本文主要是介绍图神经网络 图卷积神经网络_如何使用图神经网络监控城市中的树木,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
图神经网络 图卷积神经网络
In order to aid tree health and status monitoring, we use Graph Neural Networks to geo-localize them in urban settings in an automated and efficient way.
为了帮助树木健康和状态监测,我们使用Graph神经网络以自动化和有效的方式在城市环境中对树木进行地理定位。
为什么要监视街上的树木? (Why monitor street trees?)
Cities worldwide have initiated efforts to combat the unprecedented rising temperatures and heatwaves caused by “Urban heat islands”, which is a result of covering natural land with impervious surfaces (concrete, pavements, buildings, etc.). It turns out the solution is simple, plant more trees. Trees provide shade that covers the impervious surfaces, dispersing radiation, meanwhile releasing small amounts of vapour from their leaves creating a cooling effect. Another reason to monitor tree is to enable long-term tree health studies, have a look at some of our related works here and here.
世界各地的城市已经开始努力应对由“城市热岛”引起的前所未有的温度上升和热浪,这是由于自然表面覆盖了不透水的表面(混凝土,人行道,建筑物等)。 事实证明,解决方案很简单,种植更多的树木。 树木可以遮盖不透水的表面,分散辐射,同时从叶片上释放出少量蒸气,从而起到凉爽的作用。 监视树木的另一个原因是要进行长期的树木健康研究,在这里和这里看看我们的一些相关工作。
Geo-localizing trees in urban settings manually by in-situ surveys of field crews or volunteers is a laborious task, especially in large cities, this becomes unfeasible. Fortunately using deep learning, we can “crawl” through a city’s available imagery, and perform this task at a large scale with few resources and labour.
通过对现场工作人员或志愿者进行现场调查在城市环境中手动对树木进行地理定位是一项艰巨的任务,尤其是在大城市中,这变得不可行。 幸运的是,使用深度学习,我们可以“爬行”城市的可用图像,并以很少的资源和劳动力来大规模执行此任务。
Our task is to Detect, Reidentify and Localize static objects (precisely trees) in urban settings using multiple sources, and multiple views. Most methods require sequences of images with depth, include cameras intrinsic and extrinsic values, or perform the task on multiple stages. We utilise Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) to achieve this in a flexible, and efficient manner.
我们的任务是使用多种来源和多种视图来检测,重新识别和本地化城市环境中的静态对象(精确地为树木)。 大多数方法都需要具有深度的图像序列,包括照相机的固有值和外部值,或者在多个阶段执行任务。 我们利用图神经网络(GNN)以灵活,高效的方式实现这一目标。
保持简单,不需要额外的传感器… (Keep it simple, no extra sensors needed…)
We rely only on geotagged images that are already available for general purposes, like Street View and social-media geotagged imagery. We believe that it is unnecessary to use a special rig with sensors or depth cameras and that relying on the images’ metadata and geometry to accomplish this task is sufficient.
我们仅依赖已被通用的地理标记图像,例如街景视图和社交媒体地理标记图像。 我们认为,没有必要使用带有传感器或深度相机的特殊装备,而依靠图像的元数据和几何形状来完成此任务就足够了。
几何是什么意思? (What do you mean by geometry?)
