本文主要是介绍《数据结构、算法与应用C++语言描述》-最大高度优先左高树-C++实现,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
左高树
完整可编译运行代码见:Github::Data-Structures-Algorithms-and-Applications/_26maxHblt
定义
(大顶堆和小顶堆)堆结构是一种隐式数据结构(implicit data structure)。用完全二叉树表示的堆在数组中是隐式存储的(即没有明确的指针或其他数据能够用来重塑这种结构)。由于没有存储结构信息,这种表示方法的空间利用率很高,它实际上没有浪费空间。而且它的时间效率也很高。尽管如此,它并不适合于所有优先级队列的应用,尤其是当两个优先级队列或多个长度不同的队列需要合并的时候,这时我们就需要其他数据结构了。左高树就能满足这种需要。
考察一棵二叉树,它有一类特殊的节点叫做外部节点(external node),它代替树中的空子树。其余节点叫做内部节点(internal node)。增加了外部节点的二叉树被称为扩充二叉树(extended binary tree),图 12-6a 是一棵二叉树,其相应的扩充二叉树如图 12-6b 所示。外部节点用阴影框表示。为了方便起见,这些节点用 a~f标注。
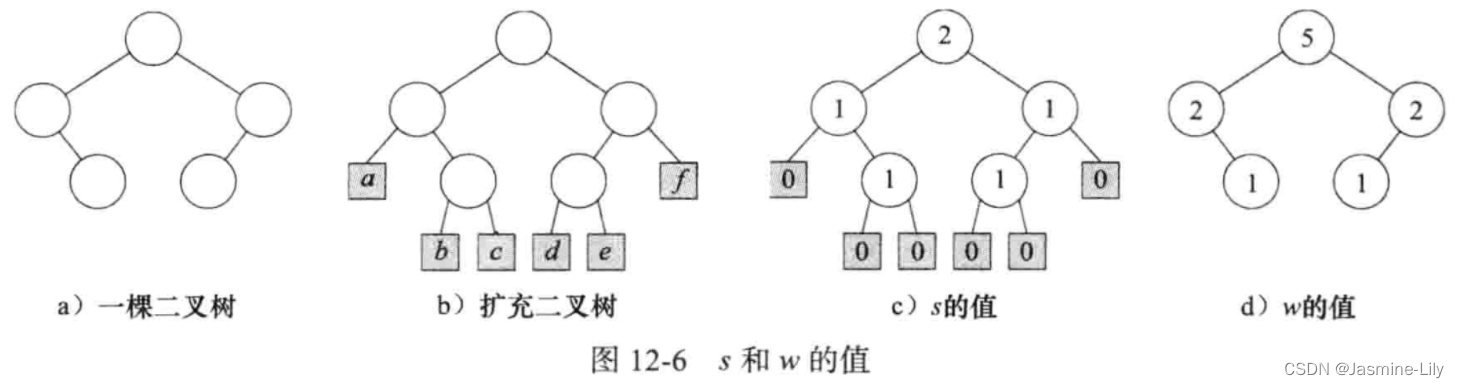
令s(x)是从节点x到其子树的外部节点的所有路径中最短的一条。根据s(x)的定义,若x是外部节点,则s的值为0;若x为内部节点,则s的值为
m i n { s ( L ) , s ( R ) } + 1 min\{s(L), s(R)\} + 1 min{s(L),s(R)}+1
其中L与R分别为x的左右孩子。扩充二叉树(如图12-6b所示)中各节点的s值如图12-6c所示。
定义 12-3 一棵二叉树称为高度优先左高树(height-biased leftist tree,HBLT),当且仅当其任何一个内部节点的左孩子的s值都大于或等于右孩子的s值。
定理 12-1 令 x 为 HBLT 的一个内部节点,则
- 1)以x为根的子树的节点数目至少为 2 S ( x ) + 1 2^{S(x)}+ 1 2S(x)+1。
- 2)若以x为根的子树有 m 个节点,那么 s(x)最多为 l o g 2 ( m + 1 ) log_2(m + 1) log2(m+1)。
- 3)从 x 到一外部节点的最右路径(即从 x 开始沿右孩子移动的路径)的长度为 s(x)。
证明 根据s(x)的定义,从x节点往下第s(x)-1层没有外部节点(否则x的s值将更小)。以x为根的子树在当前层只有1个节点x,下一层有2个节点,再下一层有4个节点……从x 层往下第 s(x)-1 层有 2 s ( x ) − 1 2^{s(x)-1} 2s(x)−1个节点,在 s(x)-1 层以下可能还有其他节点,因此子树x 的节点数目至少为 ∑ i = 0 s ( x ) − 1 2 i = 2 s ( x ) − 1 \sum_{i=0}^{s(x)-1}2^i=2^{s(x)}-1 ∑i=0s(x)−12i=2s(x)−1。从1)可以推出 2)。根据s 的定义以及 HBLT 的一个节j=0点的左孩子的 s 值总是大于或等于其右孩子,可以推出 3)。
定义 12-4 若一棵HBLT 同时还是大根树,则称为最大 HBLT(maxHBLT)。若一棵HBLT 同时还是小根树,则称为最小 HBLT(min HBLT)。
如果我们考虑的不是路径长度,而是节点数目,那么我们可以得到另一种左高树。定义重量 w(x)是以节点x为根的子树的内部节点数目。若x是外部节点,则它的重量是0;若x是内部节点,则它的重量是其孩子节点的重量之和加1,在图12-6a的二叉树中,各节点的重量如图 12-6d 所示。
定义 12-5 一棵二叉树称为重量优先左高树(weight-biased leftist tree,WBLT),当且仅当其任何一个内部节点的左孩子的w值都大于或等于右孩子的w值。若一棵WBLT同时还是大根树,则称为最大WBLT(max WBLT)。若一棵WBLT同时还是小根树,则称为最小WBLT(min WBLT)。
使用WBLT或HBLT,可以执行优先级队列的查找、插入(时间复杂度为logn)、删除操作(时间复杂度为logn),其时间复杂性与堆相同。和堆一样,WBLT与HBLT可以在线性时间内完成初始化。用WBLT或HBLT表示的两个优先级队列可在对数时间内合并为一个(log(mn),m表示x树的元素个数,n表示y树的元素个数),而用堆表示的优先级队列做不到这一点。
插入删除合并算法
最大 HBLT 的插入
最大 HBLT 的插入操作可利用最大 HBLT 的合并操作来实现。假定将元素 × 插入名为 H的最大 HBLT 中。如果构建一棵仅有一个元素 x 的最大 HBLT,然后将它与 H 进行合并,那么合并后的最大HBLT将包括H的全部元素和元素x。因此,要插入一个元素,可以先建立一棵新的只包含这个元素的 HBLT,然后将这棵新的 HBLT 与原来的 HBLT 合并。
最大 HBLT 的删除
最大元素在根中。若根被删除,则分别以左右孩子为根的子树是两棵最大 HBLT。将这两棵最大HBLT合并,便是删除后的结果。因此,删除操作可以通过删除根元素之后的两棵子树的合并来实现。
两棵最大 HBLT 的合并
合并策略最好用递归来实现。令 A、B 为需要合并的两棵最大 HBLT。若一个为空,则另一个便是合并的结果。假设两者均不为空。为实现合并,先比较两个根元素,较大者作为合并后的根。假定A的根较大,且左子树为L。令C是A的右子树与B合并而成的HBLT。先将L作为合并树的左子树,C作为合并树的右子树,然后再比较L和C的weight,决定L和C是否交换。A与 B 合并的结果是以 A 为根,以L 和C为子树的最大 HBLT。如果 L 的s值小于 C 的 s值,则C为左子树,否则L为左子树。
meld仅沿着x和y的右子树移动,因此该函数的复杂性为O(s(x)+s(y))。因为s(x)和s(y)的最大值分别为 l o g 2 ( m + 1 ) log_2(m+1) log2(m+1)和 l o g 2 ( n + 1 ) log_2(n+1) log2(n+1),其中m与n分别是x和y的元素个数,所以meld的时间复杂度为O(logm+logn)=O(log(mn))。
HBLT的初始化
初始化过程是将 n 个元素逐个插入最初为空的最大 HBLT。为得到具有线性时间的初始化算法,我们首先创建 n个仅含一个元素的最大HBLT,这 n 棵树组成一个 FIFO队列,然后从队列中依次成对删除 HBLT,然后将其合并后再插入队列末尾,直到队列只有一棵 HBLT 为止。时间复杂度为O(n)。
