本文主要是介绍AtCoder Beginner Contest 347 (ABCDEF题)视频讲解,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
A - Divisible
Problem Statement
You are given positive integers N N N and K K K, and a sequence of length N N N, A = ( A 1 , A 2 , … , A N ) A=(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N) A=(A1,A2,…,AN).
Extract all elements of A A A that are multiples of K K K, divide them by K K K, and print the quotients.
Constraints
1 ≤ N , K ≤ 100 1\leq N,K\leq 100 1≤N,K≤100
KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '&' at position 11: 1\leq A_1 &̲lt; A_2 < \l…
A A A has at least one multiple of K K K.
All given numbers are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N N N K K K
A 1 A_1 A1 A 2 A_2 A2 … \ldots … A N A_N AN
Output
Divide all elements of A A A that are multiples of K K K and print the quotients in ascending order with spaces in between.
Sample Input 1
5 2
2 5 6 7 10
Sample Output 1
1 3 5
The multiples of 2 2 2 among the elements in A A A are 2 2 2, 6 6 6, and 10 10 10. Divide them by 2 2 2 to get 1 1 1, 3 3 3, and 5 5 5, and print them in ascending order with spaces in between.
Sample Input 2
3 1
3 4 7
Sample Output 2
3 4 7
Sample Input 3
5 10
50 51 54 60 65
Sample Output 3
5 6
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int n, k;cin >> n >> k;std::vector<int> a(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++) {cin >> a[i];if (a[i] % k == 0)cout << a[i] / k << " ";}return 0;
}
B - Substring
Problem Statement
You are given a string S S S consisting of lowercase English letters. How many different non-empty substrings does S S S have?
A substring is a contiguous subsequence. For example, xxx is a substring of yxxxy but not of xxyxx.
Constraints
S S S is a string of length between 1 1 1 and 100 100 100, inclusive, consisting of lowercase English letters.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
S S S
Output
Print the answer.
Sample Input 1
yay
Sample Output 1
5
S S S has the following five different non-empty substrings:
a
y
ay
ya
yay
Sample Input 2
aababc
Sample Output 2
17
Sample Input 3
abracadabra
Sample Output 3
54
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);string s;cin >> s;int n = s.size();set<string> res;for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++)for (int j = 1; j <= n - i; j ++)res.insert(s.substr(i, j));cout << res.size() << endl;return 0;
}
C - Ideal Holidays
Problem Statement
In the Kingdom of AtCoder, a week consists of A + B A+B A+B days, with the first through A A A-th days being holidays and the ( A + 1 ) (A+1) (A+1)-th through ( A + B ) (A+B) (A+B)-th being weekdays.
Takahashi has N N N plans, and the i i i-th plan is scheduled D i D_i Di days later.
He has forgotten what day of the week it is today. Determine if it is possible for all of his N N N plans to be scheduled on holidays.
Constraints
1 ≤ N ≤ 2 × 1 0 5 1\leq N\leq 2\times 10^5 1≤N≤2×105
1 ≤ A , B ≤ 1 0 9 1\leq A,B\leq 10^9 1≤A,B≤109
KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '&' at position 10: 1\leq D_1&̲lt;D_2<\ldot…
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N N N A A A B B B
D 1 D_1 D1 D 2 D_2 D2 … \ldots … D N D_N DN
Output
Print Yes in a single line if it is possible for all of Takahashi’s N N N plans to be scheduled on holidays, and No otherwise.
Sample Input 1
3 2 5
1 2 9
Sample Output 1
Yes
In this input, a week consists of seven days, with the first through second days being holidays and the third through seventh days being weekdays.
Let us assume today is the seventh day of the week. In this case, one day later would be the first day of the week, two days later would be the second day of the week, and nine days later would also be the second day of the week, making all plans scheduled on holidays. Therefore, it is possible for all of Takahashi’s N N N plans to be scheduled on holidays.
