本文主要是介绍流场寻路(Flow Field Path Finding),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
简介
当场景中有成千上万个寻路游戏单位需要到达同一目标点时,通过常用的A*算法进行寻路不再是合适的选择,因为每个寻路游戏单位都需要依据自身所在的位置,根据算法获得一条从自身位置寻路到目标点的路径,n个游戏单位进行寻路就需要执行n次算法,这是比较大的性能开销。而流场寻路的方式便可以很好的解决这一问题,通常用于RTS(即时战略)游戏中的群体寻路。
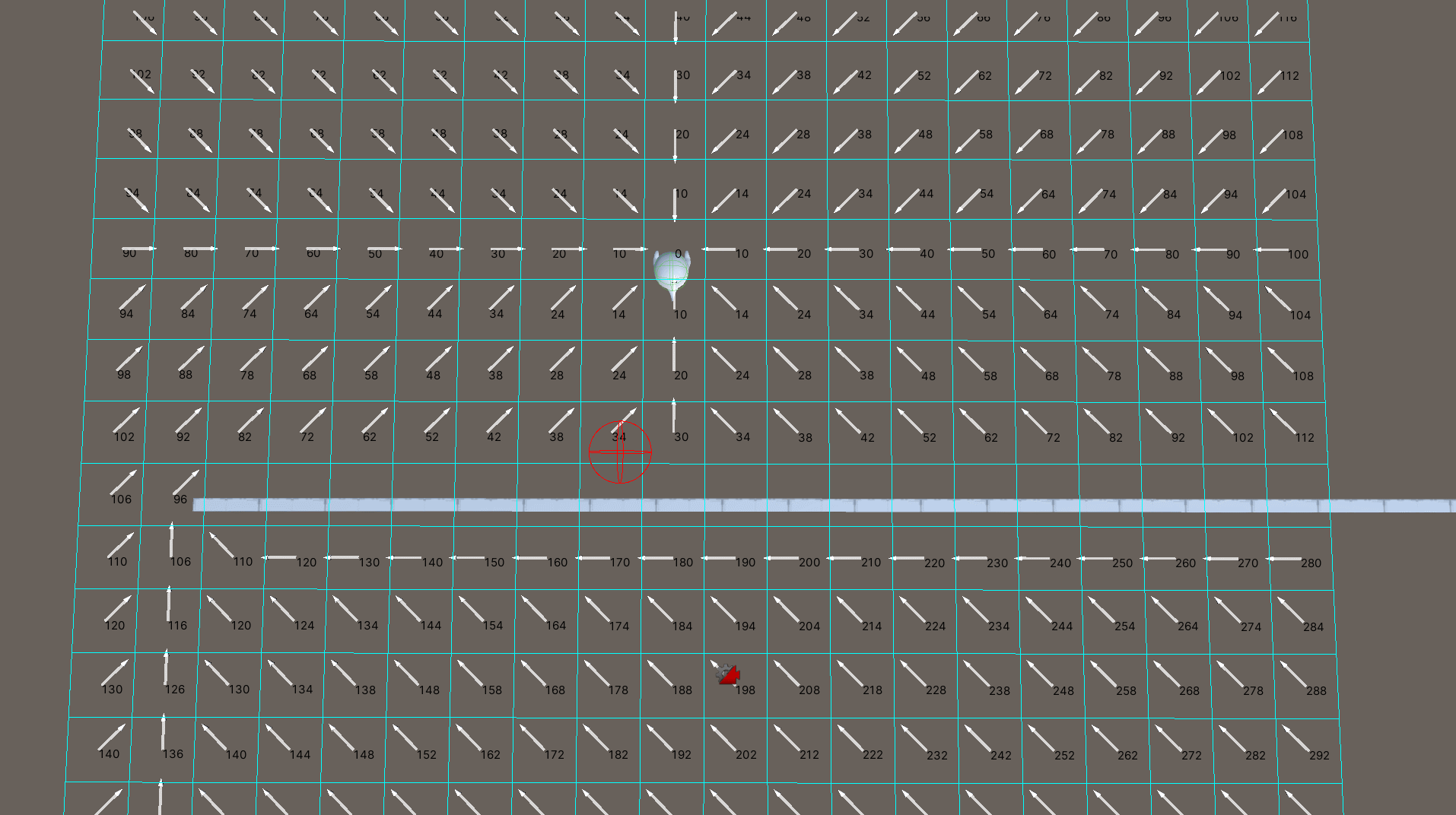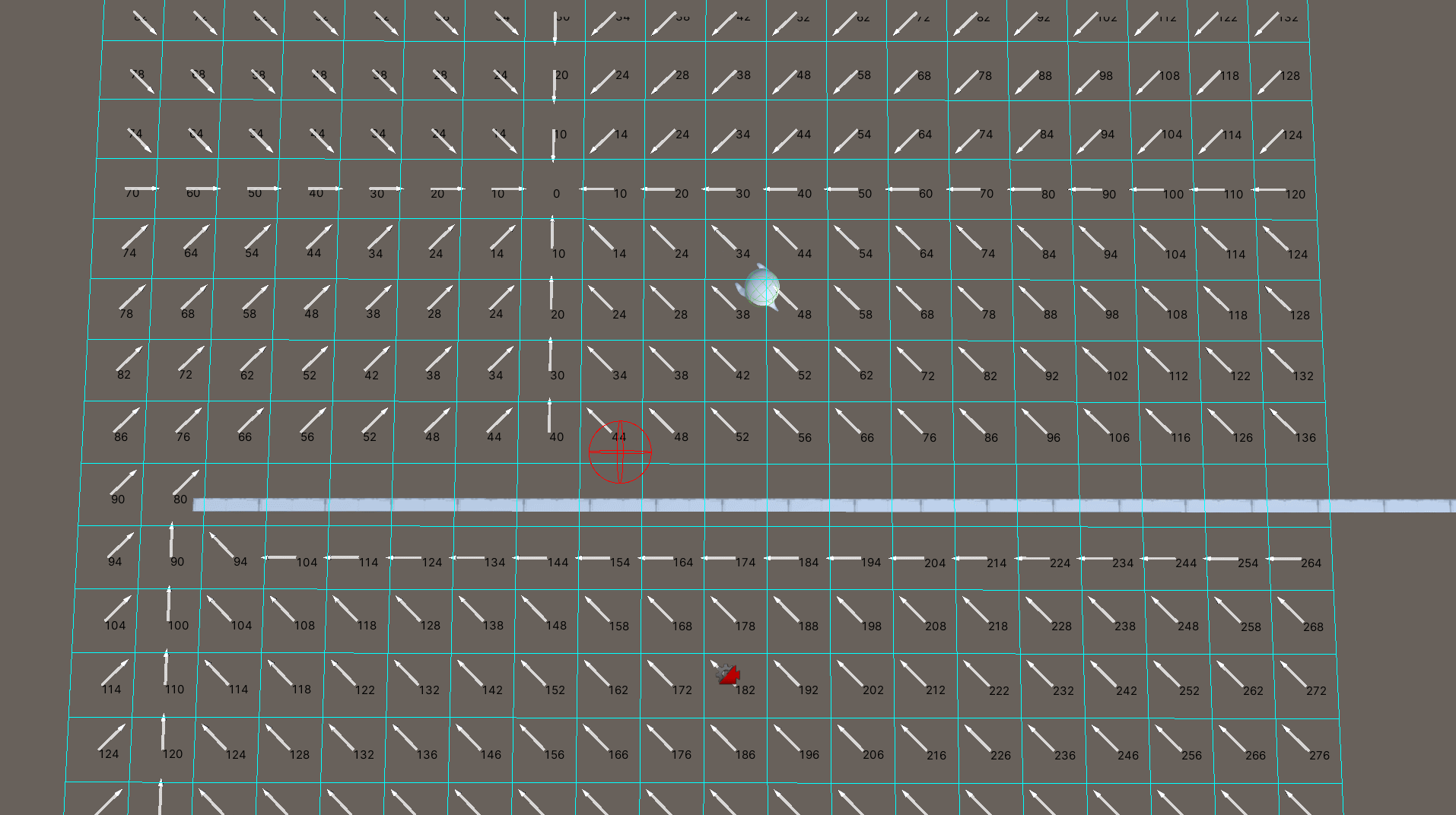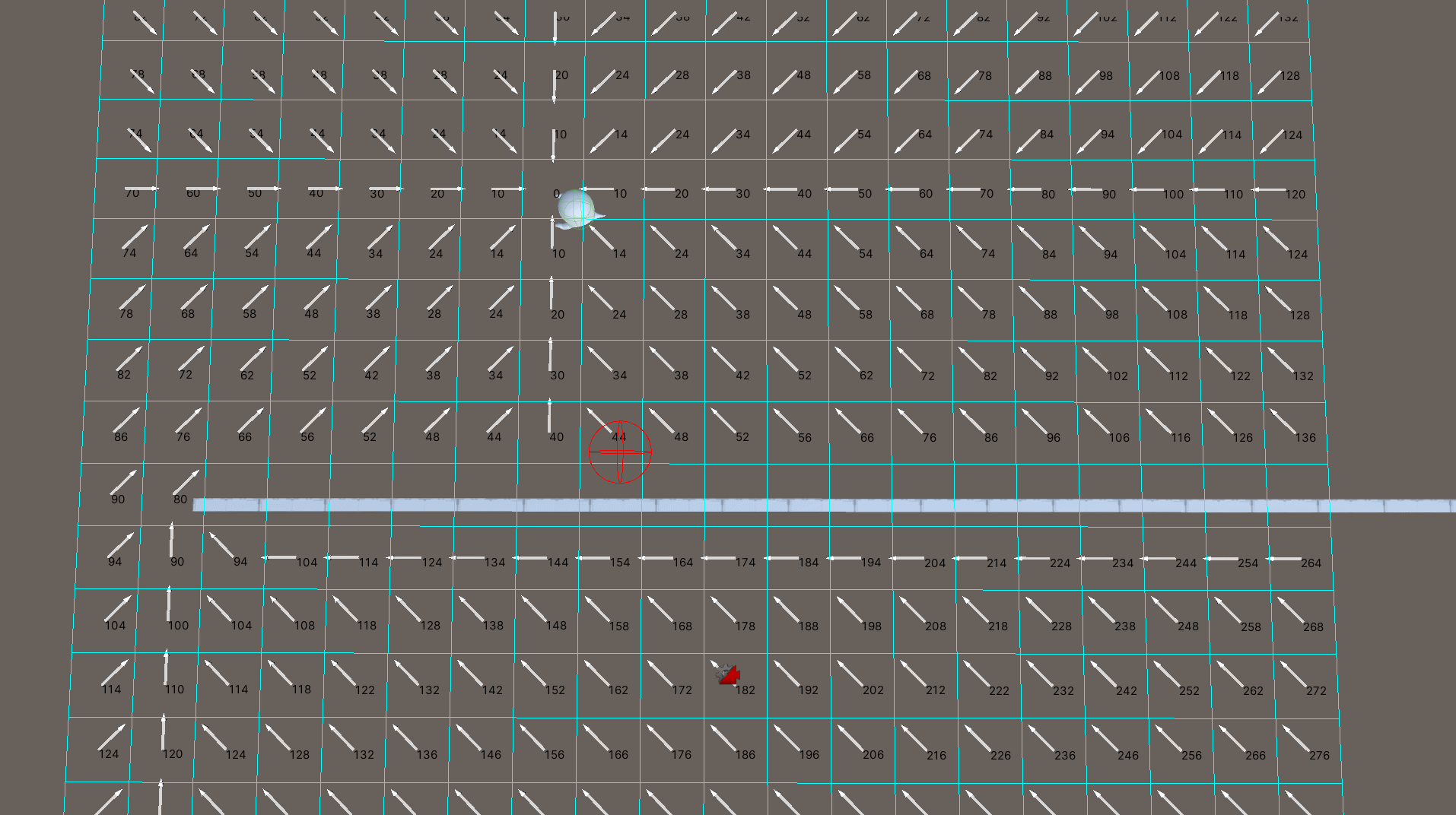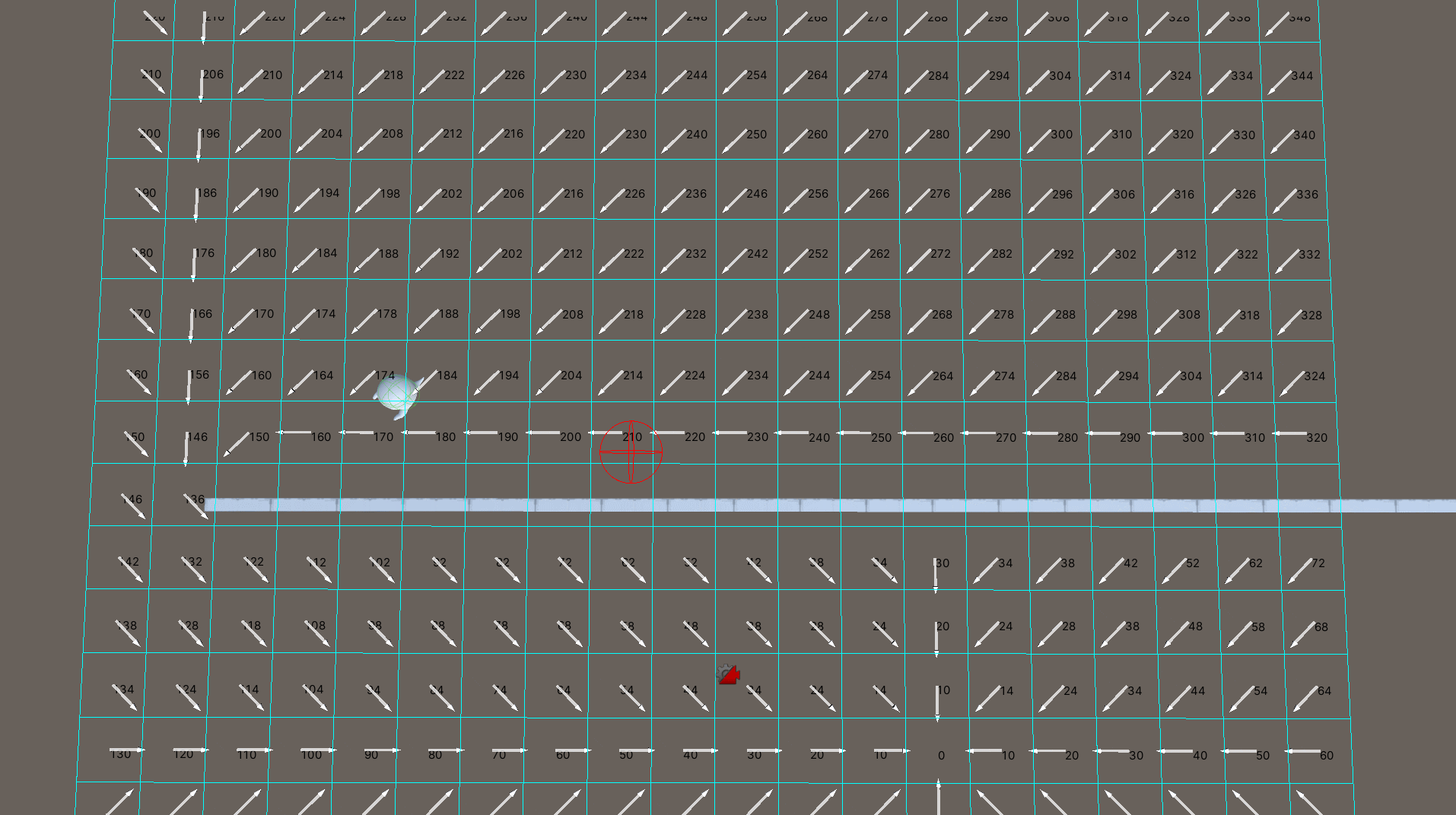
将场景分割为x * y个网格节点,当确认目标点时,流场寻路算法会依据目标点所在的网格,依次向周围获取邻节点,计算邻节点到当前节点的代价。代价大的节点指向代价小的节点便可以形成一个方向,而这些节点形成的方向,便是流场,如下图所示。

流场形成后,寻路游戏单位只需要根据自身所在的坐标位置,获得对应的网格节点,依据节点的方向进行移动最终便可以到达目标点。
网格节点
节点类除了节点索引对应的字段x、y之外,还包括表示代价的字段cost与fCost,以及形成流场的节点方向字段。cost为基础代价,场景中可能会有多种地形,例如水泥地、沼泽地等等,不同地形有不同的代价,本文暂不考虑不同地形的情况,假设所有节点所在的地形是相同的,只考虑节点是否为可行走区域,通过字段isWalkable表示,而fCost是指节点到目标节点的最终代价。
using UnityEngine;public class FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode
{public int x;public int y;public int cost;public int fCost;public Vector3 direction;public bool isWalkable;public FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode(int x, int y, bool isWalkable){this.x = x;this.y = y;this.isWalkable = isWalkable;cost = isWalkable ? 10 : int.MaxValue;fCost = int.MaxValue;}
}
