本文主要是介绍wayland(xdg_wm_base) + egl + opengles 最简实例,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、ubuntu 下相关环境准备
- 1. 获取 xdg_wm_base 依赖的相关文件
- 2. 查看 ubuntu 上安装的opengles 版本
- 3. 查看 weston 所支持的 窗口shell 接口种类
- 二、xdg_wm_base 介绍
- 三、egl_wayland_demo
- 1.egl_wayland_demo2_0.c
- 2.egl_wayland_demo3_0.c
- 3. xdg-shell-protocol.c和 xdg-shell-client-protocol.h
- 4. 编译和运行
- 4.1 编译
- 4.2 运行
- 总结
- 参考资料
前言
`本文主要介绍如何在linux 下,基于xdg_wm_base 接口的 wayland client 中 使用 egl + opengles 渲染一个最基本的三角形
软硬件环境:
硬件:PC
软件:
ubuntu22.04
EGL1.4
openGL ES3.1
weston9.0
一、ubuntu 下相关环境准备
1. 获取 xdg_wm_base 依赖的相关文件
之前的文章 weston 源码下载及编译 介绍了如何在ubuntu 22.04 下面编译 weston9.0 ,在编译结束后,在build 目录下会生成 xdg-shell-protocol.c 和 xdg-shell-client-protocol.h 这两个文件,如下图所示
xdg-shell-protocol.c 和 xdg-shell-client-protocol.h 这两个文件就是使用 xdg_wm_base 时所依赖的,这里就直接从weston9.0的目录下获取了,当然也可以使用wayland 相关的命令(wayland-scanner)去操作对应的.xml 文件来生成它们。
(wayland-scanner)是一个用于生成Wayland协议代码的工具。它是Wayland项目的一部分,用于根据XML描述文件生成C语言代码,以便在应用程序中使用Wayland协议。
Wayland-Scanner工具的用途是将Wayland协议的XML描述文件转换为可供应用程序使用的C语言代码。这些代码包括客户端和服务器端的接口定义、消息处理函数、数据结构等。通过使用Wayland-Scanner,开发人员可以根据自定义的Wayland协议描述文件生成所需的代码,从而实现与Wayland服务器的通信
2. 查看 ubuntu 上安装的opengles 版本
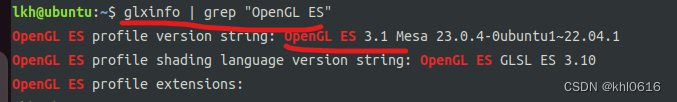
使用 glxinfo | grep “OpenGL ES” 可以查看 ubuntu 上所安装的opengles 的版本,如下图所示,代表当前 ubuntu (ubuntu22.04)上安装的是opengles版本是 opengles3.1
3. 查看 weston 所支持的 窗口shell 接口种类
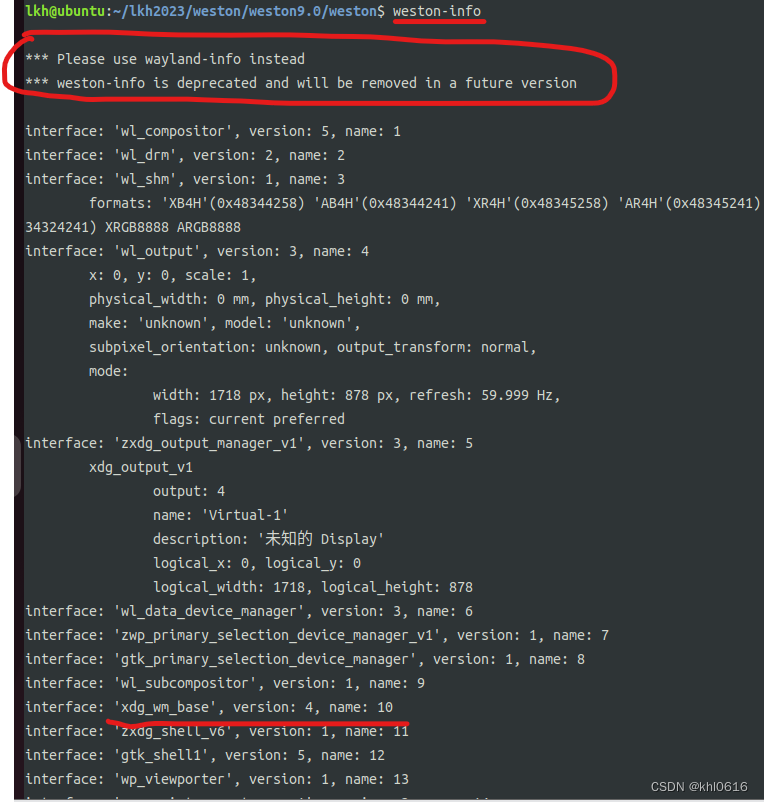
直接执行 weston-info(后面会被wayland-info 命令取代) 命令,如下图所示,可以看到,当前ubuntu(ubuntu22.04)上所支持的窗口 shell 接口种类,其中就有 xdg_wm_base, zxdg_shell_v6 等,但是没有 wl_shell , 所以从这可以看出,wl_shell 确实已经在ubuntu22.04 上废弃使用了。
二、xdg_wm_base 介绍
- xdg_wm_base是由XDG组织定义的Wayland协议接口之一,它提供了一种标准化的方法,使得窗口管理器和应用程序能够进行互动;
- xdg_wm_base定义了与窗口管理器交互的基本功能,如创建新窗口、设置窗口标题、最大化和最小化窗口等;
- 它鼓励窗口管理器使用更加灵活和自由的方式来处理窗口管理任务;
- xdg_wm_base和 wl_shell 都是Wayland协议的一部分,用于定义窗口管理器(Window Manager)与应用程序之间的通信接口。它们之间的区别在于设计理念和功能,xdg_wm_base提供了更加灵活和标准化的窗口管理器接口,窗口管理器可以根据需要实现更多的功能;
三、egl_wayland_demo
1.egl_wayland_demo2_0.c
使用 opengles2.x 接口的 egl_wayland_demo2_0.c 代码如下
#include <wayland-client.h>
#include <wayland-server.h>
#include <wayland-egl.h>
#include <EGL/egl.h>
#include <GLES2/gl2.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "xdg-shell-client-protocol.h"#define WIDTH 640
#define HEIGHT 480struct wl_display *display = NULL;
struct wl_compositor *compositor = NULL;
struct xdg_wm_base *wm_base = NULL;
struct wl_registry *registry = NULL;struct window {struct wl_surface *surface;struct xdg_surface *xdg_surface;struct xdg_toplevel *xdg_toplevel;struct wl_egl_window *egl_window;
};// Index to bind the attributes to vertex shaders
const unsigned int VertexArray = 0;static void
xdg_wm_base_ping(void *data, struct xdg_wm_base *shell, uint32_t serial)
{xdg_wm_base_pong(shell, serial);
}static const struct xdg_wm_base_listener wm_base_listener = {xdg_wm_base_ping,
};/*for registry listener*/
static void registry_add_object(void *data, struct wl_registry *registry, uint32_t name, const char *interface, uint32_t version)
