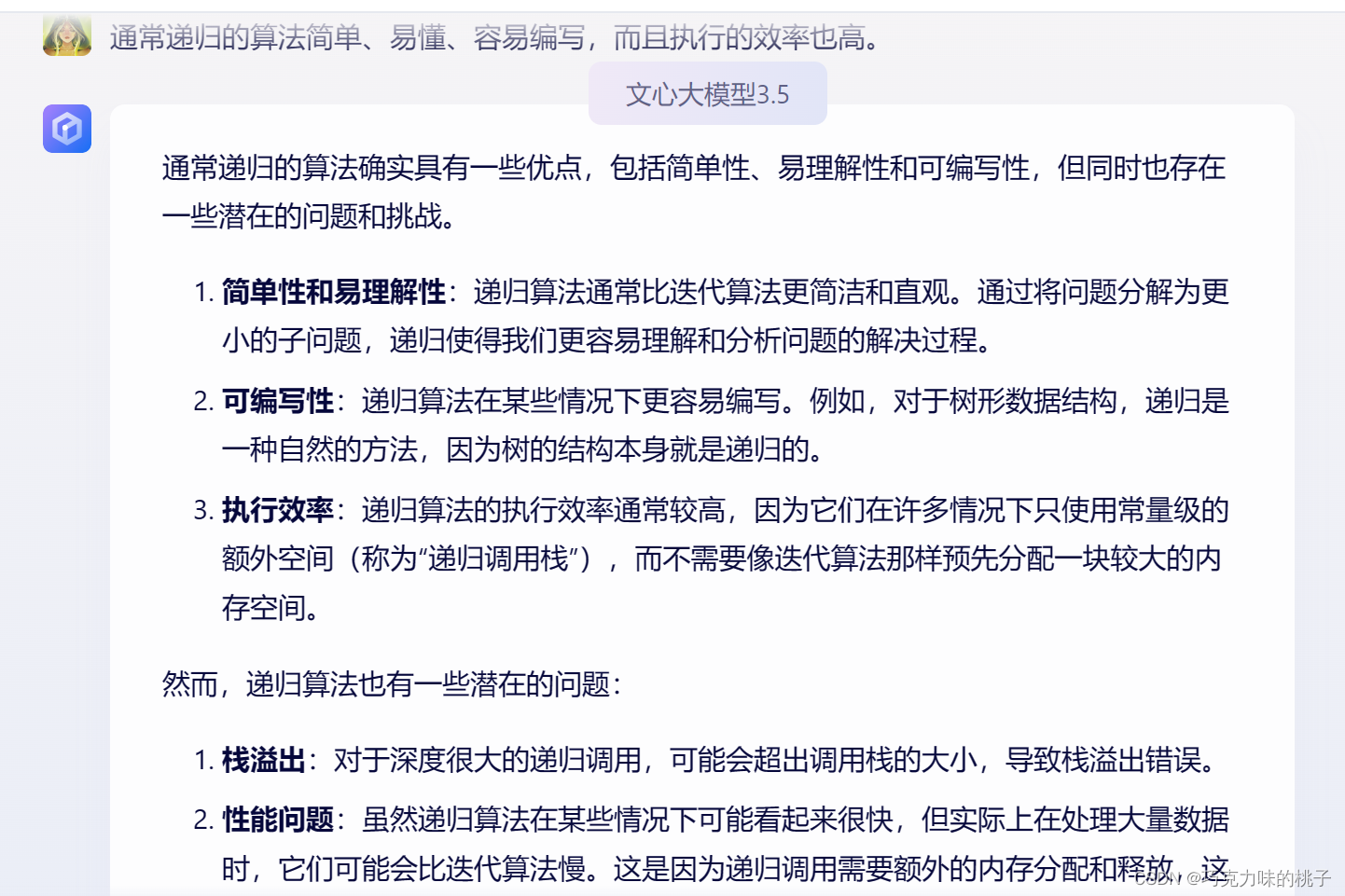
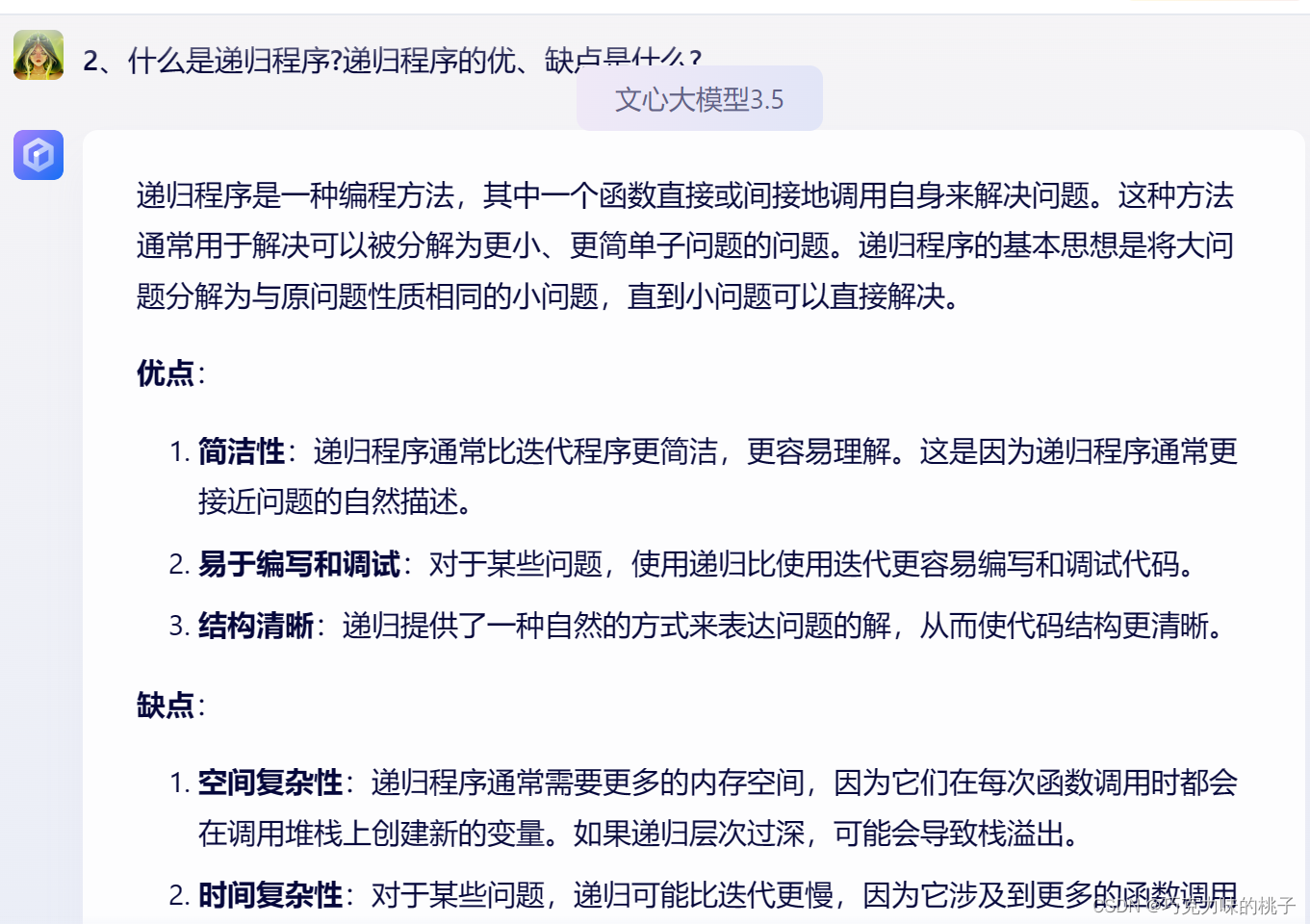
本文主要是介绍数据结构 | 北京大学期末试卷查漏补缺,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!