x * y个网格节点形成最终的网格,将所有的网格节点存储到一个字典中,通过索引i * x + j获取对应的网格节点,i表示第几行,j表示第几列,假设通过Texture资产存储地图数据,字节为255表示为可行走区域,否则为障碍区域。
public class FlowFieldPathFinding_Grid
{private readonly int x;private readonly int y;private readonly Dictionary<int, FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode> nodesDic= new Dictionary<int, FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode>();public FlowFieldPathFinding_Grid(int x, int y, bool[,] map){this.x = x;this.y = y;for (int i = 0; i < x; i++){for (int j = 0; j < y; j++){int index = i * x + j;nodesDic.Add(index, new FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode(i, j, map[i, j]));}}}public FlowFieldPathFinding_Grid(int x, int y, Texture2D map){this.x = x;this.y = y;byte[] bytes = map.GetRawTextureData();if (bytes.Length != x * y)throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException();for (int i = 0; i < x; i++){for (int j = 0; j < y; j++){int index = i * x + j;nodesDic.Add(index, new FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode(i, j, bytes[index] == 255));}}}
}
算法思路
网格类需要提供设置目标节点的方法,设置目标节点时,将其放入一个队列中,当队列的数量大于0时,不断执行以下步骤:
- 出列,获得当前节点;
- 获取当前节点的邻节点;
- 遍历邻节点,计算邻节点到当前节点的基础代价;
- 邻节点到当前节点的基础代价加上当前节点的最终代价记为t,如果t小于邻节点的最终代价,设置邻节点的最终代价为t,并将其放入队列。
