本文主要是介绍【回眸】LDA算法(数据处理与智能决策),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
前言
今天的数据处理与智能决策的作业需要用到LDA算法,接下来简单注释一下LDA算法的代码。
LDA算法的代码
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis as LDAfeature_dict = {i: label for i, label in zip(range(4),("Sepal.Length","Sepal.Width","Petal.Length","Petal.Width",))}
# print(feature_dict) # {0: 'Sepal.Length', 1: 'Sepal.Width', 2: 'Petal.Length', 3: 'Petal.Width'}df = pd.read_csv('iris.csv', sep=',')
df.columns = ["Number"] + [l for i, l in sorted(feature_dict.items())] + ['Species']
# to drop the empty line at file-end
df.dropna(how='all', inplace=True)
# print(df.tail()) # 打印数据的后五个,和 .head() 是对应的X = df[["Sepal.Length", "Sepal.Width", "Petal.Length", "Petal.Width"]].values
y = df['Species'].values
enc = LabelEncoder()
label_encoder = enc.fit(y)
y = label_encoder.transform(y) + 1label_dict = {1: 'setosa', 2: 'versicolor', 3: 'virginica'}np.set_printoptions(precision=4)
mean_vectors = []
for c1 in range(1, 4):mean_vectors.append(np.mean(X[y == c1], axis=0))# print('Mean Vector class %s : %s\n' % (c1, mean_vectors[c1 - 1]))
S_W = np.zeros((4, 4))
for c1, mv in zip(range(1, 4), mean_vectors):# scatter matrix for every classclass_sc_mat = np.zeros((4, 4))for row in X[y == c1]:# make column vectorsrow, mv = row.reshape(4, 1), mv.reshape(4, 1)class_sc_mat += (row - mv).dot((row - mv).T)# sum class scatter metricesS_W += class_sc_mat
# print('within-class Scatter Matrix:\n', S_W)
overall_mean = np.mean(X, axis=0)
S_B = np.zeros((4, 4))
for i, mean_vec in enumerate(mean_vectors):n = X[y == i + 1, :].shape[0]# make column vectormean_vec = mean_vec.reshape(4, 1)# make column vectoroverall_mean = overall_mean.reshape(4, 1)S_B += n * (mean_vec - overall_mean).dot((mean_vec - overall_mean).T)
# print('between-class Scatter matrix:\n', S_B)eig_vals, eig_vecs = np.linalg.eig(np.linalg.inv(S_W).dot(S_B))for i in range(len(eig_vals)):eigvec_sc = eig_vecs[:, i].reshape(4, 1)# print('\n Eigenvector {}: \n {}'.format(i+1, eigvec_sc.real))# print('Eigenvalue {: }: {:.2e}'.format(i+1, eig_vals[i].real))# make a list of (eigenvalue, eigenvector) tuples
eig_pairs = [(np.abs(eig_vals[i]), eig_vecs[:, i]) for i in range(len(eig_vals))]# sort the (eigenvalue, eigenvector) tuples from high to low
eig_pairs = sorted(eig_pairs, key=lambda k: k[0], reverse=True)# Visually cinfirm that the list is correctly sorted by decreasing eigenvalues
print('Eigenvalues in decreasing order: \n')
for i in eig_pairs:print(i[0])print('Variance explained:\n')
eigv_sum = sum(eig_vals)
for i, j in enumerate(eig_pairs):print('eigenvalue {0:}: {1:.2%}'.format(i + 1, (j[0] / eigv_sum).real))W = np.hstack((eig_pairs[0][1].reshape(4, 1), eig_pairs[1][1].reshape(4, 1)))
print('Matrix W: \n', W.real)X_lda = X.dot(W)
assert X_lda.shape == (150, 2), 'The matrix is not 150*2 dimensional.'def plt_step_lda():ax = plt.subplot(111)for label, marker, color in zip(range(1, 4), ('^', 's', 'o'), ('blue', 'red', 'green')):plt.scatter(x=X_lda[:, 0].real[y == label],y=X_lda[:, 1].real[y == label],marker=marker,color=color,alpha=0.5,label=label_dict[label])plt.xlabel('LD1')plt.ylabel('LD2')leg = plt.legend(loc='upper right', fancybox=True)leg.get_frame().set_alpha(0.5)plt.title('LDA: Iris projection onto the first 2 linear discriminants')# hide axis ticksplt.tick_params(axis='both', which='both', bottom='off',top='off', labelbottom='on', left='off',labelleft='on')# remove axis spinesax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)ax.spines['bottom'].set_visible(False)ax.spines['left'].set_visible(False)plt.grid()plt.tight_layout()plt.show()
#这里生成一个图
# plt_step_lda()# LDA
sklearn_lda = LDA(n_components=2)
X_lda_sklearn = sklearn_lda.fit_transform(X, y)def plot_scikit_lda(X, title):ax = plt.subplot(111)for label, marker, color in zip(range(1, 4), ('^', 's', 'o'), ('blue', 'red', 'green')):plt.scatter(x=X_lda[:, 0].real[y == label],# flip the figurey=X_lda[:, 1].real[y == label] * -1,marker=marker,color=color,alpha=0.5,label=label_dict[label])plt.xlabel('LD1')plt.ylabel('LD2')leg = plt.legend(loc='upper right', fancybox=True)leg.get_frame().set_alpha(0.5)plt.title(title)# hide axis ticksplt.tick_params(axis='both', which='both', bottom='off',top='off', labelbottom='on', left='off',labelleft='on')# remove axis spinesax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)ax.spines['bottom'].set_visible(False)ax.spines['left'].set_visible(False)plt.grid()plt.tight_layout()plt.show()
#这里也生成一个图
plot_scikit_lda(X, title='Default LDA via scikit-learn')
首先导入包
其次打印 三个类别,四个特征 均值分别如下:
Mean Vector class 1 : [5.006 3.428 1.462 0.246]
Mean Vector class 2 : [5.936 2.77 4.26 1.326]
Mean Vector class 3 : [6.588 2.974 5.552 2.026]生成的图放在下面了:
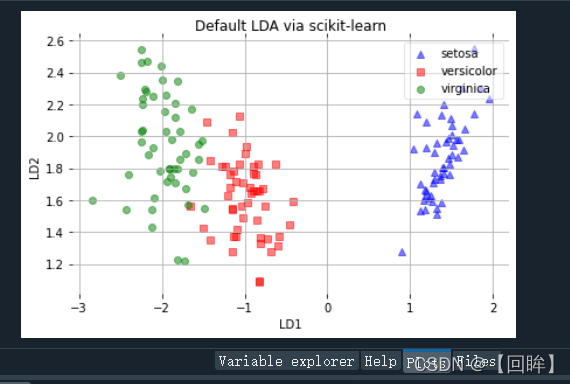

明天不见不散(^-^)V
这篇关于【回眸】LDA算法(数据处理与智能决策)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






