本文主要是介绍[树] △ 由广义表GList创建树(孩子兄弟链表CSTree)(严蔚敏《数据结构》6.73),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
题目来源:严蔚敏《数据结构》C语言版本习题册 6.73
【题目】6.73
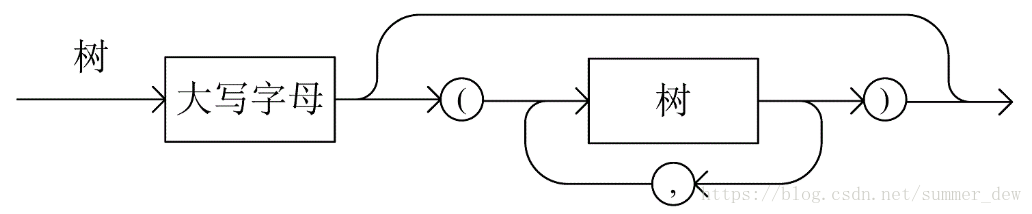
若用大写字母标识树的结点,则可用带标号的广义表形式表示一棵树,其语法图如下所示:
例如,6.71题中的树可用下列形式的广义表表示:A(B(E,F),C(G),D)
试写一递归算法,由这种广义表表示的字符序列构造树的孩子-兄弟链表(提示:按照森林和树相互递归的定义写两个互相递归调用的算法,语法图中一对圆括号内的部分可看成为森林的语法图)。
【如何看语法图】https://blog.csdn.net/summer_dew/article/details/82937736
【公式解析】
按照公式有 [树] 的定义:
- 不存在空树
- 树根:大写字母
- 没有子树:空
- 有子树:
( 树 )--> 树里面又返回树的定义 - 有多个子树:
(树1, 树2, 树...)--> 以,分割
【测试数据】
A(B(E,F),C(G),D)
A
A(B)
A(B,C)
A(B,C(D,E))
【答案】
/*-----------------------------------------|6.73 用广义表的形式构造 |-----------------------------------------*/
// @Version:1.0.1
// @Time:20181005
// @Desc:改进v0.0.1中的循环条件1,加上判断格式
// @Quesion:有一些格式检测不了"A(" "A()" "A)("
Status CreateCSTreeByGList(CSTree *pT) {char c;//创建新结点*pTfor (c=getchar(); c!='\n'; c=getchar()) {if (c>='A' && c<='Z') { //新结点的信息*pT = (CSNode *)malloc(sizeof(CSNode)); if (!*pT) exit(OVERFLOW);(*pT)->data = c; (*pT)->firstchild=(*pT)->nextsibling=NULL;} else if (c=='(') { //新结点的孩子if ( !CreateCSTreeByGList(&(*pT)->firstchild) ) return ERROR; //返回ERROR,表示此层之后发生了错误} else if (c==',') { //新结点的兄弟if ( !CreateCSTreeByGList(&(*pT)->nextsibling) ) return ERROR; //返回ERROR,表示此层之后发生了错误return OK; //新结点已经构造完了-->这里要返回} else if (c==')') { //新结点的父亲已经构建完了return OK;} else {return ERROR; //格式错误}}return TRUE; //正常结束
}
【完整答案】可以直接运行
/*-------------------|树-孩子兄弟表达法 |-------------------*/
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>#ifndef BASE
#define BASE
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define INFEASIBLE -1
#define OVERFLOW -2
typedef int Status;
typedef int bool;
#endif#define TElemType char
void visit(TElemType e) {printf("%c", e);
}
typedef struct CSNode{TElemType data;struct CSNode *firstchild, *nextsibling;
}CSNode, *CSTree;/*-------------------|6.59 输出T的所有边 |-------------------*/
void TreePrintEdge(CSTree T) {CSNode *p;for (p=T->firstchild; p; p=p->nextsibling) {printf("(%c,%c)\n", T->data, p->data); //输出T的孩子TreePrintEdge(p); //输出p的孩子}
}/*-------------------------|6.60 统计叶子结点的个数 |-------------------------*/
int TreeLeafCnt(CSTree T) {// 树的叶子结点-->没有孩子int ret=0;CSNode *p;if (!T) return 0;else if (!T->firstchild) return 1;else {for (p=T->firstchild; p; p=p->nextsibling) ret += TreeLeafCnt(p);return ret;}
}/*-------------------------|6.61 求树的度 |-------------------------*/