顺序存储
优点
支持随机访问
不会因为元素之间的逻辑关系而产生额外的存储空间
快速存取元素
缺点
删除和插入元素的时候要移动大量元素
当线性表变化比较大时,难以确定存储空间的容量
容易产生存储空间碎片
适用于:
当线性表容量已知;元素变动不大,需要快速存取元素
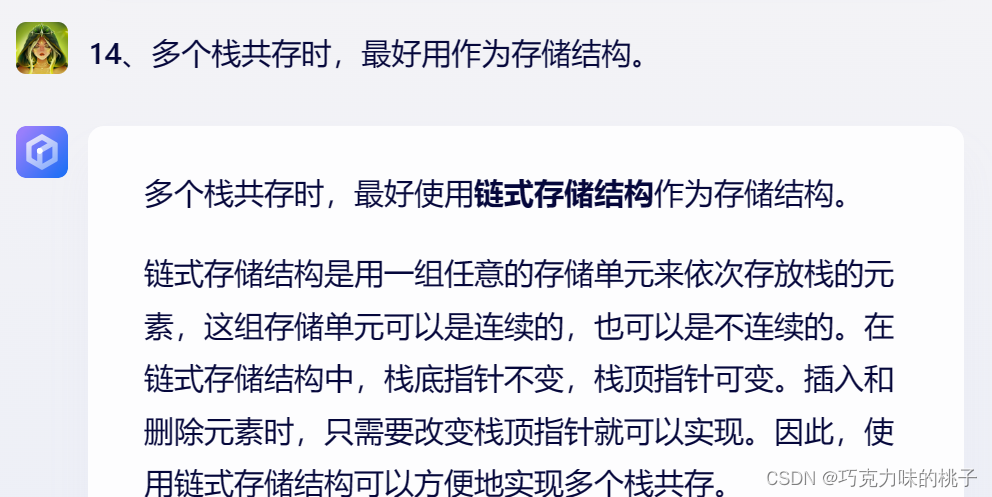
链式存储
优点
需要删除和插入元素,只需要改变后继指针
缺点
添加了后继指针,需要更多的储存空间
适用于:
容量不定,需要频繁删除和添加元素
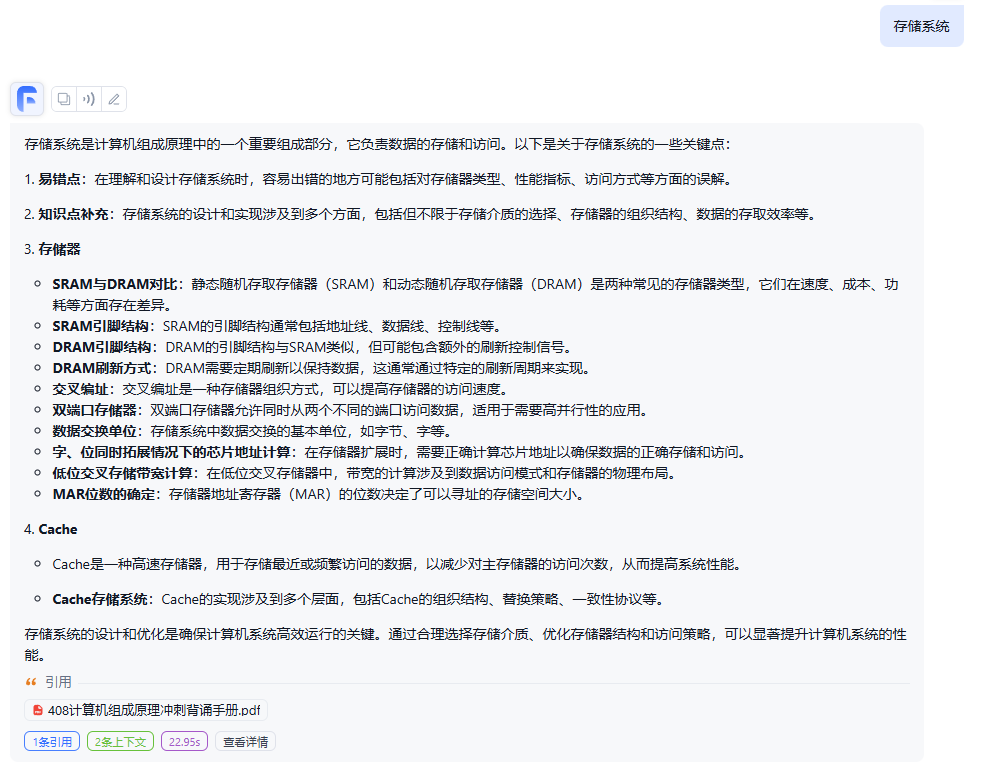
折半查找为什么要使用顺序存储结构
折半查找要求使用顺序存储结构,主要是因为这种结构能够提供直接访问元素的能力。在顺序存储结构中,元素按照顺序存储在连续的存储空间中,通常是数组。通过下标可以直接访问元素,这使得折半查找算法能够快速找到中间元素并进行比较。
此外,折半查找还需要表中元素按关键字有序排列。如果元素无序排列,那么无法保证中间元素的大小关系,导致无法准确确定查找范围,从而无法正确找到目标元素。因此,顺序存储结构和有序排列是实现折半查找的必要条件。
树的存储结构
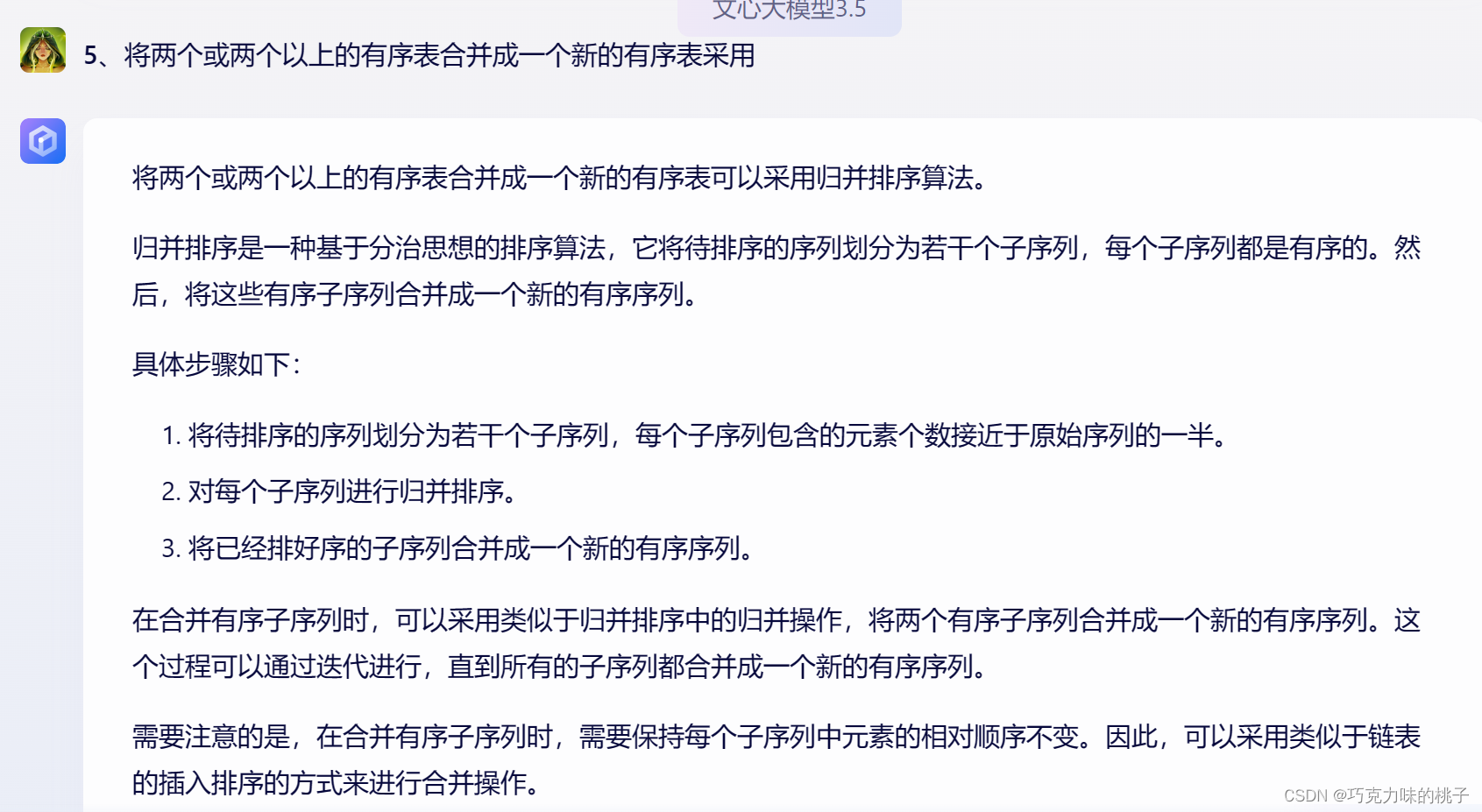
将两个或两个以上的有序表合并成一个新的有序表采用
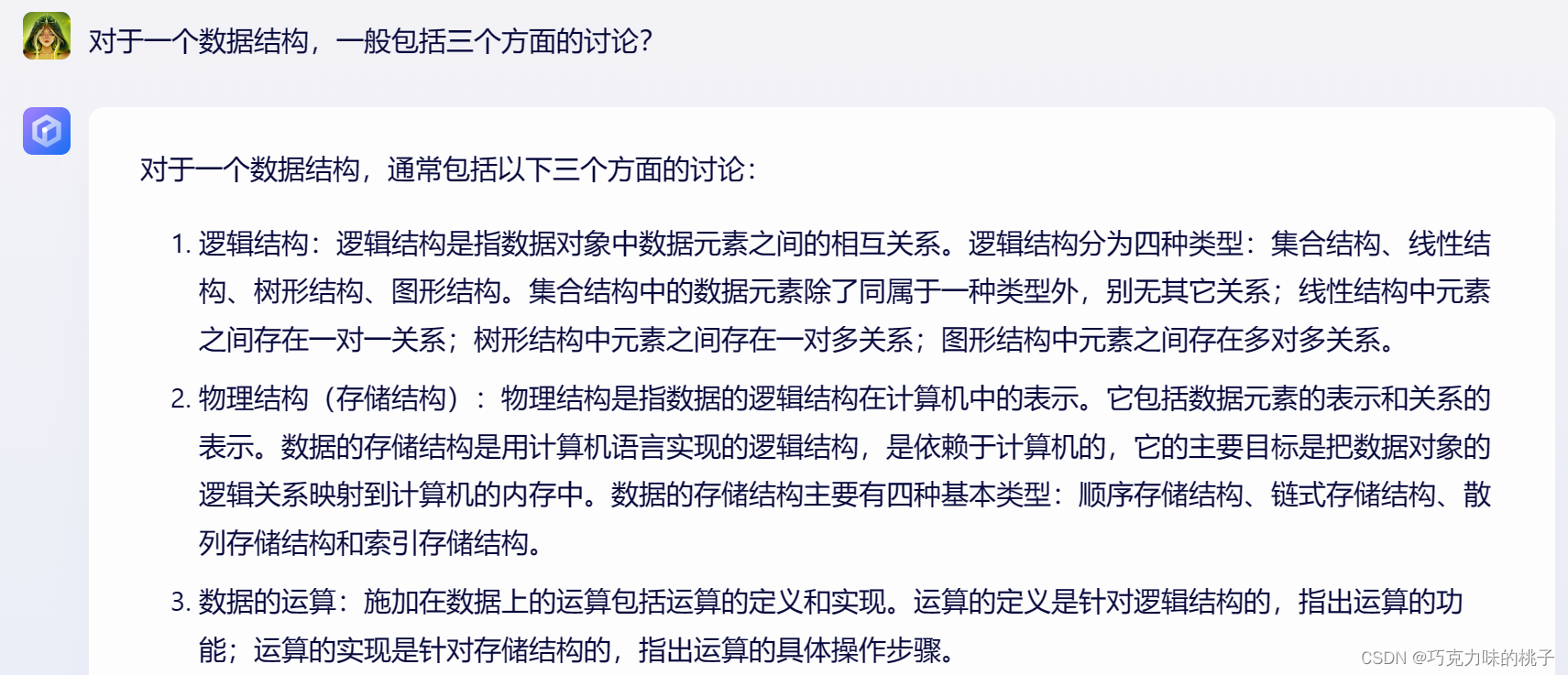
对于一个数据结构,一般包括








#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h> // 定义链表节点结构体
struct ListNode { int val; struct ListNode *next;
}; // 逆置链表函数