最大高度优先左高树的cpp实现
main.cpp
/*
Project name : _26maxHblt
Last modified Date: 2023年12月14日10点20分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 最大高度优先左高树——main函数
*/
#include "maxhblt.h"int main() {maxhbltTest();return 0;
}
maxhblt.h
/*
Project name : _26maxHblt
Last modified Date: 2023年12月14日10点20分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 最大高度优先左高树——模板头文件
*/#ifndef _26MAXHBLT_MAXHBLT_H
#define _26MAXHBLT_MAXHBLT_H#include "maxPriorityQueue.h"
#include "maxHbltTreeNode.h"
#include "myExceptions.h"
#include <queue>
#include <sstream>void maxhbltTest();using namespace std;template<class T>
class maxHblt : public maxPriorityQueue<T> {
public:maxHblt() {root = nullptr;treeSize = 0;}bool empty() const { return treeSize == 0; }int size() const { return treeSize; }const T &top() {// 返回最大元素if (treeSize == 0)throw queueEmpty();return root->element;}void pop();void push(const T &);void initialize(T *, int);void meld(maxHblt<T> &theHblt) {// 合并 *this 和 theHbltmeld(root, theHblt.root);treeSize += theHblt.treeSize;theHblt.root = nullptr;theHblt.treeSize = 0;}void erase() {// 清空树postOrder(dispose);root = nullptr;treeSize = 0;}void postOrderOutput() {// 后序遍历输出树的元素postOrder(hbltOutput);cout << endl;}void postOrder(void(*theVisit)(maxHbltTreeNode<T> *)) {visit = theVisit;/*是因为递归,所以才要这样的*/postOrder(root);/*这里调用的是静态成员函数inOrder()*/}private:maxHbltTreeNode<T> *root;//指向根的指针int treeSize;//树的结点个数void meld(maxHbltTreeNode<T> *&,maxHbltTreeNode<T> *&);// 合并两颗树static void (*visit)(maxHbltTreeNode<T> *);//是一个函数指针,返回值为void 函数参数为maxHbltTreeNode<T>*static void dispose(maxHbltTreeNode<T> *t) { delete t; }static void postOrder(maxHbltTreeNode<T> *t);static void hbltOutput(maxHbltTreeNode<T> *t) { cout << t->element << ' '; }
};template<class T>
void (*maxHblt<T>::visit)(maxHbltTreeNode<T> *) = 0; // visit functiontemplate<class T>
void maxHblt<T>::meld(maxHbltTreeNode<T> *&x,maxHbltTreeNode<T> *&y) {// 合并两棵最大高度优先左高树// x是合并后的树if (y == nullptr) // y是空树,直接返回return;if (x == nullptr) // x是空树,将y赋值给x,返回{x = y;return;}// x树永远是提供根的树// x和y都不是空树,如果x的元素小于y的元素,则交换x树和y树if (x->element < y->element)swap(x, y);// 现在 x->element.second >= y->element.second// 合并x的右子树和y树,x的根和左子树作为合并树的根和左子树meld(x->rightChild, y);// 得到的x的右子树就是x的右子树与y树合并的最大高度优先左高树// 如果需要,交换x的左子树和右子树的值if (x->leftChild == nullptr) {// 如果x的左子树为空, 则将x的左子树和右子树做交换,保证x的左子树比右子树高x->leftChild = x->rightChild;x->rightChild = nullptr;x->height = 1;} else {// 如果x的左子树的weight小于右子树的weight,则要交换左右子树的值if (x->leftChild->height < x->rightChild->height)swap(x->leftChild, x->rightChild);x->height = x->rightChild->height + 1;// 存储小的那一个}
}template<class T>
void maxHblt<T>::push(const T &theElement) {// 向树中插入元素// 创建一个新的节点maxHbltTreeNode<T> *q = new maxHbltTreeNode<T>(theElement, 1);// 将新节点与root树合并meld(root, q);treeSize++;
}template<class T>
