本文主要是介绍OctConv:八度卷积复现,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
摘要:不同于传统的卷积,八度卷积主要针对图像的高频信号与低频信号。
本文分享自华为云社区《OctConv:八度卷积复现》,作者:李长安 。
论文解读
八度卷积于2019年在论文《Drop an Octave: Reducing Spatial Redundancy in Convolutional Neural Networks with Octave Convol》提出,在当时引起了不小的反响。八度卷积对传统的convolution进行改进,以降低空间冗余。其中“Drop an Octave”指降低八个音阶,代表频率减半。
不同于传统的卷积,八度卷积主要针对图像的高频信号与低频信号。首先,我们回忆一下数字图像处理中的高频信号与低频信号的概念。图像中的低频信号和高频信号也叫做低频分量和高频分量。图像中的高频分量,指的是图像强度(亮度/灰度)变化剧烈的像素点,例如边缘(轮廓)、图像的细节处、噪声(即噪点)(该点之所以称为噪点,是因为它与周边像素点灰度值有明显差别,也就是图像强度有剧烈的变化,所以噪声是高频部分)。图像中的低频分量,指的是图像强度(亮度/灰度)变换平缓的像素点,例如大片色块的地方。例如当我们在读书的时候,我们会聚焦于书上的文字而不是书纸本身,这里的文字就是高频分量,白纸即为低频分量。
下图是论文中给出的例子,左图是原图,中图表示低频信号,右图表示高频信号。
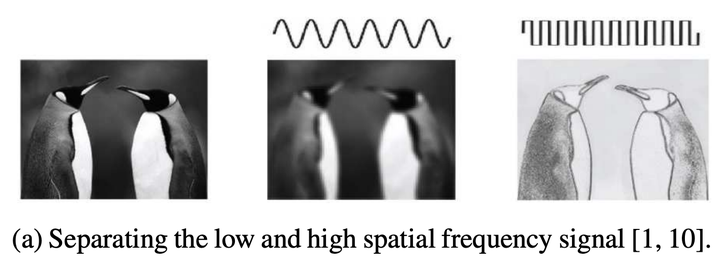
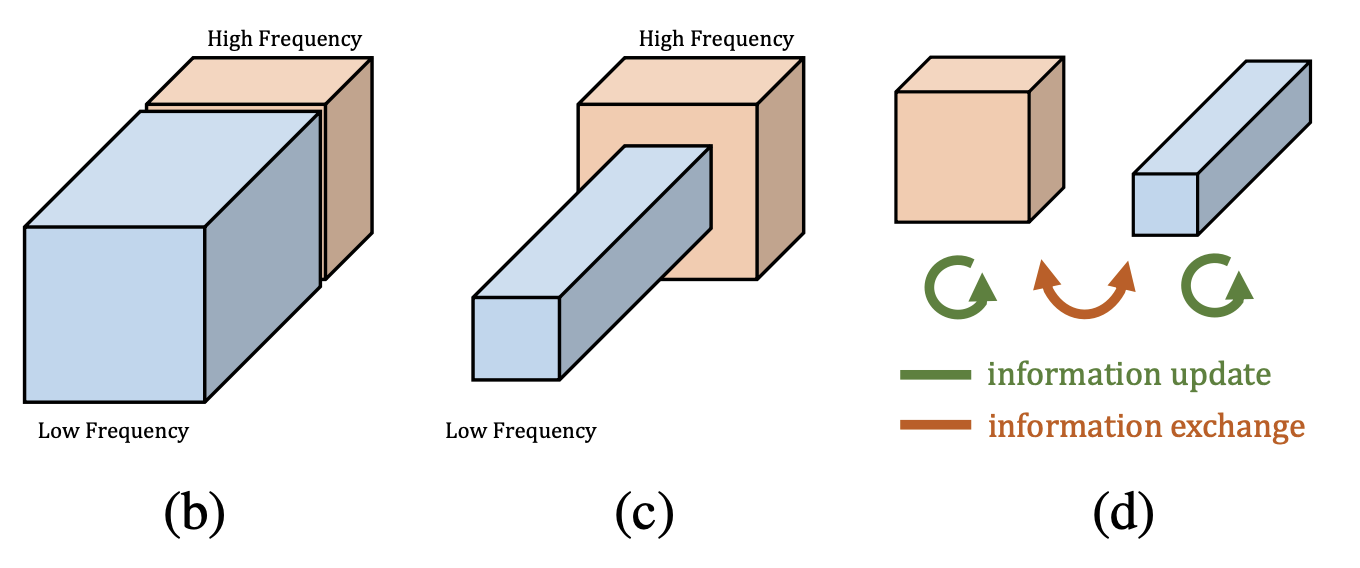
在论文中,作者提出较高的频率通常用精细的细节编码,较低的频率通常用全局结构编码。所以作者认为那么既然图像分为高低频,那么卷积产生的特征图自然也存在高低频之分。在图像处理中,模型通过高频特征图去学习图像包含的信息,因为它包含了轮廓、边缘等的信息,有助于进行显著性检测。相反,低频特征图包含的信息较少。如果我们用相同的处理方法来处理高频特征图和低频特征图,显然,前者的效益是远大于后者的。这就是特征图的冗余信息:包含信息较少的低频部分。所以在论文中作者提出了一种分而治之的方法,称之为Octave Feature Representation,对高频特征图与低频特征图分离开来进行处理。如下图所示,作者将低频特征图的分辨率降为1/2,这不仅有助于减少冗余数据,还有利于得到全局信息。
根据尺度空间理念,我们可以知道特征具有尺度不变性和旋转不变性。
- 尺度不变性:人类在识别一个物体时,不管这个物体或远或近,都能对它进行正确的辨认,这就是所谓的尺度不变性。
- 旋转不变性:当这个物体发生旋转时,我们照样可以正确地辨认它,这就是所谓的旋转不变性。
当用一个机器视觉系统分析未知场景时,计算机没有办法预先知识图像中物体尺度,因此,我们需要同时考虑图像在多尺度下的描述,获知感兴趣物体的最佳尺度。例如,高分辨率的图是人近距离的观察得到的,低分辨率的图是远距离观察得到的。
2、复现详情
2.1 Oct-Conv复现
为了同时做到同一频率内的更新和不同频率之间的交流,卷积核分成四部分:
- 高频到高频的卷积核
- 高频到低频的卷积核
- 低频到高频的卷积核
- 低频到低频的卷积核
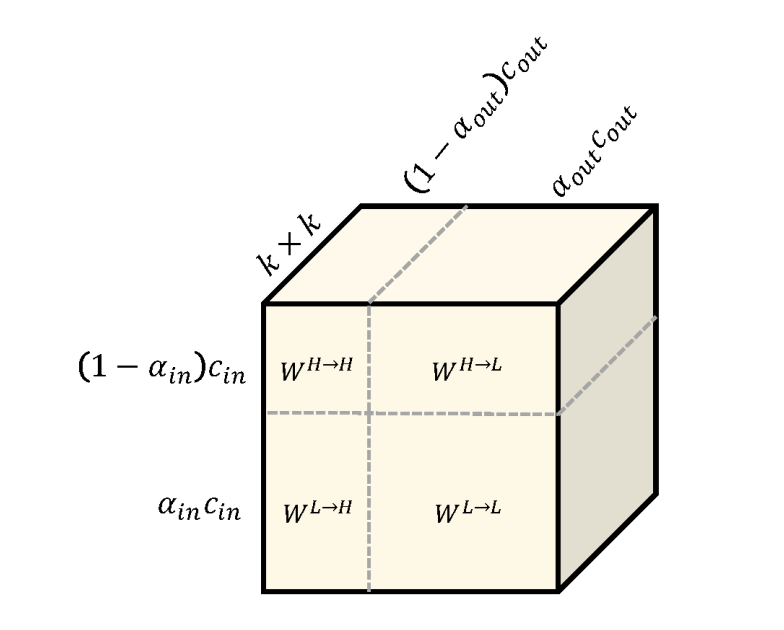
下图直观地展示了八度卷积的卷积核,可以看出四个部分共同组成了大小为 k*k 的卷积核。其中,in和out分别表示输入和输出特征图的相关属性,在这篇文章中,输入的低频占比、通道数量都和输出的一致。
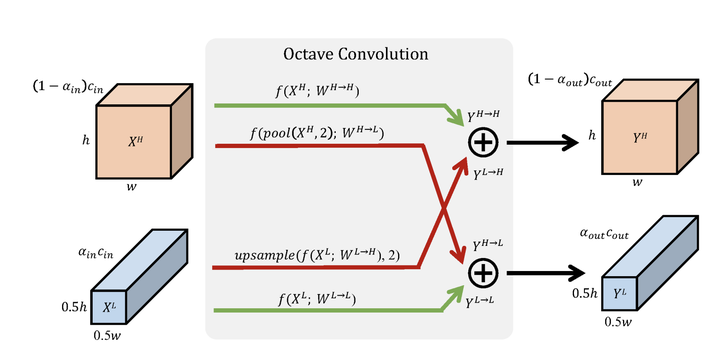
在了解了卷积核之后,下面介绍输入如何进行八度卷积操作得到输出结果。如下图所示,低频和高频的输入经过八度卷积操作得到了低频和高频的输出。红色表示高频,蓝色表示低频。绿色的箭头表示同一频率内的更新,红色的箭头表示不同频率之间的交流。
H和W分别表示特征图的长宽,可以看出低频特征图的长宽都是高频特征图的一半。因为分辨率不同,所以不同频率之间交流之前需要进行分辨率的调整:高频到低频需要进行池化(降采样)操作;低频到高频需要进行上采样操作。
import paddle
import paddle.nn as nn
import math
class OctaveConv(nn.Layer):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, alpha_in=0.5, alpha_out=0.5, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1,groups=1, bias=False):super(OctaveConv, self).__init__()self.downsample = nn.AvgPool2D(kernel_size=(2, 2), stride=2)self.upsample = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')assert stride == 1 or stride == 2, "Stride should be 1 or 2."self.stride = strideself.is_dw = groups == in_channelsassert 0 <= alpha_in <= 1 and 0 <= alpha_out <= 1, "Alphas should be in the interval from 0 to 1."self.alpha_in, self.alpha_out = alpha_in, alpha_outself.conv_l2l = None if alpha_in == 0 or alpha_out == 0 else \nn.Conv2D(int(alpha_in * in_channels), int(alpha_out * out_channels),kernel_size, 1, padding, dilation, math.ceil(alpha_in * groups))self.conv_l2h = None if alpha_in == 0 or alpha_out == 1 or self.is_dw else \nn.Conv2D(int(alpha_in * in_channels), out_channels - int(alpha_out * out_channels),kernel_size, 1, padding, dilation, groups)self.conv_h2l = None if alpha_in == 1 or alpha_out == 0 or self.is_dw else \nn.Conv2D(in_channels - int(alpha_in * in_channels), int(alpha_out * out_channels),kernel_size, 1, padding, dilation, groups)self.conv_h2h = None if alpha_in == 1 or alpha_out == 1 else \nn.Conv2D(in_channels - int(alpha_in * in_channels), out_channels - int(alpha_out * out_channels),kernel_size, 1, padding, dilation, math.ceil(groups - alpha_in * groups))def forward(self, x):x_h, x_l = x if type(x) is tuple else (x, None)x_h = self.downsample(x_h) if self.stride == 2 else x_hx_h2h = self.conv_h2h(x_h)x_h2l = self.conv_h2l(self.downsample(x_h)) if self.alpha_out > 0 and not self.is_dw else Noneif x_l is not None:x_l2l = self.downsample(x_l) if self.stride == 2 else x_lx_l2l = self.conv_l2l(x_l2l) if self.alpha_out > 0 else Noneif self.is_dw:return x_h2h, x_l2lelse:x_l2h = self.conv_l2h(x_l)x_l2h = self.upsample(x_l2h) if self.stride == 1 else x_l2hx_h = x_l2h + x_h2hx_l = x_h2l + x_l2l if x_h2l is not None and x_l2l is not None else Nonereturn x_h, x_lelse:return x_h2h, x_h2l
class Conv_BN(nn.Layer):def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, alpha_in=0.5, alpha_out=0.5, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1,groups=1, bias=False, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2D):super(Conv_BN, self).__init__()self.conv = OctaveConv(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, alpha_in, alpha_out, stride, padding, dilation,groups, bias)self.bn_h = None if alpha_out == 1 else norm_layer(int(out_channels * (1 - alpha_out)))self.bn_l = None if alpha_out == 0 else norm_layer(int(out_channels * alpha_out))def forward(self, x):x_h, x_l = self.conv(x)x_h = self.bn_h(x_h)x_l = self.bn_l(x_l) if x_l is not None else Nonereturn x_h, x_l
class Conv_BN_ACT(nn.Layer):def __init__(self, in_channels=3, out_channels=32, kernel_size=3, alpha_in=0.5, alpha_out=0.5, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1,groups=1, bias=False, norm_layer=nn.BatchNorm2D, activation_layer=nn.ReLU):super(Conv_BN_ACT, self).__init__()self.conv = OctaveConv(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, alpha_in, alpha_out, stride, padding, dilation,groups, bias)self.bn_h = None if alpha_out == 1 else norm_layer(int(out_channels * (1 - alpha_out)))self.bn_l = None if alpha_out == 0 else norm_layer(int(out_channels * alpha_out))self.act = activation_layer()def forward(self, x):x_h, x_l = self.conv(x)x_h = self.act(self.bn_h(x_h))x_l = self.act(self.bn_l(x_l)) if x_l is not None else Nonereturn x_h, x_l2.2 Oct-Mobilnetv1复现
