本文主要是介绍java中,正则表达式的使用 (最普通使用,Group,贪婪模式),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
0.最普通的使用
1.正则表达式有Group功能。
2.正则表达式中的贪婪模式, 非贪婪模式(*?)
3.find() 与 matches() 之间的区别
↓循环获取所有文件
↓文件内部内容读取操作
Files.lines 这个方法是java8中,新增加的方法。
Stream 构造类时,指定泛型,传递到方法中使用。
■扩展
1.正则表达式中^的用法
用法一: 限定开头
用法二:(否)取反
区别方法
■ Summary of regular-expression constructs
java中,正则表达式的使用
0.最普通的使用
Pattern ptn;
Matcher matStr;
String checkRE = ”^([a-zA-Z0-9])+([a-zA-Z0-9\\._-])*@([a-zA-Z0-9_-])+([a-zA-Z0-9\\._-])+$”ptn = Pattern.compile(checkRE);
matStr = ptn.matcher(str)if (!matStr.find()){return false;
}2020 / 01 / 05
以上所写的只是最基本的使用。除此之外还有以下功能
1.正则表达式有Group功能。
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;class HelloWorld {public static void main(String args[]){String checkRE = "^([a-zA-Z0-9])+@([a-zA-Z0-9\\.]+)$";Pattern ptn = Pattern.compile(checkRE);Matcher matStr = ptn.matcher("sxz@csnd.com");System.out.println(matStr.find());System.out.println(matStr.groupCount());System.out.println(matStr.group(2));}
}--
运行结果如下
true
2
csnd.com
--
使用group定义正则之后,我们不但可以使用原有的匹配功能,
还可以指定我们想要抽出部分的内容
2.正则表达式中的贪婪模式, 非贪婪模式(*?)
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;class HelloWorld {public static void main(String args[]){String checkRE = "^([a-zA-Z0-9])+@([a-zA-Z0-9\\.]+)$";Pattern ptn = Pattern.compile(checkRE);Matcher matStr = ptn.matcher("sxz@csnd.com");System.out.println(matStr.find());System.out.println(matStr.groupCount());System.out.println(matStr.group(2));System.out.println(matStr.group());System.out.println("--------------------------");// 正则表达式中的贪婪模式 默认开启checkRE = "<div>.*</div>";ptn = Pattern.compile(checkRE);matStr = ptn.matcher("sxzaadivaa<div>123</div><div>456</div>aaass");System.out.println(matStr.find());System.out.println(matStr.groupCount());System.out.println(matStr.group()+" 位置:["+matStr.start()+","+matStr.end()+"]");System.out.println("--------------------------");// 正则表达式中 非贪婪模式 (使用「?」)checkRE = "<div>.*?</div>*";ptn = Pattern.compile(checkRE);matStr = ptn.matcher("sxzaadivaa<div>123</div><div>456</div>aaass");System.out.println(matStr.find());System.out.println(matStr.groupCount());System.out.println(matStr.group()+" 位置:["+matStr.start()+","+matStr.end()+"]");System.out.println("--------------------------");}
}以上代码,运行结果如下。

