本文主要是介绍基于空间注意力机制SAM的GoogLeNet实现人脸关键点检测并自动添加表情贴纸,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
基于空间注意力机制SAM的GoogLeNet实现人脸关键点检测并自动添加表情贴纸
- 一、效果展示
- 二、数据准备
- 1.解压数据集
- 2.数据集介绍
- 查看图像
- 3.数据集定义
- 4.训练集可视化
- 5.图像预处理
- 6.使用数据预处理的方式完成数据定义
- 三、模型组网
- 1.网络介绍
- 2.Inception模块
- 3.空间注意力模块
- 4.搭建SAM-GoogLeNet-BN
- 5.网络结构可视化
- 四、模型训练
- 1.模型配置
- 2.自定义评估指标
- 3.模型训练
- 4.模型保存
- 五、模型预测
- 六、趣味应用
- 1.使用自己训练的模型
- 2.使用PaddleHub内置模型
- 个人简介
使用神经网路实现人脸关键点检测,并根据人脸关键点添加表情贴纸已广泛应用于直播、短视频、特效相机、视频社交等泛娱乐场景中,为用户提供了美颜、滤镜、贴纸等多种特效。
本文在TC.Long老师的项目(使用resnet50作为backbone)的基础上做改进,使用GoogLeNet加BN层加速模型收敛,使用空间注意力机制提高模型效果。
参考资料:
- 飞桨深度学习学院——「高层API深度学习7日打卡营」
- 飞桨『高层API助你快速上手深度学习』之人脸关键点检测
- 一文搞懂卷积网络之一(【动态图】从LeNet到GoogLeNet)
- 新年美食鉴赏——基于注意力机制CBAM的美食101分类
- Hub人脸关键点检测实现耳朵和鼻子贴纸
一、效果展示
人脸关键点检测,是输入一张人脸图片,模型会返回人脸关键点的一系列坐标,从而定位到人脸的关键信息。最后再根据人脸关键点将表情贴纸添加到人脸上。

二、数据准备
1.解压数据集
本项目所采用的数据集来源为github的开源项目
目前该数据集已上传到 AI Studio 人脸关键点识别,加载后可以直接使用下面的命令解压。
!unzip data/data69065/data.zip
解压后的数据集结构为
data/
|—— test
| |—— Abdel_Aziz_Al-Hakim_00.jpg... ...
|—— test_frames_keypoints.csv
|—— training
| |—— Abdullah_Gul_10.jpg... ...
|—— training_frames_keypoints.csv
其中,training 和 test 文件夹分别存放训练集和测试集。training_frames_keypoints.csv 和 test_frames_keypoints.csv 存放着训练集和测试集的标签。接下来,我们先来观察一下 training_frames_keypoints.csv 文件,看一下训练集的标签是如何定义的。
2.数据集介绍
key_pts_frame = pd.read_csv('data/training_frames_keypoints.csv') # 读取数据集
print('Number of images: ', key_pts_frame.shape[0]) # 输出数据集大小
key_pts_frame.head(5) # 看前五条数据
Number of images: 3462
| Unnamed: 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | ... | 126 | 127 | 128 | 129 | 130 | 131 | 132 | 133 | 134 | 135 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Luis_Fonsi_21.jpg | 45.0 | 98.0 | 47.0 | 106.0 | 49.0 | 110.0 | 53.0 | 119.0 | 56.0 | ... | 83.0 | 119.0 | 90.0 | 117.0 | 83.0 | 119.0 | 81.0 | 122.0 | 77.0 | 122.0 |
| 1 | Lincoln_Chafee_52.jpg | 41.0 | 83.0 | 43.0 | 91.0 | 45.0 | 100.0 | 47.0 | 108.0 | 51.0 | ... | 85.0 | 122.0 | 94.0 | 120.0 | 85.0 | 122.0 | 83.0 | 122.0 | 79.0 | 122.0 |
| 2 | Valerie_Harper_30.jpg | 56.0 | 69.0 | 56.0 | 77.0 | 56.0 | 86.0 | 56.0 | 94.0 | 58.0 | ... | 79.0 | 105.0 | 86.0 | 108.0 | 77.0 | 105.0 | 75.0 | 105.0 | 73.0 | 105.0 |
| 3 | Angelo_Reyes_22.jpg | 61.0 | 80.0 | 58.0 | 95.0 | 58.0 | 108.0 | 58.0 | 120.0 | 58.0 | ... | 98.0 | 136.0 | 107.0 | 139.0 | 95.0 | 139.0 | 91.0 | 139.0 | 85.0 | 136.0 |
| 4 | Kristen_Breitweiser_11.jpg | 58.0 | 94.0 | 58.0 | 104.0 | 60.0 | 113.0 | 62.0 | 121.0 | 67.0 | ... | 92.0 | 117.0 | 103.0 | 118.0 | 92.0 | 120.0 | 88.0 | 122.0 | 84.0 | 122.0 |
5 rows × 137 columns
上表中每一行都代表一条数据,其中,第一列是图片的文件名,之后从第0列到第135列,就是该图的关键点信息。因为每个关键点可以用两个坐标表示,所以 136/2 = 68,就可以看出这个数据集为68点人脸关键点数据集。
目前常用的人脸关键点标注,有如下点数的标注:
- 5点
- 21点
- 68点
- 98点
本次数据集采用68点标注,标注顺序如下:

- 1-17:人脸的下轮廓
- 18-27:眉毛
- 28-36: 鼻子
- 37-48:眼睛
- 49-68:嘴巴
# 计算标签的均值和标准差,用于标签的归一化
key_pts_values = key_pts_frame.values[:,1:] # 取出标签信息
data_mean = key_pts_values.mean() # 计算均值
data_std = key_pts_values.std() # 计算标准差
print('标签的均值为:', data_mean)
print('标签的标准差为:', data_std)
标签的均值为: 104.4724870017331
标签的标准差为: 43.17302271754281
查看图像
def show_keypoints(image, key_pts):"""Args:image: 图像信息key_pts: 关键点信息,展示图片和关键点信息"""plt.imshow(image.astype('uint8')) # 展示图片信息for i in range(len(key_pts)//2,):plt.scatter(key_pts[i*2], key_pts[i*2+1], s=20, marker='.', c='b') # 展示关键点信息
# 展示单条数据
n = 421 # n为数据在表格中的索引
image_name = key_pts_frame.iloc[n, 0] # 获取图像名称
key_pts = key_pts_frame.iloc[n, 1:].as_matrix() # 将图像label格式转为numpy.array的格式
key_pts = key_pts.astype('float').reshape(-1) # 获取图像关键点信息
print(key_pts.shape)
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5)) # 展示的图像大小
show_keypoints(mpimg.imread(os.path.join('data/training/', image_name)), key_pts) # 展示图像与关键点信息
plt.show() # 展示图像
(136,)

3.数据集定义
使用飞桨框架高层API的 paddle.io.Dataset 自定义数据集类,具体可以参考官网文档 自定义数据集。