int TreeDegree(CSTree T) {// 最大的孩子数int max=-1;int cnt=0;CSNode *child;if (!T) return -1; //空树else if (!T->firstchild) return 0; //只有一个根结点,度为0else {for (cnt=0,child=T->firstchild; child; child=child->nextsibling) cnt++; //求自己的度max = cnt; //当前的最大值for (child=T->firstchild; child; child=child->nextsibling) {cnt = TreeDegree(child);if (cnt>max) max=cnt;}return max;}
}/*-------------------------|6.62 求树的深度 |-------------------------*/
int TreeDepth(CSTree T) {int h1,h2;if (!T) return 0;else {h1 = TreeDepth(T->firstchild)+1; //T孩子的深度+1h2 = TreeDepth(T->nextsibling); //T兄弟的深度return h1>h2 ? h1 : h2;}
}/*---------------------------------|6.66 双亲表示法-->孩子兄弟表达式|---------------------------------*/
#define MAX_TREE_SIZE 50typedef struct PTNode{TElemType data;int parent; //双亲的位置域
}PTNode;
typedef struct{PTNode nodes[MAX_TREE_SIZE];int r,n;
}PTree;
CSTree CreateCSTreeByPTree(PTree T) {CSNode *tmp[MAX_TREE_SIZE]; //创建一个辅助的数组,仿照PTree结点的位置存放CSNode *p, *q;int i,parent;if (T.n<=0) return NULL;for (i=0; i<T.n; i++) { //双亲表按层序存储//创建新结点p = (CSNode *)malloc(sizeof(CSNode)); if(!p) exit(OVERFLOW);//赋值p->data = T.nodes[i].data;p->firstchild=p->nextsibling=NULL;//连接parent=T.nodes[i].parent; //父亲if (parent!=-1) { //不是根结点if (tmp[parent]->firstchild==NULL) tmp[parent]->firstchild=p; //第一个孩子else { //不是第一个孩子for (q=tmp[parent]->firstchild; q->nextsibling; q=q->nextsibling) ; //找到最后一个孩子q->nextsibling = p; //连接}}tmp[i]=p;}return tmp[0];
}/*---------------------------------|6.67 二元组(F,C)创建CSTree |---------------------------------*/
#define maxSize 50
Status CreateCSTreeByDuplet(CSTree *pT) {char input[5];CSNode *queue[maxSize];int front,rear;CSNode *p, *q;front=rear=0; //对队列初始化for (scanf("%s", input); input[1]!='^'; scanf("%s", input)) {//创建结点p = (CSNode *)malloc(sizeof(CSNode)); if (!p) exit(OVERFLOW);p->data=input[1];p->firstchild=p->nextsibling=NULL;//入队列queue[rear]=p;rear=(rear+1)%maxSize;//找爸爸if (input[0]=='^') { //根结点-->不需要找爸爸*pT = p; //传出去} else {for (q=queue[front]; q->data!=input[0]; front=(front+1)%maxSize,q=queue[front]) ; //找爸爸//找哥哥if (!q->firstchild) q->firstchild=p; //它是最大的else { //它不是最大的for(q=q->firstchild; q->nextsibling; q=q->nextsibling) ; //找最近的哥哥q->nextsibling = p; //和哥哥牵手}}}return OK;
}/*-----------------------------------------|6.68 层次序列+每个结点的度-->构造CSTree |-----------------------------------------*/
CSTree CreateCSTreeByLevelDegree(char *levelstr, int *num) {int cnt,i,parent;CSNode *p;CSNode *tmp[maxSize];//先创建结点for (i=0; i < strlen(levelstr); ++i) {p = (CSNode *)malloc(sizeof(CSNode)); if (!p) exit(OVERFLOW);p->data = levelstr[i];p->firstchild=p->nextsibling=NULL;tmp[i]=p;}//连接parent=0; //孩子的爸爸cnt=0; //计数器:表示已经找了几个孩子i=1; //遍历结点,为他们找爸爸while (i<strlen(levelstr)) {if (num[parent]==0 || cnt==num[parent]) { //这个父亲没有孩子 || parent的孩子已经找完了cnt=0; //计数器归0parent++; //位移一位continue;}//这个父亲有孩子(i是parent的孩子)cnt++;if (cnt==1) { //i是parent的第一个孩子tmp[parent]->firstchild = tmp[i];} else { //不是第一个孩子tmp[i-1]->nextsibling = tmp[i]; //它是前面的兄弟}i++;}return tmp[0];
