本文主要是介绍MOOC数据结构(下)(自主模式)-玩具(Toy),希望对大家解决编程问题提供一定的参考价值,需要的开发者们随着小编来一起学习吧!
玩具(Toy)
Description
ZC God is best at logical reasoning. One day, he talks about his childhood digital toys.
The toy is like a Rubik's cube, but not a Rubik's cube. Specifically, it is not a 3 * 3 * 3 structure, but a 4 * 2 structure.
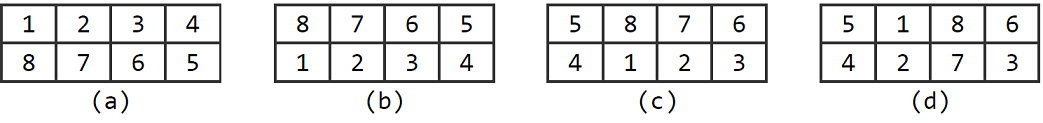
According to the play of the toy, we can repeatedly transform it in the following three ways:
A. Exchange the upper and lower lines. For example, the result of the transformation of Figure (a) is shown in Figure (b).
B. Loop right shift (ZC God knows what this means from an early age). For example, the result of the transformation of Figure (b) is shown in Figure (c).
C. The center rotates clockwise. For example, the result of the transformation of Figure (c) is shown in Figure (d).
ZC God is a genius in this respect. He often has a hand that has not dried his nose, the other hand has quickly restored the toy in any state to the initial state shown in Figure (a). In the year when the material was extremely scarce, ZC God had only one such toy; today, the material is extremely rich, and you have many toys in different states. Now, please restore them all.
Input
The first line is a positive integer, which is the total number of Rubik's cube toys you have.
In each one of the following N lines, 8 positive integers, i.e. an arrangement of 1~8, are included, indicating the current state of the toy.
Here, the representation rule of the cube state is that the first four numbers represent the first line of the cube from left to right, and the last four numbers represent the second line from right to left. For example, the initial state is expressed as "1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8".
Output
A total of N lines, each line containing an integer, in turn corresponding to the minimum number of transform needs to be performed to restore each toy.
In particular, if a toy is not recoverable, the corresponding line outputs -1.
Example
Input
2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
8 6 3 5 4 2 7 1Output
0
2Restrictions
For 60% of the data, N = 1
For 100% of the data,1 <= N <= 1,000
Time: 1 sec
Memory: 20 MB
Hints
State transition diagram and its search
描述
ZC神最擅长逻辑推理,一日,他给大家讲述起自己儿时的数字玩具。
该玩具酷似魔方,又不是魔方。具体来说,它不是一个3 * 3 * 3的结构,而是4 * 2的结构。

按照该玩具约定的玩法,我们可反复地以如下三种方式对其做变换:
A. 交换上下两行。比如,图(a)经此变换后结果如图(b)所示。
B. 循环右移(ZC神从小就懂得这是什么意思的)。比如,图(b)经此变换后结果如图(c)所示。
C. 中心顺时针旋转。比如,图(c)经此变换后结果如图(d)所示。
ZC神自小就是这方面的天才,他往往是一只手还没揩干鼻涕,另一只手已经迅速地将处于任意状态的玩具复原至如图(a)所示的初始状态。物质极其匮乏的当年,ZC神只有一个这样的玩具;物质极大丰富的今天,你已拥有多个处于不同状态的玩具。现在,就请将它们全部复原吧。
输入
第一行是一个正整数,即你拥有的魔方玩具总数N。
接下来共N行,每行8个正整数,是1~8的排列,表示该玩具的当前状态。
这里,魔方状态的表示规则为:前四个数自左向右给出魔方的第一行,后四个数自右向左给出第二行。比如,初始状态表示为“1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8”。
输出
共N行,各含一个整数,依次对应于复原各玩具所需执行变换的最少次数。
特别地,若某个玩具不可复原,则相应行输出-1。
样例
见英文题面
限制
对于60%的数据,N = 1
对于100%的数据,1 <= N <= 1,000
时间:1 sec
空间:20MB
提示
状态转换图及其搜索
C++:
/*@Date : 2018-03-09 13:58:53@Author : 酸饺子 (changzheng300@foxmail.com)@Link : https://github.com/SourDumplings@Version : $Id$
*//*