# 按照Dataset的使用规范,构建人脸关键点数据集
from paddle.io import Datasetclass FacialKeypointsDataset(Dataset):# 人脸关键点数据集"""步骤一:继承paddle.io.Dataset类"""def __init__(self, csv_file, root_dir, transform=None):"""步骤二:实现构造函数,定义数据集大小Args:csv_file (string): 带标注的csv文件路径root_dir (string): 图片存储的文件夹路径transform (callable, optional): 应用于图像上的数据处理方法"""self.key_pts_frame = pd.read_csv(csv_file) # 读取csv文件self.root_dir = root_dir # 获取图片文件夹路径self.transform = transform # 获取 transform 方法def __getitem__(self, idx):"""步骤三:实现__getitem__方法,定义指定index时如何获取数据,并返回单条数据(训练数据,对应的标签)"""image_name = os.path.join(self.root_dir,self.key_pts_frame.iloc[idx, 0])# 获取图像image = mpimg.imread(image_name)# 图像格式处理,如果包含 alpha 通道,那么忽略它if(image.shape[2] == 4):image = image[:,:,0:3]# 获取关键点信息key_pts = self.key_pts_frame.iloc[idx, 1:].as_matrix()key_pts = key_pts.astype('float').reshape(-1) # [136, 1]# 如果定义了 transform 方法,使用 transform方法if self.transform:image, key_pts = self.transform([image, key_pts])# 转为 numpy 的数据格式image = np.array(image, dtype='float32')key_pts = np.array(key_pts, dtype='float32')return image, key_ptsdef __len__(self):"""步骤四:实现__len__方法,返回数据集总数目"""return len(self.key_pts_frame) # 返回数据集大小,即图片的数量
4.训练集可视化
实例化数据集并显示一些图像
# 构建一个数据集类
face_dataset = FacialKeypointsDataset(csv_file='data/training_frames_keypoints.csv',root_dir='data/training/')# 输出数据集大小
print('数据集大小为: ', len(face_dataset))
# 根据 face_dataset 可视化数据集
num_to_display = 5for i in range(num_to_display):# 定义图片大小fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20,10))# 随机选择图片rand_i = np.random.randint(0, len(face_dataset))sample = face_dataset[rand_i]# 输出图片大小和关键点的数量print(i, sample[0].shape, sample[1].shape)# 设置图片打印信息ax = plt.subplot(1, num_to_display, i + 1)ax.set_title('Sample #{}'.format(i))# 输出图片show_keypoints(sample[0], sample[1])
数据集大小为: 3462
0 (180, 164, 3) (136,)
1 (274, 288, 3) (136,)
2 (172, 169, 3) (136,)
3 (177, 154, 3) (136,)
4 (258, 243, 3) (136,)





上述代码虽然完成了数据集的定义,但是还有一些问题,如:
- 每张图像的大小不一样,图像大小需要统一以适配网络输入要求
- 图像格式需要适配模型的格式输入要求
- 数据量比较小,没有进行数据增强
这些问题都会影响模型最终的性能,所以需要对数据进行预处理。
5.图像预处理
对图像进行预处理,包括灰度化、归一化、重新设置尺寸、随机裁剪,修改通道格式等等,以满足数据要求;每一类的功能如下:
- 灰度化:丢弃颜色信息,保留图像边缘信息;识别算法对于颜色的依赖性不强,加上颜色后鲁棒性会下降,而且灰度化图像维度下降(3->1),保留梯度的同时会加快计算。
- 归一化:加快收敛
- 重新设置尺寸:数据增强
- 随机裁剪:数据增强
- 修改通道格式:改为模型需要的结构
# 标准化自定义 transform 方法
class TransformAPI(object):"""步骤一:继承 object 类"""def __call__(self, data):"""步骤二:在 __call__ 中定义数据处理方法"""processed_data = datareturn processed_data
import paddle.vision.transforms.functional as Fclass GrayNormalize(object):# 将图片变为灰度图,并将其值放缩到[0, 1]# 将 label 放缩到 [-1, 1] 之间def __call__(self, data):image = data[0] # 获取图片key_pts = data[1] # 获取标签image_copy = np.copy(image)key_pts_copy = np.copy(key_pts)# 灰度化图片gray_scale = paddle.vision.transforms.Grayscale(num_output_channels=3)image_copy = gray_scale(image_copy)# 将图片值放缩到 [0, 1]image_copy = image_copy / 255.0# 将坐标点放缩到 [-1, 1]mean = data_mean # 获取标签均值std = data_std # 获取标签标准差key_pts_copy = (key_pts_copy - mean)/stdreturn image_copy, key_pts_copyclass Resize(object):# 将输入图像调整为指定大小def __init__(self, output_size):assert isinstance(output_size, (int, tuple))self.output_size = output_sizedef __call__(self, data):image = data[0] # 获取图片key_pts = data[1] # 获取标签image_copy = np.copy(image) key_pts_copy = np.copy(key_pts)h, w = image_copy.shape[:2]if isinstance(self.output_size, int):if h > w:new_h, new_w = self.output_size * h / w, self.output_sizeelse:new_h, new_w = self.output_size, self.output_size * w / helse:new_h, new_w = self.output_sizenew_h, new_w = int(new_h), int(new_w)img = F.resize(image_copy, (new_h, new_w))# scale the pts, tookey_pts_copy[::2] = key_pts_copy[::2] * new_w / wkey_pts_copy[1::2] = key_pts_copy[1::2] * new_h / hreturn img, key_pts_copyclass RandomCrop(object):# 随机位置裁剪输入的图像def __init__(self, output_size):assert isinstance(output_size, (int, tuple))if