本文主要是介绍arkts状态管理使用(@State、@Prop、@Link、@Provide、@Consume、@objectLink和@observed),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、状态管理
1.在声明式UI中,是以状态驱动视图更新:
①状态(State):指驱动视图更新的数据(被装饰器标记的变量)
②视图(View):基于UI描述渲染得到用户界面
注意:
①@State装饰器标记的变量必须初始化,不能为空值
②@State支持object、class、string、number、boolean、enum类型以及这些类型的数组
③嵌套类型以及数组中的对象属性无法触发视图更新
例子:
class Person{name:stringage:numberfriend:Personconstructor(name:string,age:number,friend?:Person) {this.name=namethis.age=agethis.friend=friend}}@Entry
@Component
struct Index {@State message: string = 'Hello World'
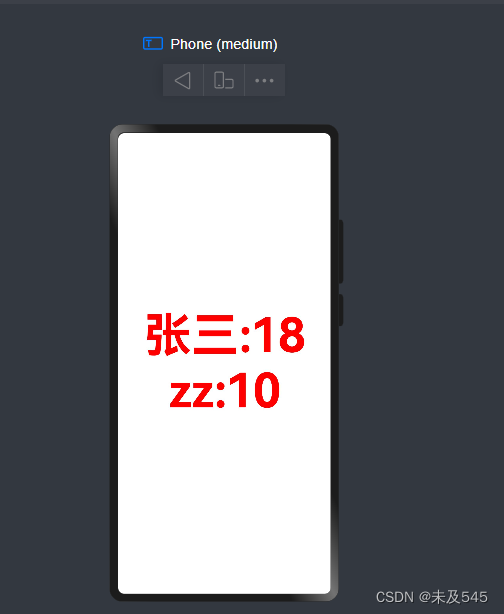
@State P:Person=new Person('张三',18,new Person('zz',10))build() {Row() {Column() {// 正常发生变化Text(`${this.P.name}:${this.P.age}`).fontSize(80).fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold).fontColor("red").onClick(()=>{this.P.name="李四"this.P.age++})// 嵌套的对象点击视图不发生变化Text(`${this.P.friend.name}:${this.P.friend.age}`).fontSize(80).fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold).fontColor("red").onClick(()=>{this.P.friend.name="ss"this.P.friend.age++})}.width('100%')}.height('100%')}
}效果:
2.@State和@Prop单项数据同步(父向子传值)
①父组件
//2.引入子组件
import { AnLi }from "./AnLi"
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
// 1.父组件声明变量
@State a:number=0build() {Stack(){Column(){// 3.父向子传值AnLi({a:this.a})Button("点击").onClick(()=>{this.a++})}.height("30%").width("100%").backgroundColor("green")}.height("50%").width("100%").backgroundColor("red").alignContent(Alignment.Center)}}②子组件
@Component
export struct AnLi {//4.@prop接收父组件传过来的变量
@Prop a:numberbuild(){Column(){Text( `${this.a}`)}}}2.@State和@Link数据双向同步
①父组件
//2.引入子组件
import { AnLi }from "./AnLi"
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
// 1.父组件声明变量
@State a:number=0build() {Stack(){Column(){Text( `${this.a}`)// 3.父向子传值AnLi({a:this.a})Button("点击").onClick(()=>{this.a++})}.height("30%").width("100%").backgroundColor("green")}.height("50%").width("100%").backgroundColor("red").alignContent(Alignment.Center)}}②子组件
@Component
export struct AnLi {//4.@Link接收父组件传过来的变量
@Link a:numberbuild(){Column(){Text( `${this.a}`)}}}效果如下:
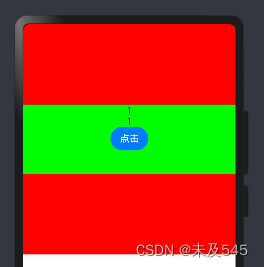
3.@Provide和@Consume与后代组件双向同步例子如下:
//入口组件,根组件
import { AnLi }from "./AnLi"
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {@Provide a:number=1build() {Stack(){Column(){AnLi()}.height("30%").width("100%").backgroundColor("green")}.height("50%").width("100%").backgroundColor("red").alignContent(Alignment.Center)}}//父组件
import { Consum }from "./Consum"
@Component
export struct AnLi {build(){Column(){Consum()}
}}//子组件
@Component
export struct Consum {@Consume a:numberbuild(){Column(){Text( `${this.a}`)Text( `${this.a}`)Button("加以").onClick(()=>{this.a++})}}}效果如下:
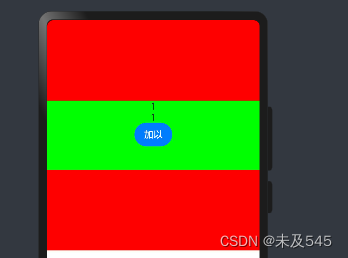
4.@objectLink和@observed装饰器用于在涉及嵌套对象或数组元素为对象的场景中进行双向数据同步
- 被@Observed装饰的类,可以被观察到属性的变化;
- 子组件中@ObjectLink装饰器装饰的状态变量用于接收@Observed装饰的类的实例,和父组件中对应的状态变量建立双向数据绑定。这个实例可以是数组中的被@Observed装饰的项,或者是class object中的属性,这个属性同样也需要被@Observed装饰。
- 单独使用@Observed是没有任何作用的,需要搭配@ObjectLink或者@Prop使用。
限制条件
- 使用@Observed装饰class会改变class原始的原型链,@Observed和其他类装饰器装饰同一个class可能会带来问题。
- @ObjectLink装饰器不能在@Entry装饰的自定义组件中使用。
@Observed
class ClassA {public c: number;constructor(c: number) {this.c = c;}
}@Observed
class ClassB {public a: ClassA;constructor(a: ClassA) {this.a = a;}
}@Component
struct ComB{@ObjectLink a:ClassA;build(){Button(`ViewA this.a.c=${this.a.c} +1`).onClick(() => {this.a.c += 1;})}
}@Entry
@Component
struct Index {@State b: ClassB = new ClassB(new ClassA(0));build() {Stack(){Column(){ComB({a:this.b.a})}.height("30%").width("100%").backgroundColor("green")}.height("50%").width("100%").backgroundColor("red").alignContent(Alignment.Center)}}效果如下:

这篇关于arkts状态管理使用(@State、@Prop、@Link、@Provide、@Consume、@objectLink和@observed)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