Sample Input 2
2 5 10
10 15
Sample Output 2
No
Sample Input 3
4 347 347
347 700 705 710
Sample Output 3
Yes
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;const int N = 2e5 + 10;int n, a, b;
int d[N];signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin >> n >> a >> b;int l1 = -1e18, r1 = 1e18, l2 = -1e18, r2 = 1e18;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++) {cin >> d[i];d[i] %= (a + b);int tl = (0 - d[i] + a + b) % (a + b), tr = (a - 1 - d[i] + a + b) % (a + b);if (tl > tr) {l1 = max(0ll, l1), r1 = min(r1, tr);l2 = max(l2, tl), r2 = min(a + b - 1, r2);} elsel1 = max(l1, tl), r1 = min(r1, tr), l2 = max(l2, tl), r2 = min(r2, tr);}if (l1 <= r1 || l2 <= r2) cout << "Yes" << endl;else cout << "No" << endl;return 0;
}
D - Popcount and XOR
Problem Statement
You are given non-negative integers a a a, b b b, and C C C.
Determine if there is a pair of non-negative integers ( X , Y ) (X, Y) (X,Y) that satisfies all of the following five conditions. If such a pair exists, print one.
KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '&' at position 10: 0 \leq X &̲lt; 2^{60}
KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '&' at position 10: 0 \leq Y &̲lt; 2^{60}
popcount ( X ) = a \operatorname{popcount}(X) = a popcount(X)=a
popcount ( Y ) = b \operatorname{popcount}(Y) = b popcount(Y)=b
X ⊕ Y = C X \oplus Y = C X⊕Y=C
Here, ⊕ \oplus ⊕ denotes the bitwise XOR.
If multiple pairs ( X , Y ) (X, Y) (X,Y) satisfy the conditions, you may print any of them.
1101, so $\operatorname{popcount}(13)=3$. What is bitwise XOR? For non-negative integers $x, y$, the bitwise exclusive OR $x \oplus y$ is defined as follows. The $2^k$'s place $\ (k\geq0)$ in the binary representation of $x \oplus y$ is $1$ if exactly one of the $2^k$'s places $\ (k\geq0)$ in the binary representations of $x$ and $y$ is $1$, and $0$ otherwise. For example, $9$ and $3$ in binary are
1001 and
0011, respectively, so $9 \oplus 3 = 10$ (in binary,
1010). #### Constraints
0 ≤ a ≤ 60 0 \leq a \leq 60 0≤a≤60
0 ≤ b ≤ 60 0 \leq b \leq 60 0≤b≤60
KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '&' at position 10: 0 \leq C &̲lt; 2^{60}
All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
a a a b b b C C C
Output
If there is a pair of non-negative integers that satisfies the conditions, choose one such pair ( X , Y ) (X, Y) (X,Y) and print X X X and Y Y Y in this order, with a space in between.
If no such pair exists, print -1.
Sample Input 1
3 4 7
Sample Output 1
28 27
The pair ( X , Y ) = ( 28 , 27 ) (X, Y) = (28, 27) (X,Y)=(28,27) satisfies the conditions.
Here, X X X and Y Y Y in binary are 11100 and 11011, respectively.
X X X in binary is 11100, so popcount ( X ) = 3 \operatorname{popcount}(X) = 3 popcount(X)=3.
Y Y Y in binary is 11011, so popcount ( Y ) = 4 \operatorname{popcount}(Y) = 4 popcount(Y)=4.
X ⊕ Y X \oplus Y X⊕Y in binary is 00111, so X ⊕ Y = 7 X \oplus Y = 7 X⊕Y=7.
If multiple pairs of non-negative integers satisfy the conditions, you may print any of them, so printing 42 45, for example, would also be accepted.
Sample Input 2
34 56 998244353
Sample Output 2
-1
No pair of non-negative integers satisfies the conditions.
Sample Input 3
39 47 530423800524412070
Sample Output 3
540431255696862041 10008854347644927
Note that the values to be printed may not fit in 32 32 32-bit integers.
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);int a, b, c;cin >> a >> b >> c;int r1 = 0, r2 = 0;for (int i = 0; i < 61; i ++)if (c >> i & 1) {if (a > b) r1 += (1ll << i), a --;else r2 += (1ll << i), b --;}if (a != b || a < 0 || b < 0) {cout << -1 << endl;return 0;}for (int i = 0; i < 61; i ++)if (!(c >> i & 1) && a && b)r1 += (1ll << i), r2 += (1ll << i), a --, b --;if (a || b) {cout << -1 << endl;return 0;}cout << r1 << " " << r2 << endl;return 0;
}
E - Set Add Query
Problem Statement
There is an integer sequence A = ( A 1 , A 2 , … , A N ) A=(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N) A=(A1,A2,…,AN) of length N N N, where all elements are initially set to 0 0 0. Also, there is a set S S S, which is initially empty.