isinstance(output_size, int):self.output_size = (output_size, output_size)else:assert len(output_size) == 2self.output_size = output_sizedef __call__(self, data):image = data[0]key_pts = data[1]image_copy = np.copy(image)key_pts_copy = np.copy(key_pts)h, w = image_copy.shape[:2]new_h, new_w = self.output_sizetop = np.random.randint(0, h - new_h)left = np.random.randint(0, w - new_w)image_copy = image_copy[top: top + new_h,left: left + new_w]key_pts_copy[::2] = key_pts_copy[::2] - leftkey_pts_copy[1::2] = key_pts_copy[1::2] - topreturn image_copy, key_pts_copyclass ToCHW(object):# 将图像的格式由HWC改为CHWdef __call__(self, data):image = data[0]key_pts = data[1]transpose = T.Transpose((2, 0, 1)) # 改为CHWimage = transpose(image)return image, key_pts
看一下每种图像预处理方法的的效果。
import paddle.vision.transforms as T# 测试 Resize
resize = Resize(256)# 测试 RandomCrop
random_crop = RandomCrop(128)# 测试 GrayNormalize
norm = GrayNormalize()# 测试 Resize + RandomCrop,图像大小变到250*250, 然后截取出224*224的图像块
composed = paddle.vision.transforms.Compose([Resize(250), RandomCrop(224)])test_num = 666 # 测试的数据下标
data = face_dataset[test_num]transforms = {'None': None, 'norm': norm,'random_crop': random_crop,'resize': resize ,'composed': composed}
for i, func_name in enumerate(['None', 'norm', 'random_crop', 'resize', 'composed']):# 定义图片大小fig = plt.figure(figsize=(20,10))# 处理图片if transforms[func_name] != None:transformed_sample = transforms[func_name](data)else:transformed_sample = data# 设置图片打印信息ax = plt.subplot(1, 5, i + 1)ax.set_title(' Transform is #{}'.format(func_name))# 输出图片show_keypoints(transformed_sample[0], transformed_sample[1])





图像归一化后,肉眼看上去是黑色的,这是因为像素值由0-255缩放到了0-1,越趋近于0越黑,越趋近于255越白,所以归一化后的图像看上去是黑的
6.使用数据预处理的方式完成数据定义
让我们将 Resize、RandomCrop、GrayNormalize、ToCHW 应用于新的数据集
from paddle.vision.transforms import Composedata_transform = Compose([Resize(256), RandomCrop(224), GrayNormalize(), ToCHW()])# create the transformed dataset
train_dataset = FacialKeypointsDataset(csv_file='data/training_frames_keypoints.csv',root_dir='data/training/',transform=data_transform)
print('Number of train dataset images: ', len(train_dataset))for i in range(4):sample = train_dataset[i]print(i, sample[0].shape, sample[1].shape)test_dataset = FacialKeypointsDataset(csv_file='data/test_frames_keypoints.csv',root_dir='data/test/',transform=data_transform)print('Number of test dataset images: ', len(test_dataset))
Number of train dataset images: 3462
0 (3, 224, 224) (136,)
1 (3, 224, 224) (136,)
2 (3, 224, 224) (136,)
3 (3, 224, 224) (136,)
Number of test dataset images: 770
三、模型组网
1.网络介绍
分类任务中,有多少个类别,输出维度就是多少。不同的是,人脸关键点检测任务中,输出为 人脸关键点的数量*2,即每个人脸关键点的横坐标与纵坐标,这样就可以完成人脸关键点检测任务了。
-
Inception模块

-
空间注意力模块

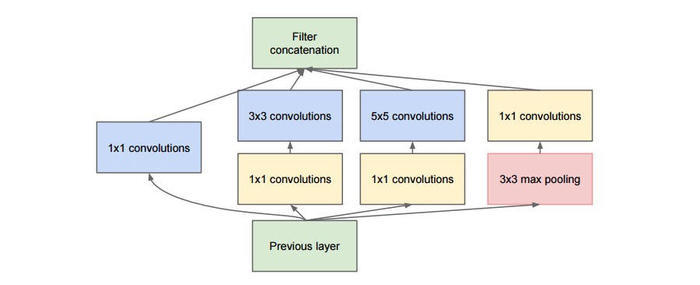
2.Inception模块
GoogLeNet是由Inception模块进行组成的,GoogLeNet采用了模块化的结构,因此修改网络结构时非常简单方便。
import paddle
import paddle.nn as nn# GoogLeNet加BN层加速模型收敛
class Inception(nn.Layer): # 定义Inception块(Inception v1)def __init__(self,c1, c2, c3, c4):super(Inception, self).__init__()self.relu = nn.ReLU()self.p1_1 = nn.Conv2D(c1[0], c1[1], 1)self.p2_1 = nn.Conv2D(c1[0], c2[0], 1)self.p2_2 = nn.Conv2D(c2[0], c2[1], 3, padding=1)self.p3_1 = nn.Conv2D(c1[0], c3[0], 1)self.p3_2 = nn.Conv2D(c3[0], c3[1], 5, padding=2)self.p4_1 = nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)self.p4_2 = nn.Conv2D(c1[0], c4, 1)def forward(self, x):p1 = self.relu(self.p1_1(x))p2 = self.relu(self.p2_2(self.p2_1(x)))p3 = self.relu(self.p3_2(self.p3_1(x)))p4 = self.relu(self.p4_2(self.p4_1(x)))return paddle.concat([p1, p2, p3, p4], axis=1)
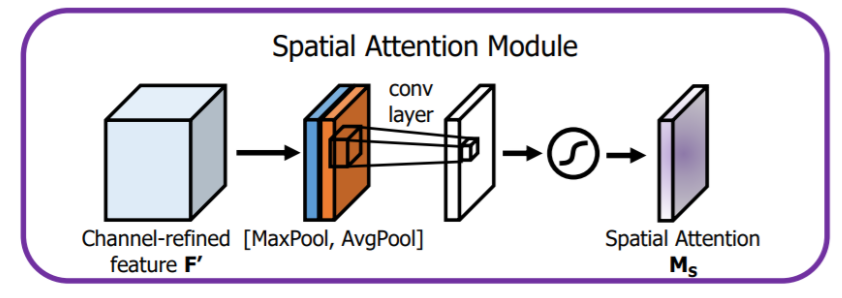
3.空间注意力模块
空间注意力聚焦在“哪里”是最具信息量的部分。计算空间注意力的方法是沿着通道轴应用平均池化和最大池操作,然后将它们连接起来生成一个有效的特征描述符。
import paddle
import paddle.nn as nn# 空间注意力机制
