本文主要是介绍RANSAC法拟合平面的实现,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
RANSAC法拟合平面
本文衔接前一篇《最小二乘法实现平面拟合》,基于C++实现了PCL官方的平面拟合,用一个复杂铸件的点云图像进行测试。时间有限,难以确保程序不会出现bug,该文章仅供参考。
效果
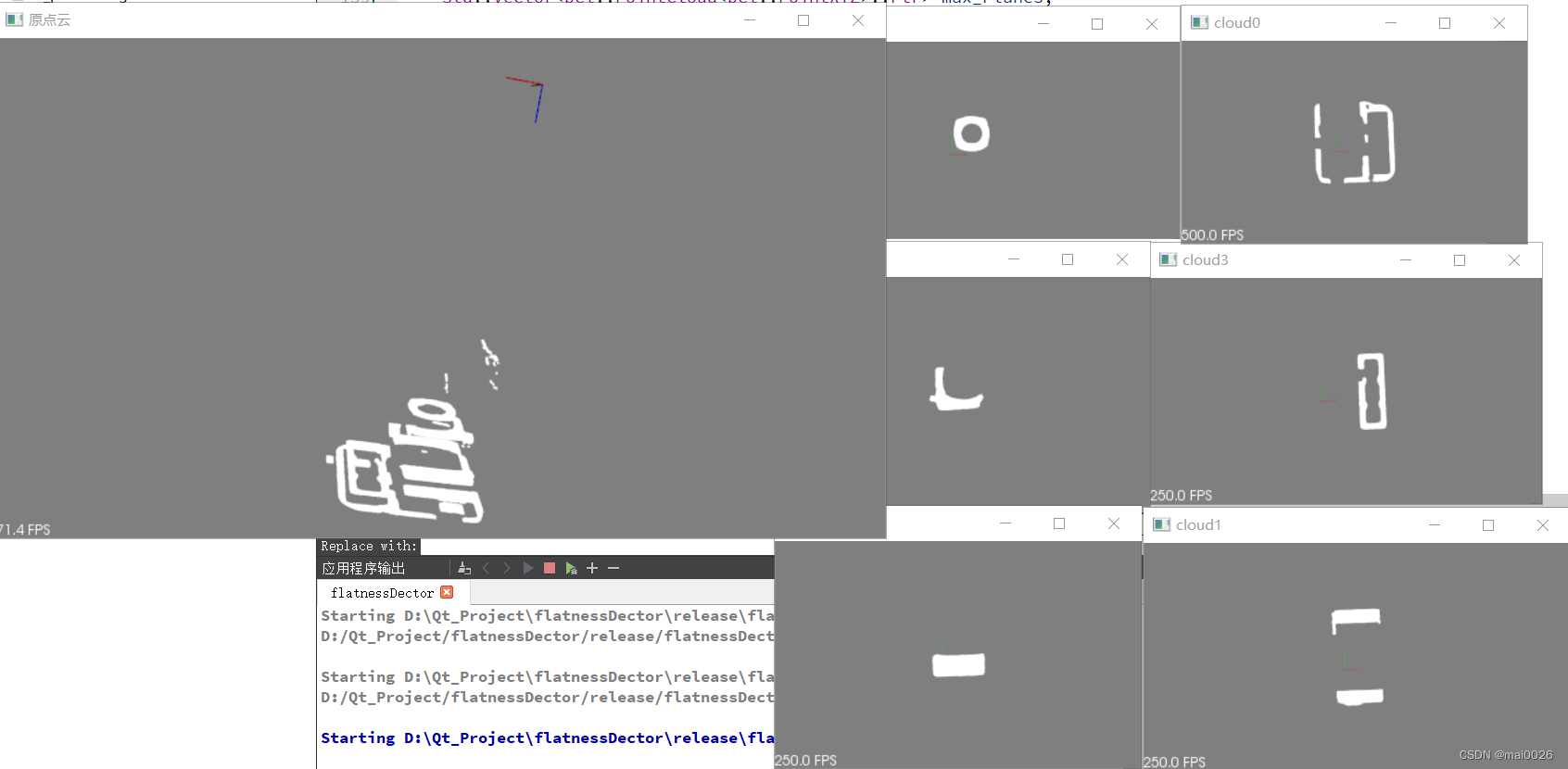
原点云换一个角度
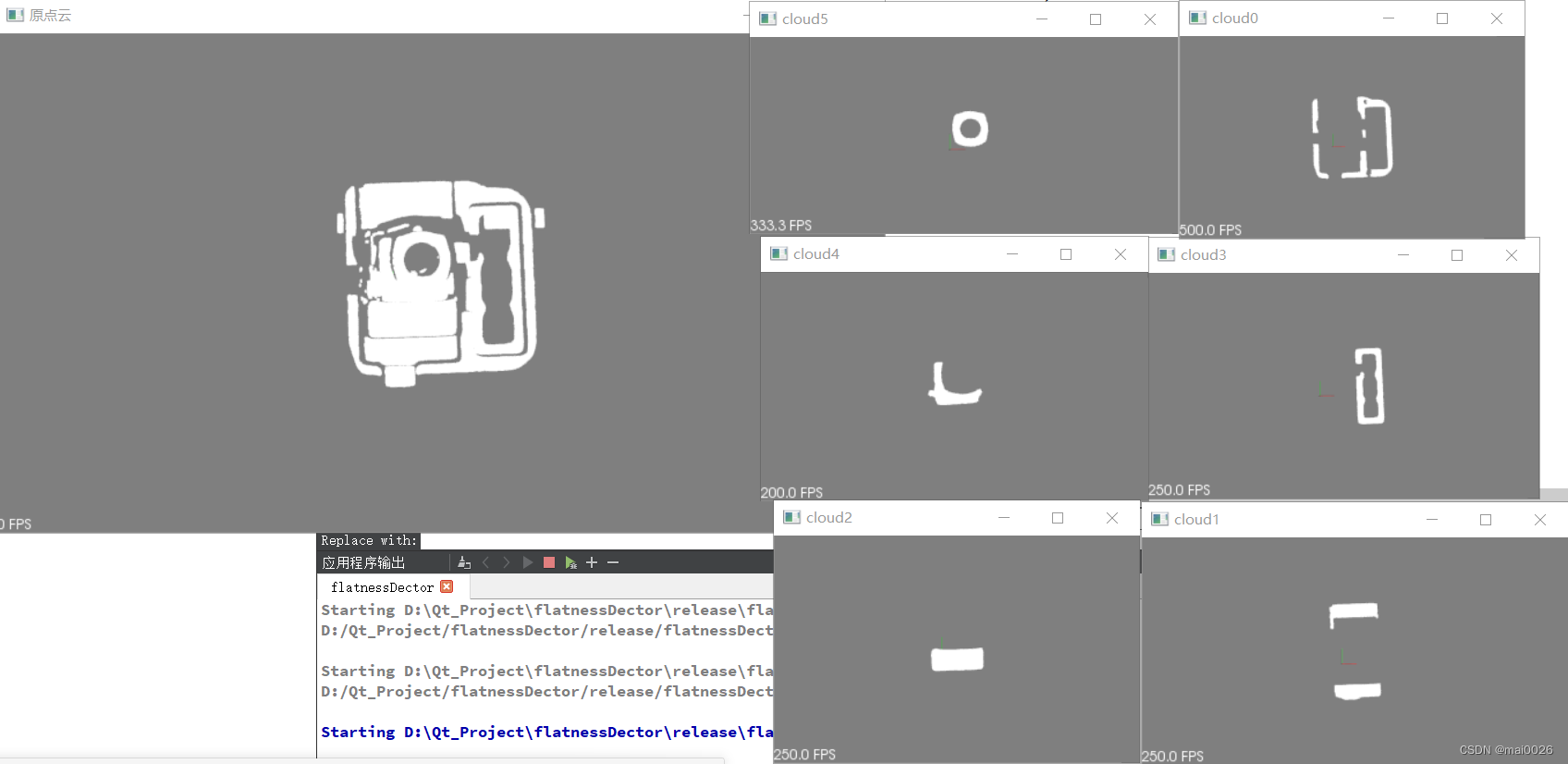
原点云是一个复杂的铸件,通过RANSAC法拟合平面将铸件点云分割为许多个平面。
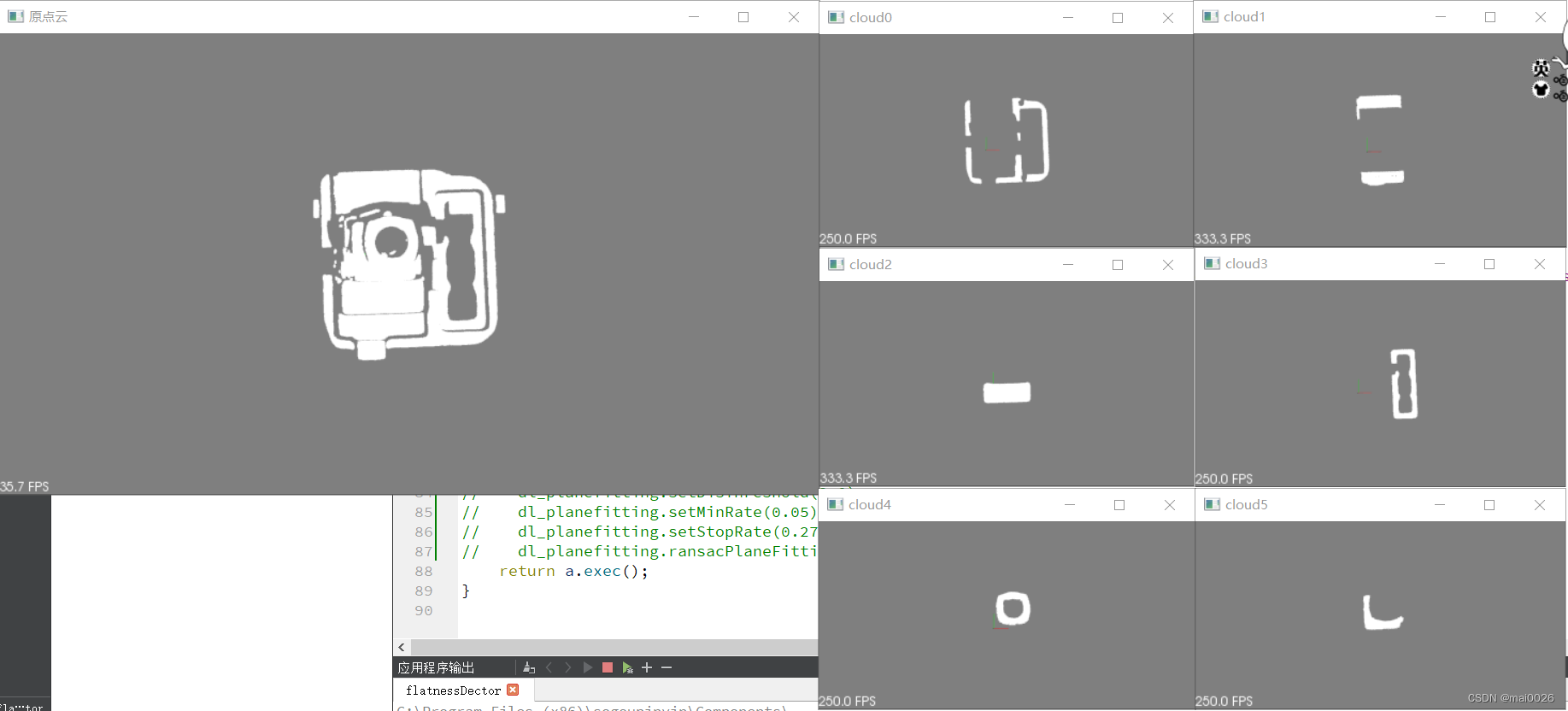
与PCL官网提供的接口的效果进行对比,下图为官方接口的效果,可以看出自己复现的算法与官方提供的算法接口效果基本相同。
RANSAC原理
计算机视觉基本原理——RANSAC
算法逻辑
1、在未经处理过的点云上随机取3个点,用这3个点拟合一个平面(方法参考《PCL最小二乘法拟合平面》)。
2、若拟合平面的内点数量达到一定阈值则将这次迭代的内点与外点都保存到一个容器内。
3、重复迭代1、2步骤一定的次数。
4、选择内点容器内元素中点的数量最多的元素作为结果保存在结果容器中,外点容器中对应的元素作为第一步的输入点云重复上述流程,直到结果容器中的点的个数超过一定阈值,结束迭代。
算法实现
将上述提到的最小二乘法封装成了一个类
dl_planefitting.h
#ifndef DL_PLANEFITTING_H
#define DL_PLANEFITTING_H#include <QObject>
#include<pcl/io/io.h>
#include<pcl/io/pcd_io.h>//pcd 读写类相关的头文件。
#include<pcl/io/ply_io.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include<Eigen/Dense>
#include <random>
#include <windows.h>//平面拟合类
class DL_Plane : public QObject
{Q_OBJECT
public:explicit DL_Plane(QObject *parent = nullptr);/*https://blog.csdn.net/konglingshneg/article/details/82585868设平面方程为ax+by+cz+d=0两边同时除d则有(a/d)X+(b/d)Y+(c/d)z+1=0令a0=-a/c;a1=-b/c;a2=-d/c 即(a0/a2)X+(a1/a2)Y +(-1/a2)Z+1=0最后直线方程写成AX+BY+CZ+1=0*///平面表示参数double A;double B;double C;//距离阈值double distance = 1.0;//拟合点pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_;//平面内点pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr plane_;//平面外点pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr nonplane_;//平面拟合Eigen::Vector3d getFlat(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud);//设置输入点云void setInputCloud(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud);//更新平面参数void updateParameter(Eigen::Vector3d x);//求点到平面距离double getDistance(pcl::PointXYZ point);//求平面点云void planeFitting(double dis);//取平面点云pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr getPlanePoints(void);//设置参数void setParameter(double dis);//平面拟合处理void planeProcess(void);//点云可视化void showCloud(std::string windowname,pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud);