Perform the following Q Q Q queries in order. Find the value of each element in the sequence A A A after processing all Q Q Q queries. The i i i-th query is in the following format:
An integer x i x_i xi is given. If the integer x i x_i xi is contained in S S S, remove x i x_i xi from S S S. Otherwise, insert x i x_i xi to S S S. Then, for each j = 1 , 2 , … , N j=1,2,\ldots,N j=1,2,…,N, add ∣ S ∣ |S| ∣S∣ to A j A_j Aj if j ∈ S j\in S j∈S.
Here, ∣ S ∣ |S| ∣S∣ denotes the number of elements in the set S S S. For example, if S = { 3 , 4 , 7 } S=\lbrace 3,4,7\rbrace S={3,4,7}, then ∣ S ∣ = 3 |S|=3 ∣S∣=3.
Constraints
1 ≤ N , Q ≤ 2 × 1 0 5 1\leq N,Q\leq 2\times10^5 1≤N,Q≤2×105
1 ≤ x i ≤ N 1\leq x_i\leq N 1≤xi≤N
All given numbers are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N N N Q Q Q
x 1 x_1 x1 x 2 x_2 x2 … \ldots … x Q x_Q xQ
Output
Print the sequence A A A after processing all queries in the following format:
A 1 A_1 A1 A 2 A_2 A2 … \ldots … A N A_N AN
Sample Input 1
3 4
1 3 3 2
Sample Output 1
6 2 2
In the first query, 1 1 1 is inserted to S S S, making S = { 1 } S=\lbrace 1\rbrace S={1}. Then, ∣ S ∣ = 1 |S|=1 ∣S∣=1 is added to A 1 A_1 A1. The sequence becomes A = ( 1 , 0 , 0 ) A=(1,0,0) A=(1,0,0).
In the second query, 3 3 3 is inserted to S S S, making S = { 1 , 3 } S=\lbrace 1,3\rbrace S={1,3}. Then, ∣ S ∣ = 2 |S|=2 ∣S∣=2 is added to A 1 A_1 A1 and A 3 A_3 A3. The sequence becomes A = ( 3 , 0 , 2 ) A=(3,0,2) A=(3,0,2).
In the third query, 3 3 3 is removed from S S S, making S = { 1 } S=\lbrace 1\rbrace S={1}. Then, ∣ S ∣ = 1 |S|=1 ∣S∣=1 is added to A 1 A_1 A1. The sequence becomes A = ( 4 , 0 , 2 ) A=(4,0,2) A=(4,0,2).
In the fourth query, 2 2 2 is inserted to S S S, making S = { 1 , 2 } S=\lbrace 1,2\rbrace S={1,2}. Then, ∣ S ∣ = 2 |S|=2 ∣S∣=2 is added to A 1 A_1 A1 and A 2 A_2 A2. The sequence becomes A = ( 6 , 2 , 2 ) A=(6,2,2) A=(6,2,2).
Eventually, the sequence becomes A = ( 6 , 2 , 2 ) A=(6,2,2) A=(6,2,2).
Sample Input 2
4 6
1 2 3 2 4 2
Sample Output 2
15 9 12 7
Solution
具体见文末视频。
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;const int N = 2e5 + 10;int n, q;
int a[N], s[N], res[N], id[N];
int cnt[N], lst[N];signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin >> n >> q;int idx = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= q; i ++) {cin >> a[i];if (!id[a[i]]) id[a[i]] = ++ idx;}set<int> S;int r = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= q; i ++) {cnt[a[i]] ++;if (S.count(a[i])) S.erase(a[i]);else S.insert(a[i]);s[i] = s[i - 1] + S.size();r = max(id[a[i]], r);if (S.size()) res[1] += S.size(), res[r + 1] -= S.size();}for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)res[i] += res[i - 1], lst[i] = q;for (int i = q; i >= 1; i --) {if (cnt[a[i]] % 2 == 0) {res[id[a[i]]] -= (s[lst[a[i]]] - s[i - 1]);} else {lst[a[i]] = i - 1;}cnt[a[i]] --;}for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)cout << res[id[i]] << " ";return 0;
}
F - Non-overlapping Squares
Problem Statement
There is an N × N N\times N N×N grid, and the cell at the i i i-th row from the top and the j j j-th column from the left ( 1 ≤ i , j ≤ N ) (1\leq i,j\leq N) (1≤i,j≤N) contains the integer A i , j A _ {i,j} Ai,j.
