本文主要是介绍Faster RCNN源码解读4-其他收尾工作:ROI_pooling、分类、回归等,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
Faster RCNN复现
Faster RCNN源码解读1-整体流程和各个子流程梳理
Faster RCNN源码解读2-_anchor_component()为图像建立anchors(核心和关键1)
Faster RCNN源码解读3.1-_region_proposal() 筛选anchors-_proposal_layer()(核心和关键2)
Faster RCNN源码解读3.2-_region_proposal()筛选anchors-_anchor_target_layer()(核心和关键2)
Faster RCNN源码解读3.3-_region_proposal() 筛选anchors-_proposal_target_layer()(核心和关键2)
Faster RCNN源码解读4-其他收尾工作:ROI_pooling、分类、回归等
Faster RCNN源码解读5-损失函数
理论介绍:有关Faster RCNN理论介绍的文章,可以自行搜索,这里就不多说理论部分了。
复现过程:代码配置过程没有记录,具体怎么把源码跑起来需要自己搜索一下。
faster rcnn源码确实挺复杂的,虽然一步步解析了,但是觉得还是没有领会其中的精髓,只能算是略知皮毛。在这里将代码解析的过程给大家分享一下,希望对大家有帮助。先是解析了代码的整体结构,然后对各个子结构进行了分析。代码中的注释,有的是原来就有的注释,有的是参考网上别人的,有的是自己理解的,里面或多或少会有些错误,如果发现,欢迎指正!
本文解析的源码地址:https://github.com/lijianaiml/tf-faster-rcnn-windows
之前通过_region_proposal() 产生w*h*9个anchors,并通过相关操作筛选出256个包含正负样本的rois,接下来进行最后的分类和回归操作。
_crop_pool_layer()
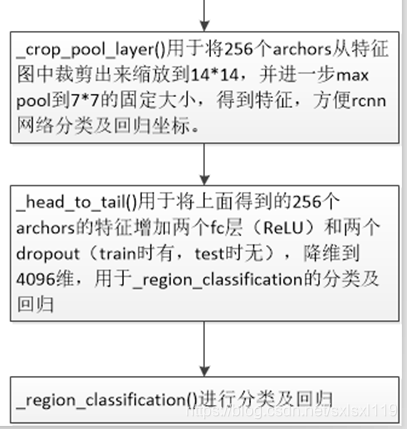
_crop_pool_layer用于将256个archors从特征图中裁剪出来缩放到14*14,并进一步max pool到7*7的固定大小,得到特征,方便rcnn网络分类及回归坐标,得到pool5。
'''_crop_pool_layer用于将256个archors从特征图中裁剪出来缩放到14*14,并进一步max pool到7*7的固定大小,得到特征,方便rcnn网络分类及回归坐标。该函数先得到特征图对应的原始图像的宽高,而后将原始图像对应的rois进行归一化,并使用tf.image.crop_and_resize(该函数需要归一化的坐标信息)缩放到[cfg.POOLING_SIZE * 2,cfg.POOLING_SIZE * 2],最后通过slim.max_pool2d进行pooling,输出大小依旧一样(25677*512)。tf.slice(rois, [0, 0], [-1, 1])是对输入进行切片。其中第二个参数为起始的坐标,第三个参数为切片的尺寸。注意,对于二维输入,后两个参数均为y,x的顺序;对于三维输入,后两个均为z,y,x的顺序。当第三个参数为-1时,代表取整个该维度。上面那句是将roi的从0,0开始第一列的数据(y为-1,代表所有行,x为1,代表第一列)'''def _crop_pool_layer(self, bottom, rois, name):with tf.variable_scope(name) as scope:batch_ids = tf.squeeze(tf.slice(rois, [0, 0], [-1, 1], name="batch_id"), [1]) #得到第一列,为类别# Get the normalized coordinates of bounding boxesbottom_shape = tf.shape(bottom)height = (tf.to_float(bottom_shape[1]) - 1.) * np.float32(self._feat_stride[0])width = (tf.to_float(bottom_shape[2]) - 1.) * np.float32(self._feat_stride[0])x1 = tf.slice(rois, [0, 1], [-1, 1], name="x1") / width #由于crop_and_resize的bboxes范围为0-1,得到归一化的坐标y1 = tf.slice(rois, [0, 2], [-1, 1], name="y1") / heightx2 = tf.slice(rois, [0, 3], [-1, 1], name="x2") / widthy2 = tf.slice(rois, [0, 4], [-1, 1], name="y2") / height# Won't be back-propagated to rois anyway, but to save timebboxes = tf.stop_gradient(tf.concat([y1, x1, y2, x2], axis=1))pre_pool_size = cfg.POOLING_SIZE * 2# 根据bboxes裁减出256个特征,并缩放到14*14(channels和bottem的channels一样)batchsize为256crops = tf.image.crop_and_resize(bottom, bboxes, tf.to_int32(batch_ids), [pre_pool_size, pre_pool_size], name="crops")return slim.max_pool2d(crops, [2, 2], padding='SAME') #max pool后得到7*7的特征_head_to_tail()
_head_to_tail用于将上面得到的256个archors的特征(经过ROI_pooling操作后的pool5)增加两个fc层(ReLU)和两个dropout(train时有,test时无),降维到4096维,用于_region_classification的分类及回归。_head_to_tail位于lib / nets / vgg16.py中,得到fc7。
'''_head_to_tail用于将上面得到的256个archors的特征增加两个fc层(ReLU)
和两个dropout(train时有,test时无),降维到4096维,用于_region_classification的分类及回归。'''def _head_to_tail(self, pool5, is_training, reuse=None):with tf.variable_scope(self._scope, self._scope, reuse=reuse):pool5_flat = slim.flatten(pool5, scope='flatten')fc6 = slim.fully_connected(pool5_flat, 4096, scope='fc6')if is_training:fc6 = slim.dropout(fc6, keep_prob=0.5, is_training=True, scope='dropout6')fc7 = slim.fully_connected(fc6, 4096, scope='fc7')if is_training:fc7 = slim.dropout(fc7, keep_prob=0.5, is_training=True, scope='dropout7')return fc7_region_classification()
根据上面得到的fc7,通过_region_classification进行分类及回归。
'''fc7通过_region_classification进行分类及回归。fc7先通过fc层(无ReLU)降维到21层(类别数,得到cls_score),得到概率cls_prob及预测值cls_pred(用于rcnn的分类)。另一方面fc7通过fc层(无ReLU),降维到21*4,得到bbox_pred(用于rcnn的回归)。'''def _region_classification(self, fc7, is_training, initializer, initializer_bbox):cls_score = slim.fully_connected(fc7, self._num_classes, weights_initializer=initializer,trainable=is_training,activation_fn=None, scope='cls_score')cls_prob = self._softmax_layer(cls_score, "cls_prob")cls_pred = tf.argmax(cls_score, axis=1, name="cls_pred")bbox_pred = slim.fully_connected(fc7, self._num_classes * 4, weights_initializer=initializer_bbox,trainable=is_training,activation_fn=None, scope='bbox_pred')self._predictions["cls_score"] = cls_scoreself._predictions["cls_pred"] = cls_predself._predictions["cls_prob"] = cls_probself._predictions["bbox_pred"] = bbox_predreturn cls_prob, bbox_pred
这篇关于Faster RCNN源码解读4-其他收尾工作:ROI_pooling、分类、回归等的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






