本文主要是介绍文献速递:帕金森的疾病分享--多模态机器学习预测帕金森病,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文献速递:帕金森的疾病分享–多模态机器学习预测帕金森病
Title
题目
Multi-modality machine learning predicting Parkinson’s disease
多模态机器学习预测帕金森病
01
文献速递介绍
对于渐进性神经退行性疾病,早期和准确的诊断是有效开发和使用新干预措施的关键。这种早期检测范式旨在在患者认识到症状和体征之前,当疾病过程最容易接受干预时,识别、分析并防止或管理疾病。
这里我们描述的工作通过数据驱动的方式使用成本效益高的方法促进准确和早期诊断。这份报告还描述了在促进生产规模分析多模态基因组和临床数据的背景下,应用一个开源自动机器学习(ML),GenoML,的情况。
国家人类基因组研究所发布的最新战略愿景声明,到2030年,表观遗传学和转录组学的特征将常规地纳入到基因型对表型影响的预测模型中。生物医学研究人员目前正处于两项科学进展的交汇点,这将促进早期检测和远程识别潜在高风险个体:首先,大量临床、人口统计和遗传/基因组数据集的可用性;其次,机器学习(ML)流程自动化和人工智能的进展,以最大化利用这些大量的、容易获得的数据的价值。
首次就诊时的正确临床诊断,只有80%在病理学上确认为帕金森病(PD)。以前的生物标志物研究,特别是在神经退行性疾病中,主要关注广为人知的统计方法和线性模型,使用单一指标或少数几个指标进行预测。在过去几年中,多项研究使用ML探索了不同的模态,如CSF生物标志物、成像、RNA或包括与运动相关的指标,甚至可穿戴传感器数据。虽然这些努力在分类上表现良好,但我们寻求基于相对低成本且容易获得的数据构建模型。
Results
结果
We have shown that integrating multiple modalities improved model performance in predicting PD diagnosis in a mixed population of cases and controls. For a summary of basic clinical and demographic features, please refer to Table 1 and for a summary of the analysis, please refer to Fig. 1. Additional information in regards to cohorts and interpretation for ML metrics and models are included in Supplementary Notes 2, 3. Our multi-modality model showed a higher area under the curve (AUC;89.72%) than just the clinico-demographic data available prior to neurological assessment (87.52%), the genetics-only model from genome sequencing data and polygenic risk score (PRS; 70.66%), or the transcriptomics-only model from genome-wide whole blood RNA sequencing data (79.73%) in withheld PPMI samples(see Table 2 and Fig. 2 for summaries). This model’s performance improved after tuning, described below and in Table 3, where the mean AUC metric in the untuned model in PPMI is 80.75 with a standard deviation of 8.84 (range = 69.44–88.51) and the mean AUC at tuning in PPMI is 82.17 with a standard deviation of 8.96 (range = 70.93–90.17). Similar improvements can be seen when this model is validated in the PDBP dataset (AUC from the combined modality model at 83.84% before tuning) detailed in Table 4 and Fig. 3. Additionally, the multimodal model also had the lowest false positive and false negative rates compared to other models, only focusing on a single modality, in both the withheld test set in PPMI and in the PDBP validation set. Thus, moving from single to multiple data modalities yielded better results in not only AUC but across all performance metrics
结合多种模态的预测超越了基于单一模态的预测