void maxHblt<T>::pop() {// 删除最大元素if (root == nullptr)throw queueEmpty();// 当树不为空时maxHbltTreeNode<T> *left = root->leftChild,*right = root->rightChild;delete root;root = left;meld(root, right);treeSize--;
}template<class T>
void maxHblt<T>::initialize(T *theElements, int theSize) {// 初始化hblt 使用theElements[1:theSize].queue<maxHbltTreeNode<T> *> q;erase(); // 清空左高树for (int i = 1; i <= theSize; i++)// 创建节点,全部放入队列中q.push(new maxHbltTreeNode<T>(theElements[i]));// 不断取出两个节点进行合并for (int i = 1; i <= theSize - 1; i++) {maxHbltTreeNode<T> *b = q.front();q.pop();maxHbltTreeNode<T> *c = q.front();q.pop();meld(b, c);// 合并生成的树放到队列中q.push(b);}if (theSize > 0)root = q.front();treeSize = theSize;
}/*后序遍历 递归*/
template<class T>
void maxHblt<T>::postOrder(maxHbltTreeNode<T> *t) {if (t != nullptr) {postOrder(t->leftChild);/*后序遍历左子树*/postOrder(t->rightChild);/*后序遍历右子树*/visit(t);/*访问树根*/}
}#endif //_26MAXHBLT_MAXHBLT_H
maxhblt.cpp
/*
Project name : _26maxHblt
Last modified Date: 2023年12月14日10点20分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 最大高度优先左高树——测试函数
*/#include <iostream>
#include "maxhblt.h"using namespace std;void maxhbltTest()
{maxHblt<int> h, j;int a[6] = {0, 7, 9, 1, 8, 11};h.initialize(a, 5);cout << "One tree in postorder is" << endl;cout << "Tree size is " << h.size() << endl;h.postOrderOutput();int b[5] = {0, 2, 6, 4, 9};j.initialize(b,4);cout << "Other tree in postorder is" << endl;cout << "Tree size is " << j.size() << endl;j.postOrderOutput();h.meld(j);cout << "After melding, the tree in postorder is" << endl;cout << "Tree size is " << h.size() << endl;h.postOrderOutput();int w = h.top();h.pop();int x = h.top();h.pop();int y = h.top();h.pop();int z = h.top();h.pop();cout << "After popping four elements, the tree is" << endl;cout << "Tree size is " << h.size() << endl;h.postOrderOutput();cout << "The popped elements, in order, are" << endl;cout << w << " " << x << " " << y << " " << z << endl;h.push(10);h.push(20);h.push(5);cout << "After pushing 10, 20 & 5, the tree is" << endl;cout << "Leftist tree in postorder" << endl;cout << "Tree size is " << h.size() << endl;h.postOrderOutput();h.push(15);h.push(30);h.push(2);cout << "After pushing 15, 30 & 15, the tree is" << endl;cout << "Leftist tree in postorder" << endl;cout << "Tree size is " << h.size() << endl;h.postOrderOutput();cout << "The max element is " << h.top() << endl;cout << "Popped max element " << h.top() << endl;h.pop();cout << "Leftist tree in postorder" << endl;cout << "Tree size is " << h.size() << endl;h.postOrderOutput();x = h.top();h.pop();cout << "Popped max element " << x << endl;cout << "Tree size is " << h.size() << endl;cout << "Leftist tree in postorder" << endl;h.postOrderOutput();while (true){try{x = h.top();h.pop();cout << "Popped max element " << x << endl;cout << "Tree size is " << h.size() << endl;}catch(queueEmpty) {break;}}
}
maxPriorityQueue.h
/*
