本文主要是介绍AXI-Stream协议详解(3)—— AXI4-Stream IP核原理分析,希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
一、前言
在之前的文章中,我们介绍了AXI-S协议的一些基础知识,这是我们进行本文学习的前置基础,因此建议在开始本文章的学习前,完整阅读以下两篇文章:
AXI-Stream协议详解(1)—— Introduction![]() https://blog.csdn.net/apple_53311083/article/details/134058532?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501AXI-Stream协议详解(2)—— Interface Signals
https://blog.csdn.net/apple_53311083/article/details/134058532?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501AXI-Stream协议详解(2)—— Interface Signals![]() https://blog.csdn.net/apple_53311083/article/details/134065597?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
https://blog.csdn.net/apple_53311083/article/details/134065597?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
二、带AXI-Stream接口的IP核
1、IP核创建
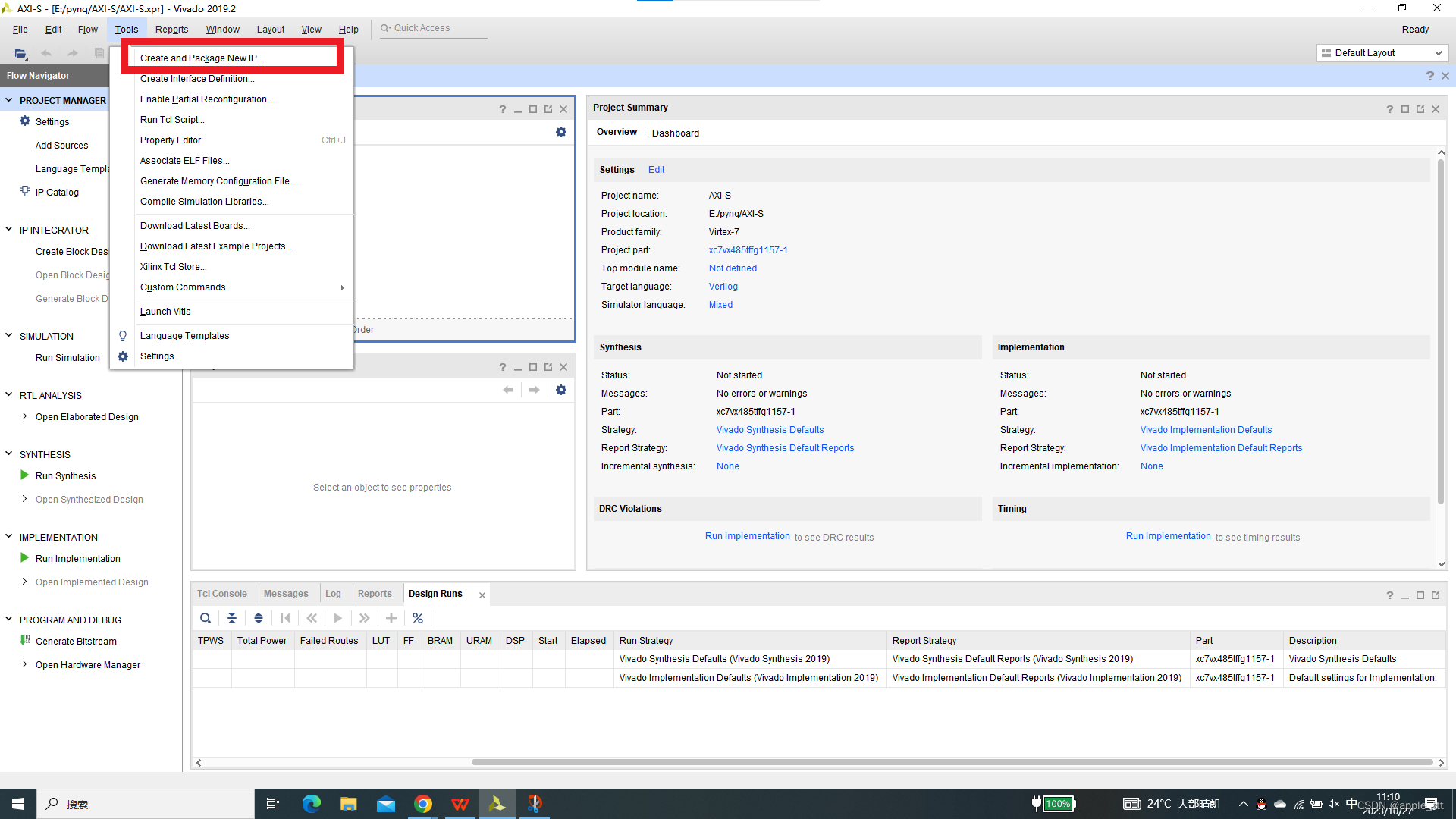
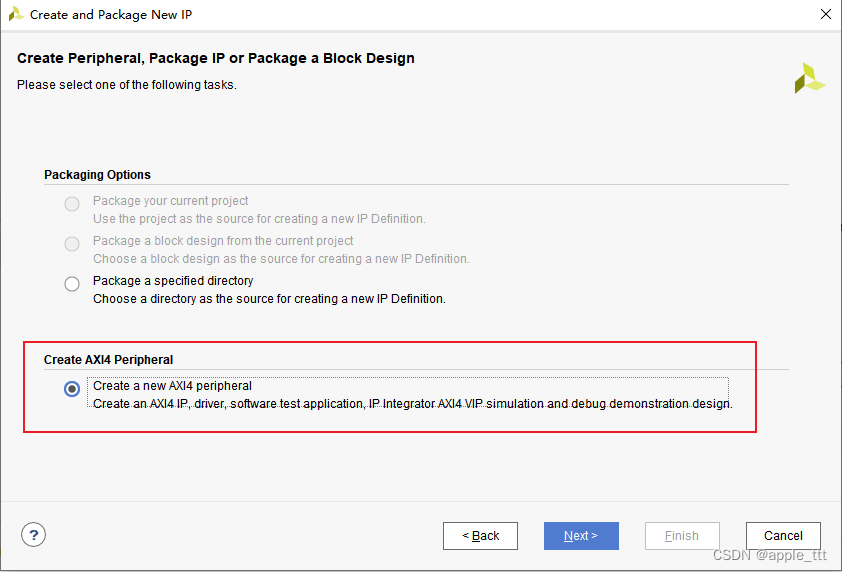
在这里我们选择最底下的一项,创建一个带有AXI接口的IP核
接下来我们设置IP核的一些细节信息,这里把名称改成了axis_m,代表这是AXI-Stream协议的主机。
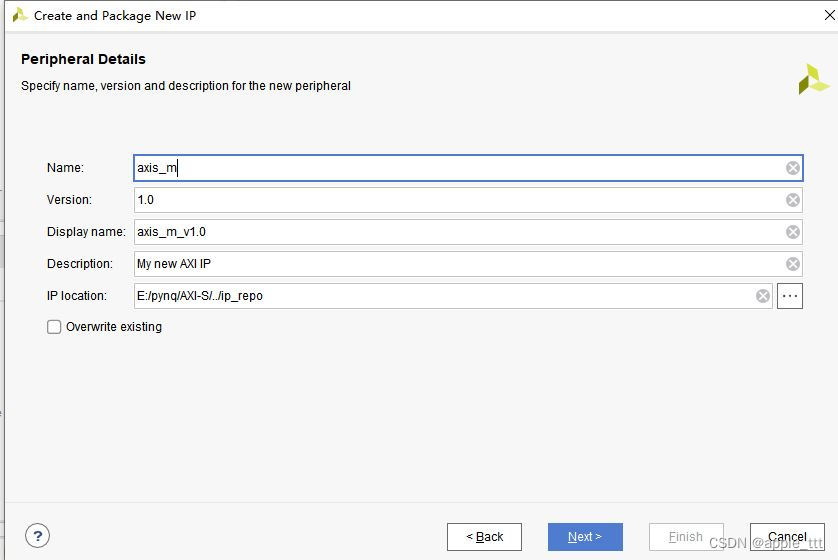
选择stream协议,选择主机类型,相应地完成名称更改,这里的数据位宽我们暂时不做更改,保持默认的32bit就行。
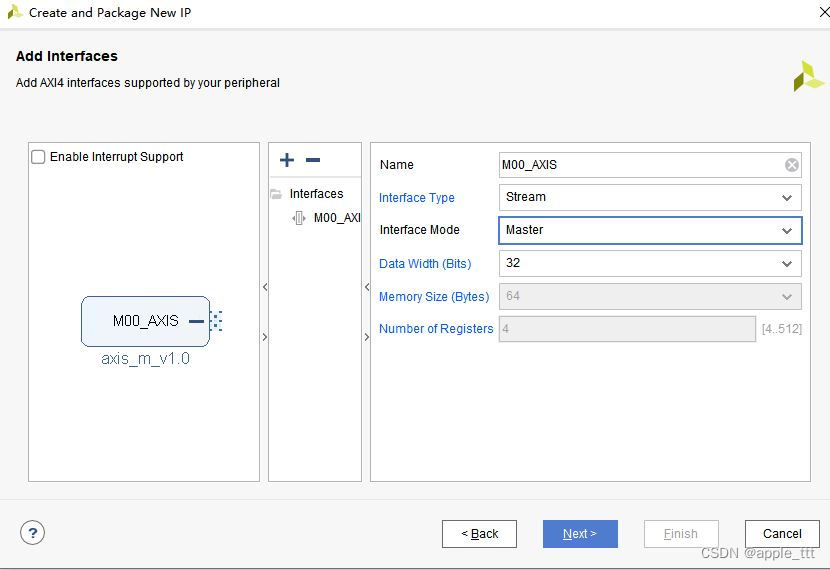
最后这里直接添加到IP库里就完成了。
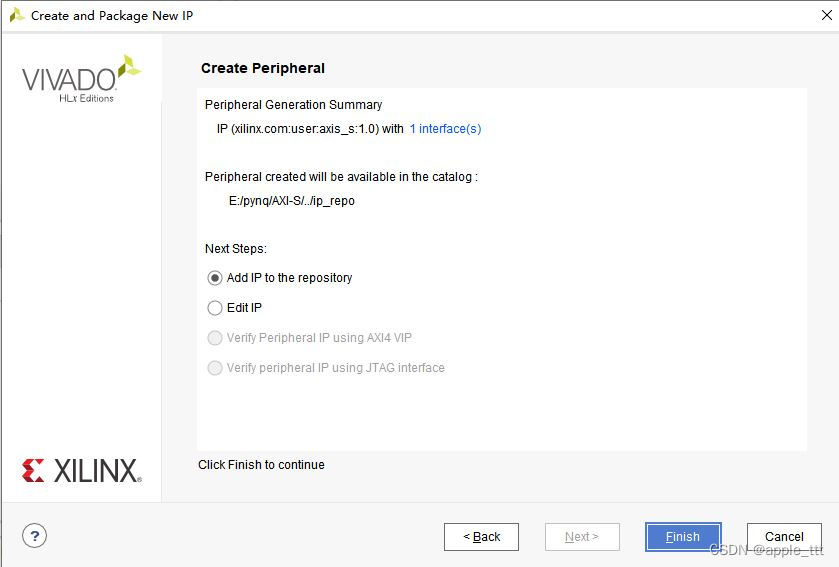
然后我们通过同样的方式可以完成axi_s(带有AXI-S接口的从机)的创建,这里就省略创建过程了。
2、IP核学习
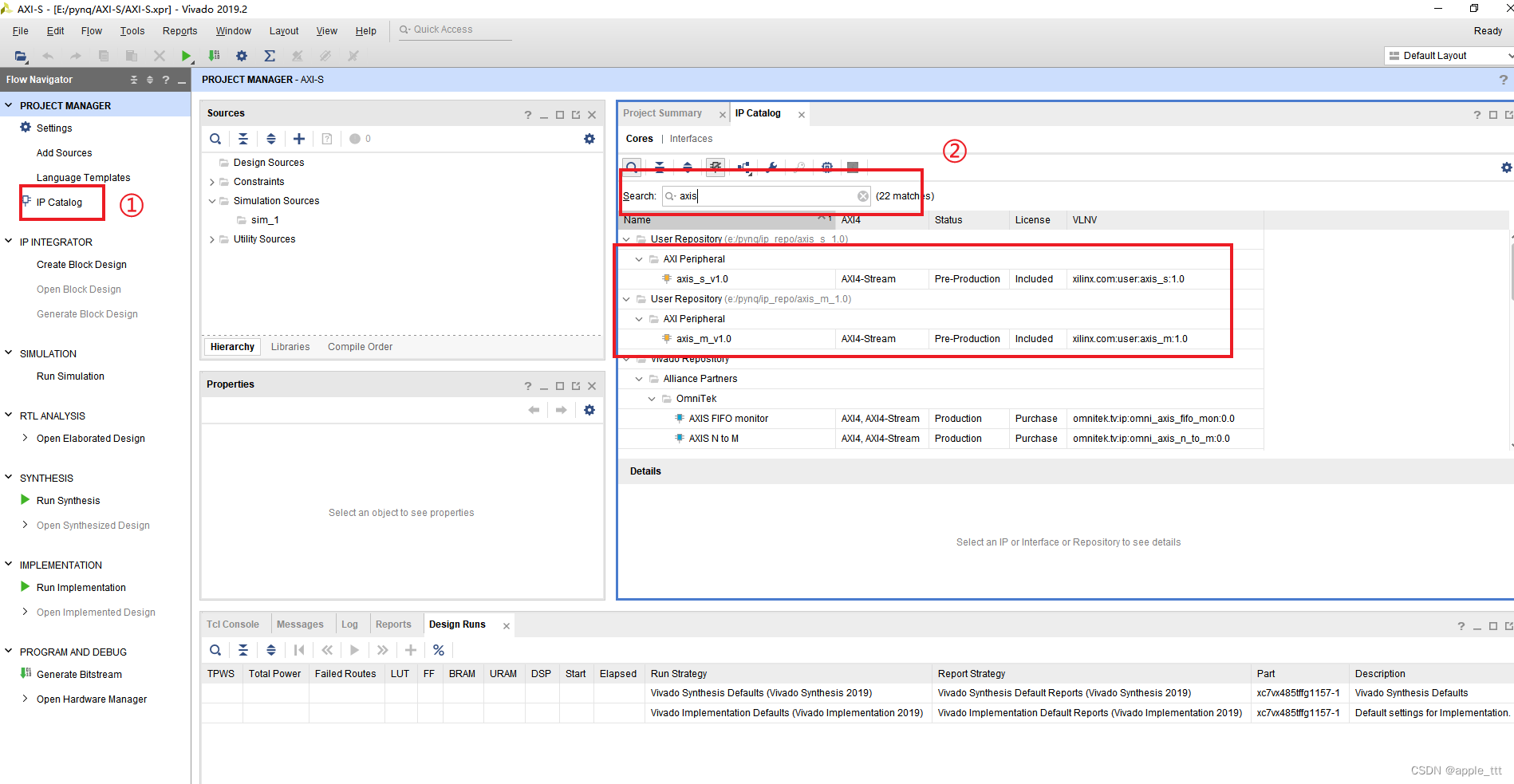
在IP Catlog下搜索找到我们之前创建的2个带有AXI-Stream协议的IP核
右击选择Edit in packager
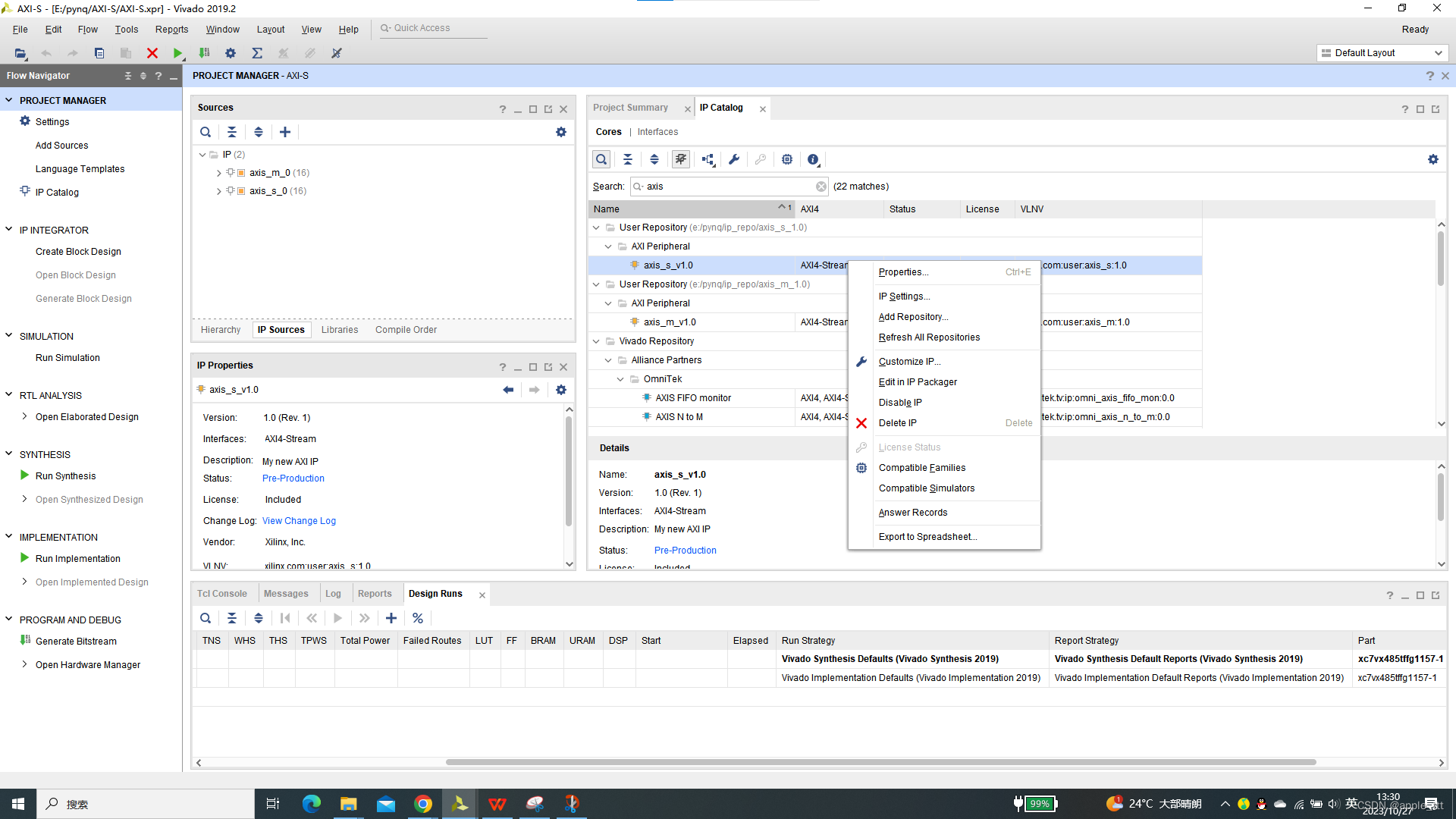
我们先以从机为例,显示如何找到AXI-S的设计部分,直接点击OK直到打开一个新的vivado界面
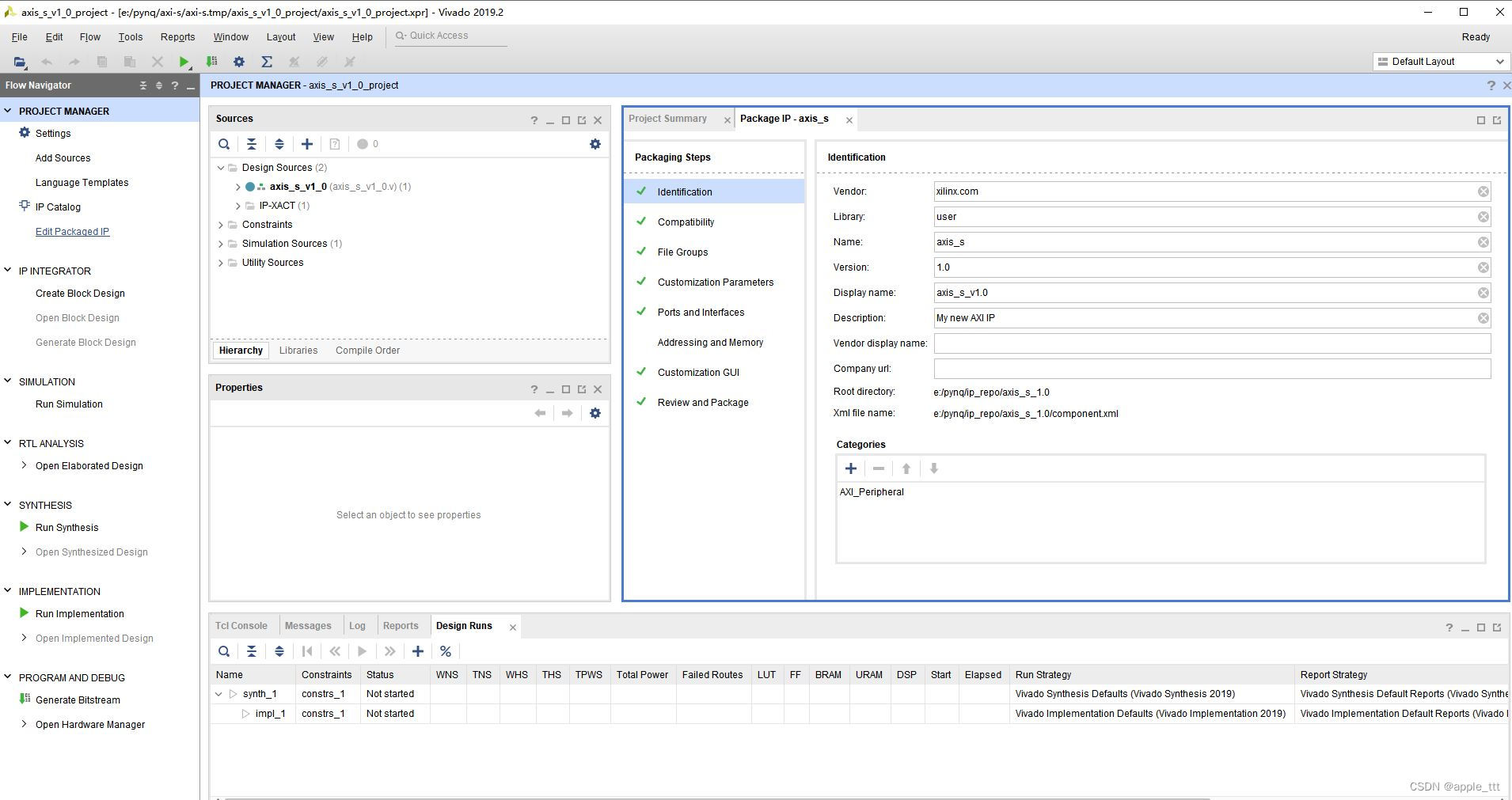
可以看到里面有两个模块
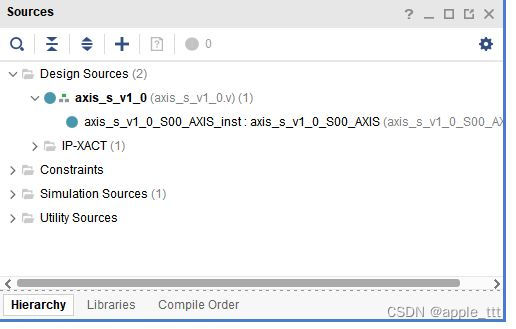
我们依次打开两个文件,同时可以把axis_m IP核中的文件同时打开,方便我们进行学习,打开过程同上,这里不做重复。
对于axis_s_v1_0和axis_m_v1_0这两个模块来说,只是完成了对底层模块的一个例化,所以没有什么可以过多赘述的。
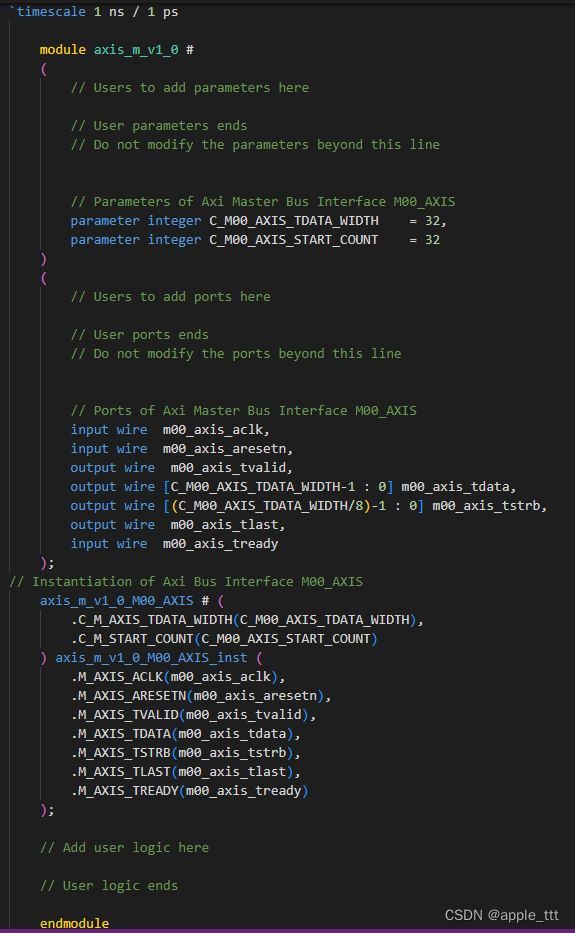
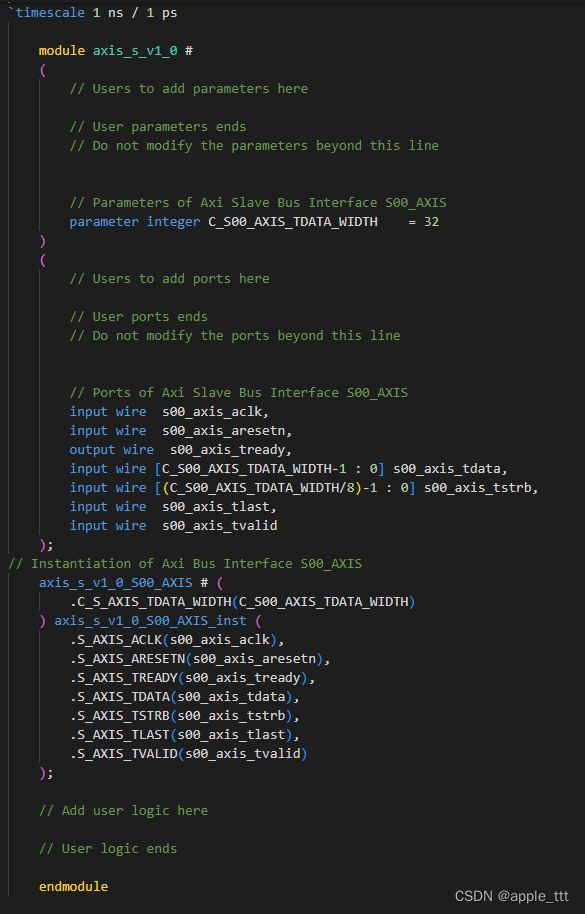
下面我们着重介绍axis_s_v1_0_S00_AXIS和axis_m_v1_0_M00_AXIS两个模块
三、AXI-Stream源代码学习
其实Xilinx官方已经给出了非常详细的英文注释,可以帮助我们快速了解整个AXI-S协议的实现方式,写的真的非常好。这里也只是在其基础上做一个简单的翻译和补充,首先给出笔者中文注释版本,再给出官方的注释版本,推荐阅读后者。
1、AXIS主机部分
1.1 中文注释
`timescale 1 ns / 1 psmodule axis_m_v1_0_M00_AXIS #(/*用户可以在此自定义参数*/parameter integer C_M_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH = 32, // 发送数据的位宽// 初始化的最大计数时钟(等待系统稳定的时间)parameter integer C_M_START_COUNT = 32)(/*用户可以在此自定义端口*///全局信号input wire M_AXIS_ACLK, // 时钟信号input wire M_AXIS_ARESETN, // 复位信号(低电平有效)output wire M_AXIS_TVALID, //有效信号,代表主机已经准备好了output wire [C_M_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXIS_TDATA, //数据信号output wire [(C_M_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH/8)-1 : 