private://拟合平面参数double a0;double a1;double a2;
signals:public slots:
};//RANSAC法拟合类
class DL_PlaneFitting : public DL_Plane
{
public://总点的数量int all_pointsnum;//迭代次数int iteration_time = 1000;//距离阈值double dis_threshold = 2.0;//平面点数量与点云总数最小比例double min_rate = 0.05;//终止条件double stop_rate = 0.25;//内点点集std::vector<pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr> plane_points_;//最终输出std::vector<std::vector<pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr>> result_;//对应输出点集的int列表std::vector<int> max_output;DL_PlaneFitting();void updatePlaneParameter(DL_Plane *dl_plane,Eigen::Vector3d x);//参数设置void setIterationTime(int num){iteration_time = num;}void setDisThreshold(double dis){dis_threshold = dis;}void setMinRate(double rate){min_rate = rate;}void setStopRate(double rate){stop_rate = rate;}//RANSAC法拟合平面void ransacPlaneFitting();void getResultPlanes();
private:double dis;//随机生成的三个假平面点pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr flatpoints_;//从点云中随机生成三个点void randomGenerate(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr restpoints,int p_num);
};#endif // DL_PLANEFITTING_Hdl_planefitting.cpp
#include "dl_planefitting.h"DL_Plane::DL_Plane(QObject *parent) : QObject(parent)
{pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr plane (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr nonplane (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);cloud_ = cloud;plane_ = plane;nonplane_ = nonplane;
}//设置输入点云
void DL_Plane::setInputCloud(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud){cloud_ = cloud;
}//求解点到平面距离(使用前要更新平面参数)
double DL_Plane::getDistance(pcl::PointXYZ point){double up = std::abs(A*point.x+B*point.y+C*point.z+1);double down = std::sqrt(std::pow(A,2)+std::pow(B,2)+std::pow(C,2));double dis = up/down;return dis;
}//平面拟合算法
