本文主要是介绍数据结构-->线性表-->单链表,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!

链表的定义
链表:链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。
与顺序表不同的是,链表里的每节都是独立申请下来的空间,我们称之为“节点、结点”。
节点的组成主要由两个部分:当前节点要保存的数据和保存下一个节点的地址(指针变量)。
链表的节点(结点)
链表中的每个节点都是独立申请的(需要插入数据时才去申请一块节点的空间),我们需要通过指针变量来保存下一个节点位置才能从当前节点找到下一个节点。
给出每个节点对应的结构体代码:以保存的节点是整形为例:
struct SListNode
{int data; //节点数据struct SListNode* next; //指针变量⽤保存下⼀个节点的地址
};当我们想要保存一个整型数据时,实际是向操作系统申请了一块内存,这个内存不仅要保存整型数据,也需要保存下一个节点的地址(当下一个节点为空时保存的地址为空)。
链式结构在逻辑上是连续的,在物理结构上不一定连续
节点一般是从堆上申请的
从堆上申请来的空间,是按照一定策略分配出来的,每次申请的空间可能连续,可能不连续。
链表的分类
对于链表的分类来说:一共有8种

最常用的两种链表结构
虽然链表结构很多,但最常用的只有两种结构
单链表:也叫无头单向非循环链表,结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构。
带头双向循环链表:结构最复杂,一般用在单独存储数据。实际中使用的链表数据结构,都是带头双向循环链表。这个链表虽然结构复杂,但是使用代码实现以后会发现法结构会带来更多优势。
首先我们给出我们要实现的单链表的头文件:
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int SLDataType;
typedef struct SList
{SLDataType data;struct SList* next;
}SL;
//打印
void SLPrint(SL* phead);
//销毁
void SLDestroy(SL** pphead);
//开辟新链表节点
SL* Buynode(SLDataType x);
//链表头插
void SLPushFront(SL** pphead,SLDataType x);
//链表尾插
void SLPushBack(SL** pphead,SLDataType x);
//链表头删
void SLPopFront(SL** pphead);
//链表尾删
void SLPopBack(SL** pphead);
//链表对节点的查找
SL* SLFind(SL** pphead,SLDataType x);
//对指定位置之前插入数据
void SLInsert(SL** pphead,SL* pos,SLDataType x);
//在指定位置之后插入数据
void SLInsertafter(SL* pos, SLDataType x);
//删除pos节点
void SLErase(SL** pphead,SL* pos);
//删除pos之后的节点
void SLEraseafter(SL* pos);对单链表打印
这里直接进行遍历就ok
//打印
void SLPrint(SL* phead)
{SL* pcur = phead;while (pcur){printf("%d->", pcur->data);pcur = pcur->next;}printf("NULL");
}销毁单链表
逐个销毁,销毁某一个节点时,保存他的下一个节点的地址。
//销毁
void SLDestroy(SL** pphead)
{assert(pphead);assert(*pphead);SL* pcur = *pphead;while (pcur){SL* next = (*pphead)->next;free(pcur);pcur = next;}*pphead = NULL;
}开辟节点空间
为新的数据开辟空间
//开辟节点空间
SL* Buynode(SLDataType x)
{SL* newnode = (SL*)malloc(sizeof(SL));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail\n");return;}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;return newnode;
}单链表头插
记得先后顺序,个人感觉容易犯错
//链表头插
void SLPushFront(SL** pphead, SLDataType x)
{assert(pphead);SL* new = Buynode(x);//个人觉得易错new->next = *pphead;*pphead = new;
}单链表尾插
如果头结点为空,则相当于头插
如果头结点不为空,就正常找尾节点然后插入。
//链表尾插
void SLPushBack(SL** pphead, SLDataType x)
{assert(pphead);SL* new = Buynode(x);if (*pphead == NULL){*pphead = new;return;}SL* pcur = *pphead;while (pcur->next){pcur = pcur->next;}pcur->next = new;
}单链表头删
对于删除来说,需要断言pphead和*pphead,pphead是存放*pphead的地址不能为NULL,
*pphead是为了判断单链表不能为NULL
//链表头删
void SLPopFront(SL** pphead)
