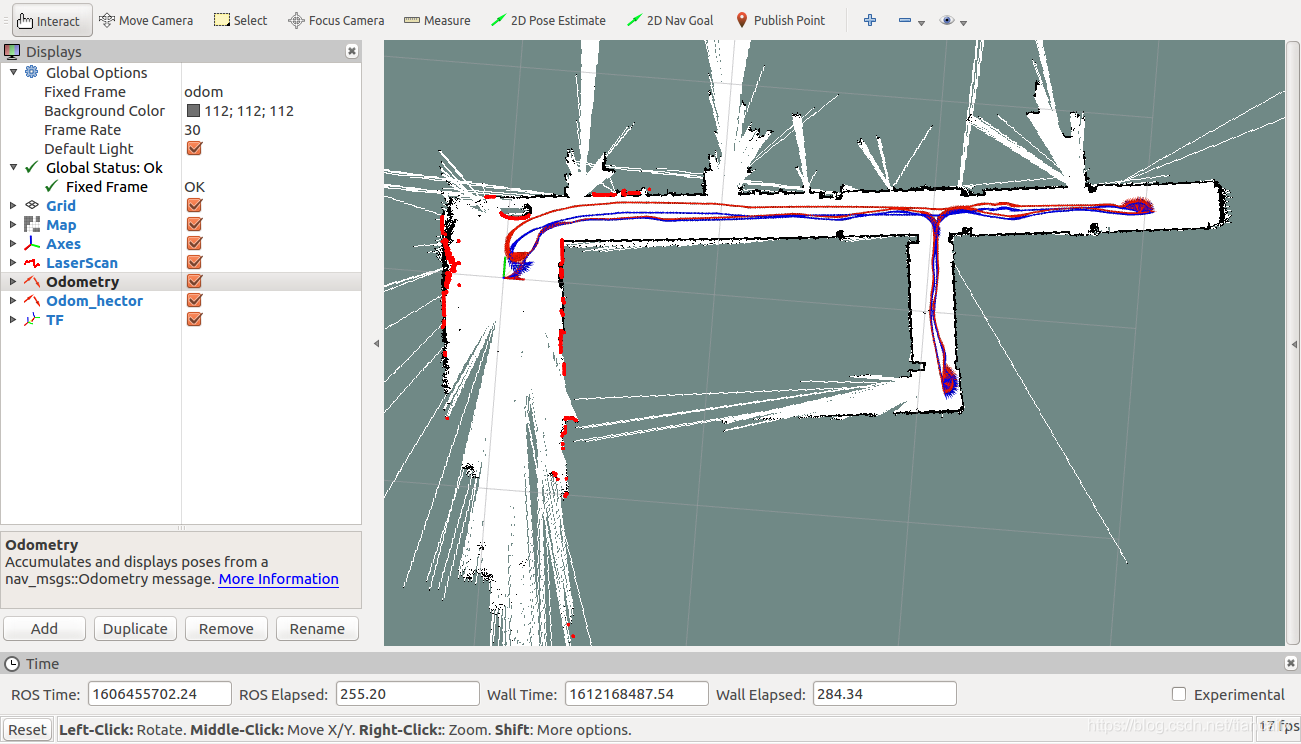 红色轨迹是小车上的编码器的结果,蓝色轨迹是hector_slam输出的里程计结果.
红色轨迹是小车上的编码器的结果,蓝色轨迹是hector_slam输出的里程计结果.
通过在建图的过程中对比雷达与地图的匹配,以及对比红色蓝色的轨迹,可以发现,hector计算出的里程计还是挺准确的,即使是回来的过程中,雷达与地图也是始终匹配上的.
但是,在回来的过程中,编码器产生的里程计与hector的里程计产生了较大的偏差.
通过最后小车停止时,雷达数据与地图依然能够很好的匹配这一现象,可以认为hector产生的里程计的准确程度大于小车自身的里程计.
至于走廊边缘那边界不清晰的问题,通过观看建图过程发现,主要是由于远距离的雷达点跳动产生的.
计算耗时
同时,终端会打印处如下信息,可以看到,执行一次回调的时间主要花费在了进行数据转换和扫描匹配上.如果时间打印的再详细些的话就会发现时间主要用在扫描匹配部分.
当运行时间长了之后,会发现进行扫描匹配的时间明显变长了.
数据转换与扫描匹配用时: 0.0942895 秒。
执行一次回调用时: 0.094357 秒。
数据转换与扫描匹配用时: 0.0934194 秒。
执行一次回调用时: 0.093491 秒。
# 一段时间之后
数据转换与扫描匹配用时: 0.119987 秒。
执行一次回调用时: 0.120077 秒。
数据转换与扫描匹配用时: 0.13254 秒。
执行一次回调用时: 0.133221 秒。
雷达是10hz的,处理一次回调就要花0.12秒了,这时就会在运算过程中丢弃雷达数据.**这个原因猜测是由于地图变大之后,与地图的匹配更加耗时导致的.**具体是哪一部分导致的还有待推敲。
我在代码里将多分辨率地图的层数设置成了3层,如果设置成2层的话也会减小时间消耗.但是匹配的效果就会变差.
hector里程计的频率
如果一直通过rostopic hz 来查看 雷达与odom_hector的频率的话,就会发现,到后期 odom_hector的频率已经从 10hz 下降到 7.9hz 了.
topic rate min_delta max_delta std_dev window
=================================================================
/laser_scan 9.986 0.09054 0.1107 0.003959 20
/map 0.5228 1.913 1.913 0.0 20
/odom_hector 10.2 0.08047 0.1209 0.01026 2
# 一段时间之后topic rate min_delta max_delta std_dev window
=================================================================
/laser_scan 10.0 0.08059 0.1166 0.004054 1984
/map 0.5004 1.783 2.174 0.06475 1984
/odom_hector 7.979 0.08047 0.3229 0.02474 100
4 总结与Next
本篇文章对Hecot的代码进行了简单的重构,发布了map与odom的tf,实现了一个基于scan_to_map的里程计,并构建出了第一张较成功的栅格地图.
下一篇文章将对 Hector 论文中的公式进行手动推倒,以及相应的代码讲解.
再下一篇文章将使用里程计数据进行SLAM,将基于 Karto 进行相关代码的实现.
文章将在 公众号: 从零开始搭SLAM 进行同步更新,欢迎大家关注,可以在公众号中添加我的微信,进激光SLAM交流群,大家一起交流SLAM技术。
同时,也希望您将这个公众号推荐给您身边做激光SLAM的人们,大家共同进步。
如果您对我写的文章有什么建议,或者想要看哪方面功能如何实现的,请直接在公众号中回复,我可以收到,并将认真考虑您的建议。

这篇关于从零开始搭二维激光SLAM --- 简单重写 Hector SLAM的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