You are given an integer M M M. When choosing three non-overlapping M × M M\times M M×M grids, find the maximum possible sum of the integers written in the chosen grids.
2 ≤ N ≤ 1000 2\leq N\leq 1000 2≤N≤1000
1 ≤ M ≤ N / 2 1\leq M\leq N/2 1≤M≤N/2
0 ≤ A i , j ≤ 1 0 9 0\leq A _ {i,j}\leq10 ^ 9 0≤Ai,j≤109
All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N N N M M M
A 1 , 1 A _ {1,1} A1,1 A 1 , 2 A _ {1,2} A1,2 … \ldots … A 1 , N A _ {1,N} A1,N
A 2 , 1 A _ {2,1} A2,1 A 2 , 2 A _ {2,2} A2,2 … \ldots … A 2 , N A _ {2,N} A2,N
⋮ \vdots ⋮ ⋮ \ \vdots ⋮ ⋱ \ddots ⋱ ⋮ \vdots ⋮
A N , 1 A _ {N,1} AN,1 A N , 2 A _ {N,2} AN,2 … \ldots … A N , N A _ {N,N} AN,N
Output
Print the answer.
Sample Input 1
7 3
3 1 4 1 5 9 2
6 5 3 5 8 9 7
9 3 2 3 8 4 6
2 6 4 3 3 8 3
2 7 9 5 0 2 8
8 4 1 9 7 1 6
9 3 9 9 3 7 5
Sample Output 1
154
From the given grid, if we choose three 3 × 3 3\times3 3×3 grids as shown in the figure below (this corresponds to setting ( i 1 , j 1 , i 2 , j 2 , i 3 , j 3 ) = ( 1 , 5 , 2 , 1 , 5 , 2 ) (i _ 1,j _ 1,i _ 2,j _ 2,i _ 3,j _ 3)=(1,5,2,1,5,2) (i1,j1,i2,j2,i3,j3)=(1,5,2,1,5,2)), the sum of the numbers written in the chosen grids will be 154 154 154.
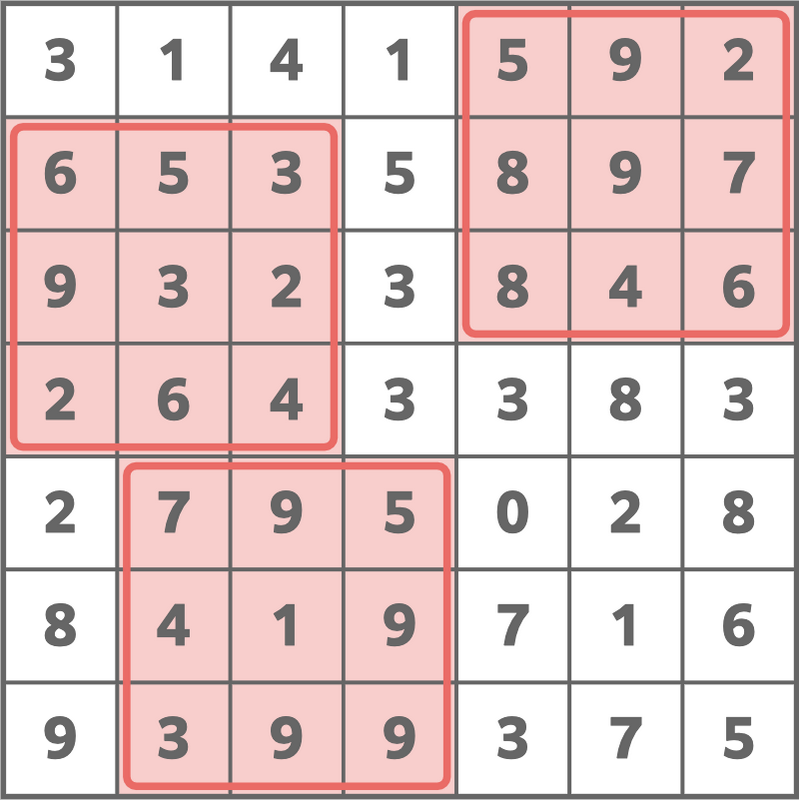
There is no way to make the sum 155 155 155 or greater while satisfying the conditions in the problem statement, so print 154 154 154.