Oct-Mobilnetv1的复现即将Mobilnetv1中的原始的Conv2D替换为Oct-Conv,其他均保持不变,在后面打印了Oct-Mobilnetv1的网络结构以及参数量,方便大家查看。
# Oct-Mobilnetv1
import paddle.nn as nn
__all__ = ['oct_mobilenet']
def conv_bn(inp, oup, stride):return nn.Sequential(nn.Conv2D(inp, oup, 3, stride, 1),nn.BatchNorm2D(oup),nn.ReLU())
def conv_dw(inp, oup, stride, alpha_in=0.5, alpha_out=0.5):return nn.Sequential(Conv_BN_ACT(inp, inp, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, groups=inp, \alpha_in=alpha_in, alpha_out=alpha_in if alpha_out != alpha_in else alpha_out),Conv_BN_ACT(inp, oup, kernel_size=1, alpha_in=alpha_in, alpha_out=alpha_out))
class OctMobileNet(nn.Layer):def __init__(self, num_classes=1000):super(OctMobileNet, self).__init__()self.features = nn.Sequential(conv_bn( 3, 32, 2),conv_dw( 32, 64, 1, 0, 0.5),conv_dw( 64, 128, 2),conv_dw(128, 128, 1),conv_dw(128, 256, 2), conv_dw(256, 256, 1),conv_dw(256, 512, 2),conv_dw(512, 512, 1),conv_dw(512, 512, 1),conv_dw(512, 512, 1),conv_dw(512, 512, 1),conv_dw(512, 512, 1, 0.5, 0),conv_dw(512, 1024, 2, 0, 0),conv_dw(1024, 1024, 1, 0, 0),)self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2D((1, 1))self.fc = nn.Linear(1024, num_classes)def forward(self, x):x_h, x_l = self.features(x)x = self.avgpool(x_h)x = x.reshape([-1, 1024])x = self.fc(x)return x
def oct_mobilenet(**kwargs):"""Constructs a Octave MobileNet V1 model"""return OctMobileNet(**kwargs)2.3 OctResNet的复现
Oct-ResNet的复现即将ResNet中的原始的Conv2D替换为Oct-Conv,其他均保持不变,在后面打印了Oct-ResNet的网络结构以及参数量,方便大家查看。
import paddle.nn as nn
__all__ = ['OctResNet', 'oct_resnet50', 'oct_resnet101', 'oct_resnet152', 'oct_resnet200']
class Bottleneck(nn.Layer):expansion = 4def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, groups=1,base_width=64, alpha_in=0.5, alpha_out=0.5, norm_layer=None, output=False):super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()if norm_layer is None:norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2Dwidth = int(planes * (base_width / 64.)) * groups# Both self.conv2 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1self.conv1 = Conv_BN_ACT(inplanes, width, kernel_size=1, alpha_in=alpha_in, alpha_out=alpha_out, norm_layer=norm_layer)self.conv2 = Conv_BN_ACT(width, width, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, groups=groups, norm_layer=norm_layer,alpha_in=0 if output else 0.5, alpha_out=0 if output else 0.5)self.conv3 = Conv_BN(width, planes * self.expansion, kernel_size=1, norm_layer=norm_layer,alpha_in=0 if output else 0.5, alpha_out=0 if output else 0.5)self.relu = nn.ReLU()self.downsample = downsampleself.stride = stridedef forward(self, x):identity_h = x[0] if type(x) is tuple else xidentity_l = x[1] if type(x) is tuple else Nonex_h, x_l = self.conv1(x)x_h, x_l = self.conv2((x_h, x_l))x_h, x_l = self.conv3((x_h, x_l))if self.downsample is not None:identity_h, identity_l = self.downsample(x)x_h += identity_hx_l = x_l + identity_l if identity_l is not None else Nonex_h = self.relu(x_h)x_l = self.relu(x_l) if x_l is not None else Nonereturn x_h, x_l
class OctResNet(nn.Layer):def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=1000, zero_init_residual=False,groups=1, width_per_group=64, norm_layer=None):super(OctResNet, self).__init__()if norm_layer is None:norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2Dself.inplanes = 64self.groups = groupsself.base_width = width_per_groupself.conv1 = nn.Conv2D(3, self.inplanes, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3,)self.bn1 = norm_layer(self.inplanes)self.relu = nn.ReLU()self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0], norm_layer=norm_layer, alpha_in=0)self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2, norm_layer=norm_layer)self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2, norm_layer=norm_layer)self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2, norm_layer=norm_layer, alpha_out=0, output=True)self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2D((1, 1))self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes)def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, alpha_in=0.5, alpha_out=0.5, norm_layer=None, output=False):if norm_layer is None:norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2Ddownsample = Noneif stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:downsample = nn.Sequential(Conv_BN(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, alpha_in=alpha_in, alpha_out=alpha_out))layers = []layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample, self.groups,self.base_width, alpha_in, alpha_out, norm_layer, output))self.inplanes = planes * block.expansionfor _ in range(1, blocks):layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, groups=self.groups,base_width=self.base_width, norm_layer=norm_layer,alpha_in=0 if output else 0.5, alpha_out=0 if output else 0.5, output=output))return nn.Sequential(*layers)def forward(self, x):x = self.conv1(x)x = self.bn1(x)x = self.relu(x)x = self.maxpool(x)x_h, x_l = self.layer1(x)x_h, x_l = self.layer2((x_h,x_l))x_h, x_l = self.layer3((x_h,x_l))x_h, x_l = self.layer4((x_h,x_l))x = self.avgpool(x_h)x = x.reshape([x.shape[0], -1])x = self.fc(x)return x
