本文主要是介绍Towards-Realtime-MOT源代码学习之build_targets_thres()函数,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
该函数用于获取真实的置信度、目标框与id,其中目标框为投射到18*10大小特征图上的目标框
def build_targets_thres(target, anchor_wh, nA, nC, nGh, nGw):ID_THRESH = 0.5FG_THRESH = 0.5BG_THRESH = 0.4nB = len(target) # number of images in batchassert(len(anchor_wh)==nA)tbox = torch.zeros(nB, nA, nGh, nGw, 4).cuda() # batch size, anchors, grid sizetconf = torch.LongTensor(nB, nA, nGh, nGw).fill_(0).cuda()tid = torch.LongTensor(nB, nA, nGh, nGw, 1).fill_(-1).cuda() 传入进来的参数:nA=4,nC=1,nGh=10,nGw=18,anchor_wh=tensor([[ 2.6562, 7.9688],[ 3.7500, 11.2500],[ 5.3125, 13.1250],[10.6250, 10.0000]], device='cuda:0'),target=[tensor([ [0.0000e+00, 3.5300e+02, 9.1962e-02, 5.0159e-01, 5.3863e-02, 2.5566e-01],
[0.0000e+00, 3.5500e+02, 6.0608e-01, 4.6625e-01, 5.1671e-02, 2.6615e-01],
...
[0.0000e+00, 4.0100e+02, 4.5224e-02, 1.2969e-01, 4.6705e-02, 2.1583e-01],
[0.0000e+00, 4.0200e+02, 1.0326e-01, 1.0715e-01, 3.7565e-02, 1.9927e-01]],
device='cuda:0')],target为一个list,里面装的Tensor的shape为[36, 6],
nB = 1,表示batchsize
tbox.shape = torch.Size([1, 4, 10, 18, 4])
tconf.shape = torch.Size([1, 4, 10, 18])
tid.shape = torch.Size([1, 4, 10, 18, 1])
for b in range(nB):t = target[b]t_id = t[:, 1].clone().long().cuda()t = t[:,[0,2,3,4,5]]nTb = len(t) # number of targetsif nTb == 0:continue进入for循环之后
t=target[0]=tensor([[0.0000e+00, 3.5300e+02, 9.1962e-02, 5.0159e-01, 5.3863e-02, 2.5566e-01],
...
[0.0000e+00, 4.0200e+02, 1.0326e-01, 1.0715e-01, 3.7565e-02, 1.9927e-01]],
device='cuda:0')
t.shape = torch.Size([36, 6])
t_id = tensor([353, 355, 356, 357, 358, 359, 366, 367, 368, 369, 378, 379, 382, 386,
388, 394, 401, 402, 353, 355, 356, 357, 358, 359, 366, 367, 368, 369,
378, 379, 382, 386, 388, 394, 401, 402], device='cuda:0')
t = t[:,[0,2,3,4,5]]=tensor([ [0.0000, 0.0920, 0.5016, 0.0539, 0.2557],
...
[0.0000, 0.1033, 0.1072, 0.0376, 0.1993]], device='cuda:0')
nTb = 36
gxy, gwh = t[: , 1:3].clone() , t[:, 3:5].clone()
gxy[:, 0] = gxy[:, 0] * nGw
gxy[:, 1] = gxy[:, 1] * nGh
gwh[:, 0] = gwh[:, 0] * nGw
gwh[:, 1] = gwh[:, 1] * nGhgxy = t[: , 1:3].clone()=tensor([ [0.0920, 0.5016],
...,
[0.1033, 0.1072]], device='cuda:0')
gwh= t[:, 3:5].clone()=tensor([ [0.0539, 0.2557],
...,
[0.0376, 0.1993]], device='cuda:0')
gxy.shape=gwh.shape=torch.Size([36, 2]),gxy,gwh均乘上nGh和nGw之后:
gxy=tensor([ [ 1.6553, 5.0159],
...,
[ 1.8587, 1.0715]], device='cuda:0')
gwh=tensor([ [0.9695, 2.5566],
...,
[0.6762, 1.9927]], device='cuda:0')
gxy[:, 0] = torch.clamp(gxy[:, 0], min=0, max=nGw -1)
gxy[:, 1] = torch.clamp(gxy[:, 1], min=0, max=nGh -1)此时gxy=tensor([[ 1.6553, 5.0159],
...
