本文主要是介绍损失函数:DIOU loss手写实现,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
下面是纯diou代码
'''计算两个box的中心点距离d'''# d = math.sqrt((x2 - x1) ** 2 + (y2 - y1) ** 2)d = math.sqrt((pred[:, -1] - target[:, -1]) ** 2 + (pred[:, -2] - target[:, -2]) ** 2)# 左边xpred_l = pred[:, -1] - pred[:, -1] / 2target_l = target[:, -1] - target[:, -1] / 2# 上边ypred_t = pred[:, -2] - pred[:, -2] / 2target_t = target[:, -2] - target[:, -2] / 2# 右边xpred_r = pred[:, -1] + pred[:, -1] / 2target_r = target[:, -1] + target[:, -1] / 2# 下边ypred_b = pred[:, -2] + pred[:, -2] / 2target_b = target[:, -2] + target[:, -2] / 2'''计算两个box的bound的对角线距离'''bound_l = torch.min(pred_l, target_l) # leftbound_r = torch.max(pred_r, target_r) # rightbound_t = torch.min(pred_t, target_t) # topbound_b = torch.max(pred_b, target_b) # bottomc = math.sqrt((bound_r - bound_l) ** 2 + (bound_b - bound_t) ** 2)dloss = iou - (d ** 2) / (c ** 2)loss = 1 - dloss.clamp(min=-1.0, max=1.0)
第一步 计算两个box的中心点距离d
首先要知道pred和target的输出结果是什么
pred[:,:2]第一个:表示多个图片,第二个:2表示前两个数值,代表矩形框中心点(Y,X)
pred[:,2:]第一个:表示多个图片,第二个2:表示后两个数值,代表矩形框长宽(H,W)
target[:,:2]同理,
d =
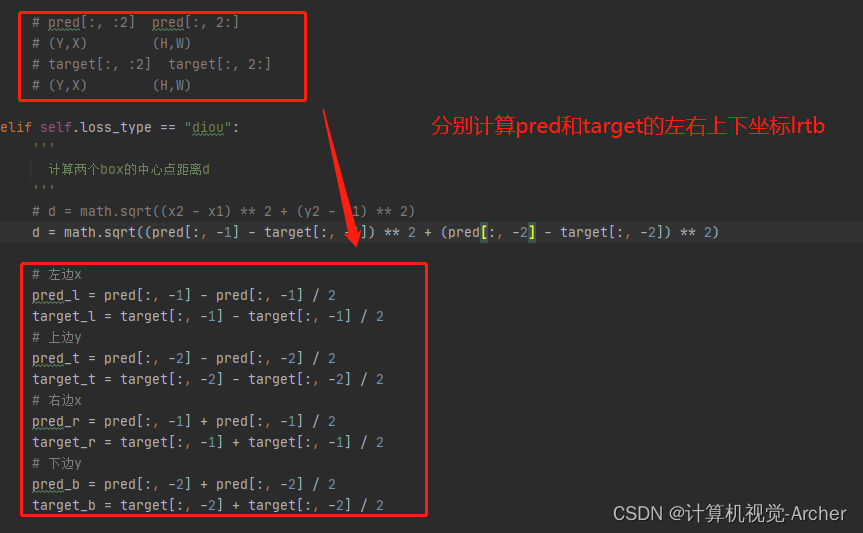
根据上面的分析来计算左右上下坐标lrtb
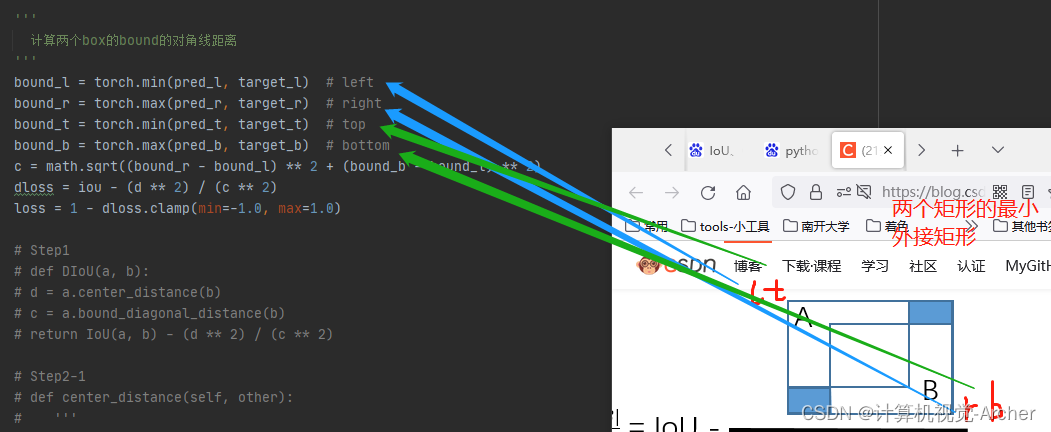
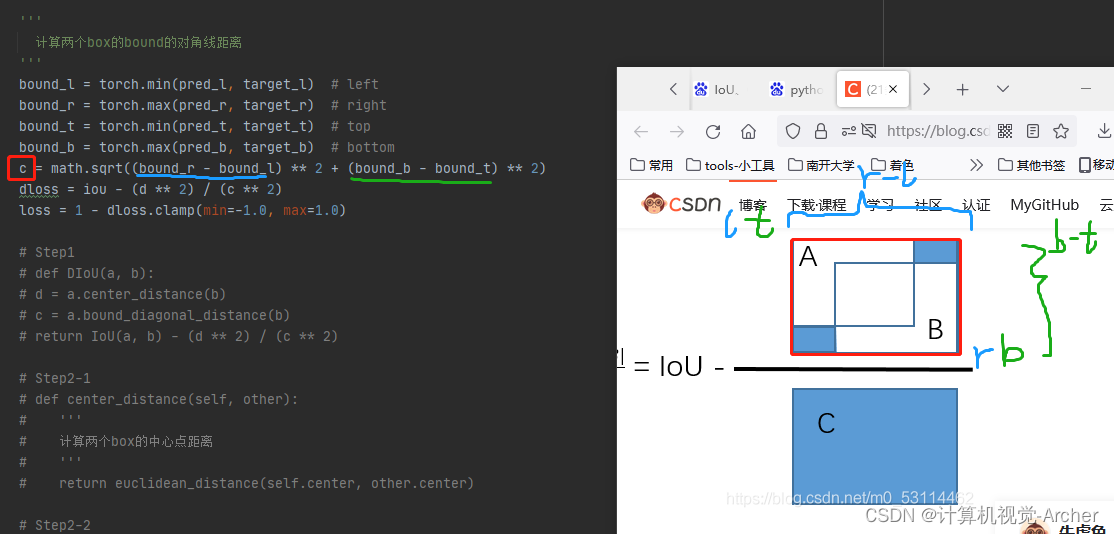
然后计算内部2个矩形的最小外接矩形的对角线长度c
d是两个预测矩形中心点的距离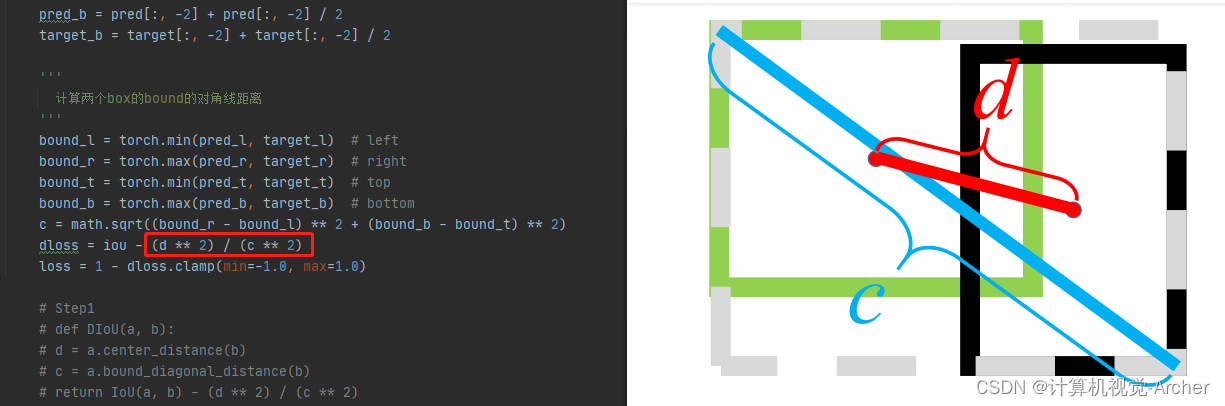
下面接受各种极端情况
A 两个框中心对齐时候,d/c=0,iou可能0-1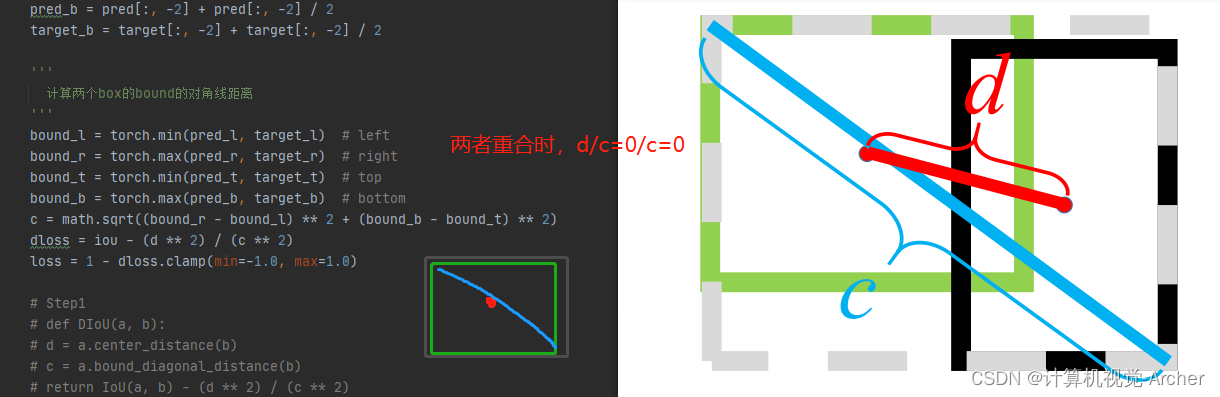
A 两个框相距很远时,d/c=1,iou=0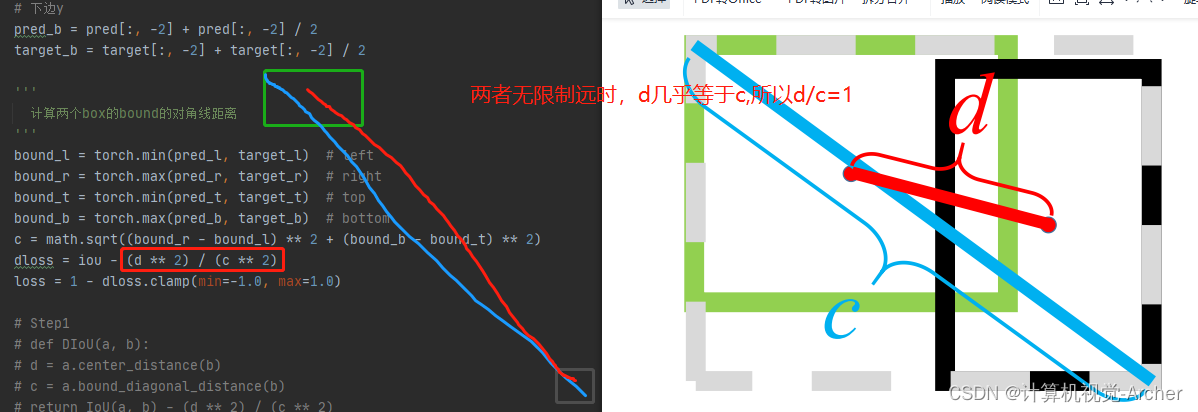
