本文主要是介绍FreeRTOS 实时操作系统第九讲 - 链表 (数据结构),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、链表简述
链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。链表由一系列节点(链表中每一个元素称为节点)组成,节点可以在运行时动态生成。每个节点包括两个部分:一个是存储数据元素的数据域,另一个是存储下一个节点地址的指针域。
链表作为 C 语言的一种基础数据结构,在平时写程序中用得并不多,但在操作系统中使用得非常多。如果需要读懂 FreeRTOS 系统的源码,必须弄懂链表,如果只是应用 FreeRTOS 系统,简要了解即可。
如下图:链表好比一个圆形的晾衣架,晾衣架上有很多钩子,钩子首尾相连;链表也是,链表由节点组成,节点与节点之间也是首尾相连。

晾衣架的钩子本身不能代表很多东西,但钩子却可以挂载很多东西;同样,链表也类似,链表的节点本身不能储存很多内容,但节点跟晾衣架的钩子一样,可以挂载很多数据。
另外,链表分为单向链表与双向链表,单向链表很少用,用得较多的是双向链表。
二、单向链表与双向链表
1、单向链表
单向链表如下图,该链表中共有 n 个节点,前一个节点都有一个指针指向后一个节点,首尾相连,组成一个圈。
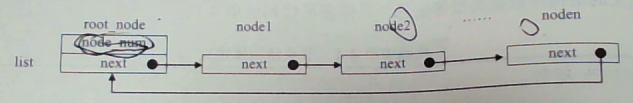
2、双链链表
双向链表如下图,该链表中共有 n 个节点,前一个节点都有两个指针分别指向前后节点,首尾相连,组成一个圈。

3、链表与数组的差异
链表是通过节点把离散的数据 (比如操作系统中任务) 链接成一个表,通过对节点的插入与删除操作实现对数据的储存。 而数组是通过开辟一段连续的内存来储存数据,这是数组与链表的最大区别。
三、FreeRTOS 中链表实现代码
说明:FreeRTOS 操作系统中的列表与列表项,分别对应 C 语言中的链表与节点。
1、列表项定义
/** Definition of the only type of object that a list can contain.*/
struct xLIST_ITEM
{listFIRST_LIST_ITEM_INTEGRITY_CHECK_VALUE /*< Set to a known value if configUSE_LIST_DATA_INTEGRITY_CHECK_BYTES is set to 1. */configLIST_VOLATILE TickType_t xItemValue; /*< The value being listed. In most cases this is used to sort the list in descending order. */struct xLIST_ITEM * configLIST_VOLATILE pxNext; /*< Pointer to the next ListItem_t in the list. */struct xLIST_ITEM * configLIST_VOLATILE pxPrevious; /*< Pointer to the previous ListItem_t in the list. */void * pvOwner; /*< Pointer to the object (normally a TCB) that contains the list item. There is therefore a two way link between the object containing the list item and the list item itself. */void * configLIST_VOLATILE pvContainer; /*< Pointer to the list in which this list item is placed (if any). */listSECOND_LIST_ITEM_INTEGRITY_CHECK_VALUE /*< Set to a known value if configUSE_LIST_DATA_INTEGRITY_CHECK_BYTES is set to 1. */
};
typedef struct xLIST_ITEM ListItem_t; /* For some reason lint wants this as two separate definitions. */
列表项结构体参数含义如下:
- 用于检测列表数据是否完整
- 辅助值 (比如用于任务的优先级),用于帮助节点进行顺序排列
- 指向下一个节点的指针
- 指向上一个节点的指针
- 指向拥有该节点的内核对象,通常是 TCB(任务控制块 / 任务句柄)
- 指向该节点所在的链表
- 用于检测列表数据是否完整
2、列表定义
