本文主要是介绍Li‘s 核磁共振影像数据处理-17-FSL-FAST 脑组织类型分割,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
讲解视频内容请移步Bilibili:
https://space.bilibili.com/542601735
入群讨论请加vhochzeitstorte
请注明“核磁共振学习”
公众号:美好事物中转站
FAST (FMRIB’s Automated Segmentation Tool) segments a 3D image of the brain into different tissue types (Grey Matter, White Matter, CSF, etc.), whilst also correcting for spatial intensity variations (also known as bias field or RF inhomogeneities). The underlying method is based on a hidden Markov random field model and an associated Expectation-Maximization algorithm. The whole process is fully automated and can also produce a bias field-corrected input image and a probabilistic and/or partial volume tissue segmentation. It is robust and reliable, compared to most finite mixture model-based methods, which are sensitive to noise.
FAST (FMRIB的自动分割工具)将大脑的3D图像分割成不同的组织类型(灰质,白质,脑脊液等),同时校正空间强度变化(也称为偏置场或射频不均匀性)。该方法基于隐马尔科夫随机场模型和相关的期望最大化算法。整个过程是完全自动化的,还可以产生偏场校正输入图像和概率和/或部分体积组织分割。与大多数基于有限混合模型的方法相比,该方法对噪声敏感,具有较强的鲁棒性和可靠性。
几种分割手段
强度模型(intensity model)
概率模型(probability model)

MRF模型
使用空间邻域信息
高斯混合模型
结合强度模型和MRF
部分容积模型
考虑一个voxel内可能包含多于一种组织。
FSL-FAST的时候,它做了什么?
1、初始估计分割,Tree-K-means
2、迭代:偏置场估计、强度模型+MRF
3、部分容积模型(partial volume model)
FSL-FAST实践
基本界面

高级选项

Main MRF parameter:MRF加权,值越大MRF作用越大。
Number of iterations for bias field removal:迭代次数。
Bias field smoothing(FWHM in mm):偏置场空间平滑度。
Use a-priori probability maps for initialization,使用先验概率图。
Standard to Input FLIRT transform:先验概率图到个体脑的转换矩阵文件。
Use file of initial tissue-type means:先验概率图各组织的平均值。
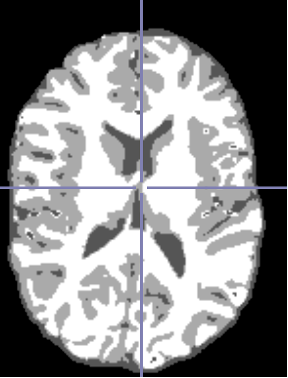
输出结果

课后小任务
用脚本的方式实现组织分割。
这篇关于Li‘s 核磁共振影像数据处理-17-FSL-FAST 脑组织类型分割的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!