{if (!strcmp(interface, "wl_compositor")) {compositor = wl_registry_bind(registry, name, &wl_compositor_interface, 1);} else if (strcmp(interface, "xdg_wm_base") == 0) {wm_base = wl_registry_bind(registry, name,&xdg_wm_base_interface, 1);xdg_wm_base_add_listener(wm_base, &wm_base_listener, NULL);}
}void registry_remove_object(void *data, struct wl_registry *registry, uint32_t name)
{}static struct wl_registry_listener registry_listener = {registry_add_object, registry_remove_object};/*for shell surface listener*/static void shell_surface_ping (void *data, struct wl_shell_surface *shell_surface, uint32_t serial)
{wl_shell_surface_pong (shell_surface, serial);
}
static void shell_surface_configure (void *data, struct wl_shell_surface *shell_surface, uint32_t edges, int32_t width, int32_t height) {struct window *window = data;wl_egl_window_resize (window->egl_window, width, height, 0, 0);
}
static void shell_surface_popup_done (void *data, struct wl_shell_surface *shell_surface)
{}static struct wl_shell_surface_listener shell_surface_listener = {&shell_surface_ping, &shell_surface_configure, &shell_surface_popup_done};static void create_window (struct window *window, int32_t width, int32_t height)
{}
static void
handle_surface_configure(void *data, struct xdg_surface *surface,uint32_t serial)
{//struct window *window = data;xdg_surface_ack_configure(surface, serial);//window->wait_for_configure = false;
}static const struct xdg_surface_listener xdg_surface_listener = {handle_surface_configure
};static void
handle_toplevel_configure(void *data, struct xdg_toplevel *toplevel,int32_t width, int32_t height,struct wl_array *states)
{
}static void
handle_toplevel_close(void *data, struct xdg_toplevel *xdg_toplevel)
{
}static const struct xdg_toplevel_listener xdg_toplevel_listener = {handle_toplevel_configure,handle_toplevel_close,
};bool initWaylandConnection()
{ if ((display = wl_display_connect(NULL)) == NULL){printf("Failed to connect to Wayland display!\n");return false;}if ((registry = wl_display_get_registry(display)) == NULL){printf("Faield to get Wayland registry!\n");return false;}wl_registry_add_listener(registry, ®istry_listener, NULL);wl_display_dispatch(display);if (!compositor){printf("Could not bind Wayland protocols!\n");return false;}return true;
}bool initializeWindow(struct window *window)
{initWaylandConnection();window->surface = wl_compositor_create_surface (compositor);window->xdg_surface = xdg_wm_base_get_xdg_surface(wm_base, window->surface);if (window->xdg_surface == NULL){printf("Failed to get Wayland xdg surface\n");return false;} else {xdg_surface_add_listener(window->xdg_surface, &xdg_surface_listener, window);window->xdg_toplevel =xdg_surface_get_toplevel(window->xdg_surface);xdg_toplevel_add_listener(window->xdg_toplevel,&xdg_toplevel_listener, window);xdg_toplevel_set_title(window->xdg_toplevel, "egl_wayland_demo");}return true;