class SAM_Module(nn.Layer): def __init__(self): super(SAM_Module, self).__init__() self.conv_after_concat = nn.Conv2D(in_channels=2, out_channels=1, kernel_size=7, stride=1, padding=3) self.sigmoid_spatial = nn.Sigmoid() def forward(self, x): # Spatial Attention Module module_input = x avg = paddle.mean(x, axis=1, keepdim=True) mx = paddle.argmax(x, axis=1, keepdim=True)mx = paddle.cast(mx, 'float32')x = paddle.concat([avg, mx], axis=1)x = self.conv_after_concat(x) x = self.sigmoid_spatial(x) x = module_input * x return x
4.搭建SAM-GoogLeNet-BN
class SAM_GoogLeNet_BN(nn.Layer):def __init__(self, num_keypoints=68):super(SAM_GoogLeNet_BN, self).__init__()self.relu = nn.ReLU()self.bn64 = nn.BatchNorm(num_channels=64)self.bn192 = nn.BatchNorm(192)self.bn256 = nn.BatchNorm(256)self.bn480 = nn.BatchNorm(480)self.bn512 = nn.BatchNorm(512)self.bn528 = nn.BatchNorm(528)self.bn832 = nn.BatchNorm(832)self.bn1024 = nn.BatchNorm(1024)self.conv1 = nn.Conv2D(in_channels=3, out_channels=64, kernel_size=7, padding=3, stride=2, data_format='NCHW')self.SAM_Module1 = SAM_Module()self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)self.conv2_1 = nn.Conv2D(64, 64, 1,)self.conv2_2 = nn.Conv2D(64, 192, 3, padding=1)self.SAM_Module2 = SAM_Module()self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)self.block3_a = Inception((192, 64), (96, 128), (16, 32), 32)self.block3_b = Inception((256, 128), (128, 192), (32, 96), 64)self.SAM_Module3 = SAM_Module()self.pool3 = nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)self.block4_a = Inception((480, 192), (96, 208), (16, 48), 64)self.block4_b = Inception((512, 160), (112, 224), (24, 64), 64)self.block4_c = Inception((512, 128), (128, 256), (24, 64), 64)self.block4_d = Inception((512, 112), (144, 288), (32, 64), 64)self.block4_e = Inception((528, 256), (160, 320), (32, 128), 128)self.SAM_Module4 = SAM_Module()self.pool4 = nn.MaxPool2D(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)self.block5_a = Inception((832, 256), (160, 320), (32, 128), 128)self.block5_b = Inception((832, 384), (192, 384), (48, 128), 128)self.pool5 = nn.AvgPool2D(kernel_size=7, stride=1)self.drop = nn.Dropout(0.2)self.fc1 = nn.Linear(1024, 512)self.fc2 = nn.Linear(512, num_keypoints * 2)# 网络的前向计算过程def forward(self, x):x = self.conv1(x)x = self.relu(x)x = self.SAM_Module1(x)x = self.relu(self.conv2_2(self.relu(self.conv2_1(self.bn64(self.pool1(x))))))x = self.SAM_Module2(x)x = self.block3_b(self.block3_a(self.bn192(self.pool2(x))))x = self.SAM_Module3(x)x = self.block4_e(self.block4_d(self.block4_c(self.block4_b(self.block4_a(self.bn480(self.pool3(x)))))))x = self.SAM_Module4(x)x = self.bn1024(self.pool5(self.block5_b(self.block5_a(self.bn832(self.pool4(x))))))x = self.drop(x)x = fluid.layers.reshape(x, [-1, 1024])x = self.fc1(x)x = self.relu(x)x = self.fc2(x)return x
5.网络结构可视化
使用model.summary查看网络结构。
model = paddle.Model(SAM_GoogLeNet_BN(num_keypoints=68))
model.summary((1, 3, 224, 224))
---------------------------------------------------------------------------Layer (type) Input Shape Output Shape Param #
===========================================================================Conv2D-1239 [[1, 3, 224, 224]] [1, 64, 112, 112] 9,472 ReLU-1010 [[1, 512]] [1, 512] 0 Conv2D-1240 [[1, 2, 112, 112]] [1, 1, 112, 112] 99 Sigmoid-36 [[1, 1, 112, 112]] [1, 1, 112, 112] 0 SAM_Module-36 [[1, 64, 112, 112]] [1, 64, 112, 112] 0 MaxPool2D-61 [[1, 64, 112, 112]] [1, 64, 56, 56] 0 BatchNorm-225 [[1, 64, 56, 56]] [1, 64, 56, 56] 256 Conv2D-1241 [[1, 64, 56, 56]] [1, 64, 56, 56] 4,160 Conv2D-1242 [[1, 64, 56, 56]] [1, 192, 56, 56] 110,784 Conv2D-1243 [[1, 2, 56, 56]] [1, 1, 56, 56] 99 Sigmoid-37 [[1, 1, 56, 56]] [1, 1, 56, 56] 0 SAM_Module-37 [[1, 192, 56, 56]] [1, 192, 56, 56] 0 MaxPool2D-62 [[1, 192, 56, 56]] [1, 192, 28, 28] 0 BatchNorm-226 [[1, 192, 28, 28]] [1, 192, 28, 28] 768 Conv2D-1244 [[1, 192, 28, 28]] [1, 64, 28, 28] 12,352 ReLU-1011 [[1, 32, 28, 