本文主要是介绍BloomFilter 简介及在 Hadoop reduce side join 中的应用,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
1、BloomFilter能解决什么问题?
以少量的内存空间判断一个元素是否属于这个集合, 代价是有一定的错误率
2、工作原理
1. 初始化一个数组, 所有位标为0, A={x1, x2, x3,…,xm} (x1, x2, x3,…,xm 初始为0)
2. 将已知集合S中的每一个数组, 按以下方式映射到A中
2.0 选取n个互相独立的hash函数 h1, h2, … hk
2.1 将元素通过以上hash函数得到一组索引值 h1(xi), h2(xi),…,hk(xi)
2.2 将集合A中的上述索引值标记为1(如果不同元素有重复, 则重复覆盖为1, 这是一个觅等操作)
3. 对于一个元素x, 将其根据2.0中选取的hash函数, 进行hash, 得到一组索引值 h1(x), h2(x), …,hk(x)
如果集合A中的这些索引位置上的值都是1, 表示这个元素属于集合S, 否则则不属于S
举例说明:
建立一个容量为500万的Bit Array结构(Bit Array的大小和keyword的数量决定了误判的几率),将集合中的每个keyword通过32个hash函数分别计算出32个数字,然后对这32个数字分别用500万取模,然后将Bit Array中对应的位置为1,我们将其称为特征值。简单的说就是将每个keyword对应到Bit Array中的32个位置上,见下图:
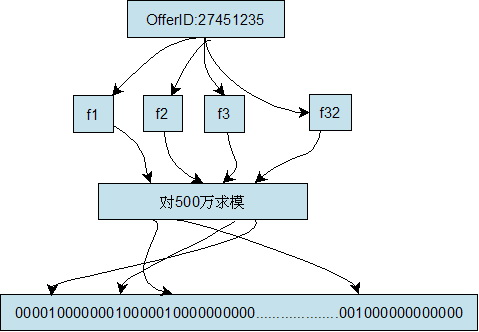
当需要快速查找某个keyword时,只要将其通过同样的32个hash函数运算,然后映射到Bit Array中的对应位,如果Bit Array中的对应位全部是1,那么说明该keyword匹配成功(会有误判的几率)。
3、几个前提
1. hash函数的计算不能性能太差, 否则得不偿失
2. 任意两个hash函数之间必须是独立的.
即任意两个hash函数不存在单一相关性, 否则hash到其中一个索引上的元素也必定会hash到另一个相关的索引上, 这样多个hash没有意义
4、错误率
工作原理的第3步, 的出来的结论, 一个是绝对靠谱的, 一个是不能100%靠谱的。在判断一个元素是否属于某个集合时,有可能会把不属于这个集合的元素误认为属于这个集合(false positive)。因此,Bloom Filter不适合那些“零错误”的应用场合。而在能容忍低错误率的应用场合下,Bloom Filter通过极少的错误换取了存储空间的极大节省。关于具体的错误率,这和最优的哈希函数个数以及位数组的大小有关,而这是可以估算求得一个最优解的:
哈希函数个数k、位数组大小m及字符串数量n之间存在相互关系。相关文献证明了对于给定的m、n,当 k = ln(2)* m/n 时出错的概率是最小的。 具体的请看:http://blog.csdn.net/jiaomeng/article/details/1495500
5、基本特征
从以上对基本原理和数学基础的分析,我们可以得到Bloom filter的如下基本特征,用于指导实际应用。
(1)存在一定错误率,发生在正向判断上(存在性),反向判断不会发生错误(不存在性);
(2)错误率是可控制的,通过改变位数组大小、hash函数个数或更低碰撞率的hash函数来调节;
(3)保持较低的错误率,位数组空位至少保持在一半以上;
(4)给定m和n,可以确定最优hash个数,即k = ln2 * (m/n),此时错误率最小;
(5)给定允许的错误率E,可以确定合适的位数组大小,即m >= log2(e) * (n * log2(1/E)),继而确定hash函数个数k;
(6)正向错误率无法完全消除,即使不对位数组大小和hash函数个数进行限制,即无法实现零错误率;
(7)空间效率高,仅保存“存在状态”,但无法存储完整信息,需要其他数据结构辅助存储;
(8)不支持元素删除操作,因为不能保证删除的安全性。
6、应用场景举例:
(1)拼写检查、数据库系统、文件系统
(2)假设要你写一个网络蜘蛛(web crawler)。由于网络间的链接错综复杂,蜘蛛在网络间爬行很可能会形成“环”。为了避免形成“环”,就需要知道蜘蛛已经访问过那些URL。给一个URL,怎样知道蜘蛛是否已经访问过呢?