Project name : _26maxHblt
Last modified Date: 2023年12月14日10点20分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 优先级队列——虚基类
*/#ifndef _26MAXHBLT_MAXPRIORITYQUEUE_H
#define _26MAXHBLT_MAXPRIORITYQUEUE_H
using namespace std;template<class T>
class maxPriorityQueue
{
public:virtual ~maxPriorityQueue() {}virtual bool empty() const = 0;// return true iff queue is emptyvirtual int size() const = 0;// return number of elements in queuevirtual const T& top() = 0;// return reference to the max elementvirtual void pop() = 0;// remove the top elementvirtual void push(const T& theElement) = 0;// add theElement to the queue
};
#endif //_26MAXHBLT_MAXPRIORITYQUEUE_H
maxHbltTreeNode.h
/*
Project name : _26maxHblt
Last modified Date: 2023年12月14日10点20分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 最大高度优先左高树——树的节点类
*/#ifndef _26MAXHBLT_MAXHBLTTREENODE_H
#define _26MAXHBLT_MAXHBLTTREENODE_H
template<class T>
struct maxHbltTreeNode
{int height;// 存储权重T element;maxHbltTreeNode<T>* leftChild,//左子树*rightChild;//右子树/*默认构造函数*/maxHbltTreeNode() { leftChild = rightChild = nullptr; height = 0; element = 0;}/*只初始化element*/explicit maxHbltTreeNode(T melement){element = melement;height = 1;leftChild = rightChild = nullptr;}maxHbltTreeNode(T melement, int mheight){element = melement;height = mheight;leftChild = rightChild = nullptr;}/*三个元素都初始化*/maxHbltTreeNode(T& melement, int mheight, maxHbltTreeNode<T>* mleftChild, maxHbltTreeNode<T>* mrightChild){element = melement;height = mheight;leftChild = mleftChild;rightChild = mrightChild;}
};
#endif //_26MAXHBLT_MAXHBLTTREENODE_H
myExceptions.h
/*
Project name : allAlgorithmsTest
Last modified Date: 2022年8月13日17点38分
Last Version: V1.0
Descriptions: 综合各种异常
*/
#pragma once
#ifndef _MYEXCEPTIONS_H_
#define _MYEXCEPTIONS_H_
#include <string>
#include<iostream>
#include <utility>using namespace std;// illegal parameter value
class illegalParameterValue : public std::exception
{
public:explicit illegalParameterValue(string theMessage = "Illegal parameter value"){message = std::move(theMessage);}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:string message;
};// illegal input data
class illegalInputData : public std::exception
{
public:explicit illegalInputData(string theMessage = "Illegal data input"){message = std::move(theMessage);}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:string message;
};// illegal index
class illegalIndex : public std::exception
{
public:explicit illegalIndex(string theMessage = "Illegal index"){message = std::move(theMessage);}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:string message;
};// matrix index out of bounds
class matrixIndexOutOfBounds : public std::exception
{
public:explicit matrixIndexOutOfBounds(string theMessage = "Matrix index out of bounds"){message = std::move(theMessage);}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:string message;