def oct_resnet50(pretrained=False, **kwargs):"""Constructs a Octave ResNet-50 model.Args:pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet"""model = OctResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], **kwargs)return model
def oct_resnet101(pretrained=False, **kwargs):"""Constructs a Octave ResNet-101 model.Args:pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet"""model = OctResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], **kwargs)return model
def oct_resnet152(pretrained=False, **kwargs):"""Constructs a Octave ResNet-152 model.Args:pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet"""model = OctResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 8, 36, 3], **kwargs)return model
def oct_resnet200(pretrained=False, **kwargs):"""Constructs a Octave ResNet-200 model.Args:pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet"""model = OctResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 24, 36, 3], **kwargs)return model3、对比实验
实验数据:Cifar10
CIFAR-10 是由 Hinton 的学生 Alex Krizhevsky 和 Ilya Sutskever 整理的一个用于识别普适物体的小型数据集。一共包含 10 个类别的 RGB 彩色图 片:飞机( a叩lane )、汽车( automobile )、鸟类( bird )、猫( cat )、鹿( deer )、狗( dog )、蛙类( frog )、马( horse )、船( ship )和卡车( truck )。图片的尺寸为 32×32 ,数据集中一共有 50000 张训练圄片和 10000 张测试图片。 CIFAR-10 的图片样例如图所示。

3.1 Oct_MobilNetv1模型网络结构可视化
Octmobilnet_model = oct_mobilenet(num_classes=10)
# inputs = paddle.randn((1, 2, 224, 224))
# print(model(inputs))
paddle.summary(Octmobilnet_model,(16,3,224,224))3.2 Oct_MobilNetV1模型训练
import paddle
from paddle.metric import Accuracy
from paddle.vision.transforms import Compose, Normalize, Resize, Transpose, ToTensor
callback = paddle.callbacks.VisualDL(log_dir='visualdl_log_dir_octmobilenet')
normalize = Normalize(mean=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],std=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],data_format='HWC')
transform = Compose([ToTensor(), Normalize(), Resize(size=(224,224))])
cifar10_train = paddle.vision.datasets.Cifar10(mode='train',transform=transform)
cifar10_test = paddle.vision.datasets.Cifar10(mode='test',transform=transform)
# 构建训练集数据加载器
train_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(cifar10_train, batch_size=768, shuffle=True, drop_last=True)
# 构建测试集数据加载器
test_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(cifar10_test, batch_size=768, shuffle=True, drop_last=True)
Octmobilnet_model = paddle.Model(oct_mobilenet(num_classes=10))