我们已经展示了,将多种模态整合在一起可以提高模型在混合病例和对照组人群中预测PD诊断的性能。关于基本临床和人口统计特征的摘要,请参见表1,关于分析的摘要,请参见图1。关于队列和解释ML指标及模型的附加信息包含在补充说明2、3中。我们的多模态模型显示出的曲线下面积(AUC;89.72%)高于仅有的临床-人口统计数据(在神经学评估之前可获得的数据;87.52%)、仅基因组测序数据和多基因风险评分(PRS;70.66%)的遗传学模型,或仅来自全基因组全血RNA测序数据的转录组学模型(79.73%)在保留的PPMI样本中(见表2和图2以获取摘要)。在调整后,此模型的性能得到改善,如下所述及表3中,未调整模型在PPMI的平均AUC指标为80.75,标准差为8.84(范围=69.44–88.51),而在PPMI调整后的平均AUC为82.17,标准差为8.96(范围=70.93–90.17)。当这个模型在PDBP数据集中得到验证时,可以看到类似的改进(调整前结合模态模型的AUC为83.84%),详细内容见表4和图3。此外,与其他仅关注单一模态的模型相比,多模态模型在保留的PPMI测试集和PDBP验证集中都具有最低的假阳性和假阴性率。因此,从单一数据模态转向多种数据模态不仅在AUC上,而且在所有性能指标上都取得了更好的结果。
Fig
图

Fig. 1 Workflow and Data Summary. Scientific notation in the workflow diagram denotes minimum p values from reference GWAS or differential expression studies as a pre-screen for feature inclusion. Blue indicates subsets of genetics data (also denoted as “G”), green indicates subsets of transcriptomics data (also denoted as *omics or “O”), yellow indicates clinico-demographic data (also denoted as C + D),and purple indicates combined data modalities. PD Parkinson’s disease, AMP-PD accelerating medicines partnership in Parkinson’s disease, PPMI Parkinson’s progression marker initiative, PDBP Parkinson’s disease biomarker program, WGS whole-genome sequencing, GWAS genome-wide association study, QC quality control, MAF minor allele frequency, PRS polygenic risk score.
图1 工作流程和数据摘要。工作流程图中的科学记号表示来自参考GWAS或差异表达研究的最小p值,作为特征包含的预筛选。蓝色表示遗传数据子集(也标记为“G”),绿色表示转录组数据子集(也标记为*组学或“O”),黄色表示临床-人口统计数据(也标记为C + D),紫色表示结合了数据模态。PD帕金森病,AMP-PD加速医药合作伙伴关系帕金森病项目,PPMI帕金森病进展标志物计划,PDBP帕金森病生物标志物计划,WGS全基因组测序,GWAS全基因组关联研究,QC质量控制,MAF小等位基因频率,PRS多基因风险评分。
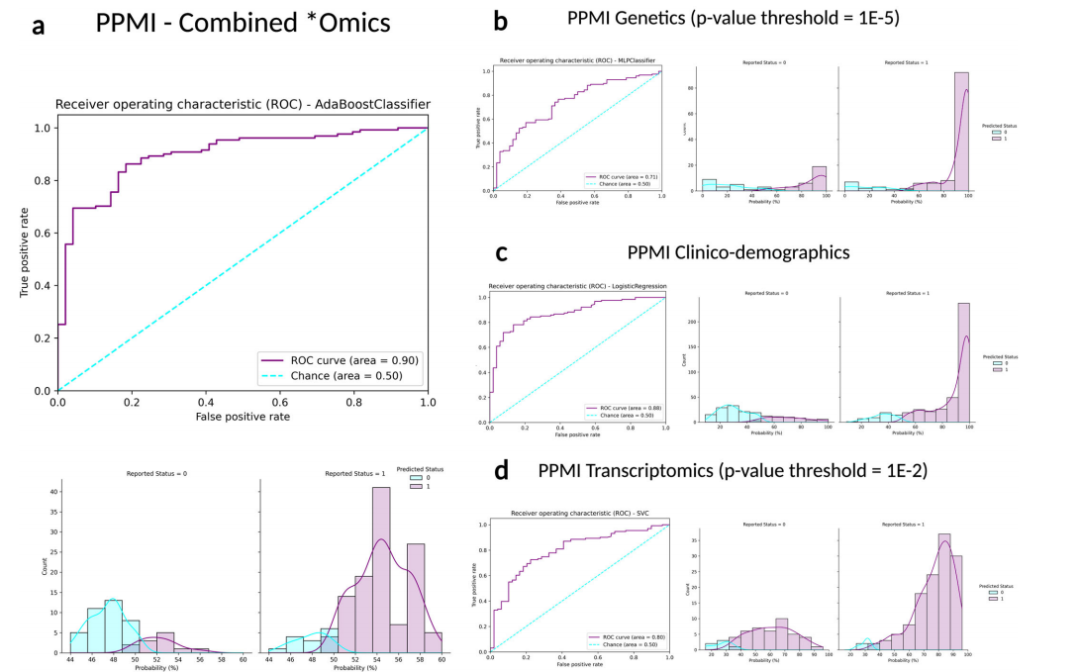
Fig. 2Receiver operating characteristic curves and case probability density plots in withheld training samples at default thresholds comparing performance metrics in different data modalities from the PPMI dataset. P values mentioned indicate the threshold of
significance used per datatype, except for the inclusion of all clinico-demographic features. a PPMI combined *omics dataset (genetics p value threshold = 1E-5, transcriptomics p value threshold = 1E-2, and clinico-demographic information); b PPMI genetics-only dataset (p value threshold = 1E-5); c PPMI clinico-demographics only dataset; d PPMI transcriptomics-only dataset (p value threshold = 1E-2). Note that x-axis limits may vary as some models produce less extreme probability distributions than others inherently based on fit to the input data and the algorithm used, further detailed images are included in Supplementary Fig. 5. PPMI Parkinson’s progression marker initiative, ROC receiver operating characteristic curve.