------------------------------------
3.find() 与 matches() 之间的区别
find()
package com.sxz.test;import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;public class TestPatternFindMatches {public static void main(String[] args) {int count = 0;String regEx = "[\\u4e00-\\u9fa5]";String str = "中文fdas ";Pattern p = Pattern.compile(regEx);Matcher m = p.matcher(str);while (m.find()) {count = count + 1;System.out.println(m.groupCount());System.out.println(m.group());}System.out.println("共有 " + count + "个 ");}
}
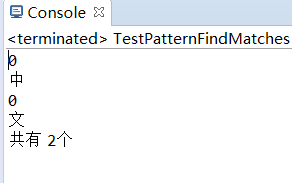
---
matches() //下面 代码 33行中使用
整理中。。。
package com.sxz.test;import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
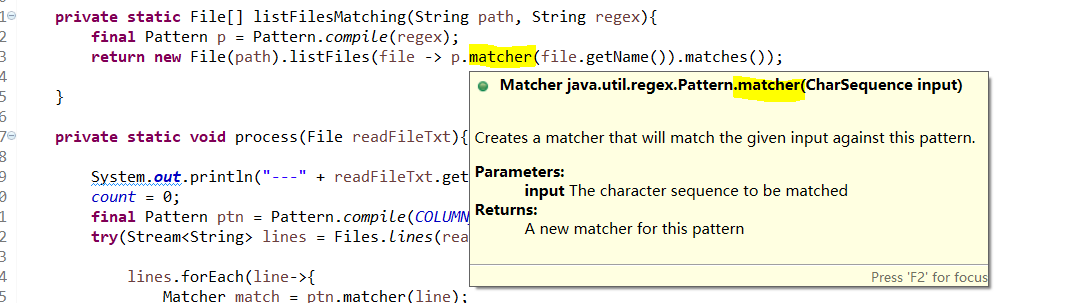
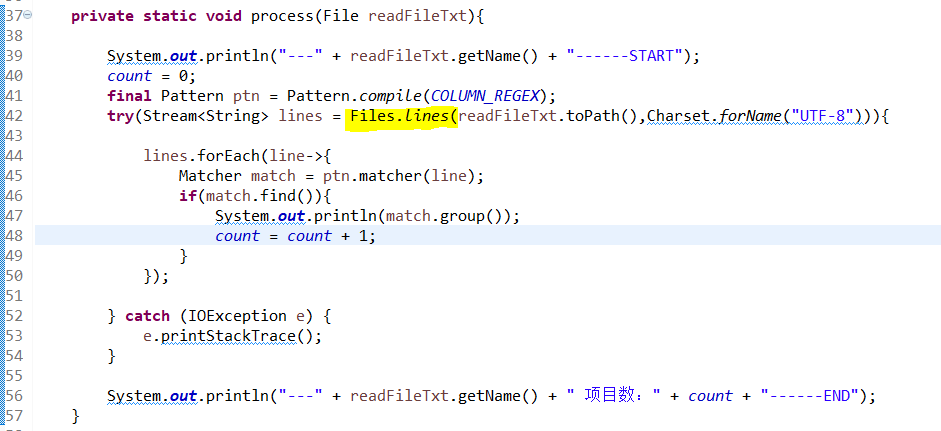
import java.util.stream.Stream;public class TestFileOperate {private static String BATH_PATH = "C:\\test\\";private static String COLUMN_REGEX="<itemName>.*?</itemName>";public static int count;public static void main(String[] args) {getFileNameAndPrintColumnName("test001");}public static void getFileNameAndPrintColumnName(String folderName){File[] files = listFilesMatching(BATH_PATH + folderName, ".*\\.(txt|TXT)$");List<File> listFile = Arrays.asList(files);listFile.stream().forEach(readFileTxt -> process(readFileTxt));}private static File[] listFilesMatching(String path, String regex){final Pattern p = Pattern.compile(regex);return new File(path).listFiles(file -> p.matcher(file.getName()).matches());}private static void process(File readFileTxt){System.out.println("---" + readFileTxt.getName() + "------START");count = 0;final Pattern ptn = Pattern.compile(COLUMN_REGEX);try(Stream<String> lines = Files.lines(readFileTxt.toPath(),Charset.forName("UTF-8"))){lines.forEach(line->{Matcher match = ptn.matcher(line);if(match.find()){System.out.println(match.group());count = count + 1;}});} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("---" + readFileTxt.getName() + " 项目数:" + count + "------END");}}---
↓循环获取所有文件

----

----
---
 ---
---
↓文件内部内容读取操作
============================================
---
Files这类,是1.7中,新增加的类。