/** Definition of the type of queue used by the scheduler.*/
typedef struct xLIST
{listFIRST_LIST_INTEGRITY_CHECK_VALUE /*< Set to a known value if configUSE_LIST_DATA_INTEGRITY_CHECK_BYTES is set to 1. */volatile UBaseType_t uxNumberOfItems;ListItem_t * configLIST_VOLATILE pxIndex; /*< Used to walk through the list. Points to the last item returned by a call to listGET_OWNER_OF_NEXT_ENTRY (). */MiniListItem_t xListEnd; /*< List item that contains the maximum possible item value meaning it is always at the end of the list and is therefore used as a marker. */listSECOND_LIST_INTEGRITY_CHECK_VALUE /*< Set to a known value if configUSE_LIST_DATA_INTEGRITY_CHECK_BYTES is set to 1. */
} List_t;
列表结构体参数含义如下:
- 用于检测列表数据是否完整
- 链表节点计数器,用于记录该链表下有多少个节点,根节点除外
- 链表节点索引指针,用于遍历节点
- 链表最后一个节点。 链表是一个圈,首尾相连的,首就是尾,尾也是首。 从字面理解就是链表的最后一个节点,其实也是链表的第一个节点,称之为生产者。 该生产者的数据类型是一个精简的节点,具体如下图。
- 用于检测列表数据是否完整
节点 (列表项) 精简定义:
struct xMINI_LIST_ITEM
{listFIRST_LIST_ITEM_INTEGRITY_CHECK_VALUE /*< Set to a known value if configUSE_LIST_DATA_INTEGRITY_CHECK_BYTES is set to 1. */configLIST_VOLATILE TickType_t xItemValue;struct xLIST_ITEM * configLIST_VOLATILE pxNext;struct xLIST_ITEM * configLIST_VOLATILE pxPrevious;
};
typedef struct xMINI_LIST_ITEM MiniListItem_t;
四、链表与节点初始化函数
说明:FreeRTOS 操作系统中的列表与列表项,分别对对 C 语言中的链表与节点。
1、列表项初始化函数
void vListInitialiseItem( ListItem_t * const pxItem )
{/* Make sure the list item is not recorded as being on a list. */pxItem->pvContainer = NULL;/* Write known values into the list item ifconfigUSE_LIST_DATA_INTEGRITY_CHECK_BYTES is set to 1. */listSET_FIRST_LIST_ITEM_INTEGRITY_CHECK_VALUE( pxItem );listSET_SECOND_LIST_ITEM_INTEGRITY_CHECK_VALUE( pxItem );
}
说明: 列表项初始化,只需将 pvContainer 初始化为 NULL 即可,表示该节点还没有插入到任何链表。 初始化后如下图:
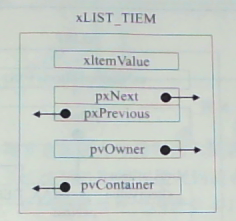
2、列表初始化函数
void vListInitialise( List_t * const pxList )
{/* The list structure contains a list item which is used to mark theend of the list. To initialise the list the list end is insertedas the only list entry. */pxList->pxIndex = ( ListItem_t * ) &( pxList->xListEnd ); /*lint !e826 !e740 The mini list structure is used as the list end to save RAM. This is checked and