所以d/c属于0-1
dloss=iou-d/c属于-1到1
因此设置loss=1-dloss属于0-2
展示iou\giou\diou代码,这是YOLOX自带的损失函数,其中dloss是我自己写的
YOLOX是下载自
GitHub - Megvii-BaseDetection/YOLOX: YOLOX is a high-performance anchor-free YOLO, exceeding yolov3~v5 with MegEngine, ONNX, TensorRT, ncnn, and OpenVINO supported. Documentation: https://yolox.readthedocs.io/YOLOX is a high-performance anchor-free YOLO, exceeding yolov3~v5 with MegEngine, ONNX, TensorRT, ncnn, and OpenVINO supported. Documentation: https://yolox.readthedocs.io/ - GitHub - Megvii-BaseDetection/YOLOX: YOLOX is a high-performance anchor-free YOLO, exceeding yolov3~v5 with MegEngine, ONNX, TensorRT, ncnn, and OpenVINO supported. Documentation: https://yolox.readthedocs.io/![]() https://github.com/Megvii-BaseDetection/YOLOX
https://github.com/Megvii-BaseDetection/YOLOX
class IOUloss(nn.Module):def __init__(self, reduction="none", loss_type="iou"):super(IOUloss, self).__init__()self.reduction = reductionself.loss_type = loss_typedef forward(self, pred, target):assert pred.shape[0] == target.shape[0]pred = pred.view(-1, 4)target = target.view(-1, 4)tl = torch.max((pred[:, :2] - pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] - target[:, 2:] / 2))# pred target都是[H,W,Y,X]# (Y,X)-(H,W) 左上角br = torch.min((pred[:, :2] + pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] + target[:, 2:] / 2))# (X,Y)+(H,W) 右下角area_p = torch.prod(pred[:, 2:], 1) # HxWarea_g = torch.prod(target[:, 2:], 