28]] [1, 32, 28, 28] 0 Conv2D-1245 [[1, 192, 28, 28]] [1, 96, 28, 28] 18,528 Conv2D-1246 [[1, 96, 28, 28]] [1, 128, 28, 28] 110,720 Conv2D-1247 [[1, 192, 28, 28]] [1, 16, 28, 28] 3,088 Conv2D-1248 [[1, 16, 28, 28]] [1, 32, 28, 28] 12,832 MaxPool2D-63 [[1, 192, 28, 28]] [1, 192, 28, 28] 0 Conv2D-1249 [[1, 192, 28, 28]] [1, 32, 28, 28] 6,176 Inception-82 [[1, 192, 28, 28]] [1, 256, 28, 28] 0 Conv2D-1250 [[1, 256, 28, 28]] [1, 128, 28, 28] 32,896 ReLU-1012 [[1, 64, 28, 28]] [1, 64, 28, 28] 0 Conv2D-1251 [[1, 256, 28, 28]] [1, 128, 28, 28] 32,896 Conv2D-1252 [[1, 128, 28, 28]] [1, 192, 28, 28] 221,376 Conv2D-1253 [[1, 256, 28, 28]] [1, 32, 28, 28] 8,224 Conv2D-1254 [[1, 32, 28, 28]] [1, 96, 28, 28] 76,896 MaxPool2D-64 [[1, 256, 28, 28]] [1, 256, 28, 28] 0 Conv2D-1255 [[1, 256, 28, 28]] [1, 64, 28, 28] 16,448 Inception-83 [[1, 256, 28, 28]] [1, 480, 28, 28] 0 Conv2D-1256 [[1, 2, 28, 28]] [1, 1, 28, 28] 99 Sigmoid-38 [[1, 1, 28, 28]] [1, 1, 28, 28] 0 SAM_Module-38 [[1, 480, 28, 28]] [1, 480, 28, 28] 0 MaxPool2D-65 [[1, 480, 28, 28]] [1, 480, 14, 14] 0 BatchNorm-228 [[1, 480, 14, 14]] [1, 480, 14, 14] 1,920 Conv2D-1257 [[1, 480, 14, 14]] [1, 192, 14, 14] 92,352 ReLU-1013 [[1, 64, 14, 14]] [1, 64, 14, 14] 0 Conv2D-1258 [[1, 480, 14, 14]] [1, 96, 14, 14] 46,176 Conv2D-1259 [[1, 96, 14, 14]] [1, 208, 14, 14] 179,920 Conv2D-1260 [[1, 480, 14, 14]] [1, 16, 14, 14] 7,696 Conv2D-1261 [[1, 16, 14, 14]] [1, 48, 14, 14] 19,248 MaxPool2D-66 [[1, 480, 14, 14]] [1, 480, 14, 14] 0 Conv2D-1262 [[1, 480, 14, 14]] [1, 64, 14, 14] 30,784 Inception-84 [[1, 480, 14, 14]] [1, 512, 14, 14] 0 Conv2D-1263 [[1, 512, 14, 14]] [1, 160, 14, 14] 82,080 ReLU-1014 [[1, 64, 14, 14]] [1, 64, 14, 14] 0 Conv2D-1264 [[1, 512, 14, 14]] [1, 112, 14, 14] 57,456 Conv2D-1265 [[1, 112, 14, 14]] [1, 224, 14, 14] 226,016 Conv2D-1266 [[1, 512, 14, 14]] [1, 24, 14, 14] 12,312 Conv2D-1267 [[1, 24, 14, 14]] [1, 64, 14, 14] 38,464 MaxPool2D-67 [[1, 512, 14, 14]] [1, 512, 14, 14] 0 Conv2D-1268 [[1, 512, 14, 14]] [1, 64, 14, 14] 32,832 Inception-85 [[1, 512, 14, 14]] [1, 512, 14, 14] 0 Conv2D-1269 [[1, 512, 14, 14]] [1, 128, 14, 14] 65,664 ReLU-1015 [[1, 64, 14, 14]] [1, 64, 14, 14] 0 Conv2D-1270 [[1, 512, 14, 14]] [1, 128, 14, 14] 65,664 Conv2D-1271 [[1, 128, 14, 14]] [1, 256, 14, 14] 295,168 Conv2D-1272 [[1, 512, 14, 14]] [1, 24, 14, 14] 12,312 Conv2D-1273 [[1, 24, 14, 14]] [1, 64, 14, 14] 38,464 MaxPool2D-68 [[1, 512, 14, 14]] [1, 512, 14, 14] 0 Conv2D-1274 [[1, 512, 14, 14]] [1, 64, 14, 14] 32,832 Inception-86 [[1, 512, 14, 14]] [1, 512, 14, 14] 0 Conv2D-1275 [[1, 512, 14, 14]] [1, 112, 14, 14] 57,456 ReLU-1016 [[1, 64, 14, 14]] [1, 64, 14, 14] 0 Conv2D-1276 [[1, 512, 14, 14]] [1, 144, 14, 14] 73,872 Conv2D-1277 [[1, 144, 14, 14]] [1, 288, 14, 14] 373,536 Conv2D-1278 [[1, 512, 14, 14]] [1, 32, 14, 14] 16,416 Conv2D-1279 [[1, 32, 14, 14]] [1, 64, 14, 14] 51,264 MaxPool2D-69 [[1, 512, 14, 14]] [1, 512, 14, 14] 0 Conv2D-1280 [[1, 512, 14, 14]] [1, 64, 14, 14] 32,832 Inception-87 [[1, 512, 14, 14]] [1, 528, 14, 14] 0 Conv2D-1281 [[1, 528, 14, 14]] [1, 256, 14, 14] 135,424 ReLU-1017 [[1, 128, 14, 14]] [1, 128, 14, 14] 0 Conv2D-1282 [[1, 528, 14, 14]] [1, 160, 14, 14] 84,640 Conv2D-1283 [[1, 160, 14, 14]] [1, 320, 14, 14] 461,120 Conv2D-1284 [[1, 528, 14, 14]] [1, 32, 14, 14] 16,928 Conv2D-1285 [[1, 32, 14, 14]] [1, 128, 14, 14] 102,528 MaxPool2D-70 [[1, 528, 14, 14]] [1, 528, 14, 14] 0 Conv2D-1286 [[1, 528, 14, 14]] [1, 128, 14, 14] 67,712 Inception-88 [[1, 528, 14, 14]] [1, 832, 14, 14] 0 Conv2D-1287 [[1, 2, 14, 14]] [1, 1, 14, 14] 99 Sigmoid-39 [[1, 1, 14, 14]] [1, 1, 14, 14] 0 SAM_Module-39 [[1, 832, 14, 14]] [1, 832, 14, 14] 0 MaxPool2D-71 [[1, 832, 14, 14]] [1, 832, 7, 7] 0 BatchNorm-231 [[1, 832, 7, 7]] [1, 832, 7, 7] 3,328 Conv2D-1288 [[1, 832, 7, 7]] [1, 256, 7, 7] 213,248 ReLU-1018 [[1, 