本文主要是介绍二叉排序树(BST)/二叉查找树的建立(BST是笔试面试的常客),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
分享一下我老师大神的人工智能教程!零基础,通俗易懂!http://blog.csdn.net/jiangjunshow
也欢迎大家转载本篇文章。分享知识,造福人民,实现我们中华民族伟大复兴!
二叉排序树又叫二叉查找树,英文名称是:Binary Sort Tree. BST的定义就不详细说了,我用一句话概括:左 < 中 < 右。 根据这个原理,我们可以推断:BST的中序遍历必定是严格递增的。
在建立一个BST之前,大家可以做一下这个题目(很简单的):
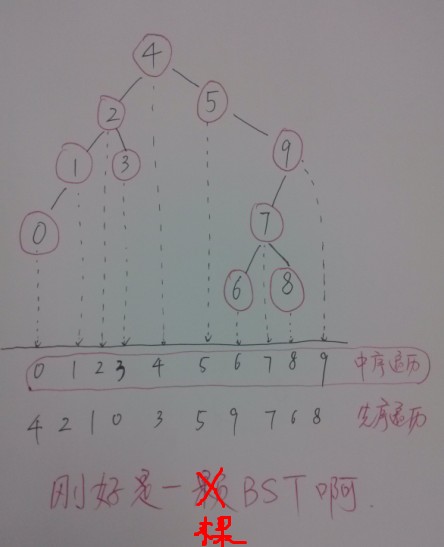
已知,某树的先序遍历为:4, 2, 1 ,0, 3, 5, 9, 7, 6, 8. 中序遍历为: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9. 请画出该树。
我们知道,树的基本遍历有4种方式,分别是:
先序遍历;中序遍历;后续遍历;层次遍历。事实上,知道任意两种方式,并不能唯一地确定树的结构,但是,只要知道中序遍历和另外任意一种遍历方式,就一定可以唯一地确定一棵树,于是,上面那个题目的答案如下:
下面,我们来看看BST的建立过程,程序如下(没考虑内存泄露):
#include <iostream>using namespace std;// BST的结点typedef struct node{ int key; struct node *lChild, *rChild;}Node, *BST;// 在给定的BST中插入结点,其数据域为element, 使之称为新的BSTbool BSTInsert(Node * &p, int element){ if(NULL == p) // 空树 { p = new Node; p->key = element; p->lChild = p->rChild = NULL; return true; } if(element == p->key) // BST中不能有相等的值 return false; if(element < p->key) // 递归 return BSTInsert(p->lChild, element); return BSTInsert(p->rChild, element); // 递归}// 建立BSTvoid createBST(Node * &T, int a[], int n){ T = NULL; int i; for(i = 0; i < n; i++) { BSTInsert(T, a[i]); }}// 先序遍历void preOrderTraverse(BST T){ if(T) { cout << T->key << " "; preOrderTraverse(T->lChild); preOrderTraverse(T->rChild); }}// 中序遍历void inOrderTraverse(BST T){ if(T) { inOrderTraverse(T->lChild); cout << T->key << " "; inOrderTraverse(T->rChild); }}int main(){ int a[10] = {4, 5, 2, 1, 0, 9, 3, 7, 6, 8}; int n = 10; BST T; // 并非所有的a[]都能构造出BST,所以,最好对createBST的返回值进行判断 createBST(T, a, n); preOrderTraverse(T); cout << endl; inOrderTraverse(T); cout << endl; return 0;}给我老师的人工智能教程打call!http://blog.csdn.net/jiangjunshow

这篇关于二叉排序树(BST)/二叉查找树的建立(BST是笔试面试的常客)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!