1)en = (tl < br).type(tl.type()).prod(dim=1)area_i = torch.prod(br - tl, 1) * enarea_u = area_p + area_g - area_iiou = (area_i) / (area_u + 1e-16)if self.loss_type == "iou":loss = 1 - iou ** 2elif self.loss_type == "giou":c_tl = torch.min((pred[:, :2] - pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] - target[:, 2:] / 2))c_br = torch.max((pred[:, :2] + pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] + target[:, 2:] / 2))area_c = torch.prod(c_br - c_tl, 1)giou = iou - (area_c - area_u) / area_c.clamp(1e-16)loss = 1 - giou.clamp(min=-1.0, max=1.0)# pred[:, :2] pred[:, 2:]# (Y,X) (H,W)# target[:, :2] target[:, 2:]# (Y,X) (H,W)elif self.loss_type == "diou":'''计算两个box的中心点距离d'''# d = math.sqrt((x2 - x1) ** 2 + (y2 - y1) ** 2)d = math.sqrt((pred[:, -1] - target[:, -1]) ** 2 + (pred[:, -2] - target[:, -2]) ** 2)# 左边xpred_l = pred[:, -1] - pred[:, -1] / 2target_l = target[:, -1] - target[:, -1] / 2# 上边ypred_t = pred[:, -2] - pred[:, -2] / 2target_t = target[:, -2] - target[:, -2] / 2# 右边xpred_r = pred[:, -1] + pred[:, -1] / 2target_r = target[:, -1] + target[:, -1] / 2# 下边ypred_b = pred[:, -2] + pred[:, -2] / 2target_b = target[:, -2] + target[:, -2] / 2'''计算两个box的bound的对角线距离'''bound_l = torch.min(pred_l, target_l) # leftbound_r = torch.max(pred_r, target_r) # rightbound_t = torch.min(pred_t, target_t) # topbound_b = torch.max(pred_b, target_b) # bottomc = math.sqrt((bound_r - bound_l) ** 2 + (bound_b - bound_t) ** 