图2 在默认阈值下,比较PPMI数据集中不同数据模态的性能指标,保留训练样本中的接收器操作特征曲线和案例概率密度图。提到的P值表示每种数据类型使用的显著性阈值,除了包含所有临床-人口统计特征外。a PPMI综合*组学数据集(遗传学P值阈值=1E-5,转录组学P值阈值=1E-2,以及临床-人口统计信息);b PPMI仅遗传学数据集(P值阈值=1E-5);c PPMI仅临床-人口统计数据集;d PPMI仅转录组学数据集(P值阈值=1E-2)。请注意,x轴的限制可能会有所不同,因为一些模型基于对输入数据的适应度和使用的算法,天生就会产生比其他模型更不极端的概率分布,更详细的图像包含在补充图5中。PPMI帕金森病进展标志物计划,ROC接收器操作特征曲线。
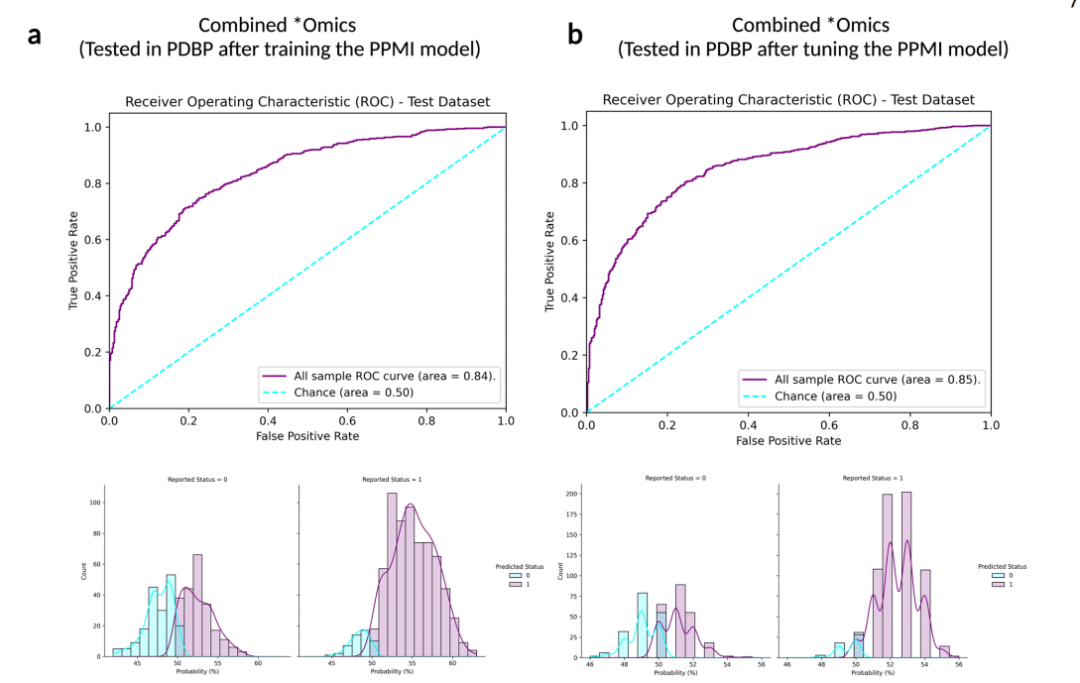
Fig. 3Receiver operating characteristic and case probability density plots in the external dataset (PDBP) at validation for the trained and then tuned models at default thresholds. Probabilities are predicted case status (r1), so controls (status of 0) skews towards more samples on the left, and positive PD cases (status of 1) skews more samples on the right. a Testing in PDBP the combined *omics model (genetics p value threshold = 1E-5, transcriptomics p value threshold = 1E-2, and clinico-demographic information) developed in PPMI prior to tuning the hyperparameters of the model; b Testing in PDBP the combined *omics model (genetics p value threshold = 1E-5, transcriptomics p value threshold = 1E-2, and clinico-demographic information) developed in PPMI after tuning the hyperparameters of the model. PPMI Parkinson’s progression marker initiative, PDBP Parkinson’s disease biomarker program, ROC receiver operating characteristic curve.