/// <summary>
/// 设置目标节点
/// </summary>
/// <param name="target"></param>
public void SetTarget(FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode target)
{foreach (var node in nodesDic.Values){node.cost = node.isWalkable ? 10 : int.MaxValue;node.fCost = int.MaxValue;}target.cost = 0;target.fCost = 0;target.direction = Vector3.zero;Queue<FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode> queue= new Queue<FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode>();queue.Enqueue(target);while (queue.Count > 0){FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode currentNode = queue.Dequeue();List<FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode> neighbourNodes = GetNeighbouringNodes(currentNode);for (int i = 0; i < neighbourNodes.Count; i++){FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode neighbourNode = neighbourNodes[i];if (neighbourNode.cost == int.MaxValue) continue;neighbourNode.cost = CalculateCost(neighbourNode, currentNode);if (neighbourNode.cost + currentNode.fCost < neighbourNode.fCost){neighbourNode.fCost = neighbourNode.cost + currentNode.fCost;queue.Enqueue(neighbourNode);}}}
}
搜索邻节点时有两种方式,四连通与八连通,前者是指向当前节点的上、下、左、右四个方向搜索邻节点,后者是指向当前节点的上、下、左、右、左上、右上、左下、右下八个方向搜索邻节点,多数情况下会使用八连通,本文也通过八连通的方式搜索邻节点。