2)dloss = iou - (d ** 2) / (c ** 2)loss = 1 - dloss.clamp(min=-1.0, max=1.0)# Step1# def DIoU(a, b):# d = a.center_distance(b)# c = a.bound_diagonal_distance(b)# return IoU(a, b) - (d ** 2) / (c ** 2)# Step2-1# def center_distance(self, other):# '''# 计算两个box的中心点距离# '''# return euclidean_distance(self.center, other.center)# Step2-2# def euclidean_distance(p1, p2):# '''# 计算两个点的欧式距离# '''# x1, y1 = p1# x2, y2 = p2# return math.sqrt((x2 - x1) ** 2 + (y2 - y1) ** 2)# Step3# def bound_diagonal_distance(self, other):# '''# 计算两个box的bound的对角线距离# '''# bound = self.boundof(other)# return euclidean_distance((bound.x, bound.y), (bound.r, bound.b))# Step3-2# def boundof(self, other):# '''# 计算box和other的边缘外包框,使得2个box都在框内的最小矩形# '''# xmin = min(self.x, other.x)# ymin = min(self.y, other.y)# xmax = max(self.r, other.r)# ymax = max(self.b, other.b)# return BBox(xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax)# Step3-3# def euclidean_distance(p1, p2):# '''# 计算两个点的欧式距离# '''# x1, y1 = p1# x2, y2 = p2# return math.sqrt((x2 - x1) ** 2 + (y2 - y1) ** 2)if self.reduction == "mean":loss = loss.mean()elif self.reduction == "sum":loss = loss.sum()return lossGitHub - Megvii-BaseDetection/YOLOX: YOLOX is a high-performance anchor-free YOLO, exceeding yolov3~v5 with MegEngine, ONNX, TensorRT, ncnn, and OpenVINO supported. Documentation: https://yolox.readthedocs.io/
这篇关于损失函数:DIOU loss手写实现的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!