}/*-----------------------------------------|6.71 以树状的形式输出 |-----------------------------------------*/
void PrintAsTree(CSTree T,int i) {/*思路:1. 观察题目输出的序列ABEFCGD2. 此为树的先根遍历-->对应为二叉树存储的先序遍历3. 前面的空格是该结点所在的层数*/int cnt;if (T) {//输出空格for (cnt=1; cnt<i; cnt++) printf(" ");//输出字符visit(T->data);printf("\n");PrintAsTree(T->firstchild, i+1);PrintAsTree(T->nextsibling, i);}
}/*-----------------------------------------|6.73 用广义表的形式构造 |-----------------------------------------*/
// @Version:0.0.1
// @Time:20181005
// @Desc:循环条件为1,最好不要设置死循环
Status CreateCSTreeByGList1(CSTree *pT) {char c;while (1) {c = getchar();if (c>='A' && c<='Z') { //根结点*pT = (CSNode *)malloc(sizeof(CSNode)); if (!*pT) exit(OVERFLOW);(*pT)->data = c; (*pT)->firstchild=(*pT)->nextsibling=NULL;} else if (c=='(') { //是我的第一个孩子CreateCSTreeByGList1(&(*pT)->firstchild);} else if (c==',') { //是我的兄弟CreateCSTreeByGList1(&(*pT)->nextsibling);break; //这里要返回} elsebreak;}return OK;
}
// @Version:1.0.1
// @Time:20181005
// @Desc:改进v0.0.1中的循环条件1,加上判断格式
// @Quesion:有一些格式检测不了"A(" "A()" "A)("
Status CreateCSTreeByGList(CSTree *pT) {char c;//创建新结点*pTfor (c=getchar(); c!='\n'; c=getchar()) {if (c>='A' && c<='Z') { //新结点的信息*pT = (CSNode *)malloc(sizeof(CSNode)); if (!*pT) exit(OVERFLOW);(*pT)->data = c; (*pT)->firstchild=(*pT)->nextsibling=NULL;} else if (c=='(') { //新结点的孩子if ( !CreateCSTreeByGList(&(*pT)->firstchild) ) return ERROR; //返回ERROR,表示此层之后发生了错误} else if (c==',') { //新结点的兄弟if ( !CreateCSTreeByGList(&(*pT)->nextsibling) ) return ERROR; //返回ERROR,表示此层之后发生了错误return OK; //新结点已经构造完了-->这里要返回} else if (c==')') { //新结点的父亲已经构建完了return OK;} else {return ERROR; //格式错误}}return TRUE; //正常结束
}/*-----------------------------------------|6.74 以广义表的形式输出 |-----------------------------------------*/
void PrintAsGList(CSTree T) {CSNode *child;visit(T->data);if (T->firstchild) { //有孩子printf("(");for (child=T->firstchild; child->nextsibling; child=child->nextsibling) {PrintAsGList(child);printf(",");}PrintAsGList(child);printf(")");}
}int main() {
/*6.74测试数据
A(B(E,F),C(G),D)
A
A(B)
A(B,C)
A(B,C(D,E))
*/CSTree CST;int ret;while (1) {ret = CreateCSTreeByGList(&CST); //6.73if (ret) {PrintAsGList(CST); //6.74printf("\n");}elseprintf("格式错误\n");}return 0;
}
这篇关于[树] △ 由广义表GList创建树(孩子兄弟链表CSTree)(严蔚敏《数据结构》6.73)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!