[ 1.8587, 1.0715]], device='cuda:0')
gt_boxes = torch.cat([gxy, gwh], dim=1) # Shape Ngx4 (xc, yc, w, h)anchor_mesh = generate_anchor(nGh, nGw, anchor_wh)
anchor_list = anchor_mesh.permute(0,2,3,1).contiguous().view(-1, 4) gt_boxes=tensor([[ 1.6553, 5.0159, 0.9695, 2.5566],
...,
[ 1.8587, 1.0715, 0.6762, 1.9927]], device='cuda:0')
anchor_mesh = tensor([[[[ 0.0000, 1.0000, 2.0000, ..., 15.0000, 16.0000, 17.0000],
...,
[ 0.0000, 1.0000, 2.0000, ..., 15.0000, 16.0000, 17.0000]],
...,
[[ 7.9688, 7.9688, 7.9688, ..., 7.9688, 7.9688, 7.9688],
...,
[ 7.9688, 7.9688, 7.9688, ..., 7.9688, 7.9688, 7.9688]]],
...,
[[[ 0.0000, 1.0000, 2.0000, ..., 15.0000, 16.0000, 17.0000],
...,
[ 0.0000, 1.0000, 2.0000, ..., 15.0000, 16.0000, 17.0000]],
...,
[[10.0000, 10.0000, 10.0000, ..., 10.0000, 10.0000, 10.0000],
...,
[10.0000, 10.0000, 10.0000, ..., 10.0000, 10.0000, 10.0000]]]],
device='cuda:0')
anchor_mesh.shape= torch.Size([4, 4, 10, 18])
这里调用的generate_anchor函数如下: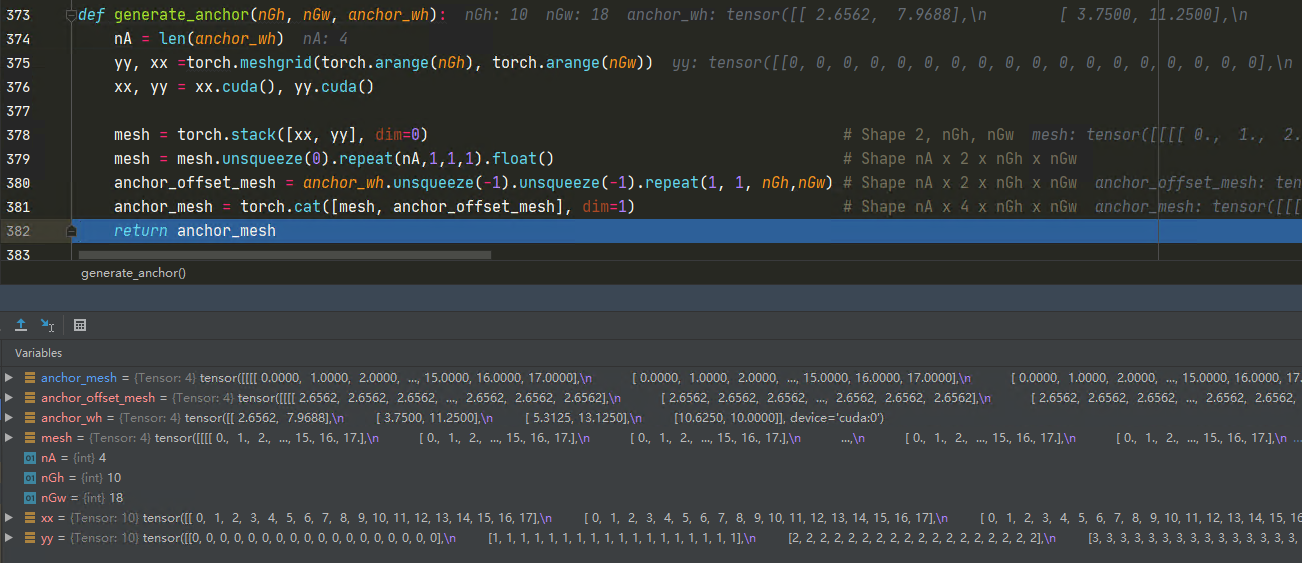
anchor_list = tensor([[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 2.6562, 7.9688],
...,
[17.0000, 9.0000, 10.6250, 10.0000]], device='cuda:0')
anchor_list.shape= torch.Size([720, 4])
iou_pdist = bbox_iou(anchor_list, gt_boxes) # Shape (nA x nGh x nGw) x Ng
iou_max, max_gt_index = torch.max(iou_pdist, dim=1) # Shape (nA x nGh x nGw), bothiou_map = iou_max.view(nA, nGh, nGw)
gt_index_map = max_gt_index.view(nA, nGh, nGw)这里调用了bbox_iou()函数计算iou,bbox_iou()函数如下:
iou_pdist = tensor([ [0.0016, 0.0000, 0.0465, ..., 0.0000, 0.0857, 0.0000],
...,
[0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, ..., 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]],device='cuda:0')
iou_pdist.shape = torch.Size([720, 36]),[720]个anchor和[36]个gt_boxes([4]表示目标框)分别求iou
iou_max.shape = 720,找出最大的720个iou值
max_gt_index.shape=720,找出最大的720个iou值对应的索引
iou_map.shape = torch.Size([4, 10, 18]),此处的view函数用于重构张量的维度
gt_index_map =torch.Size([4, 10, 18])
id_index = iou_map > ID_THRESH #将iou_map > ID_THRESH的位置置1,反之置0
fg_index = iou_map > FG_THRESH
bg_index = iou_map < BG_THRESH
ign_index = (iou_map < FG_THRESH) * (iou_map > BG_THRESH)
#这一步是把fg_index作为索引,如fg_index中的一个元素为[0,0,1],等于指定tconf中的[0,0,1]元素
tconf[b][fg_index] = 1
tconf[b][bg_index] = 0
tconf[b][ign_index] = -1id_index.shape = fg_index.shape =bg_index.shape = ign_index.shape =torch.Size([4, 10, 18])
tconf=tensor([[[[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
...,
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
...,
[[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
...,
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]]], device='cuda:0')
tconf.shape=torch.Size([1, 4, 10, 18])
gt_index = gt_index_map[fg_index]
gt_box_list = gt_boxes[gt_index]
gt_id_list = t_id[gt_index_map[id_index]]gt_index = tensor([], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.int64)
gt_box_list = tensor([], device='cuda:0', size=(0, 4)),得到符合条件的gt_boxes
gt_id_list = tensor([], device='cuda:0', dtype=torch.int64),
if torch.sum(fg_index) > 0:tid[b][id_index] = gt_id_list.unsqueeze(1)fg_anchor_list = anchor_list.view(nA, nGh, nGw, 4)[fg_index] delta_target = encode_delta(gt_box_list, fg_anchor_list)tbox[b][fg_index] = delta_target这里未进入if循环
return tconf, tbox, tid最后将真实的置信度tconf、真实的目标框tbox、真实的id即tid返回
这篇关于Towards-Realtime-MOT源代码学习之build_targets_thres()函数的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