128, 7, 7]] [1, 128, 7, 7] 0 Conv2D-1289 [[1, 832, 7, 7]] [1, 160, 7, 7] 133,280 Conv2D-1290 [[1, 160, 7, 7]] [1, 320, 7, 7] 461,120 Conv2D-1291 [[1, 832, 7, 7]] [1, 32, 7, 7] 26,656 Conv2D-1292 [[1, 32, 7, 7]] [1, 128, 7, 7] 102,528 MaxPool2D-72 [[1, 832, 7, 7]] [1, 832, 7, 7] 0 Conv2D-1293 [[1, 832, 7, 7]] [1, 128, 7, 7] 106,624 Inception-89 [[1, 832, 7, 7]] [1, 832, 7, 7] 0 Conv2D-1294 [[1, 832, 7, 7]] [1, 384, 7, 7] 319,872 ReLU-1019 [[1, 128, 7, 7]] [1, 128, 7, 7] 0 Conv2D-1295 [[1, 832, 7, 7]] [1, 192, 7, 7] 159,936 Conv2D-1296 [[1, 192, 7, 7]] [1, 384, 7, 7] 663,936 Conv2D-1297 [[1, 832, 7, 7]] [1, 48, 7, 7] 39,984 Conv2D-1298 [[1, 48, 7, 7]] [1, 128, 7, 7] 153,728 MaxPool2D-73 [[1, 832, 7, 7]] [1, 832, 7, 7] 0 Conv2D-1299 [[1, 832, 7, 7]] [1, 128, 7, 7] 106,624 Inception-90 [[1, 832, 7, 7]] [1, 1024, 7, 7] 0 AvgPool2D-7 [[1, 1024, 7, 7]] [1, 1024, 1, 1] 0 BatchNorm-232 [[1, 1024, 1, 1]] [1, 1024, 1, 1] 4,096 Dropout-22 [[1, 1024, 1, 1]] [1, 1024, 1, 1] 0 Linear-22 [[1, 1024]] [1, 512] 524,800 Linear-23 [[1, 512]] [1, 136] 69,768
===========================================================================
Total params: 6,578,884
Trainable params: 6,568,516
Non-trainable params: 10,368
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Input size (MB): 0.57
Forward/backward pass size (MB): 64.93
Params size (MB): 25.10
Estimated Total Size (MB): 90.60
---------------------------------------------------------------------------{'total_params': 6578884, 'trainable_params': 6568516}
四、模型训练
1.模型配置
训练模型前,需要设置训练模型所需的优化器,损失函数和评估指标。
- 优化器:Momentum优化器
- 损失函数:SmoothL1Loss
- 评估指标:NME
2.自定义评估指标
特定任务的 Metric 计算方式在框架既有的 Metric接口中不存在,或算法不符合自己的需求,那么需要我们自己来进行Metric的自定义。这里介绍如何进行Metric的自定义操作,更多信息可以参考官网文档自定义Metric;首先来看下面的代码。
from paddle.metric import Metricclass NME(Metric):"""1. 继承paddle.metric.Metric"""def __init__(self, name='nme', *args, **kwargs):"""2. 构造函数实现,自定义参数即可"""super(NME, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)self._name = nameself.rmse = 0self.sample_num = 0def name(self):"""3. 实现name方法,返回定义的评估指标名字"""return self._namedef update(self, preds, labels):"""4. 实现update方法,用于单个batch训练时进行评估指标计算。- 当`compute`类函数未实现时,会将模型的计算输出和标签数据的展平作为`update`的参数传入。"""N = preds.shape[0]preds = preds.reshape((N, -1, 2))labels = labels.reshape((N, -1, 2))self.rmse = 0for i in range(N):pts_pred, pts_gt = preds[i, ], labels[i, ]interocular = np.linalg.norm(pts_gt[36, ] - pts_gt[45, ])self.rmse += np.sum(np.linalg.norm(pts_pred - pts_gt, axis=1)) / (interocular * preds.shape[1])self.sample_num += 1return self.rmse / Ndef accumulate(self):"""5. 实现accumulate方法,返回历史batch训练积累后计算得到的评价指标值。每次`update`调用时进行数据积累,`accumulate`计算时对积累的所有数据进行计算并返回。结算结果会在`fit`接口的训练日志中呈现。"""return self.rmse / self.sample_numdef reset(self):"""6. 实现reset方法,每个Epoch结束后进行评估指标的重置,这样下个Epoch可以重新进行计算。"""self.rmse = 0self.sample_num = 0
# 调用飞桨框架的VisualDL模块,保存信息到目录中。
callback = paddle.callbacks.VisualDL(log_dir='visualdl_log_dir')# 定义Momentum优化器
lr = paddle.optimizer.lr.CosineAnnealingDecay(learning_rate=0.01, T_max=len(train_dataset) // 64 * 50)
optimizer = paddle.optimizer.Momentum(learning_rate=lr,parameters=model.parameters(),weight_decay=paddle.regularizer.L2Decay(0.002))# 定义SmoothL1Loss
loss = nn.SmoothL1Loss()# 使用自定义metrics
metric = NME()# 模型训练配置
model.prepare(optimizer=optimizer, loss=loss, metrics=metric)
损失函数的选择:L1Loss、L2Loss、SmoothL1Loss的对比
- L1Loss: 在训练后期,预测值与ground-truth差异较小时, 损失对预测值的导数的绝对值仍然为1,此时如果学习率不变,损失函数将在稳定值附近波动,难以继续收敛达到更高精度。
- L2Loss: 在训练初期,预测值与ground-truth差异较大时,损失函数对预测值的梯度十分大,导致训练不稳定。
- SmoothL1Loss: 在x较小时,对x梯度也会变小,而在x很大时,对x的梯度的绝对值达到上限 1,也不会太大以至于破坏网络参数。
3.模型训练
model.fit(train_dataset, test_dataset,epochs=50, shuffle=True, batch_size=64, callbacks=callback,verbose=1)
The loss value printed in the log is the current step, and the metric is the average value of previous step.