---
Files.lines 这个方法是java8中,新增加的方法。

读取一个文件中所有的行。

---

---
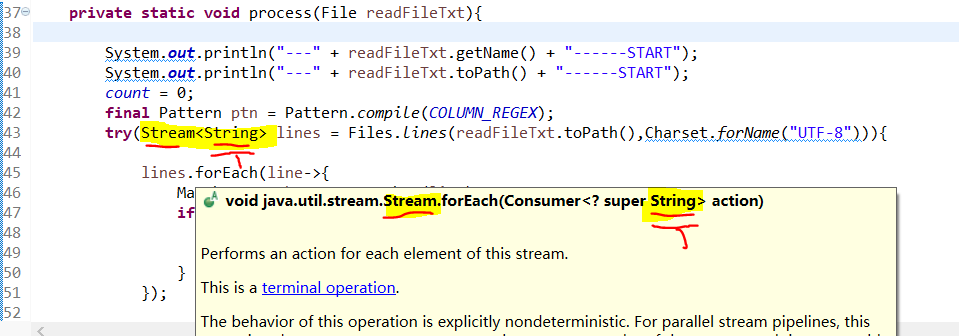
Stream中的forEach方法

----
Stream<T> 构造类时,指定泛型,传递到方法中使用。
---
■扩展
1.正则表达式中^的用法
用法一: 限定开头
文档上给出了解释是匹配输入的开始,如果多行标示被设置成了true,同时会匹配后面紧跟的字符
比如 /^A/会匹配"An e"中的A,但是不会匹配"ab A"中的A/[(^\s+)(\s+$)]/g(^cat)$(^cat$)^(cat)$^(cat$)用法二:(否)取反
当这个字符出现在一个字符集合模式的第一个字符时,他将会有不同的含义。
比如: /[^a-z\s]/会匹配"my 3 sisters"中的"3"
这里的”^”的意思是字符类的否定,
上面的正则表达式的意思是匹配不是(a到z和空白字符)的字符。 [^a]表示“匹配除了a的任意字符”。[^a-zA-Z0-9]表示“找到一个非字母也非数字的字符”。[\^abc]表示“找到一个插入符或者a或者b或者c”。区别方法
经过对比,只要是”^”这个字符是在中括号”[]”中被使用的话就是表示字符类的否定,
如果不是的话就是表示限定开头。我这里说的是直接在”[]”中使用,不包括嵌套使用。
其实也就是说”[]”代表的是一个字符集,”^”只有在字符集中才是反向字符集的意思。
----
■ Summary of regular-expression constructs
■Character classes
[abc] a, b, or c (simple class)
[^abc] Any character except a, b, or c (negation)
[a-zA-Z] a through z or A through Z, inclusive (range)
[a-d[m-p]] a through d, or m through p: [a-dm-p] (union)
[a-z&&[def]] d, e, or f (intersection)
[a-z&&[^bc]] a through z, except for b and c: [ad-z] (subtraction)
[a-z&&[^m-p]] a through z, and not m through p: [a-lq-z](subtraction) ■Predefined character classes
. Any character (may or may not match line terminators)
\d A digit: [0-9]
\D A non-digit: [^0-9]
\h A horizontal whitespace character: [ \t\xA0\u1680\u180e\u2000-\u200a\u202f\u205f\u3000]
\H A non-horizontal whitespace character: [^\h]
\s A whitespace character: [ \t\n\x0B\f\r]
\S A non-whitespace character: [^\s]
\v A vertical whitespace character: [\n\x0B\f\r\x85\u2028\u2029]
\V A non-vertical whitespace character: [^\v]
\w A word character: [a-zA-Z_0-9]
\W A non-word character: [^\w] ■Boundary matchers
^ The beginning of a line
$ The end of a line
\b A word boundary
\B A non-word boundary
\A The beginning of the input
\G The end of the previous match
\Z The end of the input but for the final terminator, if any
\z The end of the input ■Characters
x The character x
\\ The backslash character
\0n The character with octal value 0n (0 <= n <= 7)
\0nn The character with octal value 0nn (0 <= n <= 7)
\0mnn The character with octal value 0mnn (0 <= m <= 3, 0 <= n <= 7)
\xhh The character with hexadecimal value 0xhh
\uhhhh The character with hexadecimal value 0xhhhh
\x{h...h} The character with hexadecimal value 0xh...h (Character.MIN_CODE_POINT <= 0xh...h <= Character.MAX_CODE_POINT)
\t The tab character ('\u0009')
\n The newline (line feed) character ('\u000A')
\r The carriage-return character ('\u000D')
\f The form-feed character ('\u000C')
\a The alert (bell) character ('\u0007')
\e The escape character ('\u001B')
\cx The control character corresponding to x ■POSIX character classes (US-ASCII only)
\p{Lower} A lower-case alphabetic character: [a-z]
\p{Upper} An upper-case alphabetic character:[A-Z]
\p{ASCII} All ASCII:[\x00-\x7F]
\p{Alpha} An alphabetic character:[\p{Lower}\p{Upper}]
\p{Digit} A decimal digit: [0-9]