}void releaseWaylandConnection(struct window *window)
{if(window->xdg_toplevel)xdg_toplevel_destroy(window->xdg_toplevel);if(window->xdg_surface)xdg_surface_destroy(window->xdg_surface);wl_surface_destroy(window->surface);xdg_wm_base_destroy(wm_base);wl_compositor_destroy(compositor);wl_registry_destroy(registry);wl_display_disconnect(display);
}bool createEGLSurface(EGLDisplay eglDisplay, EGLConfig eglConfig, EGLSurface *eglSurface, struct window *window)
{window->egl_window = wl_egl_window_create(window->surface, WIDTH, HEIGHT);if (window->egl_window == EGL_NO_SURFACE) { printf("Can't create egl window\n"); return false;} else {printf("Created wl egl window\n");}*eglSurface = eglCreateWindowSurface(eglDisplay, eglConfig, window->egl_window, NULL);return true;
}bool opengles_init(GLuint *shaderProgram)
{GLuint fragmentShader = 0;GLuint vertexShader = 0;char msg[1000];GLsizei len;const char* const fragmentShaderSource = "precision mediump float;\n""void main()\n""{\n"" gl_FragColor = vec4 (1.0,0.0,0.0,1.0);\n""}\n";// Create a fragment shader objectfragmentShader = glCreateShader(GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER);// Load the source code into itglShaderSource(fragmentShader, 1, (const char**)&fragmentShaderSource, NULL);// Compile the source codeglCompileShader(fragmentShader);// Check that the shader compiledGLint isShaderCompiled;glGetShaderiv(fragmentShader, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &isShaderCompiled);if (!isShaderCompiled){// If an error happened, first retrieve the length of the log messageglGetShaderInfoLog(fragmentShader, sizeof msg, &len, msg);//glGetShaderiv(fragmentShader, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &infoLogLength);// Allocate enough space for the message and retrieve it//std::vector<char> infoLog;//infoLog.resize(infoLogLength);//glGetShaderInfoLog(fragmentShader, infoLogLength, &charactersWritten, infoLog.data());fprintf(stderr, "Error: compiling %s: %.*s\n", "fragment", len, msg);return false;}// Vertex shader codeconst char* const vertexShaderSource = "attribute vec4 vPosition; \n""void main()\n""{\n"" gl_Position = vPosition;\n""}\n";// Create a vertex shader objectvertexShader = glCreateShader(GL_VERTEX_SHADER);// Load the source code into the shaderglShaderSource(vertexShader, 1, (const char**)&vertexShaderSource, NULL);// Compile the shaderglCompileShader(vertexShader);// Check the shader has compiledglGetShaderiv(vertexShader, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &isShaderCompiled);if (!isShaderCompiled){// If an error happened, first retrieve the length of the log message//int infoLogLength, charactersWritten;//glGetShaderiv(vertexShader, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &infoLogLength);glGetShaderInfoLog(vertexShader, sizeof msg, &len, msg);// Allocate enough space for the message and retrieve it//std::vector<char> infoLog;//infoLog.resize(infoLogLength);//glGetShaderInfoLog(vertexShader, infoLogLength, &charactersWritten, infoLog.data());fprintf(stderr, "Error: compiling %s: %.