Epoch 1/50
step 55/55 [==============================] - loss: 0.3578 - nme: 0.0013 - 499ms/step
Eval begin...
The loss value printed in the log is the current batch, and the metric is the average value of previous step.
step 13/13 [==============================] - loss: 0.1764 - nme: 0.0011 - 466ms/step
Eval samples: 770
Epoch 2/50
step 55/55 [==============================] - loss: 0.2794 - nme: 0.0013 - 517ms/step
Eval begin...
The loss value printed in the log is the current batch, and the metric is the average value of previous step.
step 13/13 [==============================] - loss: 0.1960 - nme: 0.0012 - 425ms/step
Eval samples: 770
Epoch 3/50
step 55/55 [==============================] - loss: 0.1871 - nme: 0.0010 - 483ms/step
Eval begin...
The loss value printed in the log is the current batch, and the metric is the average value of previous step.
step 13/13 [==============================] - loss: 0.1321 - nme: 9.8054e-04 - 419ms/step
Eval samples: 770
Epoch 4/50
step 55/55 [==============================] - loss: 0.2032 - nme: 9.5976e-04 - 501ms/step
Eval begin...
The loss value printed in the log is the current batch, and the metric is the average value of previous step.
step 13/13 [==============================] - loss: 0.0729 - nme: 6.8905e-04 - 404ms/step
Eval samples: 770
4.模型保存
checkpoints_path = 'work/models'
model.save(checkpoints_path, training=False)
五、模型预测
# 定义功能函数def show_all_keypoints(image, predicted_key_pts):"""展示图像,预测关键点Args:image:裁剪后的图像 [224, 224, 3]predicted_key_pts: 预测关键点的坐标"""# 展示图像plt.imshow(image.astype('uint8'))# 展示关键点for i in range(0, len(predicted_key_pts), 2):plt.scatter(predicted_key_pts[i], predicted_key_pts[i+1], s=20, marker='.', c='m')def visualize_output(test_images, test_outputs, batch_size=1, h=20, w=10):"""展示图像,预测关键点Args:test_images:裁剪后的图像 [224, 224, 3]test_outputs: 模型的输出batch_size: 批大小h: 展示的图像高w: 展示的图像宽"""if len(test_images.shape) == 3:test_images = np.array([test_images])for i in range(batch_size):plt.figure(figsize=(h, w))ax = plt.subplot(1, batch_size, i+1)# 随机裁剪后的图像image = test_images[i]# 模型的输出,未还原的预测关键点坐标值predicted_key_pts = test_outputs[i]# 还原后的真实的关键点坐标值predicted_key_pts = predicted_key_pts * data_std + data_mean# 展示图像和关键点show_all_keypoints(np.squeeze(image), predicted_key_pts)plt.axis('off')plt.show()
# 读取图像
img = mpimg.imread('zbp.jpg')# 关键点占位符
kpt = np.ones((136, 1))transform = Compose([Resize(256), RandomCrop(224)])# 对图像先重新定义大小,并裁剪到 224*224的大小
rgb_img, kpt = transform([img, kpt])norm = GrayNormalize()
to_chw = ToCHW()# 对图像进行归一化和格式变换
img, kpt = norm([rgb_img, kpt])
img, kpt = to_chw([img, kpt])img = np.array([img], dtype='float32')# 加载保存好的模型进行预测
# model = paddle.Model(SAM_GoogLeNet_BN(num_keypoints=68))
# model.load(checkpoints_path)
# model.prepare()# 预测结果
out = model.predict_batch([img])
out = out[0].reshape((out[0].shape[0], 136, -1))# 可视化
visualize_output(rgb_img, out, batch_size=1)

六、趣味应用
当我们得到关键点的信息后,就可以进行一些趣味的应用。
1.使用自己训练的模型
def read_image(img_path):# 读取图像img = mpimg.imread(img_path)# 关键点占位符kpt = np.ones((136, 1))transform = Compose([Resize(256), RandomCrop(224)])# 对图像先重新定义大小,并裁剪到 224*224的大小rgb_img, kpt = transform([img, kpt])norm = GrayNormalize()to_chw = ToCHW()# 对图像进行归一化和格式变换img, kpt = norm([rgb_img, kpt])img, kpt = to_chw([img, kpt])img = np.array([img], dtype='float32')return img# 定义功能函数
def show_fu(image, predicted_key_pts):"""展示加了贴纸的图像Args:image:裁剪后的图像 [224, 224, 3]predicted_key_pts: 预测关键点的坐标"""# 计算坐标,15 和 34点的中间值x = (int(predicted_key_pts[28]) + int(predicted_key_pts[66]))//2y = (int(predicted_key_pts[29]) + int(predicted_key_pts[67]))//2# 打开 春节小图star_image = mpimg.imread('light.jpg')# 处理通道if(star_image.shape[2] == 4):star_image = star_image[:,:,1:4]# 将春节小图放到原图上image[y:y+len(star_image[0]), x:x+len(star_image[1]),:] = star_image# 展示处理后的图片plt.imshow(image.astype('uint8'))# 展示关键点信息for i in range(len(predicted_key_pts)//2,):plt.scatter(predicted_key_pts[i*2], predicted_key_pts[i*2+1], s=20, marker='.', c='m') # 展示关键点信息def custom_output(test_images, test_outputs, batch_size=1, h=20, w=10):"""展示图像,预测关键点Args:test_images:裁剪后的图像 [224, 224, 3]test_outputs: 模型的输出batch_size: 批大小h: 展示的图像高w: 展示的图像宽"""if len(test_images.shape) == 3:test_images = np.array([test_images])for i in range(batch_size):plt.figure(figsize=(h, w))ax = plt.subplot(1, batch_size, i+1)# 随机裁剪后的图像image = test_images[i]# 模型的输出,未还原的预测关键点坐标值predicted_key_pts = test_outputs[i]# 还原后的真实的关键点坐标值predicted_key_pts = predicted_key_pts * data_std + data_mean# 展示图像和关键点show_fu(np.squeeze(image), predicted_key_pts)plt.axis('off')plt.show()# 读取图像
img = read_image('zbp.jpg')# 加载保存好的模型进行预测
# model = paddle.Model(SAM_GoogLeNet_BN(num_keypoints=68))
# model.load(checkpoints_path)
# model.prepare()# 预测结果
out = model.predict_batch([img])
out = out[0].reshape((out[0].shape[0], 136, -1))# 可视化
custom_output(rgb_img, out, batch_size=1)