Alongside the visual features, the images come with useful metadata. This metadata usually includes the camera’s heading and geo-coordinates. Using geometry, we can assign geo-coordinates to pixels inside the image, and vice versa: finding pixels corresponding to geo-coordinates. (explained in detail in our paper)
除了视觉功能外,图像还带有有用的元数据。 该元数据通常包括相机的方向和地理坐标。 使用几何,我们可以将地理坐标分配给图像内的像素,反之亦然:找到与地理坐标对应的像素。 (在我们的论文中有详细解释)
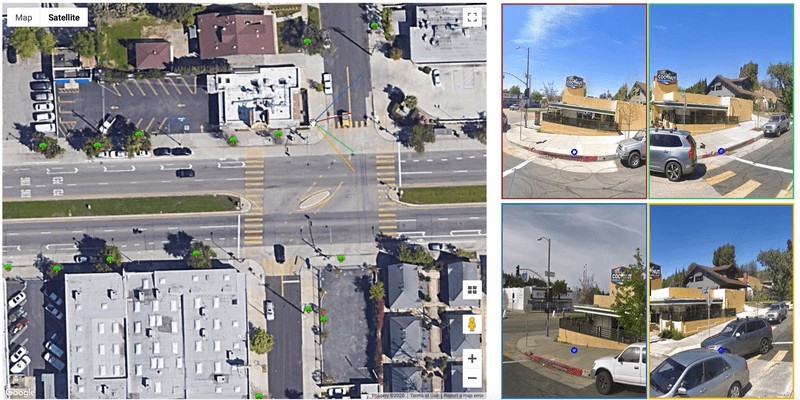

We created a web tool to demonstrate these functions in action. First, click anywhere you’d like on the street to grab the closest 4 panoramas to that spot. Then, if you proceed to move your mouse around it will grab the geo-coordinate and project in pixels inside the 4 views.These projection functions give us a rough estimate of a location, which helps us to predict which trees are corresponding to each other in multiple views, and not to count an instance of a tree more than once.
我们创建了一个Web工具来演示这些功能的实际作用。 首先,在街上任意位置单击,以获取到该地点最近的4张全景照片。 然后,如果继续移动鼠标,它将抓住地理坐标并以4个视图内的像素为单位进行投影。这些投影函数为我们提供了位置的粗略估计,这有助于我们预测哪些树木彼此对应在多个视图中,并且一次计数一个树的实例的次数不超过一次。
将场景表示为图形。 (Representing the scene as a graph.)
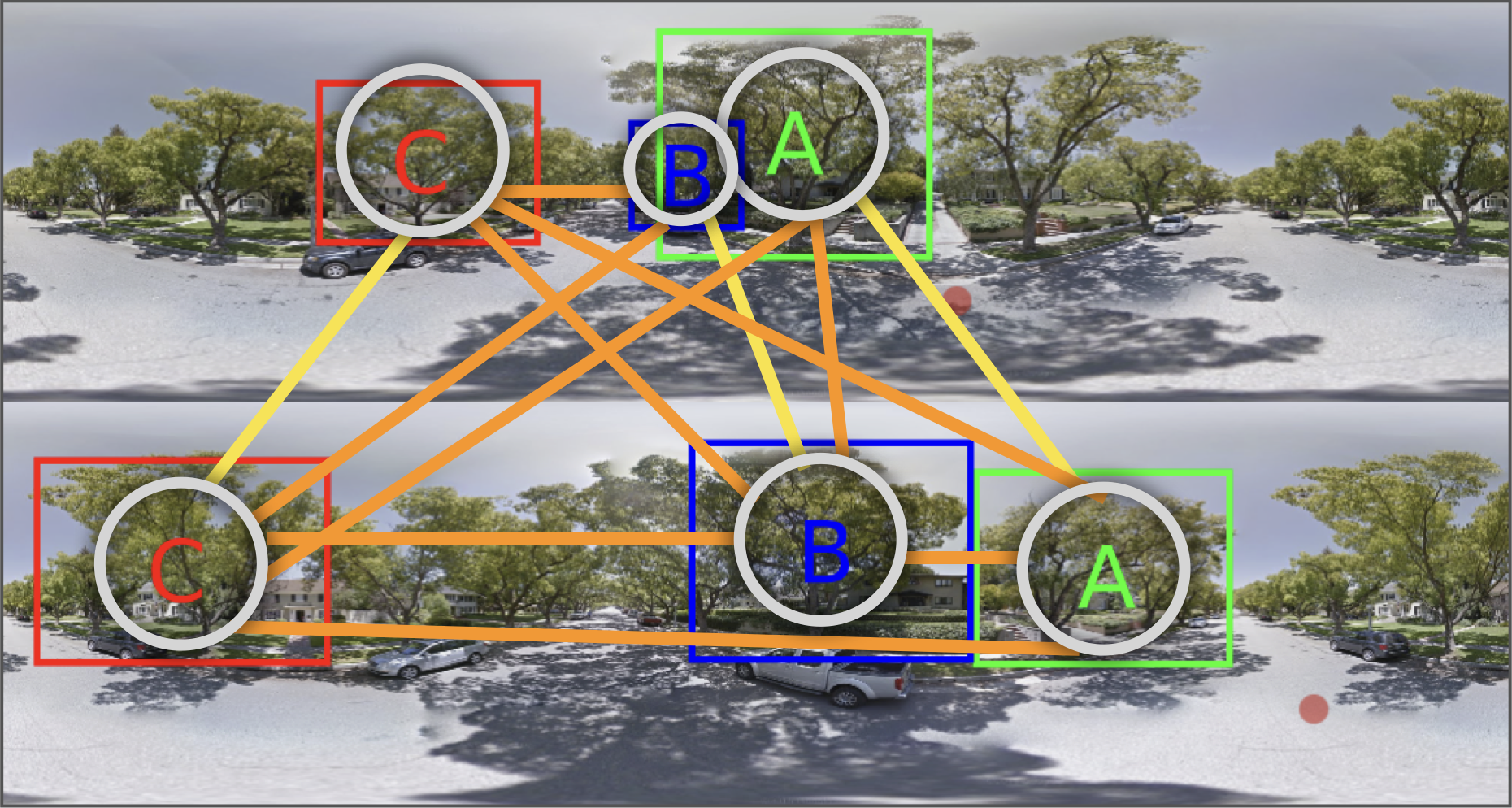
In contrast to our previous works (Wegner et al., 2016, Nassar et al., 2019) we represent our data as graphs, with the nodes representing the trees, and the edges between them depicting the correspondence between the different instances of the objects. The nodes carry the CNN features of the object, meanwhile, the edges carry the ground-truth value ([0,1]) if its a match or not. This setup gives us the flexibility to have a variable number of images and targets as input.
与我们之前的工作相反( Wegner等人,2016 , Nassar等人,2019 ),我们将数据表示为图形,节点表示树,它们之间的边缘表示对象不同实例之间的对应关系。 节点带有对象的CNN特征,同时,如果边缘匹配,则边缘带有地面真实值([0,1])。 这种设置使我们可以灵活地将可变数量的图像和目标作为输入。