*s\n", "vertex", len, msg);return false;}// Create the shader program*shaderProgram = glCreateProgram();// Attach the fragment and vertex shaders to itglAttachShader(*shaderProgram, fragmentShader);glAttachShader(*shaderProgram, vertexShader);// Bind the vertex attribute "myVertex" to location VertexArray (0)glBindAttribLocation(*shaderProgram, VertexArray, "vPosition");// Link the programglLinkProgram(*shaderProgram);// After linking the program, shaders are no longer necessaryglDeleteShader(vertexShader);glDeleteShader(fragmentShader);// Check if linking succeeded in the same way we checked for compilation successGLint isLinked;glGetProgramiv(*shaderProgram, GL_LINK_STATUS, &isLinked);if (!isLinked){// If an error happened, first retrieve the length of the log message//nt infoLogLength, charactersWritten;//glGetProgramiv(*shaderProgram, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &infoLogLength);// Allocate enough space for the message and retrieve it//std::vector<char> infoLog;//infoLog.resize(infoLogLength);//glGetShaderInfoLog(shaderProgram, infoLogLength, &charactersWritten, infoLog.data());glGetProgramInfoLog(*shaderProgram, sizeof msg, &len, msg);fprintf(stderr, "Error: compiling %s: %.*s\n", "linkprogram", len, msg);return false;}// Use the ProgramglUseProgram(*shaderProgram);return true;
}
bool renderScene(EGLDisplay eglDisplay, EGLSurface eglSurface)
{GLfloat vVertices[] = {0.0f,0.5f,0.0f, //vertex pointer-0.5f,-0.5f,0.0f,0.5f,-0.5f,0.0f};glViewport(0, 0, WIDTH, HEIGHT); //set the view portglClearColor(0.00f, 0.70f, 0.67f, 1.0f); //set rgba value for backgroud glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);glEnableVertexAttribArray(VertexArray);glVertexAttribPointer(VertexArray, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, vVertices);glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 3); //draw a triangleif (!eglSwapBuffers(eglDisplay, eglSurface)){return false;}return true;}bool render(GLuint shaderProgram, EGLDisplay eglDisplay, EGLSurface eglSurface)
{// Renders a triangle for 800 frames using the state setup in the previous functionfor (int i = 0; i < 800; ++i){wl_display_dispatch_pending(display);if (!renderScene(eglDisplay, eglSurface)) { return false; }}return true;
}void deInitializeGLState(GLuint shaderProgram)
{// Frees the OpenGL handles for the programglDeleteProgram(shaderProgram);
}void releaseEGLState(EGLDisplay eglDisplay)
{if (eglDisplay != NULL){// To release the resources in the context, first the context has to be released from its binding with the current thread.eglMakeCurrent(eglDisplay, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_CONTEXT);// Terminate the display, and any resources associated with it (including the EGLContext)eglTerminate(eglDisplay);}