optim = paddle.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate=0.001, parameters=Octmobilnet_model.parameters())
Octmobilnet_model.prepare(optim,paddle.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(),Accuracy())
Octmobilnet_model.fit(train_data=train_loader,eval_data=test_loader,epochs=12,callbacks=callback,verbose=1)3.3 MobileNetV1模型网络结构可视化
from paddle.vision.models import MobileNetV1
mobile_model = MobileNetV1(num_classes=10)
# inputs = paddle.randn((1, 2, 224, 224))
# print(model(inputs))
paddle.summary(mobile_model,(16,3,224,224))3.4 MobileNetV1模型训练
import paddle
from paddle.metric import Accuracy
from paddle.vision.transforms import Compose, Normalize, Resize, Transpose, ToTensor
callback = paddle.callbacks.VisualDL(log_dir='visualdl_log_dir_mobilenet')
normalize = Normalize(mean=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],std=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],data_format='HWC')
transform = Compose([ToTensor(), Normalize(), Resize(size=(224,224))])
cifar10_train = paddle.vision.datasets.Cifar10(mode='train',transform=transform)
cifar10_test = paddle.vision.datasets.Cifar10(mode='test',transform=transform)
# 构建训练集数据加载器
train_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(cifar10_train, batch_size=768, shuffle=True, drop_last=True)
# 构建测试集数据加载器
test_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(cifar10_test, batch_size=768, shuffle=True, drop_last=True)
mobile_model = paddle.Model(MobileNetV1(num_classes=10))
optim = paddle.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate=0.001, parameters=mobile_model.parameters())
mobile_model.prepare(optim,paddle.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(),Accuracy())
mobile_model.fit(train_data=train_loader,eval_data=test_loader,epochs=12,callbacks=callback,verbose=1)3.5 Oct_ResNet50模型网络结构可视化
octresnet50_model = oct_resnet50(num_classes=10)
paddle.summary(octresnet50_model,(16,3,224,224))3.6 Oct_ResNet50模型训练
import paddle
from paddle.metric import Accuracy
from paddle.vision.transforms import Compose, Normalize, Resize, Transpose, ToTensor
callback = paddle.callbacks.VisualDL(log_dir='visualdl_log_dir_octresnet')
normalize = Normalize(mean=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],std=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],data_format='HWC')
transform = Compose([ToTensor(), Normalize(), Resize(size=(224,224))])
cifar10_train = paddle.vision.datasets.Cifar10(mode='train',transform=transform)
cifar10_test = paddle.vision.datasets.Cifar10(mode='test',transform=transform)
# 构建训练集数据加载器
train_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(cifar10_train, batch_size=256, shuffle=True, drop_last=True)