{assert(pphead);assert(*pphead);SL* next = (*pphead)->next;free(*pphead);*pphead = next;
}单链表尾删
如果只有一个元素,就相当于头删,否则就相当于尾删
//链表尾删
void SLPopBack(SL** pphead)
{assert(pphead);assert(*pphead);if (((*pphead)->next) == NULL){free(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;}SL* prev = NULL;SL* pcur = *pphead;while (pcur->next){prev = pcur;pcur = pcur->next;}free(pcur);pcur = NULL;prev->next = NULL;
}单链表对节点的查找
遍历查找与目标值相同的,然后返回存储该值的地址
//链表对节点的查找
SL* SLFind(SL** pphead, SLDataType x)
{assert(pphead);SL* pcur = *pphead;while (pcur){if (pcur->data == x){return pcur;}pcur = pcur->next;}return NULL;
}对指定位置插入数据
1.pos在*pphead,相当于头插
2.pos不在*pphead,就正常插入
//对指定位置之前插入数据
void SLInsert(SL** pphead, SL* pos, SLDataType x)
{assert(pphead);assert(pos);assert(*pphead);SL* new = Buynode(x);if (pos == *pphead){SLPushFront(pphead, x);return;}SL* pcur = *pphead;while (pcur->next!=pos){pcur = pcur->next;}pcur->next = new;new->next = pos;
}在指定位置后插入
没什么好说的,直接找到指定位置,然后插入即可
//在指定位置之后插入数据
void SLInsertafter(SL* pos, SLDataType x)
{assert(pos);SL* new = Buynode(x);new->next = pos->next;pos->next = new;
}删除pos节点的值
如果pos为*pphead就头删,否则就正常删除pos节点的值
//删除pos节点
void SLErase(SL** pphead, SL* pos)
{assert(pphead);assert(*pphead);assert(pos);if (*pphead == pos){SLPopFront(pphead);return;}SL* pcur = *pphead;while (pcur->next != pos){pcur = pcur->next;}SL* next = pos->next;pcur->next = next;free(pos);pos=NULL;
}删除pos节点之后的值
找到pos节点,当然联系pos和pos->next->next的值
//删除pos之后的节点
void SLEraseafter(SL* pos)
{assert(pos);assert(pos->next);SL* pcur = pos->next;pos->next = pos->next->next;free(pcur);pcur = NULL;
}
最终代码
SList.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int SLDataType;
typedef struct SList
{SLDataType data;struct SList* next;
}SL;
//打印
void SLPrint(SL* phead);
//销毁
void SLDestroy(SL** pphead);
//开辟新链表节点
SL* Buynode(SLDataType x);
//链表头插
void SLPushFront(SL** pphead,SLDataType x);
//链表尾插
void SLPushBack(SL** pphead,SLDataType x);
//链表头删
void SLPopFront(SL** pphead);
//链表尾删
void SLPopBack(SL** pphead);
//链表对节点的查找
SL* SLFind(SL** pphead,SLDataType x);
//对指定位置之前插入数据
void SLInsert(SL** pphead,SL* pos,SLDataType x);
//在指定位置之后插入数据
void SLInsertafter(SL* pos, SLDataType x);
//删除pos节点
void SLErase(SL** pphead,SL* pos);
//删除pos之后的节点
void SLEraseafter(SL* pos);SList.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "SList.h"
//打印
void SLPrint(SL* phead)
{SL* pcur = phead;while (pcur){printf("%d->", pcur->data);pcur = pcur->next;}printf("NULL");
}
//销毁
void SLDestroy(SL** pphead)
{assert(pphead);assert(*pphead);SL* pcur = *pphead;while (pcur){SL* next = (*pphead)->next;free(pcur);pcur = next;}*pphead = NULL;