}int main()
{/* EGL variables*/EGLDisplay eglDisplay;EGLConfig eglConfig;EGLSurface eglSurface;EGLContext context;struct window window;//wayland client initif(!initializeWindow(&window)){printf("initializeWindow failed\n");return -1;}//egl init eglDisplay = eglGetDisplay(display);if (eglDisplay == EGL_NO_DISPLAY){printf("Failed to get an EGLDisplay\n");return -1;}EGLint eglMajorVersion = 0;EGLint eglMinorVersion = 0;if (!eglInitialize(eglDisplay, &eglMajorVersion, &eglMinorVersion)){printf("Failed to initialize the EGLDisplay\n");return -1;} else {printf(" EGL%d.%d\n", eglMajorVersion, eglMinorVersion);printf(" EGL_CLIENT_APIS: %s\n", eglQueryString(eglDisplay, EGL_CLIENT_APIS));printf(" EGL_VENDOR: %s\n", eglQueryString(eglDisplay, EGL_VENDOR));printf(" EGL_VERSION: %s\n", eglQueryString(eglDisplay, EGL_VERSION));printf(" EGL_EXTENSIONS: %s\n", eglQueryString(eglDisplay, EGL_EXTENSIONS));}int result = EGL_FALSE;result = eglBindAPI(EGL_OPENGL_ES_API);if (result != EGL_TRUE) { printf("eglBindAPI failed\n");return -1; }const EGLint configurationAttributes[] = { EGL_SURFACE_TYPE, EGL_WINDOW_BIT, EGL_RENDERABLE_TYPE, EGL_OPENGL_ES2_BIT, EGL_NONE };EGLint configsReturned;if (!eglChooseConfig(eglDisplay, configurationAttributes, &eglConfig, 1, &configsReturned) || (configsReturned != 1)){printf("Failed to choose a suitable config\n");return -1;}EGLint contextAttributes[] = { EGL_CONTEXT_CLIENT_VERSION, 2, EGL_NONE };context = eglCreateContext(eglDisplay, eglConfig, NULL, contextAttributes);if(!createEGLSurface(eglDisplay, eglConfig, &eglSurface, &window)){printf("Failed to create EGLSurface\n");return -1;}eglMakeCurrent(eglDisplay, eglSurface, eglSurface, context);const GLubyte* version = glGetString(GL_VERSION);if (version != NULL) {printf("OpenGL ES version: %s\n", version);} else {printf("Failed to get OpenGL ES version\n");}// opengles initGLuint shaderProgram = 0;opengles_init(&shaderProgram);//renderif(!render(shaderProgram, eglDisplay, eglSurface)) {printf("=========render failed\n");}//clean updeInitializeGLState(shaderProgram);// Release the EGL StatereleaseEGLState(eglDisplay);// Release the Wayland connectionreleaseWaylandConnection(&window);return 0;
}2.egl_wayland_demo3_0.c
使用 opengles3.x 接口的 egl_wayland_demo3_0.c 代码如下
#include <wayland-client.h>
#include <wayland-server.h>
#include <wayland-egl.h>
#include <EGL/egl.h>
#include <GLES3/gl3.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "xdg-shell-client-protocol.h"#define WIDTH 640
#define HEIGHT 480struct wl_display *display = NULL;
struct wl_compositor *compositor = NULL;
struct xdg_wm_base *wm_base = NULL;
struct wl_registry *registry = NULL;struct window {struct wl_surface *surface;struct xdg_surface *xdg_surface;struct xdg_toplevel *xdg_toplevel;struct wl_egl_window *egl_window这篇关于wayland(xdg_wm_base) + egl + opengles 最简实例的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