0] M_AXIS_TSTRB, //数据修饰符,辨别字节类型 output wire M_AXIS_TLAST, //last信号,拉高代表是传输中的最后一个字节input wire M_AXIS_TREADY //ready信号,代表从机准备好了);localparam NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS = 8; //发送数据的个数 //函数:以2为低求对数,用于计算位宽function integer clogb2 (input integer bit_depth); begin for(clogb2=0; bit_depth>0; clogb2=clogb2+1) bit_depth = bit_depth >> 1; end endfunction localparam integer WAIT_COUNT_BITS = clogb2(C_M_START_COUNT-1); //等待计时寄存器的位宽 localparam bit_num = clogb2(NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS); //发送数据寄存器位宽 //状态机参数 parameter [1:0] IDLE = 2'b00, //初始状态 INIT_COUNTER = 2'b01, //初始化计数器,等待计数值达到最大计数时钟,进入下一个状态SEND_STREAM = 2'b10; //数据发送状态reg [1:0] mst_exec_state; //状态寄存器 reg [bit_num-1:0] read_pointer; //FIFO读指针 // AXIS内部信号reg [WAIT_COUNT_BITS-1 : 0] count; //等待计数器(实现我们之前说的计时功能)wire axis_tvalid; //validreg axis_tvalid_delay; //延时一个时钟周期的validwire axis_tlast; //lastreg axis_tlast_delay; //延迟一个时钟周期的lastreg [C_M_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH-1 : 0] stream_data_out; //datawire tx_en; //发送使能reg tx_done; //发送完成//赋值操作assign M_AXIS_TVALID = axis_tvalid_delay; assign M_AXIS_TDATA = stream_data_out;assign M_AXIS_TLAST = axis_tlast_delay;assign M_AXIS_TSTRB = {(C_M_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH/8){1'b1}}; //全1 //控制状态机 always @(posedge M_AXIS_ACLK) begin if (!M_AXIS_ARESETN) begin mst_exec_state <= IDLE; count <= 0; end else case (mst_exec_state) IDLE: //一个周期后直接进入下一个状态 mst_exec_state <= INIT_COUNTER; INIT_COUNTER: //计数器达到最大计数值,进入次态 if ( count == C_M_START_COUNT - 1 ) begin mst_exec_state <= SEND_STREAM; end else begin count <= count + 1; mst_exec_state <= INIT_COUNTER; end SEND_STREAM: //发送状态,完成发送后回到初始态 if (tx_done) begin mst_exec_state <= IDLE; end else begin mst_exec_state <= SEND_STREAM; end endcase end //valid信号(表示主机有没有准备好),当处于发送状态,读指针小于发送数据个数时(也就是处于发送状态且还有数据要发)生效assign axis_tvalid = ((mst_exec_state == SEND_STREAM) && (read_pointer < NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS));//last信号(表示发送的最后一个字节),当读指针等于发送数据个数-1时生效assign axis_tlast = (read_pointer == NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS-1); //完成axis_tvalid_delay,axis_tlast_delay(延迟一个时钟的valid和last)的赋值always @(posedge M_AXIS_ACLK) begin if (!M_AXIS_ARESETN) begin axis_tvalid_delay <= 1'b0; axis_tlast_delay <= 1'b0; end else begin axis_tvalid_delay <= axis_tvalid; axis_tlast_delay <= axis_tlast; end end //读指针always@(posedge M_AXIS_ACLK) begin if(!M_AXIS_ARESETN) //复位 begin