Eigen::Vector3d DL_Plane::getFlat(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud){Eigen::Matrix3d rot;double x2,xy,x,y2,y,zx,zy,z;for(int i=0;i<cloud->points.size();i++){x2 += cloud->points[i].x * cloud->points[i].x;xy += cloud->points[i].x * cloud->points[i].y;x += cloud->points[i].x;y2 += cloud->points[i].y * cloud->points[i].y;y += cloud->points[i].y;zx += cloud->points[i].x * cloud->points[i].z;zy += cloud->points[i].y * cloud->points[i].z;z += cloud->points[i].z;}//为矩阵赋值rot<<x2, xy, x,xy, y2, y,x, y, cloud->points.size();//为列向量赋值Eigen::Vector3d eq(zx,zy,z);Eigen::Vector3d X = rot.colPivHouseholderQr().solve(eq);
// std::cout<<X<<std::endl;
// std::cout<<X[0]<<" "<<X[1]<<" "<<X[2]<<std::endl;return X;
}//更新平面参数
void DL_Plane::updateParameter(Eigen::Vector3d x){a0 = x[0];a1 = x[1];a2 = x[2];A=a0/a2;B=a1/a2;C=-1/a2;
}//求平面内点
void DL_Plane::planeFitting(double dis){plane_->clear();for (int i=0;i<cloud_->points.size();i++){if(getDistance(cloud_->points[i])<dis){plane_->points.push_back(cloud_->points[i]);}else{nonplane_->points.push_back(cloud_->points[i]);//std::cout<<"dis:"<<getDistance(cloud->points[i])<<std::endl;}}
}//取平面点云
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr DL_Plane::getPlanePoints(void){return plane_;
}//设置距离参数
void DL_Plane::setParameter(double dis){distance = dis;
}//平面拟合处理
void DL_Plane::planeProcess(void){Eigen::Vector3d result = getFlat(this->cloud_);updateParameter(result);planeFitting(this->distance);
}//点云可视化
void DL_Plane::showCloud(std::string windowname,pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud){pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer::Ptr viewer (new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer (windowname));viewer->setBackgroundColor (0.5, 0.5, 0.5); //设置背景viewer->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> (cloud, "sample cloud"); //显示点云viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 1, "sample cloud"); //设置点尺寸viewer->addCoordinateSystem (100.0); //设置坐标轴尺寸
// while (!viewer->wasStopped ())
// {
// viewer->spinOnce (100);
// boost::this_thread::sleep (boost::posix_time::microseconds (100000));
// }//cout<<"Point couting in "<<windowname<<": "<<cloud->size()<<endl;
}DL_PlaneFitting::DL_PlaneFitting(){}//更新平面参数
void DL_PlaneFitting::updatePlaneParameter(DL_Plane *dl_plane, Eigen::Vector3d x){dl_plane->updateParameter(x);