};// matrix size mismatch
class matrixSizeMismatch : public std::exception
{
public:explicit matrixSizeMismatch(string theMessage ="The size of the two matrics doesn't match"){message = std::move(theMessage);}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:string message;
};// stack is empty
class stackEmpty : public std::exception
{
public:explicit stackEmpty(string theMessage ="Invalid operation on empty stack"){message = std::move(theMessage);}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:string message;
};// queue is empty
class queueEmpty : public std::exception
{
public:explicit queueEmpty(string theMessage ="Invalid operation on empty queue"){message = std::move(theMessage);}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:string message;
};// hash table is full
class hashTableFull : public std::exception
{
public:explicit hashTableFull(string theMessage ="The hash table is full"){message = std::move(theMessage);}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:string message;
};// edge weight undefined
class undefinedEdgeWeight : public std::exception
{
public:explicit undefinedEdgeWeight(string theMessage ="No edge weights defined"){message = std::move(theMessage);}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:string message;
};// method undefined
class undefinedMethod : public std::exception
{
public:explicit undefinedMethod(string theMessage ="This method is undefined"){message = std::move(theMessage);}void outputMessage() {cout << message << endl;}
private:string message;
};
#endif
运行结果
"C:\Users\15495\Documents\Jasmine\prj\_Algorithm\Data Structures, Algorithms and Applications in C++\_26maxHblt\cmake-build-debug\_26maxHblt.exe"
One tree in postorder is
Tree size is 5
7 9 1 8 11
Other tree in postorder is
Tree size is 4
4 2 6 9
After melding, the tree in postorder is
Tree size is 9
1 2 6 8 4 9 7 9 11
After popping four elements, the tree is
Tree size is 5
2 4 6 1 7
The popped elements, in order, are
11 9 9 8
After pushing 10, 20 & 5, the tree is
Leftist tree in postorder
Tree size is 8
2 4 6 1 7 10 5 20
After pushing 15, 30 & 15, the tree is
Leftist tree in postorder
Tree size is 11
2 4 6 1 7 10 5 15 20 2 30
The max element is 30
Popped max element 30
Leftist tree in postorder
Tree size is 10
5 2 15 2 4 6 1 7 10 20
Popped max element 20
Tree size is 9
Leftist tree in postorder
2 4 6 1 7 2 10 5 15
Popped max element 15
Tree size is 8
Popped max element 10
Tree size is 7
Popped max element 7
Tree size is 6
Popped max element 6
Tree size is 5
Popped max element 5
Tree size is 4
Popped max element 4
Tree size is 3
Popped max element 2
Tree size is 2
Popped max element 2
Tree size is 1
Popped max element 1
Tree size is 0Process finished with exit code 0
这篇关于《数据结构、算法与应用C++语言描述》-最大高度优先左高树-C++实现的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