read_pointer <= 0; tx_done <= 1'b0; end else if (read_pointer <= NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS-1) //读指针小于等于发送数据个数-1,如果tx_en(发送使能),读指针递增,发送完成信号为0 begin if (tx_en) begin read_pointer <= read_pointer + 1; tx_done <= 1'b0; end end else if (read_pointer == NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS) begin tx_done <= 1'b1; //如果读指针等于发送数据个数,完成信号为1 end end assign tx_en = M_AXIS_TREADY && axis_tvalid; //读使能信号(从机+主机准备好)//生成数据输出 always @( posedge M_AXIS_ACLK ) begin if(!M_AXIS_ARESETN) begin stream_data_out <= 1; end else if (tx_en)begin stream_data_out <= read_pointer + 32'b1; //定义数据为指针+1end end /* 实现用户逻辑*/endmodule
1.2 源码展示
`timescale 1 ns / 1 psmodule axis_m_v1_0_M00_AXIS #(// Users to add parameters here// User parameters ends// Do not modify the parameters beyond this line// Width of S_AXIS address bus. The slave accepts the read and write addresses of width C_M_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH.parameter integer C_M_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH = 32,// Start count is the number of clock cycles the master will wait before initiating/issuing any transaction.parameter integer C_M_START_COUNT = 32)(// Users to add ports here// User ports ends// Do not modify the ports beyond this line// Global portsinput wire M_AXIS_ACLK,// input wire M_AXIS_ARESETN,// Master Stream Ports. TVALID indicates that the master is driving a valid transfer, A transfer takes place when both TVALID and TREADY are asserted. output wire M_AXIS_TVALID,// TDATA is the primary payload that is used to provide the data that is passing across the interface from the master.output wire [C_M_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH-1 : 0] M_AXIS_TDATA,// TSTRB is the byte qualifier that indicates whether the content of the associated byte of TDATA is processed as a data byte or a position byte.output wire [(C_M_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH/8)-1 : 0] M_AXIS_TSTRB,// TLAST indicates the boundary of a packet.output wire M_AXIS_TLAST,// TREADY indicates that the slave can accept a transfer in the current cycle.input wire M_AXIS_TREADY);// Total number of output data localparam NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS = 8; // function called clogb2 that returns an integer which has the // value of the ceiling of the log base 2. function integer clogb2 (input integer bit_depth); begin for(clogb2=0; bit_depth>0; clogb2=clogb2+1) bit_depth = bit_depth >> 1; end endfunction // WAIT_COUNT_BITS is the width of the wait counter. localparam integer WAIT_COUNT_BITS = clogb2(C_M_START_COUNT-1); // bit_num gives the minimum number of bits needed to address 'depth' size of FIFO. localparam bit_num = clogb2(NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS); // Define the states of state machine // The control state machine oversees the writing of input streaming data to the FIFO,// and outputs the streaming data from the FIFO parameter [1:0] IDLE = 2'b00, // This is the initial/idle state INIT_COUNTER = 2'b01, // This state initializes the counter, once // the counter reaches C_M_START_COUNT count, // the state machine changes state to SEND_STREAM SEND_STREAM = 2'b10; // In this state the // stream data is output through M_AXIS_TDATA // State variable reg [1:0] mst_exec_state; // Example design FIFO read pointer reg [bit_num-1:0] read_pointer; // AXI Stream internal signals//wait counter. The master waits for the user defined number of clock cycles before initiating a transfer.reg [WAIT_COUNT_BITS-1 : 0] count;//streaming data validwire axis_tvalid;//streaming data valid delayed by one clock cyclereg axis_tvalid_delay;//Last of the streaming data wire axis_tlast;//Last of the streaming data delayed by one clock cyclereg axis_tlast_delay;//FIFO implementation signalsreg [C_M_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH-1 : 0] stream_data_out;wire tx_en;//The master has issued all the streaming data stored in FIFOreg tx_done;// I/O Connections assignmentsassign M_AXIS_TVALID = axis_tvalid_delay;assign M_AXIS_TDATA = stream_data_out;assign M_AXIS_TLAST = axis_tlast_delay;assign M_AXIS_TSTRB = {(C_M_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH/8){1'b1}};// Control state machine implementation always @(posedge M_AXIS_ACLK) begin if (!M_AXIS_ARESETN) // Synchronous reset (active low) begin mst_exec_state <= IDLE; count <= 0; end else case (mst_exec_state) IDLE: // The slave starts accepting tdata when // there tvalid is asserted to mark the // presence of valid streaming data //if ( count == 0 ) // begin mst_exec_state <= INIT_COUNTER; // end //else // begin // mst_exec_state <= IDLE; // end INIT_COUNTER: // The slave starts accepting tdata when // there tvalid is asserted to mark the // presence of valid streaming data if ( count == C_M_START_COUNT - 1 ) begin mst_exec_state <= SEND_STREAM; end else begin count <= count + 