本文主要是介绍没有哈希时间锁定合约的跨链原子交换,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
在上一篇文章中,我们介绍了使用哈希时间锁定合约(HTLC)的跨链原子交换实现。 今天,我们介绍一种无需 HTLC 即可实现的替代方法。 这将原子交换扩展到缺乏哈希锁和时间锁的区块链。
使用 SPV 证明交易已被挖掘
让我们按照商定的价格将 Alice 的 BTC 币与 Bob 的 BSV 币进行交换。
在这篇文章中,我们展示了 BSV 智能合约能够验证区块链中包含的交易。 重要的是,这是在不依赖外部预言机的情况下实现的。 基本思想是使用工作难度证明来验证区块头。 使用 Merkle 证明,我们可以验证该区块中是否包含交易,类似于链下完成的 SPV。
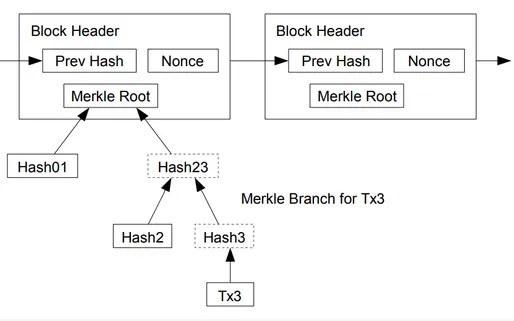
图片源于BSV Academy
这意味着 BSV 上的智能合约可以编程为根据 BTC 等区块链上特定交易的确认来执行特定操作。
在原子交换的背景下,智能合约本质上是这样说的:
“如果您将X BTC发送到Y地址,您就可以获得该合约中当前持有的BSV资产。”
该功能之所以成为可能,是因为 BSV 合约能够验证特定交易是否已在 BTC 区块链上成功开采。 合约可以对特定的BTC交易进行验证,确保预期的BTC金额已发送到正确的地址。
为了发起报价,Bob 在智能合约中确保 BSV 币的安全,并指定接收 BTC 所需的地址。 一旦 Alice 发送了 BTC,她就可以领取合约中锁定的 BSV。 此过程不涉及任何受信任的中介机构。
完整的协议序列
BSV 和 BTC 之间的原子交换协议可以按照以下步骤执行。
-
合约部署:Bob 在 BSV 链上部署智能合约。 该合约持有 Bob 打算与 Alice 交换的 BSV 资金。 该合同还包含故障安全时间锁。
-
付款和证明:Alice 将约定数量的 BTC 在 BTC 链上发送给 Bob。 在该交易被开采到区块中后,她获得了该交易的 Merkle 证明。 请注意,这是一个简单的支付交易,没有 HLTC。
-
验证和解锁:Alice 将 Merkle 证明提交给 BSV 合约。 合约验证证明并确认将 Alice 的 BTC 交易包含给 Bob。 如果证明得到验证,Alice 就可以解锁并领取合约中的 BSV 资金。
如果Bob没有及时收到付款,他可以在时间锁定到期后取回他的币。
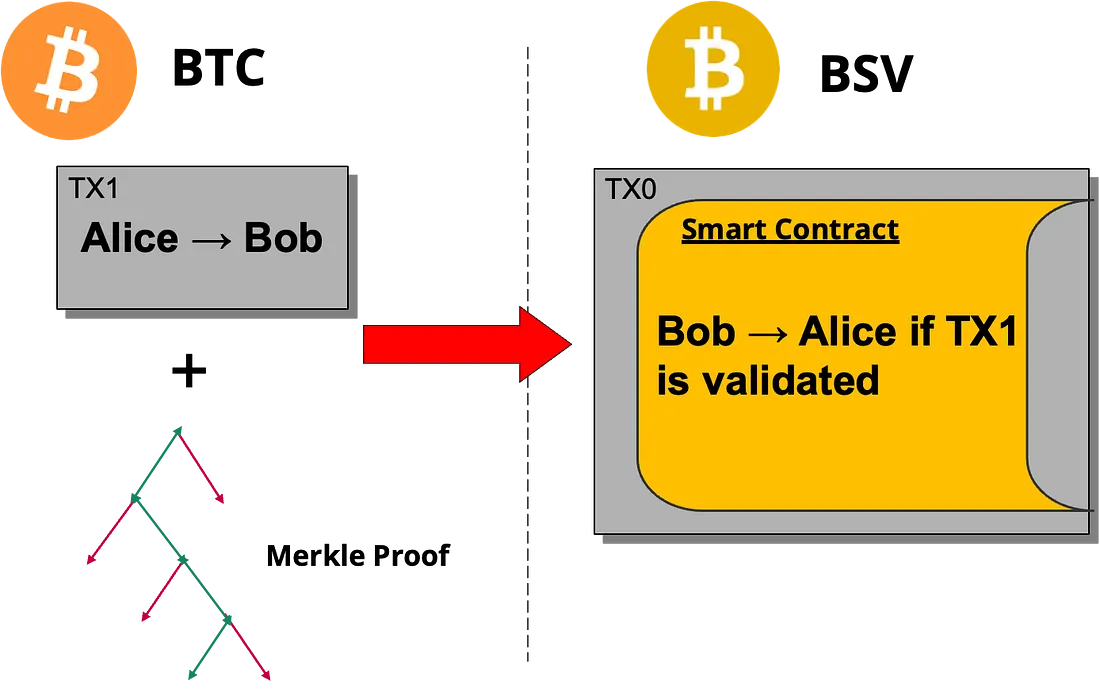
请注意,智能合约是在 BTC 付款广播之前部署的。 这样,Alice 就能保证在向 Bob 付款后,她会收到正确金额的 BSV。 该锁定时间还必须足够长,以便支付交易能够在 BTC 上进行挖掘。
通过稍加修改,Alice 在 Bob 合约部署时甚至可以是未知的。 Bob 的报价是公开的,任何人向他支付适量的 BTC 都可以解锁他锁定的 BSV。
与基于 HTLC 的原子交换相比
这种方法的一个关键优点是,即使对于没有哈希锁或时间锁的区块链,它也可以实现原子交换。 只要有一种机制可以不信任地证明其中包含交易(例如,使用 Merkle 证明),则具有智能合约功能来验证该证明的其他链就可以与其进行交换。
实现
在 BSV 中,智能合约可以在 sCrypt 中实现,如下所示。
export type VarIntRes = {val: bigintnewIdx: bigint
}class CrossChainSwap2 extends SmartContract {static readonly LOCKTIME_BLOCK_HEIGHT_MARKER = 500000000static readonly UINT_MAX = 0xffffffffnstatic readonly MIN_CONF = 3static readonly BTC_MAX_INPUTS = 3@prop()readonly aliceAddr: PubKeyHash@prop()readonly bobAddr: PubKeyHash@prop()readonly bobP2WPKHAddr: PubKeyHash@prop()readonly timeout: bigint // Can be a timestamp or block height.