}//随机生成三个点,存在flatpoints中
void DL_PlaneFitting::randomGenerate(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr restpoints,int p_num){// 生成随机的三个点拟合平面LARGE_INTEGER seed;QueryPerformanceFrequency(&seed);QueryPerformanceCounter(&seed);srand(seed.QuadPart);pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr flatpoints(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);for (int i=0;i<p_num;i++){int index1 = rand()%restpoints->points.size();flatpoints->points.push_back(restpoints->points[index1]);
// std::cout<<" "<<i<<":"<<index1;}
// std::cout<<std::endl;flatpoints_ = flatpoints;
}//RANSAC法拟合平面
void DL_PlaneFitting::ransacPlaneFitting(){//记录原点云数量int total_num = cloud_->points.size();std::cout<<"原点云总数:"<<total_num<<std::endl;//存放结果std::vector<pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr> result;//存放剩余的点pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr restpoints(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);restpoints->points = cloud_->points;//存放每次迭代的点云std::vector<pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr> max_Planes;//存放每次迭代剩余的点云std::vector<pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr> rest_Planes;int N=0;while(restpoints->points.size()>stop_rate*total_num){N+=1;std::cout<<"第"<<N<<"次迭代比例为:"<<double((restpoints->points.size()+0.01)/total_num)<<std::endl;max_Planes.clear();rest_Planes.clear();//设置每层迭代次数int n=iteration_time;while(--n>0){randomGenerate(restpoints,3);DL_Plane dl_plane;dl_plane.setInputCloud(restpoints);Eigen::Vector3d result = dl_plane.getFlat(flatpoints_);dl_plane.updateParameter(result);//设置拟合平面点的距离阈值dl_plane.planeFitting(dis_threshold);//如果拟合平面的内点数量符合要求if(dl_plane.plane_->points.size()>min_rate*total_num){max_Planes.push_back(dl_plane.plane_);rest_Planes.push_back(dl_plane.nonplane_);}}//提取最大平面作为其中一个结果int max_num=0;int index = -1;for (int i=0;i<max_Planes.size();i++){if (max_Planes[i]->points.size()>max_num){max_num = max_Planes[i]->points.size();index = i;}}result.push_back(max_Planes[index]);//重新设置剩余的点restpoints->points = rest_Planes[index]->points;std::cout<<"剩余的点的数量"<<restpoints->points.size()<<std::endl;//showCloud("cloud"+std::to_string(index),max_Planes[index]);}for(int i=0;i<result.size();i++){showCloud("cloud"+std::to_string(i),result[i]);}