1; mst_exec_state <= INIT_COUNTER; end SEND_STREAM: // The example design streaming master functionality starts // when the master drives output tdata from the FIFO and the slave// has finished storing the S_AXIS_TDATA if (tx_done) begin mst_exec_state <= IDLE; end else begin mst_exec_state <= SEND_STREAM; end endcase end //tvalid generation//axis_tvalid is asserted when the control state machine's state is SEND_STREAM and//number of output streaming data is less than the NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS.assign axis_tvalid = ((mst_exec_state == SEND_STREAM) && (read_pointer < NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS));// AXI tlast generation // axis_tlast is asserted number of output streaming data is NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS-1 // (0 to NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS-1) assign axis_tlast = (read_pointer == NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS-1); // Delay the axis_tvalid and axis_tlast signal by one clock cycle // to match the latency of M_AXIS_TDATA always @(posedge M_AXIS_ACLK) begin if (!M_AXIS_ARESETN) begin axis_tvalid_delay <= 1'b0; axis_tlast_delay <= 1'b0; end else begin axis_tvalid_delay <= axis_tvalid; axis_tlast_delay <= axis_tlast; end end //read_pointer pointeralways@(posedge M_AXIS_ACLK) begin if(!M_AXIS_ARESETN) begin read_pointer <= 0; tx_done <= 1'b0; end else if (read_pointer <= NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS-1) begin if (tx_en) // read pointer is incremented after every read from the FIFO // when FIFO read signal is enabled. begin read_pointer <= read_pointer + 1; tx_done <= 1'b0; end end else if (read_pointer == NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS) begin // tx_done is asserted when NUMBER_OF_OUTPUT_WORDS numbers of streaming data// has been out. tx_done <= 1'b1; end end //FIFO read enable generation assign tx_en = M_AXIS_TREADY && axis_tvalid; // Streaming output data is read from FIFO always @( posedge M_AXIS_ACLK ) begin if(!M_AXIS_ARESETN) begin stream_data_out <= 1; end else if (tx_en)// && M_AXIS_TSTRB[byte_index] begin stream_data_out <= read_pointer + 32'b1; end end // Add user logic here// User logic endsendmodule
2、AXIS从机部分
1.1 中文注释