(3)网络应用
P2P网络中查找资源操作,可以对每条网络通路保存Bloom Filter,当命中时,则选择该通路访问。
广播消息时,可以检测某个IP是否已发包。
检测广播消息包的环路,将Bloom Filter保存在包里,每个节点将自己添加入Bloom Filter。
信息队列管理,使用Counter Bloom Filter管理信息流量。
(4)垃圾邮件地址过滤
像网易,QQ这样的公众电子邮件(email)提供商,总是需要过滤来自发送垃圾邮件的人(spamer)的垃圾邮件。一个办法就是记录下那些发垃圾邮件的email 地址。由于那些发送者不停地在注册新的地址,全世界少说也有几十亿个发垃圾邮件的地址,将他们都存起来则需要大量的网络服务器。如果用哈希表,每存储一亿个 email 地址,就需要1.6GB 的内存(用哈希表实现的具体办法是将每一个email 地址对应成一个八字节的信息指纹,然后将这些信息指纹存入哈希表,由于哈希表的存储效率一般只有50%,因此一个email 地址需要占用十六个字节。一亿个地址大约要1.6GB, 即十六亿字节的内存)。因此存贮几十亿个邮件地址可能需要上百GB 的内存。而Bloom Filter只需要哈希表1/8 到1/4 的大小就能解决同样的问题。Bloom Filter决不会漏掉任何一个在黑名单中的可疑地址。而至于误判问题,常见的补救办法是在建立一个小的白名单,存储那些可能别误判的邮件地址。
(5)Bloomfilter在HBase中的作用
HBase利用Bloomfilter来提高随机读(Get)的性能,对于顺序读(Scan)而言,设置Bloomfilter是没有作用的(0.92以后,如果设置了bloomfilter为ROWCOL,对于指定了qualifier的Scan有一定的优化,但不是那种直接过滤文件,排除在查找范围的形式)
Bloomfilter在HBase中的开销?
Bloomfilter是一个列族(cf)级别的配置属性,如果你在表中设置了Bloomfilter,那么HBase会在生成StoreFile时包含一份bloomfilter结构的数据,称其为MetaBlock;MetaBlock与DataBlock(真实的KeyValue数据)一起由LRUBlockCache维护。所以,开启bloomfilter会有一定的存储及内存cache开销。
Bloomfilter如何提高随机读(Get)的性能?
