本文主要是介绍Decrease-and-Conquer,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
第四章 Decrease-and-Conquer
增量方法:自下而上的变化通常是以迭代方式实现;以问题的一个小地方开始。
The bottom-up variation is usually implemented iteratively, starting with a solution to the smallest instance of the problem; it is called sometimes the incremental approach.
Three major variations of decrease-and-conquer:
Decrease by a constant
Decrease by a constant factor
Variable size decrease
4.1 Insertion Sort
4.1.1 介绍
如果我们已经找到了数组中n-2个元素的正确位置,那么第 A[n-1] 个元组放在哪呢?只需要在刚刚排好序的数组中,找到
一个位置插入这最后一个元素即可
Following the technique’s idea, we assume that the smaller problem of sorting the array A[0..n − 2] has already been solved to give us a sorted array of size n − 1: A[0]≤ . . . ≤ A[n − 2]. How can we take advantage of this solution to the smaller problem to get a solution to the original problem by taking into account the element A[n − 1]? Obviously, all we need is to find an appropriate position for A[n − 1] among the sorted elements and insert it there.
这通常是通过从右到左扫描已排序的子阵列来完成的,直到遇到小于或等于[N-1]的第一个元素,在该元素后面插入一个[N-1]。
This is usually done by scanning the sorted subarray from right to left until the first element smaller than or equal to A[n − 1] is encountered to insert A[n − 1] right after that element.
虽然插入排序显然基于递归思想,但是自下而上(即迭代)实现该算法更有效。
Though insertion sort is clearly based on a recursive idea, it is more efficient to implement this algorithm bottom up, i.e., iteratively
4.1.2 伪代码:

代码实现或其他详细解析请参考: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36098284/article/details/98098798
4.1.3例子:

4.1.4 时间复杂度分析
该算法的关键是每次的比较过程,即 A[j] 和 v 的大小
The basic operation of the algorithm is the key comparison A[j] > v.
比较的次数依赖于输入的数据,最坏的情况是,当序列恰巧是降序,而我们希望得到升序的时候,从i = 1 开始,需要比较该数字其前面的所有数字,并且需要依次进行移动。最坏的情况下,比较的次数和选择排序相同。
T e number of key comparisons in this algorithm obviously depends on the nature of the input. In the worst case, A[j]> v is executed the largest number of times, i.e., for every j = i − 1, . . . , 0. Since v = A[i], it happens if and only if A[j]> A[i] for j = i − 1, . . . , 0.Thus, in the worst case, insertion sort makes exactly the same number of comparisons as selection sort
选择排序可以参考: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36098284/article/details/97812203
因此当出现这种情况的时候,时间复杂是 O(n^2)
Thus, for the worst-case input, we get A[0]>A[1] (for i = 1), A[1]> A[2] (for i = 2), . . . , A[n − 2]> A[n − 1]
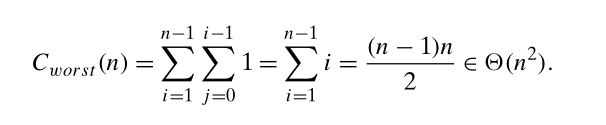
最好的情况是,序列是 升序,同时我们也想要升序,时间复杂度是 n - 1
In the best case, the comparison A [j]> v is executed only once on every iteration of the outer loop. It happens if and only if A[i − 1]≤ A[i] for every
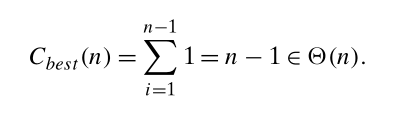
虽然平均效率是O(n^2) 使得,相对于其他的排序算法,还是比较脱出。
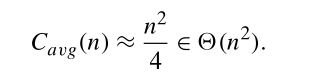
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
4.2 Topological Sort
更新时间2019.8.9!!!
持续更新
这篇关于Decrease-and-Conquer的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





![缺陷定位论文阅读:[Dongsun Kim] [TSE在投] DC: A Divide-and-Conquer Approach to IR-based Bug Localization](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/20190214112131595.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_ZmFuZ3poZW5naGVpdGk,shadow_10,text_aHR0cHM6Ly9ibG9nLmNzZG4ubmV0L3dlaXhpbl8zOTI3ODI2NQ==,size_16,color_FFFFFF,t_70)