图3在外部数据集(PDBP)上对训练并调整后的模型进行验证时的接收器操作特征和案例概率密度图,使用默认阈值。概率预测的是案例状态(r1),因此对照组(状态为0)的样本偏向左侧,阳性PD案例(状态为1)的样本偏向右侧。a 在PDBP测试结合组学模型(遗传学P值阈值=1E-5,转录组学P值阈值=1E-2,以及临床-人口统计信息),该模型在PPMI中开发,在调整模型的超参数之前;b 在PDBP测试结合组学模型(遗传学P值阈值=1E-5,转录组学P值阈值=1E-2,以及临床-人口统计信息),该模型在PPMI中开发,调整模型的超参数之后。PPMI帕金森病进展标志物计划,PDBP帕金森病生物标志物项目,ROC接收器操作特征曲线。
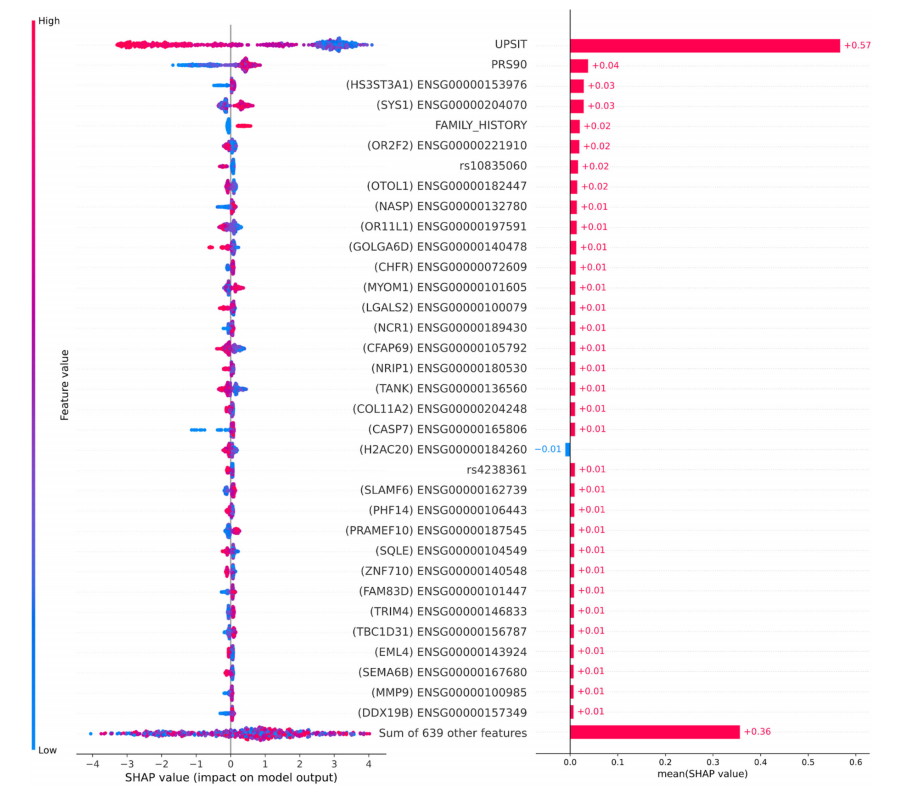
Fig. 4Feature importance plots for top 5% of features in data. The plot on the left has lower values indicated by the color blue, while higher values are indicated in red compared to the baseline risk estimate. Plot on the right indicates directionality, with features predicting for cases indicated in red, while features better-predicting controls are indicated in blue. SHAP Shapley values, UPSIT University of Pennsylvania smell identification test, PRS polygenic risk score.