/// <summary>
/// 获取指定节点的邻节点
/// </summary>
/// <param name="node">要获取邻节点的节点</param>
/// <returns>邻节点列表</returns>
public List<FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode> GetNeighbouringNodes(FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode node)
{List<FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode> neighbours = new List<FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode>();for (int i = -1; i <= 1; i++){for (int j = -1; j <= 1; j++){if (i == 0 && j == 0) continue;int x = node.x + i;int y = node.y + j;if (x >= 0 && x < this.x && y >= 0 && y < this.y)neighbours.Add(nodesDic[x * this.x + y]);}}return neighbours;
}
计价方式
每向正上、下、左右方向走一步代价为1,根据勾股定理,每向斜方向走一步代价为根号2,近似1.414,而为了便于计算、节省性能,将正方向移动一步的代价记为10,斜方向移动一步的代价记为14,都取int整数。

//计算两个节点之间的代价
private int CalculateCost(FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode node1, FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode node2)
{//取绝对值int deltaX = node1.x - node2.x;if (deltaX < 0) deltaX = -deltaX;int deltaY = node1.y - node2.y;if (deltaY < 0) deltaY = -deltaY;int delta = deltaX - deltaY;if (delta < 0) delta = -delta;//每向上、下、左、右方向移动一个节点代价增加10//每斜向移动一个节点代价增加14(勾股定理,精确来说是近似14.14~)return 14 * (deltaX > deltaY ? deltaY : deltaX) + 10 * delta;