}main.cpp
#include <QCoreApplication>
#include<opencv2\opencv.hpp>
#include<pcl/io/io.h>
#include<pcl/io/pcd_io.h>//pcd 读写类相关的头文件。
#include<pcl/io/ply_io.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include<Eigen/Dense>
#include <dl_planefitting.h>#include <pcl/filters/extract_indices.h>
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/search/kdtree.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/method_types.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/model_types.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/sac_segmentation.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/extract_clusters.h>int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{QCoreApplication a(argc, argv);DL_Plane dl_plane;pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);pcl::io::loadPCDFile<pcl::PointXYZ>("D:\\Qt_Project\\result.pcd",*cloud);dl_plane.showCloud("原点云",cloud);/*///PCL提供的平面拟合*/
// pcl::VoxelGrid<pcl::PointXYZ> vg;
// pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_filtered (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
// vg.setInputCloud (cloud);
// vg.setLeafSize (0.1f, 0.1f, 0.1f);
// vg.filter (*cloud_filtered);// std::cout << "PointCloud after filtering has: " << cloud_filtered->size () << " data points." << std::endl; //*
// // Create the segmentation object for the planar model and set all the parameters
// pcl::SACSegmentation<pcl::PointXYZ> seg;
// pcl::PointIndices::Ptr inliers (new pcl::PointIndices);
// pcl::ModelCoefficients::Ptr coefficients (new pcl::ModelCoefficients);
// pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_plane (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> ());
// seg.setOptimizeCoefficients (true);
// seg.setModelType (pcl::SACMODEL_PLANE);
// seg.setMethodType (pcl::SAC_RANSAC);