图4数据中前5%特征的特征重要性图。左侧的图中,较低的值用蓝色表示,而较高的值与基线风险估计相比用红色表示。右侧的图表明方向性,预测案例的特征用红色表示,而更好地预测对照组的特征用蓝色表示。SHAP沙普利值,UPSIT宾夕法尼亚大学嗅觉识别测试,PRS多基因风险评分。
Table
表
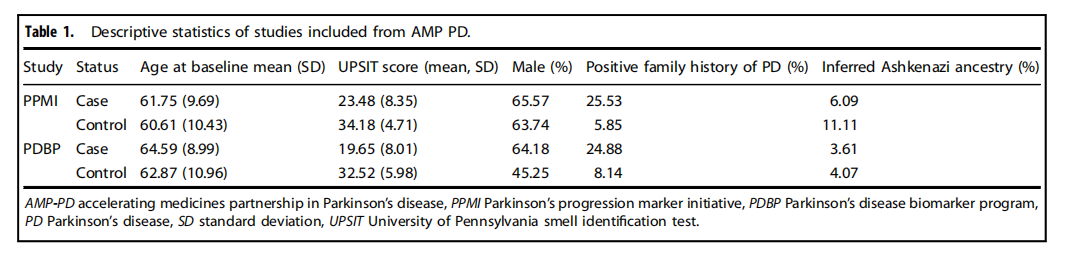
Table 1.Descriptive statistics of studies included from AMP PD.
表1.包含自AMP PD的研究的描述性统计。
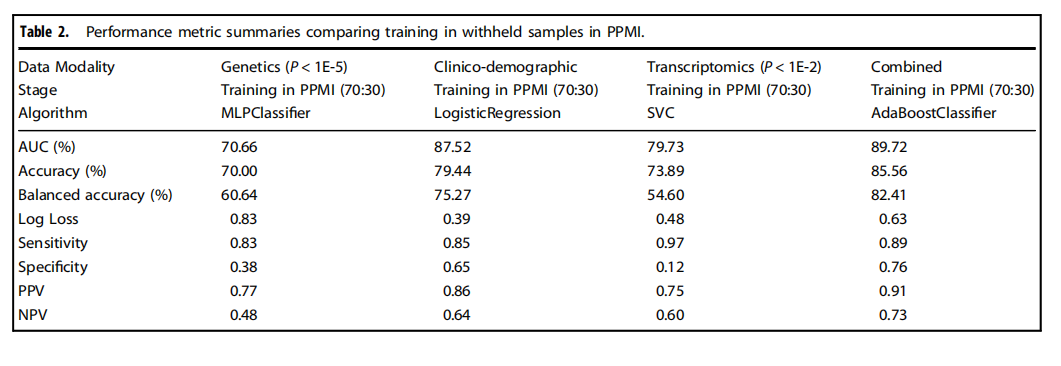
Table 2.Performance metric summaries comparing training in withheld samples in PPMI.