This sets out our problem as a “link prediction” task, which can be solved with Graph Neural Networks (GNNs). The literature on GNN is extensive, check out here and here to understand further what GNNs are and the difference between them and CNNs.
这将我们的问题设置为“链接预测”任务,可以通过图形神经网络(GNN)解决。 有关GNN的文献非常丰富,请在这里和此处查看以进一步了解GNN是什么以及它们与CNN的区别。
端到端方法。 (An end-to-end method.)
We strive with this work to come up with an end-to-end method that isn't composed of multiple stages that have to be trained separately, and tweaked parameter wise. So we created a method that could match the correspondence of objects in the scene to avoid double counting and provide the geolocation.
我们通过这项工作努力提出一种端对端方法,该方法不包含必须单独训练的多个阶段,并且对参数进行了调整。 因此,我们创建了一种可以匹配场景中对象对应关系的方法,以避免重复计算并提供地理位置。
演示地址
Our method works by following these steps:
我们的方法通过以下步骤起作用:
- A batch of images from multiple views and the corresponding camera metadata are passed through the backbone network (EfficientNet) and the multi-scale feature aggregator (BiFPN) of the object detector that provides different levels of features. 来自多个视图的一批图像和相应的相机元数据通过骨干网(EfficientNet)和提供不同级别特征的物体检测器的多尺度特征聚合器(BiFPN)传递。
- Anchors are then generated across the feature layers and passed through two sub-networks to provide classification and bounding box predictions. Based on the IoU of the ground truth with the anchors, we select the positive and negative anchors. 然后,在特征图层上生成锚,并通过两个子网传递锚,以提供分类和边界框预测。 基于带有锚点的地面真实情况的IoU,我们选择正锚点和负锚点。
- The features of these anchors are used to generate a dense fully connected graph. 这些锚点的特征用于生成密集的全连接图。
- The graph is then fed to a GNN to predict if the nodes should be matched by classifying the edge connecting them. In parallel, the regressed bounding boxes of the positive anchors are passed to the Geo-Localization Network to regress the geo-coordinate. 然后将图形馈送到GNN,以通过对连接节点的边缘进行分类来预测是否应匹配节点。 同时,将正锚的回归边界框传递到地理定位网络以回归地理坐标。
结果如何。 (How results look like.)