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head) { struct ListNode *prev = NULL, *curr = head, *next = NULL; while (curr != NULL) { next = curr->next; curr->next = prev; prev = curr; curr = next; } return prev;
} // 打印链表函数
void printList(struct ListNode* head) { struct ListNode *curr = head; while (curr != NULL) { printf("%d ", curr->val); curr = curr->next; } printf("\n");
} int main() { // 创建链表 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 struct ListNode *head = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); head->val = 1; head->next = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); head->next->val = 2; head->next->next = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); head->next->next->val = 3; head->next->next->next = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); head->next->next->next->val = 4; head->next->next->next->next = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode)); head->next->next->next->next->val = 5; head->next->next->next->next->next = NULL; printf("Original list: "); printList(head); // 逆置链表并打印结果 struct ListNode *reversedHead = reverseList(head); printf("Reversed list: "); printList(reversedHead); // 释放链表内存 struct ListNode *curr = reversedHead, *temp; while (curr != NULL) { temp = curr->next; free(curr); curr = temp; } free(reversedHead); return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include <string> using namespace std; int f(string s) { int n = s.length(); for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) { if (s[i] != s[n - i - 1]) { return 0; } } return 1;
} int main() { string s1 = "abba"; string s2 = "abab"; int result1 = f(s1); int result2 = f(s2); cout << result1 << endl; // 输出1 cout << result2 << endl; // 输出0 return 0;
}

这篇关于数据结构 | 北京大学期末试卷查漏补缺的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!