2.使用PaddleHub内置模型
import cv2
import paddlehub as hub
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.image as mpimg
import numpy as np
import math
%matplotlib inlinehub.logger.setLevel('ERROR')src_img = cv2.imread('xiaogege.jpg')module = hub.Module(name="face_landmark_localization")
result = module.keypoint_detection(images=[src_img])tmp_img = src_img.copy()
for index, point in enumerate(result[0]['data'][0]):# print(point)# cv2.putText(img, str(index), (int(point[0]), int(point[1])), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 3, (0,0,255), -1)cv2.circle(tmp_img, (int(point[0]), int(point[1])), 2, (0, 0, 255), -1)res_img_path = 'face_landmark.jpg'
cv2.imwrite(res_img_path, tmp_img)img = mpimg.imread(res_img_path)
# 展示预测68个关键点结果
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
plt.imshow(img)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()

import os
import paddlehub as hub
import matplotlib.animation as animation
from IPython.display import HTML
from math import degrees, atan2def overlay_transparent(background_img, img_to_overlay_t, x, y, overlay_size=None):bg_img = background_img.copy()# convert 3 channels to 4 channelsif bg_img.shape[2] == 3:bg_img = cv2.cvtColor(bg_img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2BGRA)if overlay_size is not None:img_to_overlay_t = cv2.resize(img_to_overlay_t.copy(), overlay_size)b, g, r, a = cv2.split(img_to_overlay_t)mask = cv2.medianBlur(a, 5)h, w, _ = img_to_overlay_t.shaperoi = bg_img[int(y - h / 2):int(y + h / 2), int(x - w / 2):int(x + w / 2)]img1_bg = cv2.bitwise_and(roi.copy(), roi.copy(), mask=cv2.bitwise_not(mask))img2_fg = cv2.bitwise_and(img_to_overlay_t, img_to_overlay_t, mask=mask)bg_img[int(y - h / 2):int(y + h / 2), int(x - w / 2):int(x + w / 2)] = cv2.add(img1_bg, img2_fg)# convert 4 channels to 3 channelsbg_img = cv2.cvtColor(bg_img, cv2.COLOR_BGRA2BGR)return bg_imgdef angle_between(p1, p2):x_diff = p2[0] - p1[0]y_diff = p2[1] - p1[1]return degrees(atan2(y_diff, x_diff))def get_eye_center_point(landmarks, idx1, idx2):center_x = (landmarks[idx1][0] + landmarks[idx2][0]) // 2center_y = (landmarks[idx1][1] + landmarks[idx2][1]) // 2return (center_x, center_y)def wear_glasses(image, glasses, eye_left_center, eye_right_center):eye_left_center = np.array(eye_left_center)eye_right_center = np.array(eye_right_center)glasses_center = np.mean([eye_left_center, eye_right_center], axis=0) # put glasses's center to this centerglasses_size = np.linalg.norm(eye_left_center - eye_right_center) * 2 # the width of glasses maskangle = -angle_between(eye_left_center, eye_right_center)glasses_h, glasses_w = glasses.shape[:2]glasses_c = (glasses_w / 2, glasses_h / 2)M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(glasses_c, angle, 1)cos = np.abs(M[0, 0])sin = np.abs(M[0, 1])# compute the new bounding dimensions of the imagenW = int((glasses_h * sin) + (glasses_w * cos))nH = int((glasses_h * cos) + (glasses_w * sin))# adjust the rotation matrix to take into account translationM[0, 2] += (nW / 2) - glasses_c[0]M[1, 2] += (nH / 2) - glasses_c[1]rotated_glasses = cv2.warpAffine(glasses, M, (nW, nH))try:image = overlay_transparent(image, rotated_glasses, glasses_center[0], glasses_center[1],overlay_size=(int(glasses_size),int(rotated_glasses.shape[0] * glasses_size / rotated_glasses.shape[1])))except:print('failed overlay image')return imageglasses_lists = []
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
module = hub.Module(name="face_landmark_localization")for i, path in enumerate(os.listdir('glasses')):image_file = 'xiaogege.jpg'glasses_file = 'glasses/' + pathimage = cv2.imread(image_file)glasses = cv2.imread(glasses_file, cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED)result = module.keypoint_detection(images=[image])landmarks = result[0]['data'][0]eye_left_point = get_eye_center_point(landmarks, 36, 39)eye_right_point = get_eye_center_point(landmarks, 42, 45)image = wear_glasses(image, glasses, eye_left_point, eye_right_point)cv2.imwrite(f'result/{i}.png', image)image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)im = plt.imshow(image, animated=True)plt.axis('off') glasses_lists.append([im])ani = animation.ArtistAnimation(fig, glasses_lists, interval=1000, blit=True, repeat_delay=1000)
.png', image)image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)im = plt.imshow(image, animated=True)plt.axis('off') glasses_lists.append([im])ani = animation.ArtistAnimation(fig, glasses_lists, interval=1000, blit=True, repeat_delay=1000)
HTML(ani.to_html5_video())

个人简介
北京联合大学 机器人学院 自动化专业 2018级 本科生 郑博培
百度飞桨开发者技术专家 PPDE
百度飞桨官方帮帮团、答疑团成员
深圳柴火创客空间 认证会员
百度大脑 智能对话训练师
我在AI Studio上获得至尊等级,点亮8个徽章,来互关呀!!!
https://aistudio.baidu.com/aistudio/personalcenter/thirdview/147378

这篇关于基于空间注意力机制SAM的GoogLeNet实现人脸关键点检测并自动添加表情贴纸的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