Sample Input 2
7 1
3 1 4 1 5 9 2
6 5 3 5 8 9 7
9 3 2 3 8 4 6
2 6 4 3 3 8 3
2 7 9 5 0 2 8
8 4 1 9 7 1 6
9 3 9 9 3 7 5
Sample Output 2
27
The following choice is optimal.
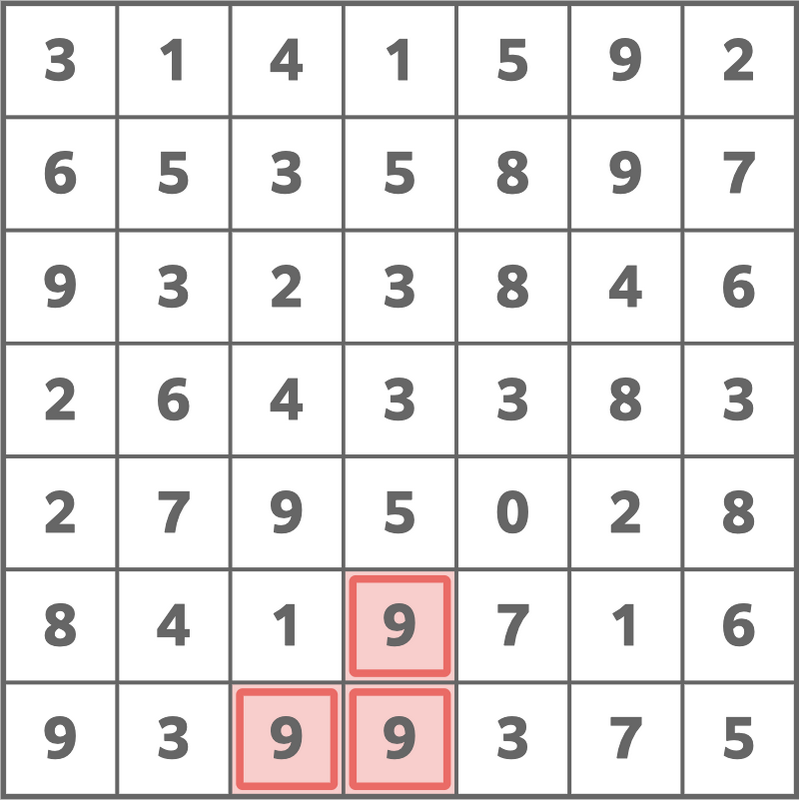
Sample Input 3
16 4
74 16 58 32 97 52 43 51 40 58 13 24 65 11 63 29
98 75 40 77 15 50 83 85 35 46 38 37 56 38 63 55
95 42 10 70 53 40 25 10 70 32 33 19 52 79 74 58
33 91 53 11 65 63 78 77 81 46 81 63 11 82 55 62
39 95 92 69 77 89 14 84 53 78 71 81 66 39 96 29
74 26 60 55 89 35 32 64 17 26 74 92 84 33 59 82
23 69 10 95 94 14 58 58 97 95 62 58 72 55 71 43
93 77 27 87 74 72 91 37 53 80 51 71 37 35 97 46
81 88 26 79 78 30 53 68 83 28 59 28 74 55 20 86
93 13 25 19 53 53 17 24 69 14 67 81 10 19 69 90
88 83 62 92 22 31 27 34 67 48 42 32 68 14 96 87
44 69 25 48 68 42 53 82 44 42 96 31 13 56 68 83
63 87 24 75 16 70 63 99 95 10 63 26 56 12 77 49
94 83 69 95 48 41 40 97 45 61 26 38 83 91 44 31
43 69 54 64 20 60 17 15 62 25 58 50 59 63 88 70
72 95 21 28 41 14 77 22 64 78 33 55 67 51 78 40
Sample Output 3
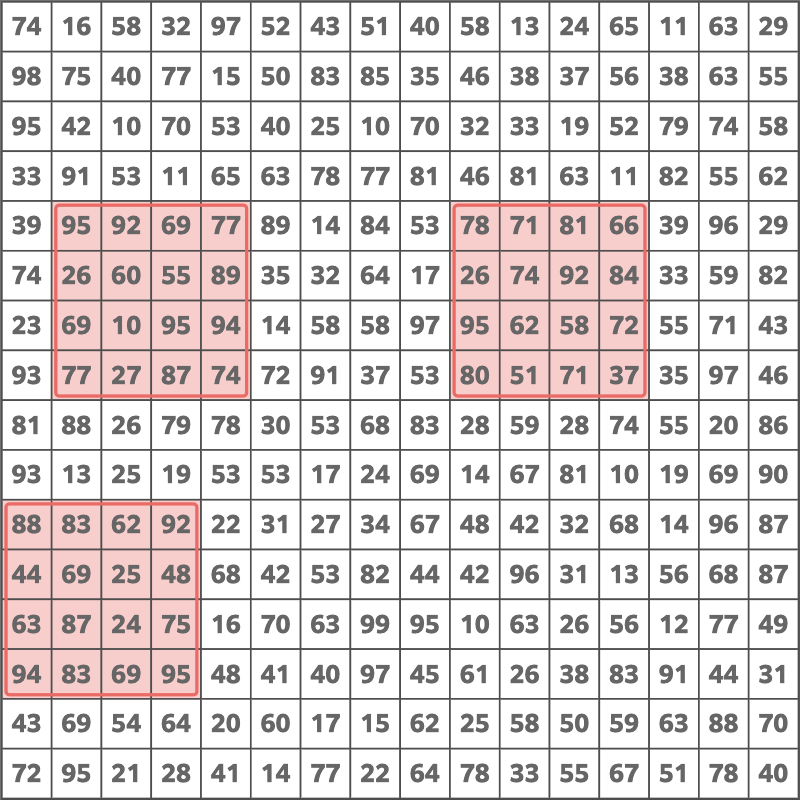
3295
The following choice is optimal.
Solution
后期补一下这题目的视频
Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define fi first
#define se second
#define int long longusing namespace std;typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;const int N = 1e3 + 10;int n, m;
int a[N][N], s[N][N], ln[N], cl[N];