\p{Alnum} An alphanumeric character:[\p{Alpha}\p{Digit}]
\p{Punct} Punctuation: One of !"#$%&'()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\]^_`{|}~
\p{Graph} A visible character: [\p{Alnum}\p{Punct}]
\p{Print} A printable character: [\p{Graph}\x20]
\p{Blank} A space or a tab: [ \t]
\p{Cntrl} A control character: [\x00-\x1F\x7F]
\p{XDigit} A hexadecimal digit: [0-9a-fA-F]
\p{Space} A whitespace character: [ \t\n\x0B\f\r] ■java.lang.Character classes (simple java character type)
\p{javaLowerCase} Equivalent to java.lang.Character.isLowerCase()
\p{javaUpperCase} Equivalent to java.lang.Character.isUpperCase()
\p{javaWhitespace} Equivalent to java.lang.Character.isWhitespace()
\p{javaMirrored} Equivalent to java.lang.Character.isMirrored() ■Classes for Unicode scripts, blocks, categories and binary properties
\p{IsLatin} A Latin script character (script)
\p{InGreek} A character in the Greek block (block)
\p{Lu} An uppercase letter (category)
\p{IsAlphabetic} An alphabetic character (binary property)
\p{Sc} A currency symbol
\P{InGreek} Any character except one in the Greek block (negation)
[\p{L}&&[^\p{Lu}]] Any letter except an uppercase letter (subtraction) ■Linebreak matcher
\R Any Unicode linebreak sequence, is equivalent to \u000D\u000A|[\u000A\u000B\u000C\u000D\u0085\u2028\u2029] ■Greedy quantifiers
X? X, once or not at all
X* X, zero or more times
X+ X, one or more times
X{n} X, exactly n times
X{n,} X, at least n times
X{n,m} X, at least n but not more than m times ■Reluctant quantifiers
X?? X, once or not at all
X*? X, zero or more times
X+? X, one or more times
X{n}? X, exactly n times
X{n,}? X, at least n times
X{n,m}? X, at least n but not more than m times ■Possessive quantifiers
X?+ X, once or not at all
X*+ X, zero or more times
X++ X, one or more times
X{n}+ X, exactly n times
X{n,}+ X, at least n times
X{n,m}+ X, at least n but not more than m times ■Logical operators
XY X followed by Y
X|Y Either X or Y
(X) X, as a capturing group ■Back references
\n Whatever the nth capturing group matched
\k<name> Whatever the named-capturing group "name" matched ■Quotation
\ Nothing, but quotes the following character
\Q Nothing, but quotes all characters until \E
\E Nothing, but ends quoting started by \Q ■Special constructs (named-capturing and non-capturing)
(?<name>X) X, as a named-capturing group
(?:X) X, as a non-capturing group
(?idmsuxU-idmsuxU) Nothing, but turns match flags i d m s u x U on - off
(?idmsux-idmsux:X) X, as a non-capturing group with the given flags i d m s u x on - off
(?=X) X, via zero-width positive lookahead
(?!X) X, via zero-width negative lookahead
(?<=X) X, via zero-width positive lookbehind
(?<!X) X, via zero-width negative lookbehind
(?>X) X, as an independent, non-capturing group
----
这篇关于java中,正则表达式的使用 (最普通使用,Group,贪婪模式)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