对于某个region的随机读,HBase会遍历读memstore及storefile(按照一定的顺序),将结果合并返回给客户端。如果你设置了bloomfilter,那么在遍历读storefile时,就可以利用bloomfilter,忽略某些storefile。
注意:hbase的bloom filter是惰性加载的,在写压力比较大的情况下,会有不停的compact并产生storefile,那么新的storefile是不会马上将bloom filter加载到内存的,等到读请求来的时候才加载。
这样问题就来了,第一,如果storefile设置的比较大,max size为2G,这会导致bloom filter也比较大;第二,系统的读写压力都比较大。这样或许会经常出现单个 GET请求花费3-5秒的超时现象。
7、reduce side join + BloomFilter 在hadoop中的应用举例:
在某些情况下,SemiJoin抽取出来的小表的key集合在内存中仍然存放不下,这时候可以使用BloomFiler以节省空间。将小表中的key保存到BloomFilter中,在map阶段过滤大表,可能有一些不在小表中的记录没有过滤掉(但是在小表中的记录一定不会过滤掉),这没关系,只不过增加了少量的网络IO而已。最后再在reduce阶段做表间join即可。
这个过程其实需要先对小表的数据做BloomFilter训练,构造一个BloomFilter样本文件(二进制的),放到分布式缓存,然后在map阶段被读入用来过滤大表。而hadoop早已经支持 BloomFilter 了,我们只需调相应的API即可,ok 下面上代码了。
01 | import java.io.BufferedReader; |
02 | import java.io.IOException; |
03 | import java.io.InputStreamReader; |
04 | import java.util.zip.GZIPInputStream; |
06 | import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; |
07 | import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataOutputStream; |
08 | import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileStatus; |
09 | import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem; |
10 | import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; |
11 | import org.apache.hadoop.util.bloom.BloomFilter; |
12 | import org.apache.hadoop.util.bloom.Key; |
13 | import org.apache.hadoop.util.hash.Hash; |
15 | public class TrainingBloomfilter { |
17 | public static int getOptimalBloomFilterSize(int numRecords, |
19 | int size = (int) (-numRecords * (float) Math.log(falsePosRate) / Math |
20 | .pow(Math.log(2), 2)); |
24 | public static int getOptimalK(float numMembers, float vectorSize) { |
25 | return (int) Math.round(vectorSize / numMembers * Math.log(2)); |
28 | public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { |
30 | Path inputFile = new Path("/tmp/decli/user1.txt"); |
31 | int numMembers = Integer.parseInt("10"); |
32 | float falsePosRate = Float.parseFloat("0.01"); |
33 | Path bfFile = new Path("/tmp/decli/bloom.bin"); |
36 | int vectorSize = getOptimalBloomFilterSize(numMembers, falsePosRate); |
37 | int nbHash = getOptimalK(numMembers, vectorSize); |
40 | BloomFilter filter = new BloomFilter(vectorSize, nbHash, |
45 | System.out.println("Training Bloom filter of size " + vectorSize |
46 | + " with " + nbHash + " hash functions, " + numMembers |
47 | + " approximate number of records, and " + falsePosRate |
48 | + " false positive rate"); |
52 | FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(new Configuration()); |
53 | for (FileStatus status : fs.listStatus(inputFile)) { |
56 | if (status.getPath().getName().endsWith(".gz")) { |
57 | rdr = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader( |
58 | new GZIPInputStream(fs.open(status.getPath())))); |
60 | rdr = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fs.open(status |
64 | System.out.println("Reading " + status.getPath()); |
65 | while ((line = rdr.readLine()) != null) { |
66 | filter.add(new Key(line.getBytes())); |
73 | System.out.println("Trained Bloom filter with " + numRecords |
76 | System.out.println("Serializing Bloom filter to HDFS at " + bfFile); |
77 | FSDataOutputStream strm = fs.create(bfFile); |
83 | System.out.println("Done training Bloom filter."); |
001 | import java.io.BufferedReader; |
002 | import java.io.DataInputStream; |
003 | import java.io.FileInputStream; |
004 | import java.io.IOException; |
005 | import java.util.StringTokenizer; |
007 | import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration; |
008 | import org.apache.hadoop.filecache.DistributedCache; |
009 | import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem; |
010 | import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path; |
011 | import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable; |
012 | import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text; |
013 | import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job; |
014 | import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper; |
015 | import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat; |
016 | import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat; |
017 | import org.apache.hadoop.util.GenericOptionsParser; |