https://dsa.cs.tsinghua.edu.cn/oj/problem.shtml?id=1151
一共有8!=40320中状态,通过哈希表建立映射(康托展开)。
大体思路就是从原始状态开始通过三种操作的反向给出一切可以达到的状态,
通过BFS进行探索。
如果某个状态已经实现过则回溯,因为BFS第一遍到达该结点的步数就是最短路径
故需要记录每个状态的访问标记和需要达到的最小步数,假设步数为-1即为未访问过。
对于逆康托要保存康托的结果,大大提高效率*/#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>using namespace std;static const int MAX = 40321;static const int factorial[8] = {1, 1, 2, 6, 24, 120, 720, 5040};struct stateInfo
{bool valid = false;int A[8];int step = -1;
};static stateInfo data[MAX];struct Queue
{int data[MAX];int front = 0, end = 0;int pop(){int temp = front;front = (front + 1) % MAX;return data[temp];}void push(int i){data[end] = i;end = (end + 1) % MAX;return;}bool empty() { return front == end; }
};template <typename T>
void print(T A[], int n)
{for (int i = 0; i != n; ++i)cout << A[i] << ' ';putchar('\n');return;
}void check_enq(int w, int v, Queue &Q)
{if (data[w].step == -1){data[w].step = data[v].step + 1;Q.push(w);}return;
}int contor(int A[], int n)
{int res = 0;for (int i = 0; i != n; ++i){int smaller = 0;for (int j = i + 1; j != n; ++j){if (A[j] < A[i]) ++smaller;}res += smaller * factorial[n-i-1];}return res;
}void re_contor(int stateNo, int n)
{int temp;bool used[n];memset(used, false, sizeof(used));int tempStateNo = stateNo;for (int i = 0; i != n - 1; ++i){temp = tempStateNo / factorial[n-i-1];int rank = 0;for (int j = 1; j != n + 1; ++j){if (!used[j-1])++rank;if (rank == temp + 1){data[stateNo].A[i] = j;used[j-1] = true;break;}}tempStateNo %= factorial[n-i-1];}for (int i = 0; i != n; ++i){if (!used[i]){data[stateNo].A[n-1] = i + 1;break;}}data[stateNo].valid = true;return;
}void swap(int &a, int &b)
{int temp = a;a = b;b = temp;return;
}// 上下互换
int op1(int A_o[])
{int A[8];memcpy(A, A_o, sizeof(A));swap(A[0], A[7]);swap(A[1], A[6]);swap(A[2], A[5]);swap(A[3], A[4]);int res = contor(A, 8);memcpy(data[res].A, A, sizeof(A));data[res].valid = true;return res;
}// 循环左移
int op2(int A_o[])
{int A[8];memcpy(A, A_o, sizeof(A));int temp1 = A[0], temp2 = A[7];A[0] = A[1];A[1] = A[2];A[2] = A[3];A[7] = A[6];A[6] = A[5];A[5] = A[4];A[3] = temp1;A[4] = temp2;int res = contor(A, 8);memcpy(data[res].A, A, sizeof(A));data[res].valid = true;return res;
}// 逆时针旋转
int op3(int A_o[])
{int A[8];memcpy(A, A_o, sizeof(A));int temp = A[1];A[1] = A[2];A[2] = A[5];A[5] = A[6];A[6] = temp;int res = contor(A, 8);memcpy(data[res].A, A, sizeof(A));data[res].valid = true;return res;
}void BFS()
{Queue Q;Q.push(0);data[0].step = 0;while (!Q.empty()){int v = Q.pop();if (!data[v].valid) re_contor(v, 8);// printf("reached stateNo = %d: ", v);// print(data[v].A, 8);int w1 = op1(data[v].A), w2 = op2(data[v].A), w3 = op3(data[v].A);check_enq(w1, v, Q);check_enq(w2, v, Q);check_enq(w3, v, Q);}return;
}int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{BFS();int N;scanf("%d", &N);for (int i = 0; i != N; ++i){int A[8];for (int j = 0; j != 8; ++j) scanf("%d", &A[j]);int stateNo = contor(A, 8);// printf("stateNo = %d for A: \n", stateNo);// print(A, 8);printf("%d\n", data[stateNo].step);}return 0;
}
这篇关于MOOC数据结构(下)(自主模式)-玩具(Toy)的文章就介绍到这儿,希望我们推荐的文章对编程师们有所帮助!