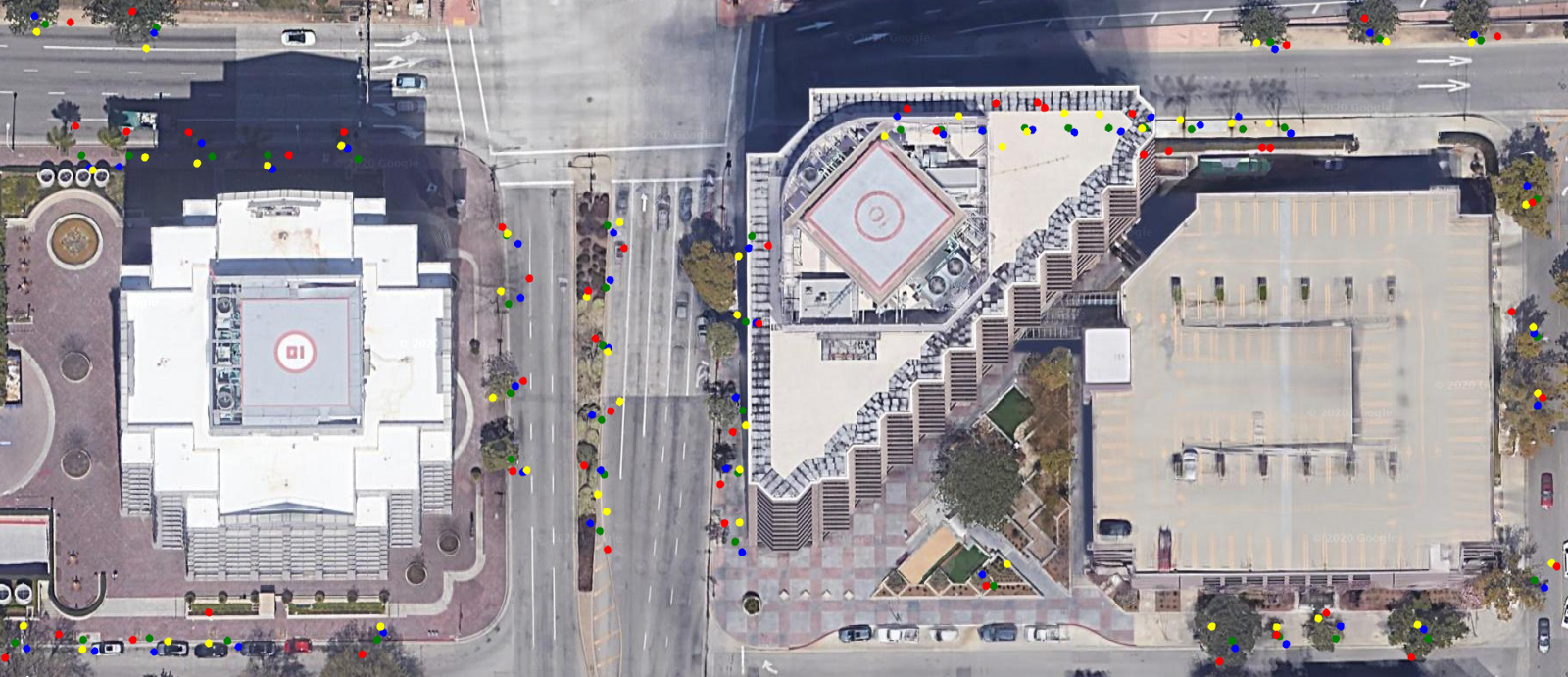
Here are some example results for the different outputs, object detection along with re-identification, and geo-location prediction.