`timescale 1 ns / 1 psmodule axis_s_v1_0_S00_AXIS #(/*用户可以自定义参数*///AXIS数据位宽parameter integer C_S_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH = 32)(/*用户可以在此自定义端口*/input wire S_AXIS_ACLK, //时钟信号input wire S_AXIS_ARESETN, //复位信号output wire S_AXIS_TREADY, //ready信号,代表从机准备好了input wire [C_S_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH-1 : 0] S_AXIS_TDATA, //数据信号input wire [(C_S_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH/8)-1 : 0] S_AXIS_TSTRB, //数据修饰符,辨别字节类型 input wire S_AXIS_TLAST, //last信号,拉高代表是传输中的最后一个字节input wire S_AXIS_TVALID //ready信号,代表从机准备好了);//函数:以2为低求对数,用于计算位宽function integer clogb2 (input integer bit_depth);beginfor(clogb2=0; bit_depth>0; clogb2=clogb2+1)bit_depth = bit_depth >> 1;endendfunctionlocalparam NUMBER_OF_INPUT_WORDS = 8; //输入数据个数localparam bit_num = clogb2(NUMBER_OF_INPUT_WORDS-1); //输入数据的位宽//状态机定义parameter [1:0] IDLE = 1'b0, //初始状态WRITE_FIFO = 1'b1; //读状态wire axis_tready; //ready信号reg mst_exec_state; //状态寄存器genvar byte_index; //字节索引wire fifo_wren; //FIFO写使能reg fifo_full_flag; //FIFO满标志reg [bit_num-1:0] write_pointer; //FIFO写指针reg writes_done; //写满标志assign S_AXIS_TREADY = axis_tready; //状态机always @(posedge S_AXIS_ACLK) begin if (!S_AXIS_ARESETN) beginmst_exec_state <= IDLE;end elsecase (mst_exec_state)IDLE: if (S_AXIS_TVALID)beginmst_exec_state <= WRITE_FIFO;endelsebeginmst_exec_state <= IDLE;endWRITE_FIFO: if (writes_done)beginmst_exec_state <= IDLE;endelsebeginmst_exec_state <= WRITE_FIFO;endendcaseend//ready信号赋值,写状态+读指针写于等于接收数据总个数assign axis_tready = ((mst_exec_state == WRITE_FIFO) && (write_pointer <= NUMBER_OF_INPUT_WORDS-1));//写指针,写完成信号always@(posedge S_AXIS_ACLK)beginif(!S_AXIS_ARESETN)beginwrite_pointer <= 0;writes_done <= 1'b0;end elseif (write_pointer <= NUMBER_OF_INPUT_WORDS-1)beginif (fifo_wren)beginwrite_pointer <= write_pointer + 1;writes_done <= 1'b0;endif ((write_pointer == NUMBER_OF_INPUT_WORDS-1)|| S_AXIS_TLAST)beginwrites_done <= 1'b1;endend end//FIFO写使能信号assign fifo_wren = S_AXIS_TVALID && axis_tready;//例化4个宽为8,深度为8的二维数组stream_data_fifo,用来充当FIFO,每个FIFO依次写入数据的0-7;8-15;16-23;24-31位generate for(byte_index=0; byte_index<= (C_S_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH/8-1); byte_index=byte_index+1)begin:FIFO_GENreg [(C_S_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH/4)-1:0] stream_data_fifo [0 : NUMBER_OF_INPUT_WORDS-1];//写入FIFO数据always @( posedge S_AXIS_ACLK )beginif (fifo_wren)// && S_AXIS_TSTRB[byte_index])beginstream_data_fifo[write_pointer] <= S_AXIS_TDATA[(byte_index*8+7) -: 8];end end end endgenerate/* 实现用户逻辑*/endmodule
1.2 源码展示