valid. *//* The list end value is the highest possible value in the list toensure it remains at the end of the list. */pxList->xListEnd.xItemValue = portMAX_DELAY;/* The list end next and previous pointers point to itself so we knowwhen the list is empty. */pxList->xListEnd.pxNext = ( ListItem_t * ) &( pxList->xListEnd ); /*lint !e826 !e740 The mini list structure is used as the list end to save RAM. This is checked and valid. */pxList->xListEnd.pxPrevious = ( ListItem_t * ) &( pxList->xListEnd );/*lint !e826 !e740 The mini list structure is used as the list end to save RAM. This is checked and valid. */pxList->uxNumberOfItems = ( UBaseType_t ) 0U;/* Write known values into the list ifconfigUSE_LIST_DATA_INTEGRITY_CHECK_BYTES is set to 1. */listSET_LIST_INTEGRITY_CHECK_1_VALUE( pxList );listSET_LIST_INTEGRITY_CHECK_2_VALUE( pxList );
}
说明: 列表初始化,主要初始化索引指针,链表计数值,与内部精简列表项。初始化后如下图:
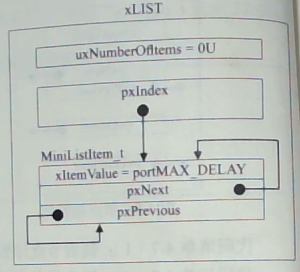
五、链表操作函数 (尾部插入、升序插入、移除)
说明:FreeRTOS 操作系统中的列表与列表项,分别对对 C 语言中的链表与节点。
1、将节点插入链表尾部
void vListInsertEnd( List_t * const pxList, ListItem_t * const pxNewListItem )
{
ListItem_t * const pxIndex = pxList->pxIndex;/* Only effective when configASSERT() is also defined, these tests may catchthe list data structures being overwritten in memory. They will not catchdata errors caused by incorrect configuration or use of FreeRTOS. */listTEST_LIST_INTEGRITY( pxList );listTEST_LIST_ITEM_INTEGRITY( pxNewListItem );/* Insert a new list item into pxList, but rather than sort the list,makes the new list item the last item to be removed by a call tolistGET_OWNER_OF_NEXT_ENTRY(). */pxNewListItem->pxNext = pxIndex;pxNewListItem->pxPrevious = pxIndex->pxPrevious;/* Only used during decision coverage testing. */mtCOVERAGE_TEST_DELAY();pxIndex->pxPrevious->pxNext = pxNewListItem;pxIndex->pxPrevious = pxNewListItem;/* Remember which list the item is in. */pxNewListItem->pvContainer = ( void * ) pxList;( pxList->uxNumberOfItems )++;
}
分析如下:
- 将新节点的 pxNext 指向根节点内的精简节点;
- 将新节点的 pxPrevious 指向之前的最后一个节点;
- 将之前最后一个节点的 pxNext 指向新节点;
- 将根节点内的精简节点 pxPrevious 指向新节点;
- 新节点的 pvContaner 指向链表;
- 链表的节点计数值加 1
尾部插入详情如下:
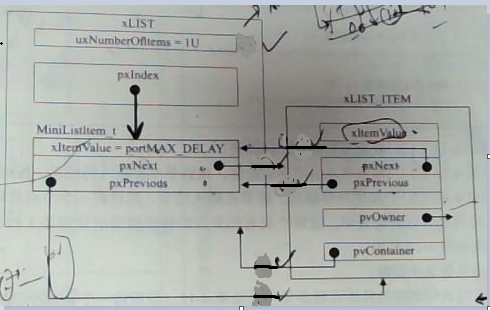
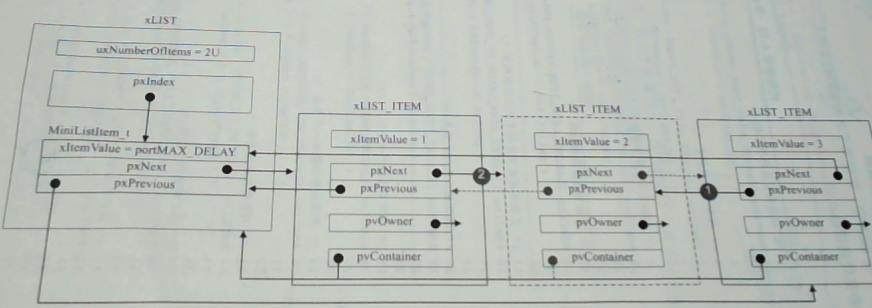
2、将节点按照升序插入链表
说明:如果两个节点的辅助值相同,则新节点在旧节点的后面插入。
void vListInsert( List_t * const pxList, ListItem_t * const pxNewListItem )
{
ListItem_t *pxIterator;
const TickType_t xValueOfInsertion = pxNewListItem->xItemValue;/* Only effective when configASSERT() is also defined, these tests may catchthe list data structures being overwritten in memory. They will not catchdata errors caused by incorrect configuration or use of FreeRTOS. */listTEST_LIST_INTEGRITY( pxList );listTEST_LIST_ITEM_INTEGRITY( pxNewListItem );/* Insert the new list item into the list, sorted in xItemValue order.If the list already contains a list item with the same item value then thenew list item should be placed after it. This ensures that TCB's which arestored in ready lists (all of which have the same xItemValue value) get ashare of the CPU. However, if the xItemValue is the same as the back markerthe iteration loop below will not end. Therefore the value is checkedfirst, and the algorithm slightly modified if necessary. */if( xValueOfInsertion == portMAX_DELAY ){pxIterator = pxList->xListEnd.pxPrevious;}else{/* *** NOTE ***********************************************************If you find your application is crashing here then likely causes arelisted below. In addition see http://www.freertos.org/FAQHelp.html formore tips, and ensure configASSERT() is defined!http://www.freertos.org/a00110.html#configASSERT1) Stack overflow -see http://www.freertos.org/Stacks-and-stack-overflow-checking.html2) Incorrect interrupt priority assignment, especially on Cortex-Mparts where numerically high priority values denote low actualinterrupt priorities, which can seem counter intuitive. Seehttp://www.freertos.org/RTOS-Cortex-M3-M4.html and the definitionof configMAX_SYSCALL_INTERRUPT_PRIORITY onhttp://www.freertos.org/a00110.html3) Calling an API function from within a critical section or whenthe scheduler is suspended, or calling an API function that doesnot end in "FromISR" from an interrupt.4) Using a queue or semaphore before it has been initialised orbefore the scheduler has been started (are interrupts firingbefore vTaskStartScheduler() has been called?).