这是不同输出,目标检测以及重新识别以及地理位置预测的一些示例结果。
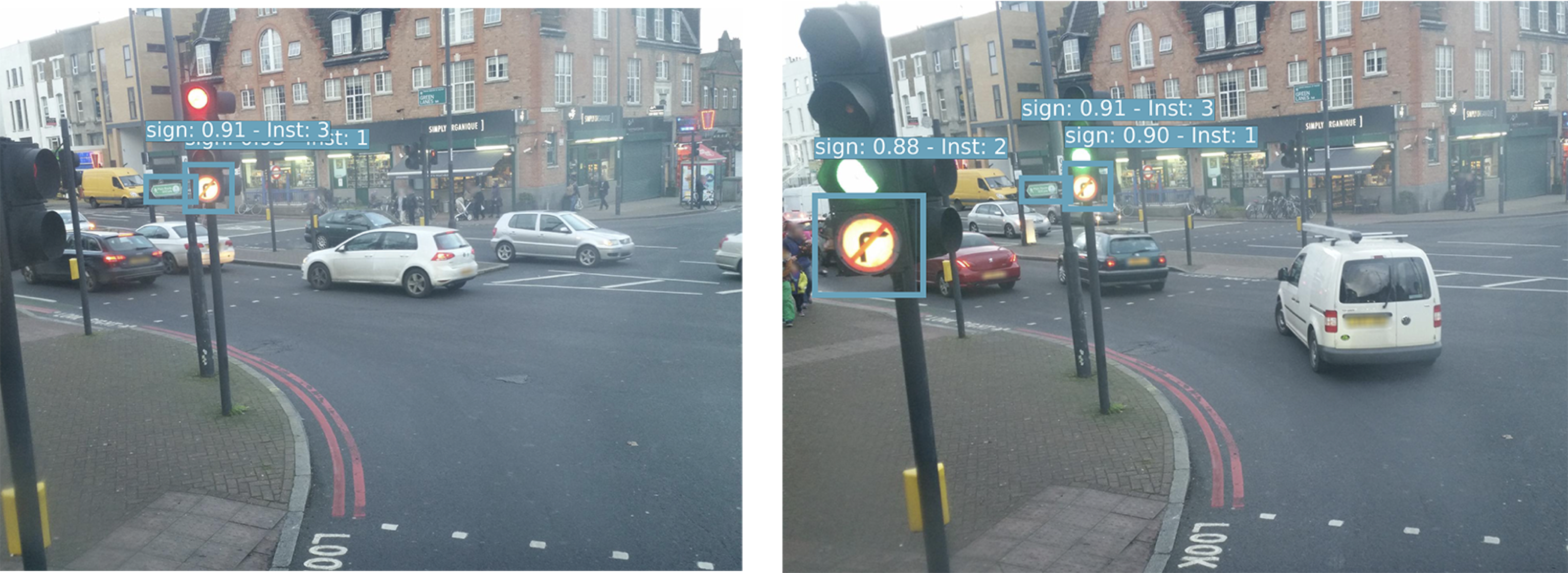
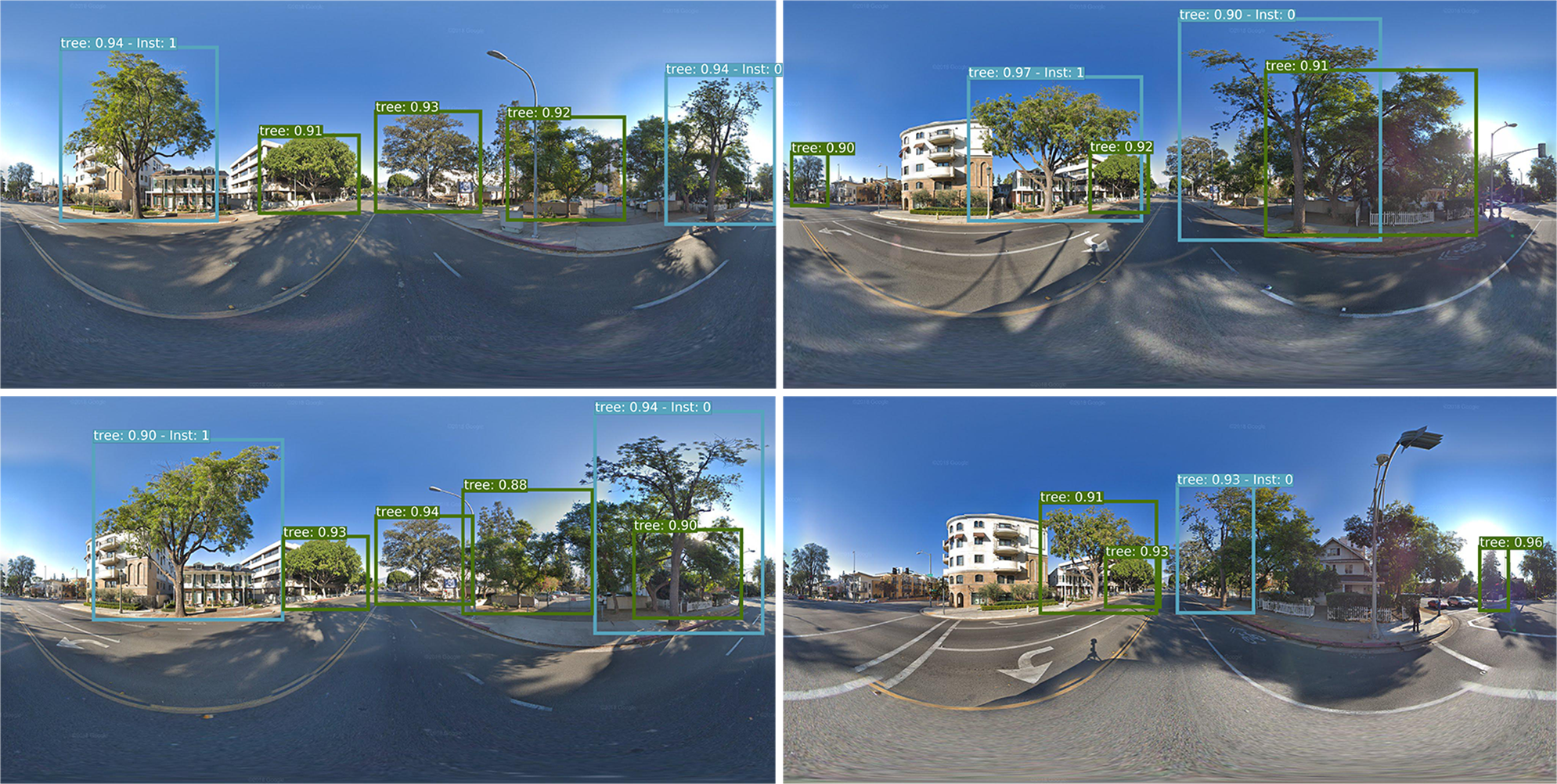


结论。 (In conclusion.)
We present an end-to-end multi-view detector that re-identifies and geo-localizes static objects. This method integrates Graph Neural Networks which add flexibility in re-identification making it possible to accommodate any number of views and still be computationally efficient. Furthermore, our approach is robust to occlusion, neighbouring objects of similar appearance, and severe changes in viewpoints. This is achieved using only RGB imagery along with its meta-data.
我们提出了一种端到端多视图检测器,它可以重新识别静态对象并对其进行地理定位。 此方法集成了Graph神经网络,该网络增加了重新标识的灵活性,从而可以容纳任意数量的视图,并且计算效率仍然很高。 此外,我们的方法对于遮挡,外观相似的相邻对象以及视点的严重变化具有鲁棒性。 仅使用RGB图像及其元数据即可实现此目的。
For the interested reader, we refer to our full research paper: here
对于感兴趣的读者,请参阅我们的完整研究论文:此处
Samy Nassar A, D’Aronco S, Lefèvre S, Wegner JD. GeoGraph: Learning graph-based multi-view object detection with geometric cues end-to-end. arXiv. 2020 Mar:arXiv-2003.
Samy Nassar A,D'Aronco S,LefèvreS,Wegner JD。 GeoGraph:学习具有端到端几何线索的基于图的多视图对象检测。 arXiv。 2020年3月:arXiv-2003。
翻译自: https://medium.com/ecovisioneth/how-to-monitor-trees-in-a-city-using-graph-neural-networks-49d09dfd3d02
图神经网络 图卷积神经网络
相关文章:
这篇关于图神经网络 图卷积神经网络_如何使用图神经网络监控城市中的树木的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!




