本文主要是介绍设计并实现一个ALU算数逻辑单元(哈工大计组实验一),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
目录
- 目标
- 设计
- 编码
- 模块接口设计
- Verilog代码实现
- 仿真测试
- 仿真代码
- 仿真波形图
目标
使用Verilog硬件编程语言完成一个简单的、具有执行16 种算术逻辑运算操作的电路,要求的16 种操作如下表所示:

设计
编码
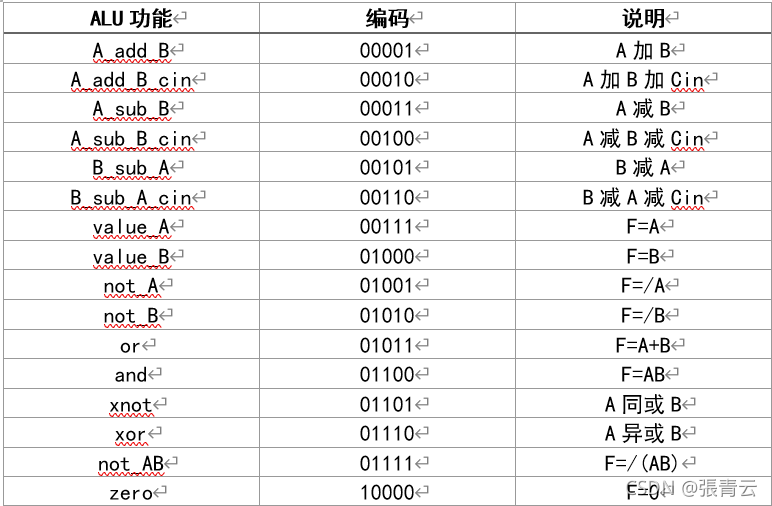
对ALU的16种运算的编码如下:
模块接口设计
信号说明如下:
• 定义四个输入信号A、B、Cin、Card。其中,A、B 为32 位运算数,Card 为5 位运算操作码,Cin 为进
位。
• 定义三个输出信号F,Cout,Zero,其中F 为运算结果,Cout 为结果进位,Zero 为零标志。
Verilog代码实现
`define T_A_add_B 5'b00001
`define T_A_add_B_cin 5'b00010
`define T_A_sub_B 5'b00011
`define T_A_sub_B_cin 5'b00100
`define T_B_sub_A 5'b00101
`define T_B_sub_A_cin 5'b00110
`define T_value_A 5'b00111
`define T_value_B 5'b01000
`define T_not_A 5'b01001
`define T_not_B 5'b01010
`define T_or 5'b01011
`define T_and 5'b01100
`define T_xnot 5'b01101
`define T_xor 5'b01110
`define T_not_AB 5'b01111
`define T_zero 5'b10000
module alu(input [31:0] A , // 操作数input [31:0] B , // 操作数input Cin , // 进位input [4 :0] Card, // 控制output [31:0] F , // 结果output Cout, // 进位output Zero // 零标识位
);// 保存运算结果wire [31:0] A_add_B_result;wire [31:0] A_add_B_cin_result;wire [31:0] A_sub_B_result;wire [31:0] A_sub_B_cin_result;wire [31:0] B_sub_A_result;wire [31:0] B_sub_A_cin_result;wire [31:0] value_A_result;wire [31:0] value_B_result;wire [31:0] not_A_result;wire [31:0] not_B_result; wire [31:0] or_result;wire [31:0] and_result; wire [31:0] xnot_result;wire [31:0] xor_result;wire [31:0] not_AB_result;wire [31:0] zero_result;// 进位wire [1:0] Cout_a;wire [1:0] Cout_b;wire [1:0] Cout_c;wire [1:0] Cout_d;wire [1:0] Cout_e;wire [1:0] Cout_f;// 如果是运算后立即赋值,而被赋值变量较宽,则按被赋值的变量宽度计算assign {Cout_a, A_add_B_result} = A + B;assign {Cout_b, A_add_B_cin_result} = A + B + Cin;assign {Cout_c, A_sub_B_result} = A - B;assign {Cout_d, A_sub_B_cin_result} = A - B - Cin;assign {Cout_e, B_sub_A_result} = B - A;assign {Cout_f, B_sub_A_cin_result} = B - A - Cin;assign value_A_result = A;assign value_B_result = B;assign not_A_result = ~A;assign not_B_result = ~B;assign or_result = A | B;assign and_result = A & B;assign xnot_result = ~(A ^ B);assign xor_result = A ^ B;assign not_AB_result = ~(A & B);assign zero_result = 0;// 计算结果:通过Card值的不同,在多个计算结果中选择一个赋值给Fassign F = ({32{Card == `T_A_add_B}} & A_add_B_result) |({32{Card == `T_A_add_B_cin}} & A_add_B_cin_result) | ({32{Card == `T_A_sub_B}} & A_sub_B_result) | ({32{Card == `T_A_sub_B_cin}} & A_sub_B_cin_result) | ({32{Card == `T_B_sub_A}} & B_sub_A_result) | ({32{Card == `T_B_sub_A_cin}} & B_sub_A_cin_result) | ({32{Card == `T_value_A}} & value_A_result) | ({32{Card == `T_value_B}} & value_B_result) | ({32{Card == `T_not_A}} & not_A_result) | ({32{Card == `T_not_B}} & not_B_result) | ({32{Card == `T_or}} & or_result) | ({32{Card == `T_and}} & and_result) | ({32{Card == `T_xnot}} & xnot_result) | ({32{Card == `T_xor}} & xor_result) | ({32{Card == `T_not_AB}} & not_AB_result) | ({32{Card == `T_zero}} & zero_result);// 判断是否产生进位assign Cout = (Card == `T_A_add_B && Cout_a != 0)|(Card == `T_A_add_B_cin && Cout_b != 0) |(Card == `T_A_sub_B && Cout_c != 0) |(Card == `T_A_sub_B_cin && Cout_d != 0) |(Card == `T_B_sub_A && Cout_e != 0) |(Card == `T_B_sub_A_cin && Cout_f != 0);// 判断结果是否位0assign Zero = F == 0;endmodule仿真测试
这里我们将A固定为{1’b1, 31’b11},B固定为{1’b1, 31’b101},通过改变Card的值来观察执行不同操作时的输出。
仿真代码
module alu_tb;// Inputsreg [31:0] A;reg [31:0] B;reg Cin;reg [4:0] Card;// Outputswire [31:0] F;wire Cout;wire Zero;// Instantiate the Unit Under Test (UUT)alu uut (.A(A), .B(B), .Cin(Cin), .Card(Card), .F(F), .Cout(Cout), .Zero(Zero));initial begin// Initialize InputsA = {1'b1, 31'b11};B = {1'b1, 31'b101};Cin = 1;Card = 5'b00001;// Wait 100 ns for global reset to finish#100;// Add stimulus hereendalways #10 Card = (Card + 1) % 16 == 0 ? 16 : (Card + 1) % 16;endmodule
仿真波形图
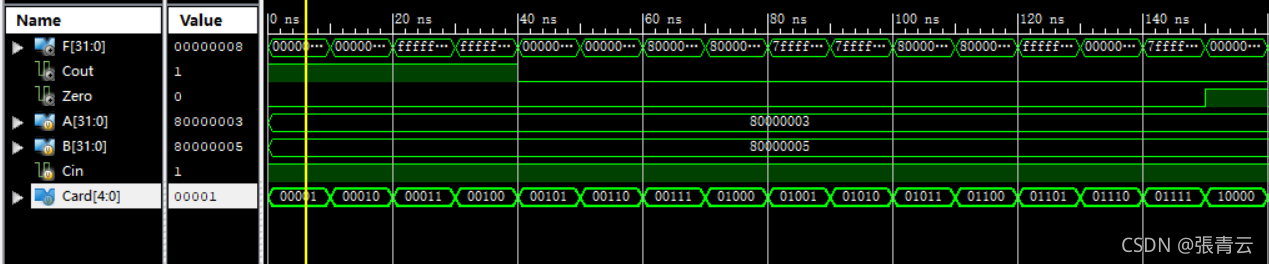
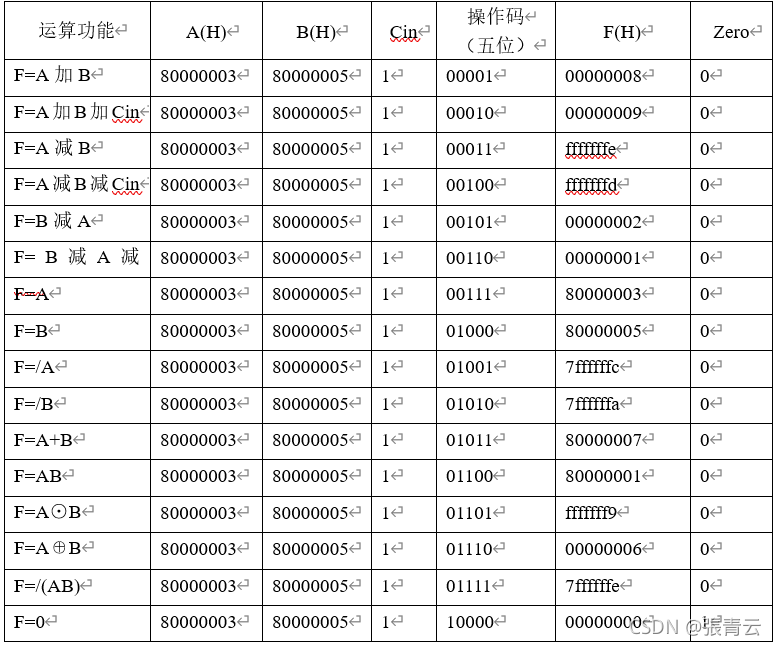
结果如下:
这篇关于设计并实现一个ALU算数逻辑单元(哈工大计组实验一)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!