}
//开辟节点空间
SL* Buynode(SLDataType x)
{SL* newnode = (SL*)malloc(sizeof(SL));if (newnode == NULL){perror("malloc fail\n");return;}newnode->data = x;newnode->next = NULL;return newnode;
}
//链表头插
void SLPushFront(SL** pphead, SLDataType x)
{assert(pphead);SL* new = Buynode(x);//个人觉得易错new->next = *pphead;*pphead = new;
}
//链表尾插
void SLPushBack(SL** pphead, SLDataType x)
{assert(pphead);SL* new = Buynode(x);if (*pphead == NULL){*pphead = new;return;}SL* pcur = *pphead;while (pcur->next){pcur = pcur->next;}pcur->next = new;
}
//链表头删
void SLPopFront(SL** pphead)
{assert(pphead);assert(*pphead);SL* next = (*pphead)->next;free(*pphead);*pphead = next;
}
//链表尾删
void SLPopBack(SL** pphead)
{assert(pphead);assert(*pphead);if (((*pphead)->next) == NULL){free(*pphead);*pphead = NULL;}SL* prev = NULL;SL* pcur = *pphead;while (pcur->next){prev = pcur;pcur = pcur->next;}free(pcur);pcur = NULL;prev->next = NULL;
}
//链表对节点的查找
SL* SLFind(SL** pphead, SLDataType x)
{assert(pphead);SL* pcur = *pphead;while (pcur){if (pcur->data == x){return pcur;}pcur = pcur->next;}return NULL;
}
//对指定位置之前插入数据
void SLInsert(SL** pphead, SL* pos, SLDataType x)
{assert(pphead);assert(pos);assert(*pphead);SL* new = Buynode(x);if (pos == *pphead){SLPushFront(pphead, x);return;}SL* pcur = *pphead;while (pcur->next!=pos){pcur = pcur->next;}pcur->next = new;new->next = pos;
}
//在指定位置之后插入数据
void SLInsertafter(SL* pos, SLDataType x)
{assert(pos);SL* new = Buynode(x);new->next = pos->next;pos->next = new;
}
//删除pos节点
void SLErase(SL** pphead, SL* pos)
{assert(pphead);assert(*pphead);assert(pos);if (*pphead == pos){SLPopFront(pphead);return;}SL* pcur = *pphead;while (pcur->next != pos){pcur = pcur->next;}SL* next = pos->next;pcur->next = next;free(pos);pos=NULL;
}
//删除pos之后的节点
void SLEraseafter(SL* pos)
{assert(pos);assert(pos->next);SL* pcur = pos->next;pos->next = pos->next->next;free(pcur);pcur = NULL;
}
Test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "SList.h"
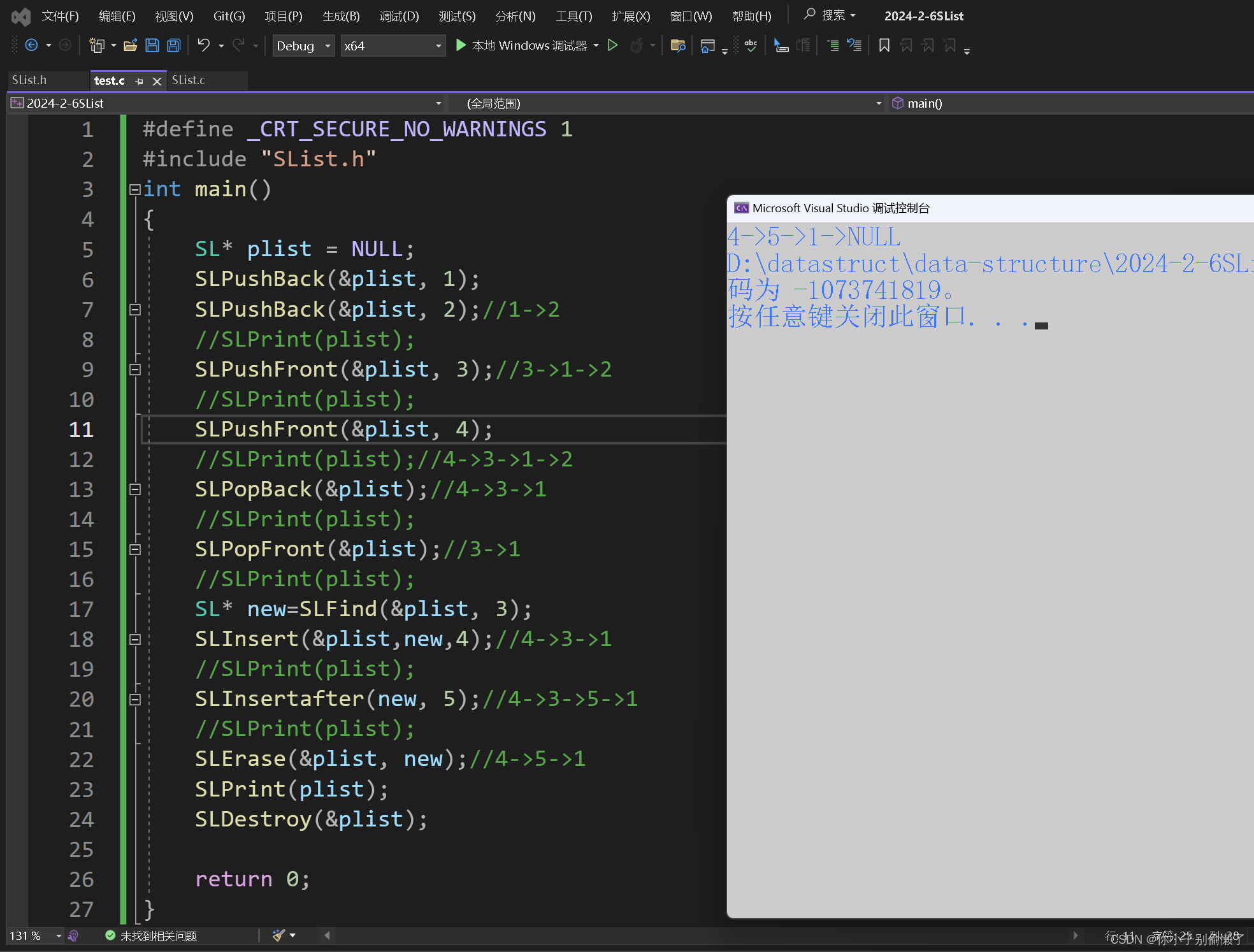
int main()
{SL* plist = NULL;SLPushBack(&plist, 1);SLPushBack(&plist, 2);//1->2//SLPrint(plist);SLPushFront(&plist, 3);//3->1->2//SLPrint(plist);SLPushFront(&plist, 4);//SLPrint(plist);//4->3->1->2SLPopBack(&plist);//4->3->1//SLPrint(plist);SLPopFront(&plist);//3->1//SLPrint(plist);SL* new=SLFind(&plist, 3);SLInsert(&plist,new,4);//4->3->1//SLPrint(plist);SLInsertafter(new, 5);//4->3->5->1//SLPrint(plist);SLErase(&plist, new);//4->5->1SLPrint(plist);SLDestroy(&plist);return 0;
}运行test函数:
以及测试过了,每个接口函数都没啥问题
这篇关于数据结构-->线性表-->单链表的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!