# 构建测试集数据加载器
test_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(cifar10_test, batch_size=256, shuffle=True, drop_last=True)
oct_resnet50 = paddle.Model(oct_resnet50(num_classes=10))
optim = paddle.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate=0.001, parameters=oct_resnet50.parameters())
oct_resnet50.prepare(optim,paddle.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(),Accuracy())
oct_resnet50.fit(train_data=train_loader,eval_data=test_loader,epochs=12,callbacks=callback,verbose=1)3.7 ResNet50模型网络结构可视化
import paddle
# build model
resmodel = resnet50(num_classes=10)
paddle.summary(resmodel,(16,3,224,224))3.8 ResNet50模型训练
import paddle
from paddle.metric import Accuracy
from paddle.vision.transforms import Compose, Normalize, Resize, Transpose, ToTensor
from paddle.vision.models import resnet50
callback = paddle.callbacks.VisualDL(log_dir='visualdl_log_dir_resnet')
normalize = Normalize(mean=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],std=[0.5, 0.5, 0.5],data_format='HWC')
transform = Compose([ToTensor(), Normalize(), Resize(size=(224,224))])
cifar10_train = paddle.vision.datasets.Cifar10(mode='train',transform=transform)
cifar10_test = paddle.vision.datasets.Cifar10(mode='test',transform=transform)
# 构建训练集数据加载器
train_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(cifar10_train, batch_size=256, shuffle=True, drop_last=True)
# 构建测试集数据加载器
test_loader = paddle.io.DataLoader(cifar10_test, batch_size=256, shuffle=True, drop_last=True)
res_model = paddle.Model(resnet50(num_classes=10))
optim = paddle.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate=0.001, parameters=res_model.parameters())
res_model.prepare(optim,paddle.nn.CrossEntropyLoss(),Accuracy())
res_model.fit(train_data=train_loader,eval_data=test_loader,epochs=12,callbacks=callback,verbose=1)3.9 实验结果
本小节提供消融实验的结果以及可视化训练结果,共计包含四个实验,分别为octmobinetv1、mobinetv1、octresnet50以及resnet50在数据集Cifar10上的结果对比。
<style> table { margin: auto; } </style>
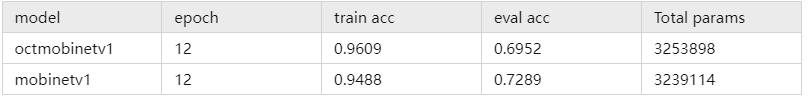
图1:Oct_MobileNetV1对比实验结果图
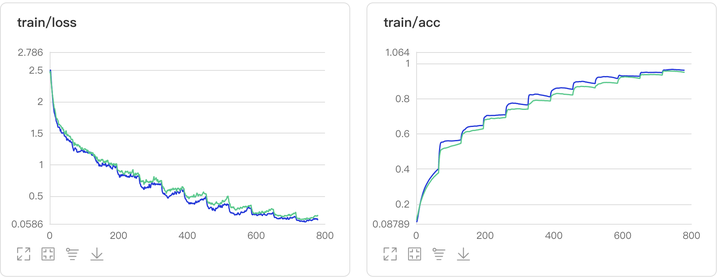
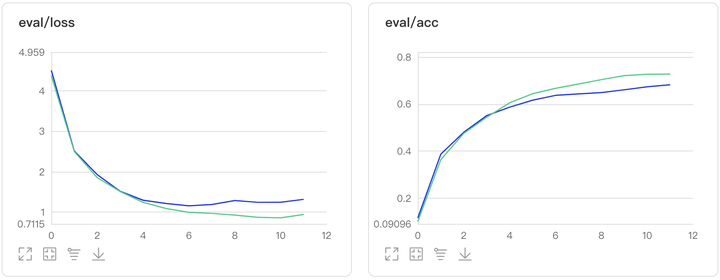
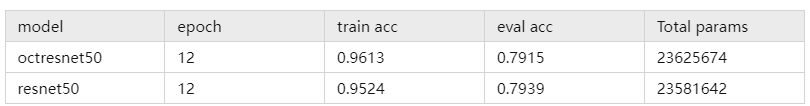
图2:Oct_ResNet50对比实验结果图


4、参考资料
d-li14/octconv.pytorch
神经网络学习之OctConv:八度卷积
Drop an Octave: Reducing Spatial Redundancy in Convolutional Neural Networks with Octave Convolution
5、总结
目前我们得到的结论与论文中的结论不符,论文提供的代码为MXnet框架,本复现参考了PyTorch版本的复现,不能确定是否为框架原因,或者一些训练设置原因,比如初始化方式或模型迭代次数不够,有待查证,大家感兴趣的也可以就这个问题与我在评论区进行交流。
点击关注,第一时间了解华为云新鲜技术~
这篇关于OctConv:八度卷积复现的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!








