本文主要是介绍The Divide-and-Conquer Paradigm分而治之范式,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
In general, the divide-and-conquer paradigm consists of the following steps.
The divide step. The input is partitioned into 1 ≤ p ≤ n parts.
The conquer step. This step consists of performing p recursive call(s) if the problem size is greater than some predefined threshold n 0 .
The combine step. The solutions to the p recursive call(s) are combined to obtain the desired output.
The combine step is very crucial to the performance of virtually all divide-and-conquer algorithms, as the efficiency of the algorithm is largely dependent on how judiciously this step is implemented .
the divide step is invariant in almost all divide-and-conquer algorithms : Partition the input data into p parts, and proceed to the conquer step. In many divide-and-conquer algorithms, it takes O ( n ) time or even only O (1) time.
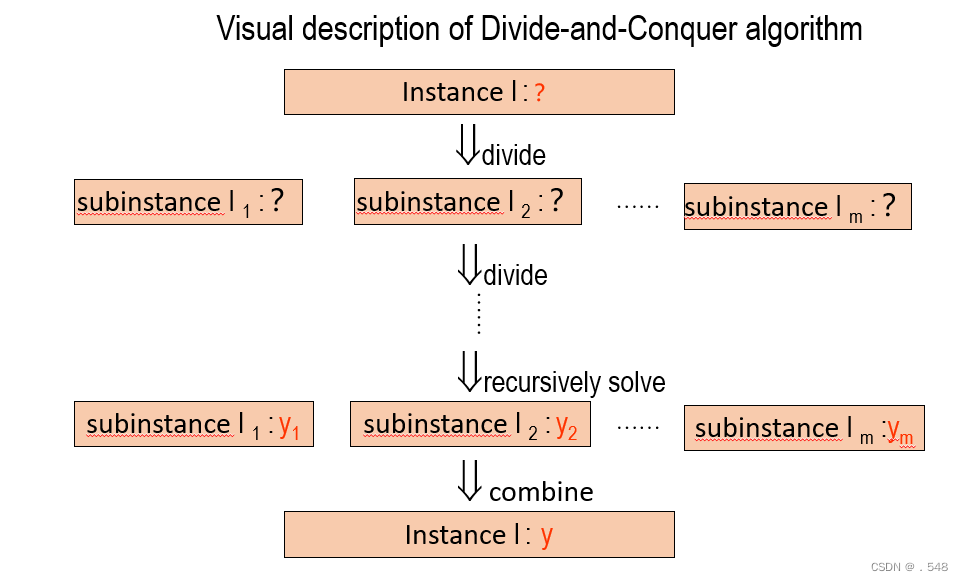
A divide-and-conquer algorithm has the following format .
If the size of the instance I is “small”, then solve the problem using a straightforward method and return the answer. Otherwise, continue to the next step .
Divide the instance I into p subinstances I 1 , I 2 , . . . , I p of approximately the same size.
Recursively call the algorithm on each subinstance I j , 1 ≤ j ≤ p , to obtain p partial solutions.
Combine the results of the p partial solutions to obtain the solution to the original instance I . Return the solution of instance I.
一般来说,分而治之模式包括以下步骤。
分割 步骤。输入被分割成 1≤p ≤ n 个部分。
治之 步骤。如果问题大小大于某个预定义阈值n0,则执行p 次递归 调用。
合并 步骤。将p 个递归 调用的解结合起来,以获得所需的输出。
合并步骤对几乎所有分而治之算法的性能都至关重要,因为算法的效率在很大程度上取决于如何明智地执行这一步骤。
在几乎 所有的分而治之算法中,除法步骤都是不变的: 将输入数据分成p 部分 ,然后进入征服步骤。在许多分而治之算法中,这一步需要O(n) 时间,甚至只需要O(1) 时间。
分而治之算法的格式如下。
如果实例I 的大小为 "小",则使用直接方法解决问题并返回答案。否则,继续下一步。
将实例I 分成p 个子实例 I1、I2、...... , Ip大小大致相同。
在每个子实例Ij 上递归调用算法,1 ≤j ≤ p,得到p 个部分 解。
合并p 个部分 解的结果,得到原始实例I 的解。
这篇关于The Divide-and-Conquer Paradigm分而治之范式的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!