018 | import org.apache.hadoop.util.bloom.BloomFilter; |
019 | import org.apache.hadoop.util.bloom.Key; |
021 | public class BloomFilteringDriver { |
023 | public static class BloomFilteringMapper extends |
024 | Mapper<Object, Text, Text, NullWritable> { |
026 | private BloomFilter filter = new BloomFilter(); |
029 | protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, |
030 | InterruptedException { |
032 | BufferedReader in = null; |
036 | Path[] paths = DistributedCache.getLocalCacheFiles(context |
037 | .getConfiguration()); |
038 | for (Path path : paths) { |
039 | if (path.toString().contains("bloom.bin")) { |
040 | DataInputStream strm = new DataInputStream( |
041 | new FileInputStream(path.toString())); |
043 | filter.readFields(strm); |
047 | } catch (IOException e) { |
054 | } catch (IOException e) { |
061 | public void map(Object key, Text value, Context context) |
062 | throws IOException, InterruptedException { |
065 | String comment = value.toString(); |
068 | if (comment == null || comment.isEmpty()) { |
072 | StringTokenizer tokenizer = new StringTokenizer(comment); |
074 | while (tokenizer.hasMoreTokens()) { |
077 | String cleanWord = tokenizer.nextToken().replaceAll("'", "") |
078 | .replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z]", " "); |
081 | if (cleanWord.length() > 0 |
082 | && filter.membershipTest(new Key(cleanWord.getBytes()))) { |
083 | context.write(new Text(cleanWord), NullWritable.get()); |
090 | public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { |
092 | Configuration conf = new Configuration(); |
093 | String[] otherArgs = new GenericOptionsParser(conf, args) |
095 | System.out.println("================ " + otherArgs[0]); |
096 | if (otherArgs.length != 3) { |
097 | System.err.println("Usage: BloomFiltering <in> <out>"); |
101 | FileSystem.get(conf).delete(new Path(otherArgs[2]), true); |
103 | Job job = new Job(conf, "TestBloomFiltering"); |
104 | job.setJarByClass(BloomFilteringDriver.class); |
105 | job.setMapperClass(BloomFilteringMapper.class); |
106 | job.setNumReduceTasks(0); |
107 | job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class); |
108 | job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class); |
109 | FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[1])); |
110 | FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(otherArgs[2])); |
112 | DistributedCache.addCacheFile(new Path("/tmp/decli/bloom.bin").toUri(), |
113 | job.getConfiguration()); |
115 | System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1); |
测试文件:
user1.txt
test
xiaowang
xiao
wang
test
user2.txt
test xiaowang
xiao wang test
test1 2xiaowang
1xiao wa2ng atest
运行命令:
hadoop jar trainbloom.jar TrainingBloomfilter
hadoop jar bloom.jar BloomFilteringDriver /tmp/decli/user2.txt /tmp/decli/result
结果:
root@master 192.168.120.236 ~/lijun06 >
hadoop fs -cat /tmp/decli/result/p*
test
xiaowang
xiao
wang
test
root@master 192.168.120.236 ~/lijun06 >
8、关于 hadoop mapreduce join 的几种方式,请参考:
http://my.oschina.net/leejun2005/blog/95186
http://my.oschina.net/leejun2005/blog/111963
9、本文参考 or 推荐阅读:
http://www.jiacheo.org/blog/304
http://blog.csdn.net/jiaomeng/article/details/1495500
http://www.iteye.com/blogs/tag/BloomFilter
http://www.cnblogs.com/dong008259/archive/2012/01/04/2311332.html
http://blog.csdn.net/liuben/article/details/6602683
http://ourmysql.com/archives/510?f=wb
https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%B8%83%E9%9A%86%E8%BF%87%E6%BB%A4%E5%99%A8
http://www.oratea.net/?p=1248
http://zjushch.iteye.com/blog/1530143
https://github.com/adamjshook/mapreducepatterns/blob/master/MRDP/src/main/java/mrdp/appendixA/BloomFilterDriver.java
https://github.com/adamjshook/mapreducepatterns/tree/master/MRDP/src/main/java/mrdp/ch3
https://github.com/alexholmes/hadoop-book/tree/master/src/main/java/com/manning/hip/ch7/bloom
bloom filter可以看做是对bit-map的扩展,只是 bitmap 一般只用了一个hash做映射,
具体可以参考:
http://www.cnblogs.com/pangxiaodong/archive/2011/08/14/2137748.html
http://kb.cnblogs.com/page/77440/
http://hongweiyi.com/2012/03/data-structure-bitmap/
http://blog.csdn.net/hit_kongquan/article/details/6255673
这篇关于BloomFilter 简介及在 Hadoop reduce side join 中的应用的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!









