本文主要是介绍usaco training刷怪旅 第一层第二题 Greedy Gift Givers,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
usaco training
关注我持续创作training题解
翻译有点奇葩,我就上原题目了,各位自己翻译吧QwQ
A group of NP (2 ≤ NP ≤ 10) uniquely named friends has decided to exchange gifts of money. Each of these friends might or might not give some money to some or all of the other friends (although some might be cheap and give to no one). Likewise, each friend might or might not receive money from any or all of the other friends. Your goal is to deduce how much more money each person receives than they give.
The rules for gift-giving are potentially different than you might expect. Each person goes to the bank (or any other source of money) to get a certain amount of money to give and divides this money evenly among all those to whom he or she is giving a gift. No fractional money is available, so dividing 7 among 2 friends would be 3 each for the friends with 1 left over – that 1 left over goes into the giver's "account". All the participants' gift accounts start at 0 and are decreased by money given and increased by money received.
In any group of friends, some people are more giving than others (or at least may have more acquaintances) and some people have more money than others.
Given:
- a group of friends, no one of whom has a name longer than 14 characters,
- the money each person in the group spends on gifts, and
- a (sub)list of friends to whom each person gives gifts,
determine how much money each person ends up with.
IMPORTANT NOTE
The grader machine is a Linux machine that uses standard Unix conventions: end of line is a single character often known as '\n'. This differs from Windows, which ends lines with two characters, '\r\ and '\n'. Do not let your program get trapped by this!
PROGRAM NAME: gift1
INPUT FORMAT
Line # Contents 1 A single integer, NP 2..NP+1 Line i+1 contains the name of group member i NP+2..end NP groups of lines organized like this:
The first line of each group tells the person's name who will be giving gifts. The second line in the group contains two numbers:
- The amount of money (in the range 0..2000) to be divided into gifts by the giver
- NGi (0 ≤ NGi ≤ NP), the number of people to whom the giver will give gifts
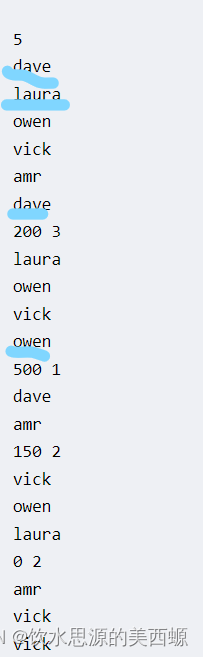
If NGi is nonzero, each of the next NGi lines lists the name of a recipient of a gift; recipients are not repeated in a single giver's list. SAMPLE INPUT (file gift1.in)
5 dave laura owen vick amr dave 200 3 laura owen vick owen 500 1 dave amr 150 2 vick owen laura 0 2 amr vick vick 0 0OUTPUT FORMAT
The output is NP lines, each with the name of a person followed by a single blank followed by the net gain or loss (final_money_value - initial_money_value) for that person. The names should be printed in the same order they appear starting on line 2 of the input.
All gifts are integers. Each person gives the same integer amount of money to each friend to whom any money is given, and gives as much as possible that meets this constraint. Any money not given is kept by the giver.
SAMPLE OUTPUT (file gift1.out)
dave 302 laura 66 owen -359 vick 141 amr -150
OUTPUT EXPLANATION
Five names: dave, laura, owen, vick, amr. Let's keep a table of the gives (money) each person 'has':
dave laura owen vick amr 0 0 0 0 0 First, 'dave' splits 200 among 'laura', 'owen', and 'vick'. That comes to 66 each, with 2 left over -200+2 +66 +66 +66 0 → -198 66 66 66 0 Second, 'owen' gives 500 to 'dave': -198+500 66 66-500 66 0 → 302 66 -434 66 0 Third, 'amr' splits 150 between 'vick' and 'owen': 302 66 -434+75 66+75 -150 → 302 66 -359 141 -150 Fourth, 'laura' splits 0 between 'amr' and 'vick'; no changes: 302 66 -359 141 -150 Finally, 'vick' gives 0 to no one: dave laura owen vick amr 302 66 -359 141 -150
语言的隔阂太严重了(不排除看文章的有英语大佬但蒟蒻看不懂)
简要说一下这题的意思:
n个人,第i个人有a[i]元钱,平均分给m元,剩下的自己拿走
简而言之就是这么一句话,毕竟是第一层,还都是模拟
一开始用的map,但因为蒟蒻太蒻了,map没AC了,就退回到原始时代了
仔细观察他的样例输入,后面挨个输入钱数的时候和前面的次数是不一样的
但不必担心,数据范围很小,直接打暴力
/*
ID:
TASK:gift1
LANG:C++
*/
# include <iostream>
# include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
# define int long long
struct node{string name;int num;
}e[105];
int n;
signed main(){freopen("gift1.in","r",stdin);freopen("gift1.out","w",stdout);scanf("%lld",&n);for (int i=1;i<=n;i++){cin>>e[i].name;e[i].num=0;}string str;int num1,sum;while(cin>>str){cin>>num1>>sum;if (num1==0||sum==0){for (int i=0;i<sum;i++){string temp;cin>>temp;}}else{int yu=num1%sum;int shang=num1/sum;int poi;string temp;for (int i=1;i<=n;i++){if (e[i].name==str){poi=i;break;}}e[poi].num-=num1;e[poi].num+=yu;for (int i=0;i<sum;i++){cin>>temp;for (int j=1;j<=n;j++){if (e[j].name==temp){e[j].num+=shang;}}}}}for (int i=1;i<=n;i++){cout<<e[i].name<<" "<<e[i].num<<"\n";}fclose(stdin);fclose(stdout);return 0;
}
这篇关于usaco training刷怪旅 第一层第二题 Greedy Gift Givers的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!