@prop()readonly targetDifficulty: bigint@prop()readonly amountBTC: bigint@prop()readonly amountBSV: bigint// ...@method()checkBtcTx(btcTx: ByteString): void {// Most things should be the same as in BSV except the witness data and flag.// - Check (first) output is P2WPKH to Bobs public key.// - Check (first) output amount is equal to this.amountBTClet idx = 4n// Make sure to serialize BTC tx without witness data.// See https://github.com/karask/python-bitcoin-utils/blob/a41c7a1e546985b759e6eb2ae4524f466be809ca/bitcoinutils/transactions.py#L913assert(slice(btcTx, idx, idx + 2n) != toByteString('0001'),'Witness data present. Please serialize without witness data.') INPUTS:const inLen = CrossChainSwap2.parseVarInt(btcTx, idx)assert(inLen.val <= BigInt(CrossChainSwap2.BTC_MAX_INPUTS),'Number of inputs too large.')idx = inLen.newIdxfor (let i = 0n; i < CrossChainSwap2.BTC_MAX_INPUTS; i++) {if (i < inLen.val) {//const prevTxID = slice(btcTx, idx, idx + 32n)idx += 32n//const outIdx = slice(btcTx, idx, idx + 4n)idx += 4nconst scriptLen = CrossChainSwap2.parseVarInt(btcTx, idx)idx = scriptLen.newIdxidx += scriptLen.val//const nSequence = slice(btcTx, idx, idx + 4n)idx += 4n}} FIRST OUTPUT:// Check if (first) output pays Bob the right amount and terminate and set res to true.const outLen = CrossChainSwap2.parseVarInt(btcTx, idx)idx = outLen.newIdxconst amount = Utils.fromLEUnsigned(slice(btcTx, idx, idx + 8n))assert(amount == this.amountBTC, 'Invalid BTC output amount.')idx += 8nconst scriptLen = CrossChainSwap2.parseVarInt(btcTx, idx)idx = scriptLen.newIdxconst script = slice(btcTx, idx, idx + scriptLen.val)assert(len(script) == 22n, 'Invalid locking script length.')assert(script == toByteString('0014') + this.bobP2WPKHAddr,'Invalid locking script.')// Data past this point is not relevant in our use-case.