**********************************************************************/for( pxIterator = ( ListItem_t * ) &( pxList->xListEnd ); pxIterator->pxNext->xItemValue <= xValueOfInsertion; pxIterator = pxIterator->pxNext ) /*lint !e826 !e740 The mini list structure is used as the list end to save RAM. This is checked and valid. */{/* There is nothing to do here, just iterating to the wantedinsertion position. */}}pxNewListItem->pxNext = pxIterator->pxNext;pxNewListItem->pxNext->pxPrevious = pxNewListItem;pxNewListItem->pxPrevious = pxIterator;pxIterator->pxNext = pxNewListItem;/* Remember which list the item is in. This allows fast removal of theitem later. */pxNewListItem->pvContainer = ( void * ) pxList;( pxList->uxNumberOfItems )++;
}
分析如下:
- 查找插入位置;
- 调整指向关系
- 新节点的 pvContaner 指向链表
- 链表的节点计数值加 1
升序插入详情如下:
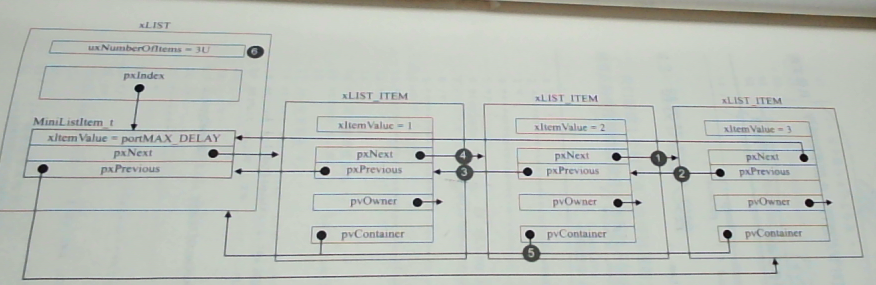
3、移除节点
UBaseType_t uxListRemove( ListItem_t * const pxItemToRemove )
{
/* The list item knows which list it is in. Obtain the list from the list
item. */
List_t * const pxList = ( List_t * ) pxItemToRemove->pvContainer;pxItemToRemove->pxNext->pxPrevious = pxItemToRemove->pxPrevious;pxItemToRemove->pxPrevious->pxNext = pxItemToRemove->pxNext;/* Only used during decision coverage testing. */mtCOVERAGE_TEST_DELAY();/* Make sure the index is left pointing to a valid item. */if( pxList->pxIndex == pxItemToRemove ){pxList->pxIndex = pxItemToRemove->pxPrevious;}else{mtCOVERAGE_TEST_MARKER();}pxItemToRemove->pvContainer = NULL;( pxList->uxNumberOfItems )--;return pxList->uxNumberOfItems;
}
分析如下:
- 通过节点获取链表;
- 调整指向关系
- 调整链表的索引指针
- 将删除节点的 pvContainer 指向 NULL;
- 链表的节点计数值减 1
- 返回链表的节点计数值
移除详情如下:
六、链表编程测试
说明:软件模拟仿真
1、只创建 1 个任务,在任务中进行链表测试
2、列表与列表项定义
说明:watch 中查看变量值,需要定义为全局变量
3、任务 1 代码

4、设置为模拟仿真,避免仿真错误,删除硬件相关的初始化代码

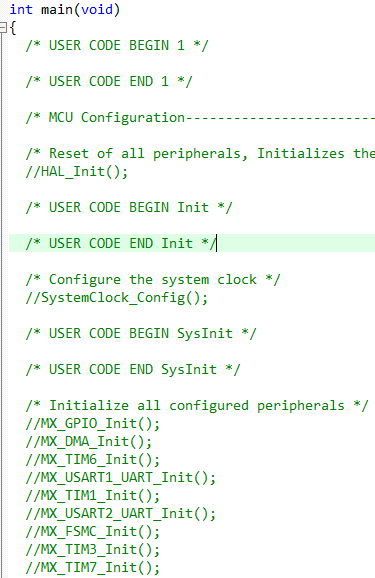
5、增加断点


6、开始仿真,并在 watch 添加列表与列表项
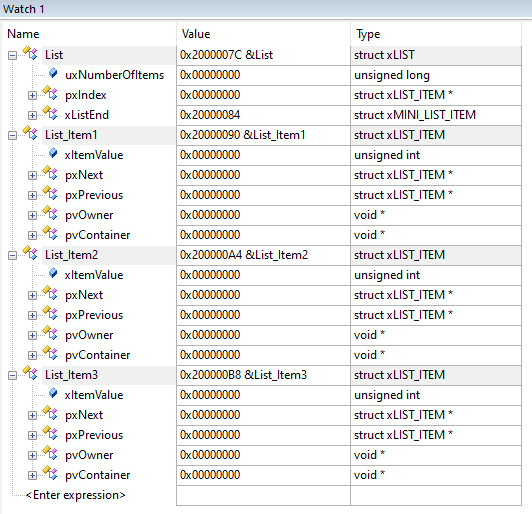
7、全速仿真至任务 1,再按 F10 单步执行,同时查看 watch 窗口
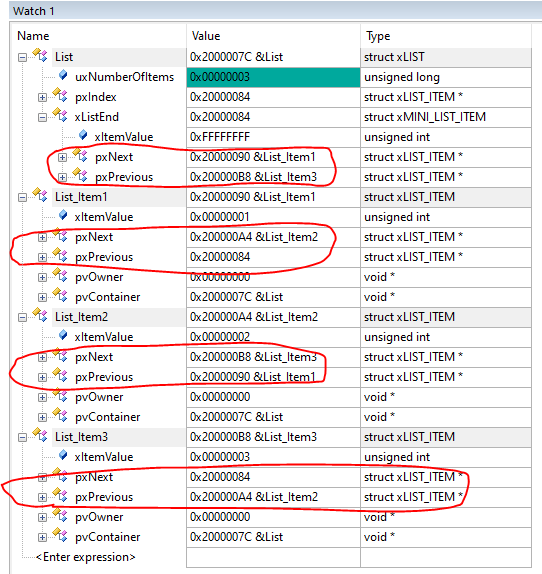
8、验证 OK。
这篇关于FreeRTOS 实时操作系统第九讲 - 链表 (数据结构)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