// seg.setMaxIterations (1000);
// seg.setDistanceThreshold (1.0);
// int nr_points = (int) cloud_filtered->size ();
// pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_f (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>);
// int i=0;
// while (cloud_filtered->size () > 0.3 * nr_points)
// {
// // Segment the largest planar component from the remaining cloud
// seg.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);
// seg.segment (*inliers, *coefficients);
// if (inliers->indices.size () == 0)
// {
// std::cout << "Could not estimate a planar model for the given dataset." << std::endl;
// break;
// }
// // Extract the planar inliers from the input cloud
// pcl::ExtractIndices<pcl::PointXYZ> extract;
// extract.setInputCloud (cloud_filtered);
// extract.setIndices (inliers);
// extract.setNegative (false);
// // Get the points associated with the planar surface
// extract.filter (*cloud_plane);
// if(cloud_plane->size()>500){
// dl_plane.showCloud("cloud"+std::to_string(i),cloud_plane);
// i+=1;
// double time = cloud_filtered->size ()/cloud_plane->points.size();
// std::cout<<"size"<<i<<" :"<<time<<std::endl;
// }
// std::cout << "PointCloud representing the planar component: " << cloud_plane->size () << " data points." << std::endl;
// // Remove the planar inliers, extract the rest
// extract.setNegative (true);
// extract.filter (*cloud_f);
// *cloud_filtered = *cloud_f;
// }/*//*/DL_PlaneFitting dl_planefitting;dl_planefitting.cloud_ = cloud;dl_planefitting.setIterationTime(1000);dl_planefitting.setDisThreshold(2.0);dl_planefitting.setMinRate(0.05);dl_planefitting.setStopRate(0.27);dl_planefitting.ransacPlaneFitting();return a.exec();
}上述完整代码
上传了工程代码与数据集。但是这个数据集是后面重新导出的,没有很认真做预处理,所以在迭代的时候可能会失败无法迭代出结果,可以调整参数集合,多试几次。
想要拿到原始数据集的话可以看我的这篇博客
tiff转PCL
这篇介绍了如何从一张记录了点云三个维度信息的.tiff文件转为点云文件。
因为本文只是对着原理简单实现了RANSAC的平面拟合,主要是为了参考学习,当然还有很多不足之处----速度远低于官方接口,也没有对失败迭代的情况进行回溯,难以避免会有拟合失败的情况出现。
成功转成点云之后不能直接拿过来RANSAC拟合,要效仿官方接口对其进行预处理。(直通滤波、离群滤波之类的)将数据集处理成比较漂亮的时候迭代成功率会很高。
这篇关于RANSAC法拟合平面的实现的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




