异常:将程序执行中发生的不正常情况(当执行一个程序时,如果出现异常,那么异常之后的代码就不在执行。)
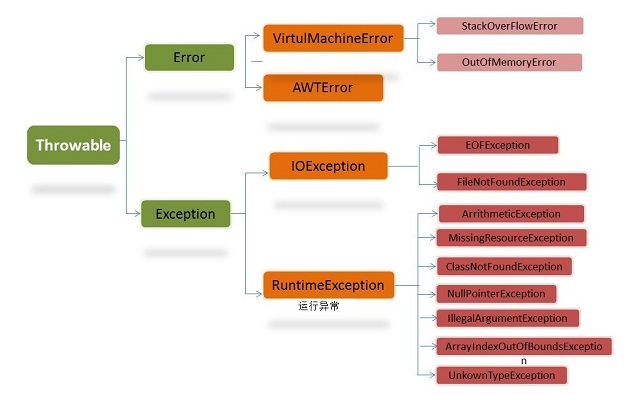
java.lang.Throwable:异常的超类
1、Error:java虚拟机无法解决的严重问题。如:JVM系统内部错误、资源耗尽等严重情况。一般无法通过编写代码处理。
2、Exception:因编码错误导致的一般性问题,可以使用针对性的代码进行处理。
① 编译异常:在编译期间会出现的异常,即在IDE环境中出现了红色的波浪线。
② 运行异常:在运行期间出现的异常。
处理异常
1、try catch finally
① 可以有多个catch语句,try中抛出的异常类对象从上往下去匹配catch中异常类型一旦满足就执行catch中的代码。
② 如果用了进到了catch处理了异常,那么后面的代码还是执行的。
③ finally不管有没有异常永远都会被执行,即使有return语句。
④ 如果在catch中又发生了异常,那么依然还会抛出异常。
笔试题一:
1 public class Main { 2 public static void methodA() { 3 try { 4 methodB(); 5 System.out.println("a1"); 6 } catch (Exception ex) { 7 System.out.println("a2"); 8 } finally { 9 System.out.println("a3"); 10 } 11 System.out.println("a4"); 12 } 13 14 public static void methodB(){ 15 try { 16 int a= 1/0; 17 System.out.println("b1"); 18 } catch (Exception ex) { 19 System.out.println("b2"); 20 } finally { 21 System.out.println("b3"); 22 } 23 System.out.println("b4"); 24 } 25 public static void main(String[] args) { 26 Main.methodA(); 27 }
输出结果:b2 b3 b4 a1 a3 a4
2、throws
try catch如果捕获到了异常,即使写了thorws,其实是不其作用的,因为catch已经处理了异常,没异常了还往外抛什么啊。
1 class Person { 2 void sleep() throws NullPointerException { 3 4 } 5 } 6 7 class Student extends Person { 8 void sleep() throws Exception { 9 10 } 11 }
编译错误,父类向子类抛出的异常的范围必须相等或越抛越小。
1 public static void A() throws ArithmeticException { 2 B(); 3 } 4 public static void B() throws Exception { 5 throw new ArithmeticException(); 6 } 7 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 8 Main.A(); 9 }
编译错误,向上抛异常的范围必须相等或越来越大。