int lu[N][N], ld[N][N], ru[N][N], rd[N][N];signed main() {cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin >> n >> m;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++)cin >> a[i][j], a[i][j] += a[i][j - 1] + a[i - 1][j] - a[i - 1][j - 1];for (int i = 1; i <= n - m + 1; i ++)for (int j = 1; j <= n - m + 1; j ++) {s[i][j] = a[i + m - 1][j + m - 1] - a[i - 1][j + m - 1] - a[i + m - 1][j - 1] + a[i - 1][j - 1];ln[i] = max(ln[i], s[i][j]), cl[j] = max(cl[j], s[i][j]);}for (int i = m; i <= n; i ++)for (int j = m; j <= n; j ++)lu[i][j] = max(max(lu[i - 1][j], lu[i][j - 1]), s[i - m + 1][j - m + 1]);for (int i = n - m + 1; i >= 1; i --)for (int j = m; j <= n; j ++)ld[i][j] = max(max(ld[i + 1][j], ld[i][j - 1]), s[i][j - m + 1]);for (int i = m; i <= n; i ++)for (int j = n - m + 1; j >= 1; j --)ru[i][j] = max(max(ru[i - 1][j], ru[i][j + 1]), s[i - m + 1][j]);for (int i = n - m + 1; i >= 1; i --)for (int j = n - m + 1; j >= 1; j --)rd[i][j] = max(max(rd[i + 1][j], rd[i][j + 1]), s[i][j]);int res = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)for (int j = 1; j <= n; j ++) {res = max(res, lu[i][j] + ru[i][j + 1] + ld[i + 1][n]);res = max(res, lu[i][j] + ld[i + 1][j] + rd[1][j + 1]);res = max(res, ld[i][j] + rd[i][j + 1] + ru[i - 1][1]);res = max(res, ru[i][j] + rd[i + 1][j] + ld[1][j - 1]);}for (int i = m; i <= n; i ++) {int mx1 = 0, mx2 = 0;for (int j = i + m; j <= n; j ++) {mx1 = max(mx1, ln[j - m + 1]), mx2 = max(mx2, cl[j - m + 1]);res = max(res, ru[i][1] + mx1 + rd[j + 1][1]);res = max(res, ld[1][i] + mx2 + rd[1][j + 1]);}}cout << res << endl;return 0;
}
视频题解
Atcoder Beginner Contest 347(A ~ E 讲解)
欢迎大家关注我的B站空间:https://space.bilibili.com/630340560
最后祝大家早日
这篇关于AtCoder Beginner Contest 347 (ABCDEF题)视频讲解的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