}@method()public swap(btcTx: ByteString,merkleProof: MerkleProof,headers: FixedArray<BlockHeader, typeof CrossChainSwap2.MIN_CONF>,alicePubKey: PubKey,aliceSig: Sig) {// Check btc tx.this.checkBtcTx(btcTx)// Calc merkle root.const txID = hash256(btcTx)const merkleRoot = MerklePath.calcMerkleRoot(txID, merkleProof)// Check if merkle root is included in the first BH.assert(merkleRoot == headers[0].merkleRoot,"Merkle root of proof doesn't match the one in the BH.")// Check target diff for headers.for (let i = 0; i < CrossChainSwap2.MIN_CONF; i++) {assert(Blockchain.isValidBlockHeader(headers[i],this.targetDifficulty),`${i}-nth BH doesn't meet target difficulty`)}// Check header chain.let h = Blockchain.blockHeaderHash(headers[0])for (let i = 0; i < CrossChainSwap2.MIN_CONF; i++) {if (i >= 1n) {const header = headers[i]// Check if prev block hash matches.assert(header.prevBlockHash == h,`${i}-th BH wrong prevBlockHash`)// Update header hash.h = Blockchain.blockHeaderHash(header)}}// Verify Alices signature.assert(hash160(alicePubKey) == this.aliceAddr, 'Alice wrong pub key.')assert(this.checkSig(aliceSig, alicePubKey))}@method()public cancel(bobPubKey: PubKey, bobSig: Sig) {// Ensure nSequence is less than UINT_MAX.assert(this.ctx.sequence < CrossChainSwap2.UINT_MAX,'input sequence should less than UINT_MAX')// Check if using block height.if (this.timeout < CrossChainSwap2.LOCKTIME_BLOCK_HEIGHT_MARKER) {// Enforce nLocktime field to also use block height.assert(this.ctx.locktime <CrossChainSwap2.LOCKTIME_BLOCK_HEIGHT_MARKER,'locktime should be less than 500000000')}assert(this.ctx.locktime >= this.timeout,'locktime has not yet expired')// Verify Bobs signature.assert(hash160(bobPubKey) == this.bobAddr, 'Bob wrong pub key.')assert(this.checkSig(bobSig, bobPubKey))}
}
源码文件crosschainswap2.ts
智能合约有两个公共方法:
swap():如果 Alice 提供了她向 Bob 支付了足够数量的 BTC 的证据,则 Alice 会调用该函数来获取资金。cancel():由 Bob 在指定的时间过后调用以提取资金。
完整的代码和测试可以在 GitHub 上找到。
这篇关于没有哈希时间锁定合约的跨链原子交换的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






