本文主要是介绍Tensorflow2.笔记 - 单层感知机(单输出,多输出)Single Layer Perceptron,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
本笔记主要记录单层感知机的相关内容,包括单层单输出,和单层多输出。
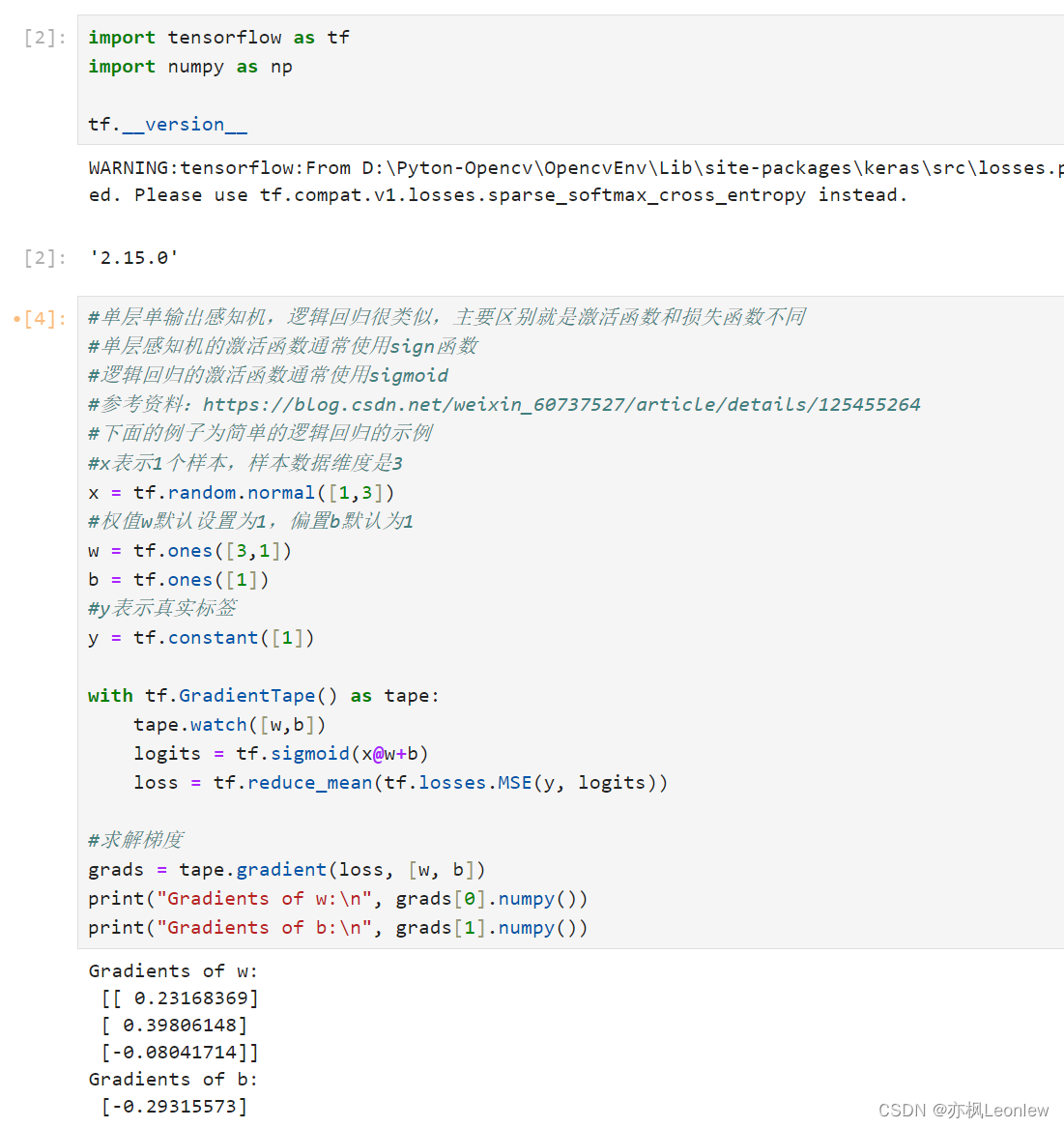
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as nptf.__version__#单层单输出感知机,逻辑回归很类似,主要区别就是激活函数和损失函数不同
#单层感知机的激活函数通常使用sign函数
#逻辑回归的激活函数通常使用sigmoid
#参考资料:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_60737527/article/details/125455264
#下面的例子为简单的逻辑回归的示例
#x表示1个样本,样本数据维度是3
x = tf.random.normal([1,3])
#权值w默认设置为1,偏置b默认为1
w = tf.ones([3,1])
b = tf.ones([1])
#y表示真实标签
y = tf.constant([1])with tf.GradientTape() as tape:tape.watch([w,b])logits = tf.sigmoid(x@w+b)loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.losses.MSE(y, logits))#求解梯度