`timescale 1 ns / 1 psmodule axis_s_v1_0_S00_AXIS #(// Users to add parameters here// User parameters ends// Do not modify the parameters beyond this line// AXI4Stream sink: Data Widthparameter integer C_S_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH = 32)(// Users to add ports here// User ports ends// Do not modify the ports beyond this line// AXI4Stream sink: Clockinput wire S_AXIS_ACLK,// AXI4Stream sink: Resetinput wire S_AXIS_ARESETN,// Ready to accept data inoutput wire S_AXIS_TREADY,// Data ininput wire [C_S_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH-1 : 0] S_AXIS_TDATA,// Byte qualifierinput wire [(C_S_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH/8)-1 : 0] S_AXIS_TSTRB,// Indicates boundary of last packetinput wire S_AXIS_TLAST,// Data is in validinput wire S_AXIS_TVALID);// function called clogb2 that returns an integer which has the // value of the ceiling of the log base 2.function integer clogb2 (input integer bit_depth);beginfor(clogb2=0; bit_depth>0; clogb2=clogb2+1)bit_depth = bit_depth >> 1;endendfunction// Total number of input data.localparam NUMBER_OF_INPUT_WORDS = 8;// bit_num gives the minimum number of bits needed to address 'NUMBER_OF_INPUT_WORDS' size of FIFO.localparam bit_num = clogb2(NUMBER_OF_INPUT_WORDS-1);// Define the states of state machine// The control state machine oversees the writing of input streaming data to the FIFO,// and outputs the streaming data from the FIFOparameter [1:0] IDLE = 1'b0, // This is the initial/idle state WRITE_FIFO = 1'b1; // In this state FIFO is written with the// input stream data S_AXIS_TDATA wire axis_tready;// State variablereg mst_exec_state; // FIFO implementation signalsgenvar byte_index; // FIFO write enablewire fifo_wren;// FIFO full flagreg fifo_full_flag;// FIFO write pointerreg [bit_num-1:0] write_pointer;// sink has accepted all the streaming data and stored in FIFOreg writes_done;// I/O Connections assignmentsassign S_AXIS_TREADY = axis_tready;// Control state machine implementationalways @(posedge S_AXIS_ACLK) begin if (!S_AXIS_ARESETN) // Synchronous reset (active low)beginmst_exec_state <= IDLE;end elsecase (mst_exec_state)IDLE: // The sink starts accepting tdata when // there tvalid is asserted to mark the// presence of valid streaming data if (S_AXIS_TVALID)beginmst_exec_state <= WRITE_FIFO;endelsebeginmst_exec_state <= IDLE;endWRITE_FIFO: // When the sink has accepted all the streaming input data,// the interface swiches functionality to a streaming masterif (writes_done)beginmst_exec_state <= IDLE;endelsebegin// The sink accepts and stores tdata // into FIFOmst_exec_state <= WRITE_FIFO;endendcaseend// AXI Streaming Sink // // The example design sink is always ready to accept the S_AXIS_TDATA until// the FIFO is not filled with NUMBER_OF_INPUT_WORDS number of input words.assign axis_tready = ((mst_exec_state == WRITE_FIFO) && (write_pointer <= NUMBER_OF_INPUT_WORDS-1));always@(posedge S_AXIS_ACLK)beginif(!S_AXIS_ARESETN)beginwrite_pointer <= 0;writes_done <= 1'b0;end elseif (write_pointer <= NUMBER_OF_INPUT_WORDS-1)beginif (fifo_wren)begin// write pointer is incremented after every write to the FIFO// when FIFO write signal is enabled.write_pointer <= write_pointer + 1;writes_done <= 1'b0;endif ((write_pointer == NUMBER_OF_INPUT_WORDS-1)|| S_AXIS_TLAST)begin// reads_done is asserted when NUMBER_OF_INPUT_WORDS numbers of streaming data // has been written to the FIFO which is also marked by S_AXIS_TLAST(kept for optional usage).writes_done <= 1'b1;endend end// FIFO write enable generationassign fifo_wren = S_AXIS_TVALID && axis_tready;// FIFO Implementationgenerate for(byte_index=0; byte_index<= (C_S_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH/8-1); byte_index=byte_index+1)begin:FIFO_GENreg [(C_S_AXIS_TDATA_WIDTH/4)-1:0] stream_data_fifo [0 : NUMBER_OF_INPUT_WORDS-1];// Streaming input data is stored in FIFOalways @( posedge S_AXIS_ACLK )beginif (fifo_wren)// && S_AXIS_TSTRB[byte_index])beginstream_data_fifo[write_pointer] <= S_AXIS_TDATA[(byte_index*8+7) -: 8];end end end endgenerate// Add user logic here// User logic endsendmodule
四、仿真测试
1、top
module top(input clk,input rst_n);wire [31:0] axis_tdata;wire [3:0] axis_tstrb;wire axis_tlast;wire axis_tready;wire axis_tvalid;axis_m_0 axis_m_u0(.m00_axis_tdata (axis_tdata),.m00_axis_tstrb (axis_tstrb), .m00_axis_tlast (axis_tlast),.m00_axis_tvalid (axis_tvalid),.m00_axis_tready (axis_tready),.m00_axis_aclk (clk),.m00_axis_aresetn (rst_n));axis_s_0 axis_s_u0(.s00_axis_tdata (axis_tdata),.s00_axis_tstrb (axis_tstrb), .s00_axis_tlast (axis_tlast),.s00_axis_tvalid (axis_tvalid),.s00_axis_tready (axis_tready),.s00_axis_aclk (clk),.s00_axis_aresetn (rst_n));endmodule
2、tb
`timescale 1ns / 1psmodule tb_top();reg clk,rst_n;initial beginclk = 0;rst_n = 1;
#10rst_n = 0;
#10rst_n = 1;
endalways #5 clk <= ~clk;top top_u1(.clk(clk),.rst_n(rst_n));endmodule
3、结果

这篇关于AXI-Stream协议详解(3)—— AXI4-Stream IP核原理分析的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!