}
流场生成
设置目标节点计算各节点的代价后生成流场,遍历节点的邻节点,如果邻节点的最终代价小于当前节点的最终代价,那么当前节点的方向便是当前节点指向邻节点的方向。若出现代价相同的情况,需要考虑哪一个邻节点更加接近目标节点。
/// <summary>
/// 生成流场
/// </summary>
public void GenerateFlowField(FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode target)
{foreach (var node in nodesDic.Values){List<FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode> neighbourNodes = GetNeighbouringNodes(node);int fCost = node.fCost;FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode temp = null;for (int i = 0; i < neighbourNodes.Count; i++){FlowFieldPathFinding_GridNode neighbourNode = neighbourNodes[i];if (neighbourNode.fCost < fCost){temp = neighbourNode;fCost = neighbourNode.fCost;node.direction = new Vector3(neighbourNode.x - node.x, 0, neighbourNode.y - node.y);}else if (neighbourNode.fCost == fCost && temp != null){if (CalculateCost(neighbourNode, target) < CalculateCost(temp, target)){temp = neighbourNode;fCost = neighbourNode.fCost;node.direction = new Vector3(neighbourNode.x - node.x, 0, neighbourNode.y - node.y);}}}}
}
这篇关于流场寻路(Flow Field Path Finding)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