grads = tape.gradient(loss, [w, b])
print("Gradients of w:\n", grads[0].numpy())
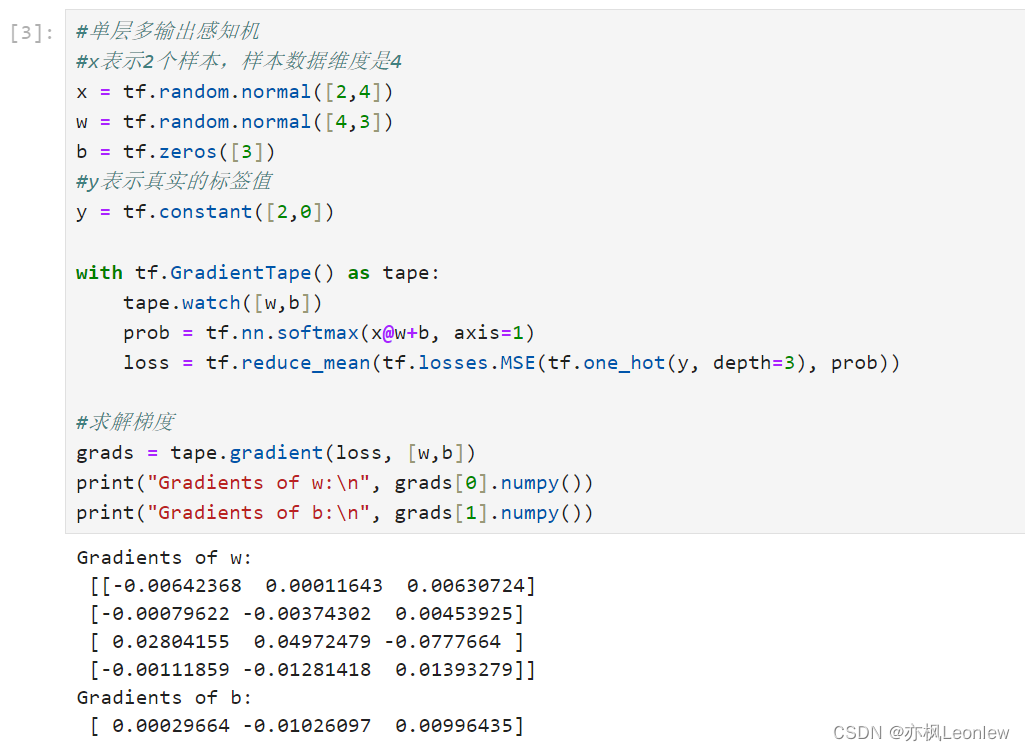
print("Gradients of b:\n", grads[1].numpy())#单层多输出感知机
#x表示2个样本,样本数据维度是4
x = tf.random.normal([2,4])
w = tf.random.normal([4,3])
b = tf.zeros([3])
#y表示真实的标签值
y = tf.constant([2,0])with tf.GradientTape() as tape:tape.watch([w,b])prob = tf.nn.softmax(x@w+b, axis=1)loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.losses.MSE(tf.one_hot(y, depth=3), prob))#求解梯度
grads = tape.gradient(loss, [w,b])
print("Gradients of w:\n", grads[0].numpy())
print("Gradients of b:\n", grads[1].numpy())
运行结果:
这篇关于Tensorflow2.笔记 - 单层感知机(单输出,多输出)Single Layer Perceptron的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