表2.比较在PPMI中保留样本训练的性能指标摘要。
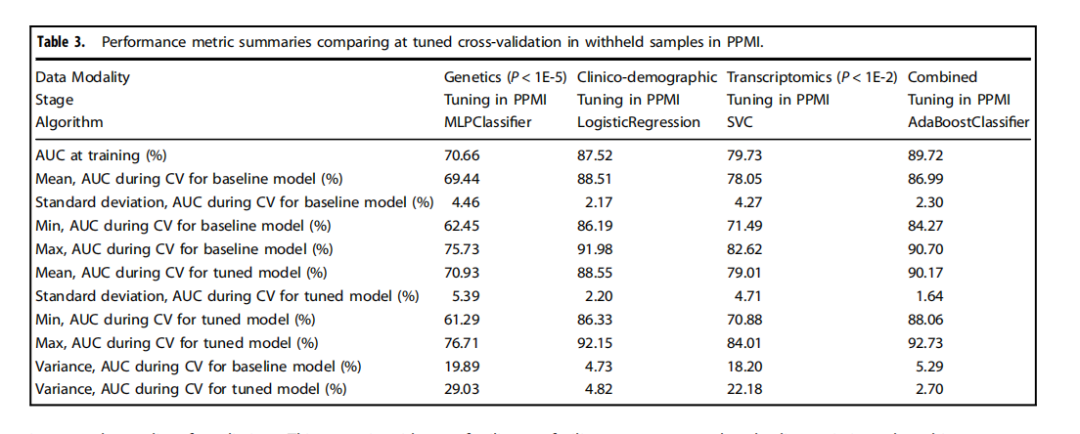
Table 3.Performance metric summaries comparing at tuned cross-validation in withheld samples in PPMI.
表3.比较在PPMI中保留样本的调整后交叉验证的性能指标摘要。
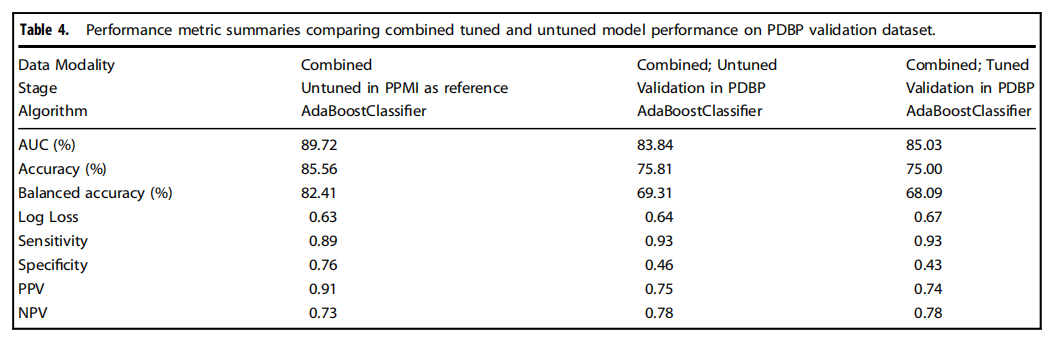
Table 4.Performance metric summaries comparing combined tuned and untuned model performance on PDBP validation dataset.
表4.比较在PDBP验证数据集上结合调整和未调整模型性能的性能指标摘要。
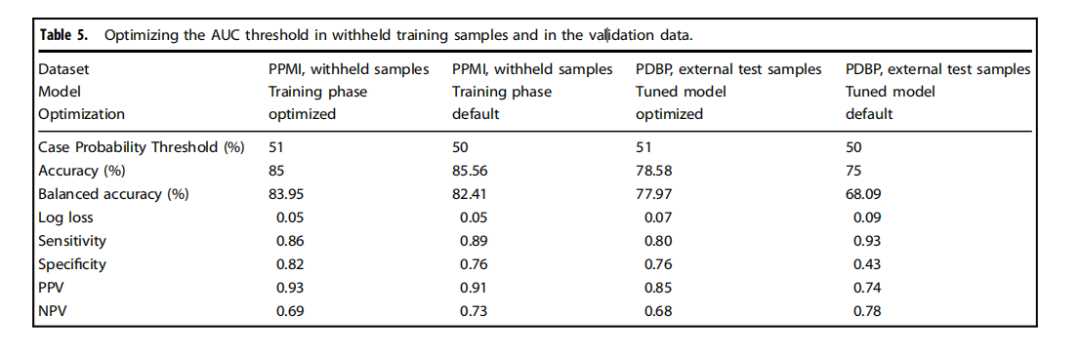
Table 5.Optimizing the AUC threshold in withheld training samples and in the validation data.
表5.在保留的训练样本和验证数据中优化AUC阈值
这篇关于文献速递:帕金森的疾病分享--多模态机器学习预测帕金森病的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






